 Antitank Encyclopedia
Antitank Encyclopedia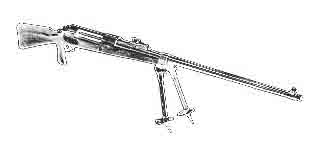


 German AT guns
German AT guns French AT guns
French AT guns Japanese AT guns
Japanese AT guns Soviet AT guns
Soviet AT guns Czech AT guns
Czech AT guns British AT guns
British AT guns US AT guns
US AT guns Others
Others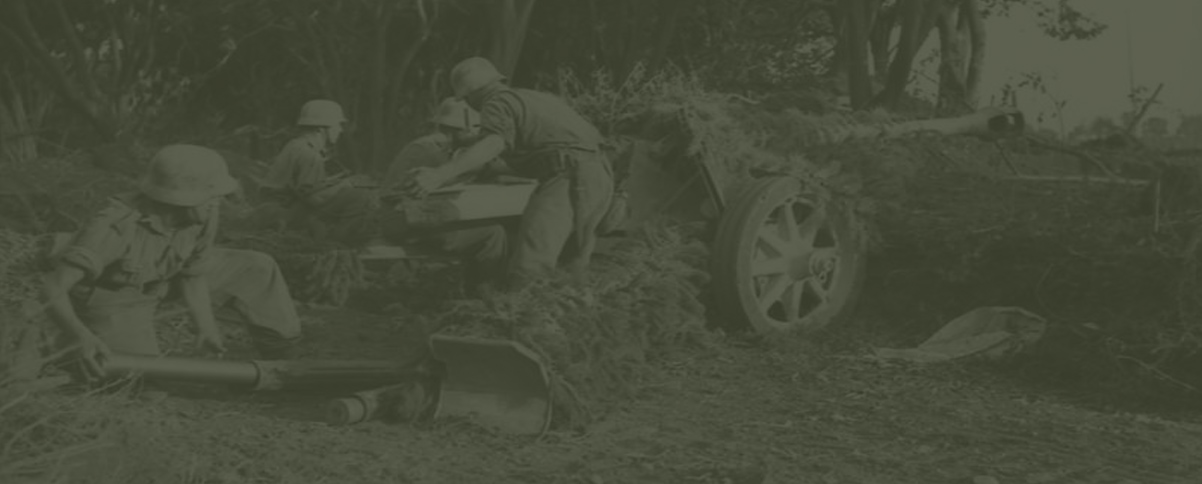
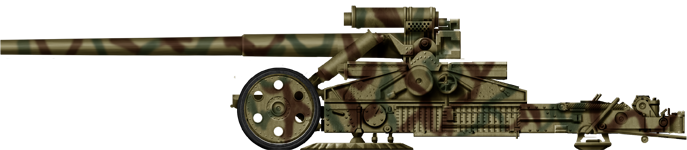
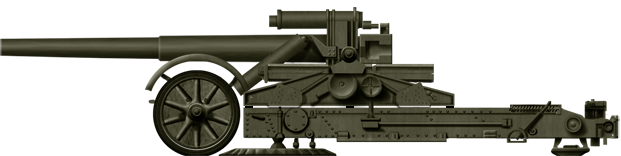
 57mm Gun M1
57mm Gun M1





⚙ Specifications M1 AT Gun | |
| Barrel | 9 ft 3 in (2.82 m)/50, cal. 2.244 in (57 mm) |
| Dimensions | 5 ft 11 in (1.8 m) x 4 ft 2 in (1.28 m) |
| Mass | 2,679 lb (1,215 kg) |
| Crew | 6: Cdr, 2 gunners, 3 loaders |
| Load/recoil | Vertical sliding-block, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -5° to +15°, 90° |
| Rate of fire | 15 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | AP Shot M70 (2.85 kg): 853 m/s (2,800 ft/s) |
| Range Effective/Max | 1,650 yd (1,510 m)/5,000 yd (4,600 m) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 57×441 mmR |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, No.22c |
 4,2 cm Pak 41
4,2 cm Pak 41

⚙ Specifications Pak 41 AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 235 cm (93 in), barrel 225 cm (89 in) bore, 55.8 cal. |
| Mass | 560 kg (1,230 lb) |
| Crew | |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-block breech |
| Elevation/traverse | -8° to +25°, 60° |
| Rate of fire | 12 round per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,500 m/s (4,900 ft/s) |
| Range | 800 m (2,600 ft) to 7,000 m (23,000 ft) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 42×406mm R |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, Zeiss optic |
 7.5 cm Panzerabwehrkanone 40
7.5 cm Panzerabwehrkanone 40

⚙ Specifications 75mm Pak-40 AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 6.2(20 ft 4) in x 2.08 x 1.2 m, barrel 46 cal. 3.45 m (11 ft 4 in) |
| Mass | 1,425 kg (3,142 lb) |
| Crew | 6 (Cdr, 2 pointers, 4 loaders) |
| Load/recoil | Semi-automatic horizontal sliding-block, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −5° to +22°; 65° |
| Rate of fire | 14 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | See notes |
| Range | 1,800 m (1,969 yd) to 7,678 m (8,397 yd) (HE) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 75×714mm R |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, Zeiss optics |
 88mm FLAK
88mm FLAK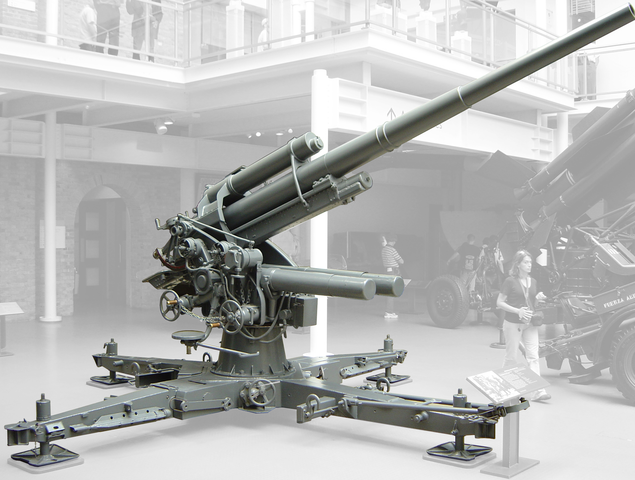

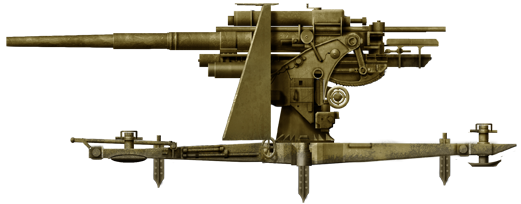
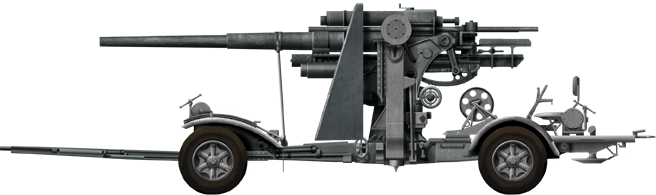
⚙ Specifications 8,8cm FLAK 36 Gun | |
| Dimensions | 5.791 m (20 ft) (barrel 4.938 m), width 2.3 m, height 2.10 m |
| Mass | 7,407 kg (16,330 lb) in mounted position |
| Crew | 10 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal semi-automatic sliding bloc, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −3° to +85° 360° |
| Rate of fire | 15–20 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 840 m/s (2,690 ft/s) |
| Range | 14,860 m (16,250 yd) ground target |
| Shell | Fixed QF 88×571mmR, 88 mm (3.46 in) |
| Carriage/sights | Sonderanhänger 202, ZF.20 sight |
 7.5 cm PAK 97/38
7.5 cm PAK 97/38

⚙ Specifications 7.5 cm PAK 97/38 AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 4.65 x 1.85 x 1.05m (15 ft 3 in x 6 ft 1 in x 3 ft 5 in) L/34.5 |
| Mass | cbt 1,190 kg (2,623 lbs); trv 1,270 kg (2,800 lbs) |
| Crew | 4-5: Gunner, Cdr, 2-3 loaders |
| Breech/recoil | Nordenfelt interrupted screw, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -10° to 18°; 60° |
| Rate of fire | 10-14 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 570 m/s (1,900 ft/s) |
| Range | HEAT 1.5 km (0.93 mi), HE frag 10 km (Sprgr.236/1(f)) |
| Shell | 75 mm (2.95 in) 75×350 mm R HEAT, AP, HE, Shrapnel |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail |
 PAK-36
PAK-36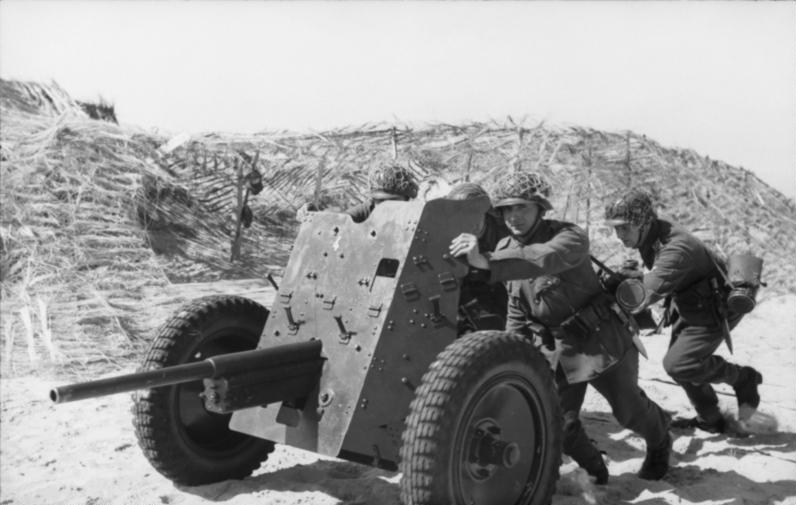
 A PAK 36 fitted with a StielGranat 41, only introduced by 1943, first seen in Fallschirmjäger units. Due to the livery of the gun, it could have been used in Tunisia, but there are more chances of a non-accurate reconstitution… The Stiergränat was equipped with two fuses, and could deliver 2.42kgs of TNT through a hollow charge, a crushing blow against any armor, up to 180mm, at the expense of the range, 300m at best.
A PAK 36 fitted with a StielGranat 41, only introduced by 1943, first seen in Fallschirmjäger units. Due to the livery of the gun, it could have been used in Tunisia, but there are more chances of a non-accurate reconstitution… The Stiergränat was equipped with two fuses, and could deliver 2.42kgs of TNT through a hollow charge, a crushing blow against any armor, up to 180mm, at the expense of the range, 300m at best.


⚙ Specifications PAK 36 AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 1.66 m (5 ft 5 in) x 1.65 m (5 ft 5 in) x 1.17 m (3 ft 10 in) |
| Mass | Travel 450 kg (990 lb), combat 327 kg (721 lb) |
| Crew | 5 (Commander, gunner, loader, two ammunition bearers) |
| Elevation/traverse | -5° to +25°, 30° right and left |
| Rate of fire | 13 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 762 m/s (2,500 ft/s) |
| Range | 5,484 m (5,997 yds) |
| Shell | 37×249mmR 37 mm (1.45 in) |
 PAK-43
PAK-43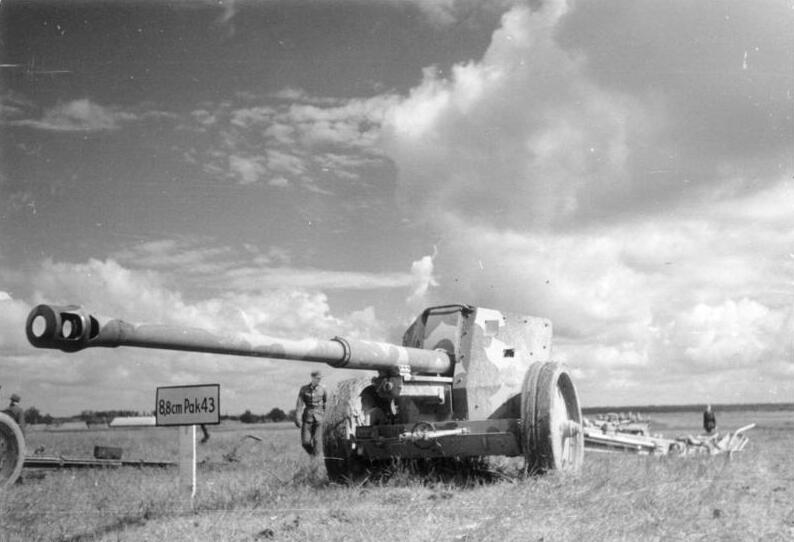
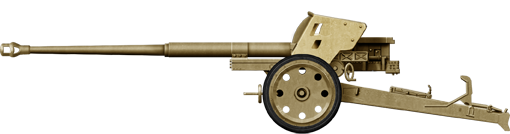
⚙ Specifications 8.8 cm PAK 43 AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 628 cm (20 ft 7 in)/71 calibres (3.46 in) |
| Mass | 3,650 kg (8,050 lb) Pak 43 |
| Crew | 6+ |
| Breech | Semi-automatic vertical sliding-block |
| Recoil | Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -8° to +40° Pak 43/-5° to +38° Pak 43/41, 360° |
| Rate of fire | 6–10 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,030 m/s (3,400 ft/s) Pzgr 40/43 |
| Carriage | Cruciform mount Pak 43, split trail Pak 43/41 |
| Shell | 88 × 822mm R 7.3 kg (16 lb) APCR Pzgr 40/43 |
| Range | 15,150 m (49,705 ft) Pak 43 |
 Cannone da 47/32 elefantino
Cannone da 47/32 elefantino

⚙ Specifications Cannone da 47/32 | |
| Dimensions | Bore: 1.525 m (5 ft 0 in) L/32, 1.680 m (6 ft)oa |
| Mass | Travel: 315 kg (694 lb), Combat: 277 kg (611 lb) |
| Crew | 4 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-wedge Breech |
| Elevation/traverse | -15° to +56° and 62° |
| Rate of fire | |
| Muzzle velocity | 630 metres per second (2,100 ft/s) AP |
| Range | 7,000 m (7,700 yd) |
| Shell | 47 x 195 mm R L/32, 47 x 328 mm R L/40, 1.5 kg (3 lb 5 oz) AP |
| Carriage/sights | Split-trail, 10,000m scope sight |
 Hotchkiss 25mm SA34
Hotchkiss 25mm SA34
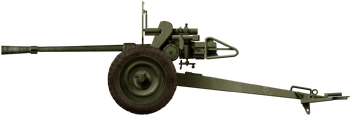
⚙ Specifications 25mm AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 3.71/3.46 (SA-L 34/37) x 1.10/1.03 m x 1.05 m (SA 34) |
| Mass | 490 kg (SA 34), 300 kg (SA-L 37) |
| Crew | 6 |
| Elevation/traverse | 60°; -5° to +15° |
| Rate of fire | 8 – 20 rpm, up to 25 rpm with a well-trained crew |
| Range | 800 meters - 3,500 meters |
| Shell | 25 x 193.5 mm, L/72 (SA-34), L/77 (SA-37) |
 Puteaux 47mm SA37
Puteaux 47mm SA37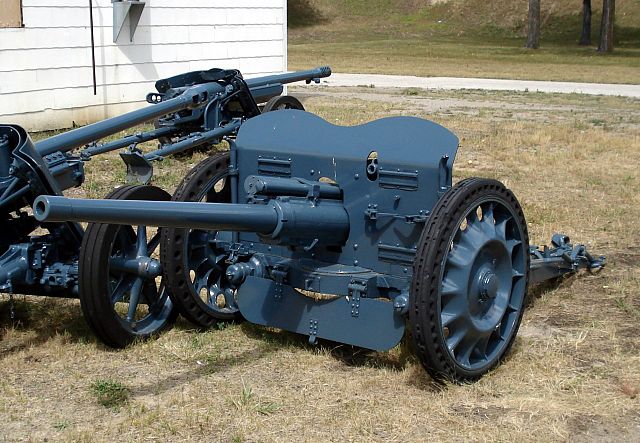
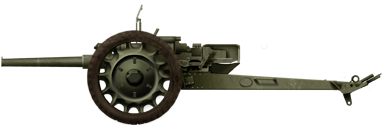
⚙ Specifications 47mm SA37 AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 4.1oa/2.49 barrel x 1.6 x 1.1 (13 ft 5 in, 8 ft 2 in, 5 ft 3 in, 3 ft 7 in) |
| Mass | 1,070 kg (2,359 lbs) |
| Crew | 6: Cdr, Gunner, 4 loaders/assistants |
| Elevation/traverse | -13° to +16.5° - Traverse 68° |
| Rate of fire | 15 to 20 rounds/min |
| Muzzle velocity | 855 m/s (2,805 ft/s) |
| Range | 2,000 m (2,187 yds) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 1.73 kg (3.74 lbs) 47x380 mm R APCBC |
| Carriage/sights | Split-trail, standard scope |
 Bohler 4,7cm AT
Bohler 4,7cm AT
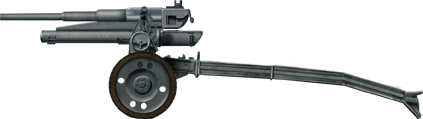
⚙ Specifications Bohler 4.7 cm (1.9 in) AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | Bore: 1.525 m (5 ft) L/32, 1.680 m (6 ft) oa |
| Mass | 315 kg (694 lb) travel, 277 kg (611 lb) combat |
| Crew | 6 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-wedge |
| Elevation/traverse | -15° to +56°, 62° |
| Rate of fire | c3/min. |
| Muzzle velocity | 630 metres per second (2,100 ft/s) AP |
| Range | 7,000 m (7,700 yd) |
| Shell | 47x195 mm R L/32 or 47x328 mm R L/40 1.5 kg (3 lb 5 oz) AP |
| Carriage/sights | Split-trail |
 ZIS-2 57 mm antitank gun
ZIS-2 57 mm antitank gun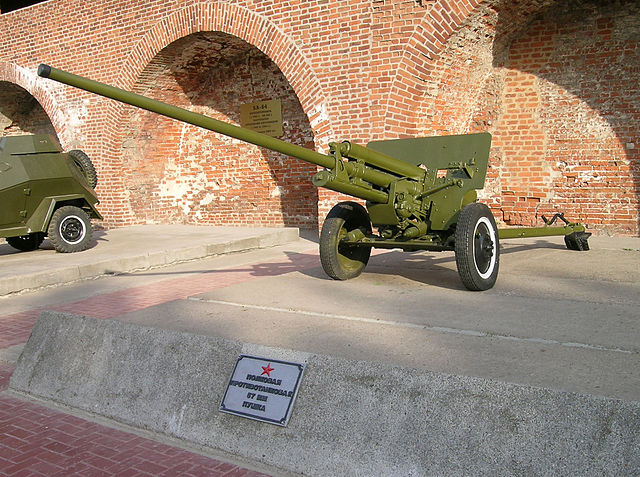
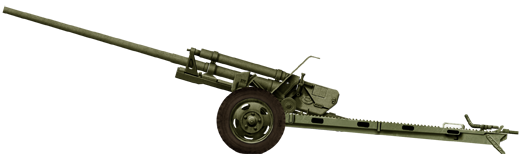
⚙ Specifications ZIS-2 AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 7.03 m (23 ft 1 in)oa x 3.95 m (13 ft 0 in) x 1.37 m (4 ft 6 in) |
| Mass | 1,250 kg (2,756 lb) |
| Crew | 7 |
| Load/recoil | Semi-automatic vertical sliding-wedge, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -5° to 25°; 56° |
| Rate of fire | 25 rpm cyclic, 10 rpm practical |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,000 m/s (3,300 ft/s) |
| Range | 8.4 km (5.21 miles) indirect fire |
| Shell | Fixed QF 57×480 mmR AP 2.24 in |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, optical 3,000m |
 76mm Divisional Gun M1939 (USV)
76mm Divisional Gun M1939 (USV)

⚙ Specifications 76mm Div. Gun M1939 | |
| Dimensions | 5.95 m (19 ft 6 in) x 1.94 m (6 ft 4 in) x 1.7 m (5 ft 7 in) |
| Mass | Ct 1,470 kg (3,240 lb), Tv 2,500 kg (5,500 lb) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Load/recoil | Semi-automatic vertical sliding-wedge, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -6° to 45°, 60° |
| Rate of fire | 15 rpm practical |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,000 m/s (3,300 ft/s) |
| Range | 13.29 km (8.26 mi) max |
| Shell | 76.2 × 385 mm. R |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, optical 3,000m |
 45 mm antitank gun M1937
45 mm antitank gun M1937

⚙ Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 6.4 m (21 ft) barrel 2.07 m (6 ft 9 in); 46 cal. |
| Mass | 560 kg (1,234 lbs), travel 1,200 kg (2,645 lbs) |
| Crew | |
| Load/recoil | Semi-automatic vertical sliding-wedge/Hydro-spring |
| Elevation/traverse | -8° to 25°/60° |
| Rate of fire | 15-20 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 760 m/s (2,493 ft/s) |
| Range | 4.4 km (2.73 mi) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 45x310 mm. R 45 mm (1.77 in) |
| Carriage/sights | Split-trail |
 37 mm Type 94 IJA antitank gun
37 mm Type 94 IJA antitank gun
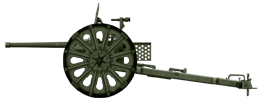
⚙ Specifications 37 mm QF AT gun | |
| Dimensions | 2.9 m (9 ft 6 in) long oa, 1.19 m (3 ft 11 in) wide |
| Mass | 324 kg (714 lb) approx |
| Crew | 2-3 |
| Load/recoil | Sliding horizontal breech |
| Elevation/traverse | -10° to +25°, 60° |
| Rate of fire | 30 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 700 m/s (2,300 ft/s) |
| Range | Effective 2,870 m, max 4,500 m (4,900 yds) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 37×165 mm. R .69 kg (1 lb 8 oz) |
| Carriage/sights | Straight telescopic |
 Mauser TankGewehr 1918
Mauser TankGewehr 1918
 Author's rendition of the Mauser TankGewehr 1918
Author's rendition of the Mauser TankGewehr 1918
⚙ Mauser TankGewehr 1918 Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 1,69m oa, barrel 96 cm, 13.2 mm |
| Mass | 18.5 kg |
| Crew | On rifleman, one loader |
| Load/recoil | Standard rifle double action lever |
| Rate of fire | 10 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 780 m/s |
| Range | 300-500 |

 3,7 cm FLAK 18/36/37
3,7 cm FLAK 18/36/37

⚙ Specifications 3,7 cm FLAK AA Gun | |
| Dimensions | barrel 2.11 m (83 in) x 37 mm (1.5 in) |
| Mass | 1,550 kg (3,420 lb) or 1,250 kg Flak 43 |
| Crew | 6–7 |
| Load/recoil | gas-operated bolt, 6-round clips |
| Elevation/traverse | -8° to +85°; 360° |
| Rate of fire | 160 rpm cyclic |
| Muzzle velocity | 840 m/s (2,800 ft/s) AP |
| Range | 7,995 m (8,743 yd) ground range |
| Shell | 37 × 263 mm B 623–659 g (1.373–1.453 lb) |
| Carriage/sights | three-legged platform |
 Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60
Bofors 40 mm Automatic Gun L/60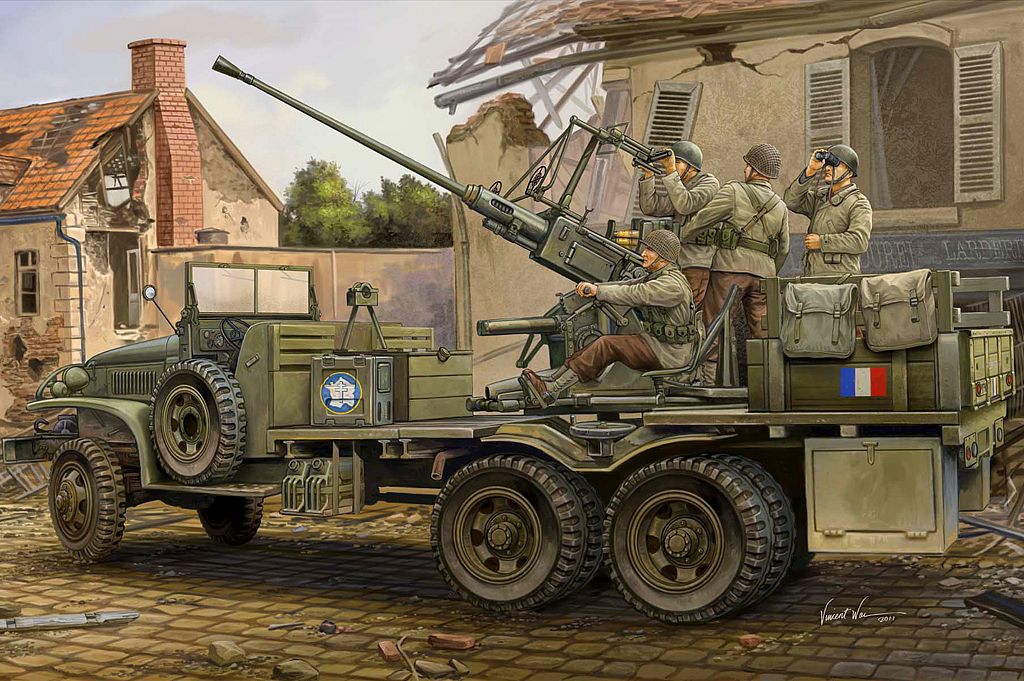
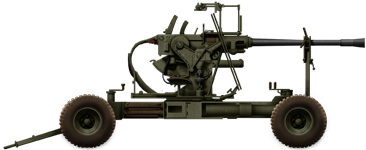
⚙ Specifications Bofors 2-pdr Gun | |
| Dimensions | 2.25 m (7 ft 5 in) barrel and mount |
| Mass | 522 kg (1,151 lb) |
| Crew | 4 |
| Load/recoil | Auto extraction, cam-operated recoil powered autoloader, Vertical sliding-wedge |
| Elevation/traverse | −5°/+90° @55°/s, Full 360° @50°/s |
| Rate of fire | 140 rpm low elevation angles, 120 rpm high |
| Muzzle velocity | 850–880 m/s (2,800–2,900 ft/s) |
| Range | 7,160 m (23,490 ft) |
| Shell | 40 × 311 mm R 0.9 kg (2 lb 0 oz) |
| Carriage/sights | Various (see notes), optical |
 2cm Flakvierling 38
2cm Flakvierling 38
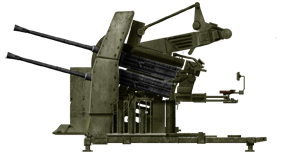

⚙ Specifications 20 mm FLAKvierling 38 | |
| Dimensions | 4,08 x 1,30 x 1,81 x 1,60 m |
| Mass | 3200 Ibs |
| Crew | 3 |
| Load/recoil | 20 rounds clips |
| Rate of fire | 800 rpm practical, 1400 cyclic |
| Muzzle velocity | 900 m/s |
| Range | 2,200m |
| Shell | 20 x 138 mm (0.79 in) |
| Carriage/sights | Optical, fixed quad mount |
 37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 (61-K)
37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 (61-K)
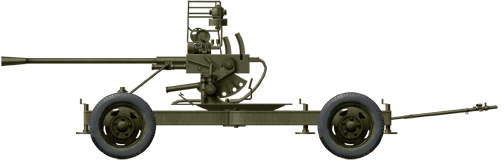
⚙ Specifications 37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 (61-K) | |
| Dimensions | 1.5 in Barrel length 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) L/67 |
| Mass | 2,100 kg (4,600 lb) |
| Crew | 8 |
| Load/recoil | Hydro-spring |
| Elevation/traverse | −5° to 85°, 360° |
| Rate of fire | 160-170 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 880 m/s (2,900 ft/s) |
| Range | 4/5 km (13/16,000 ft) ceiling |
| Shell | 37 × 252 mmSR, 730 g (1.61 lb) Frag-T, 770 g (1.70 lb) AP-T |
| Carriage/sights | Four-wheeled with twin outriggers |

 25 mm Hotchkiss AA
25 mm Hotchkiss AA
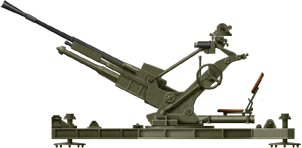
⚙ Specifications mitrailleuse de 25 mm CA M1938 | |
| Dimensions | 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) L/60 |
| Mass | 850 kg (1,870 lb) |
| Crew | 9 |
| Load/recoil | Gas operated, gravity feed 15 rds Mags. |
| Elevation/traverse | 10° to +85°, 360° |
| Rate of fire | Cyclic: 200–260 rpm, Effective: 110 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | HE: 900 m/s (2,953 ft/s) |
| Range | 6.8 km (4.2 mi) at 45° HE |
| Shell | HE 0.29 kg or AP: 0.32 kg (11 oz) |
| Carriage | Two wheeled single axle with cruciform outriggers |
 2cm FLAK 38
2cm FLAK 38
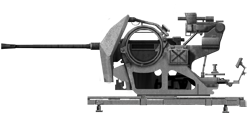
⚙ 2cm Flak 38 Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 4.08 m, barrel 1.3 m L/65 1.81 x 1.6 m |
| Mass | 405 kg (893 lb) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Load/recoil | 20 round box magazine |
| Elevation/traverse | -12°to ±90°, Traverse 360° |
| Rate of fire | 450 rpm (cyclic)/180 rpm (practical) |
| Muzzle velocity | 900 m/s (2,953 ft/s) |
| Range | ceiling 2,200 m (2,406 yds), ground 5,783 m (5,230 yds) |
| Shell | 20×138mmB Caliber 20 mm (.79 in) |
| Carriage/sights | Wheeled, 1 axle, shielded, Zeiss graduated scope. |
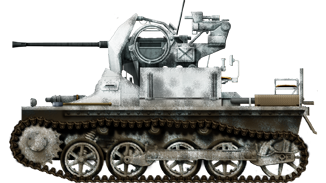
 Vickers 3-inches M1931
Vickers 3-inches M1931
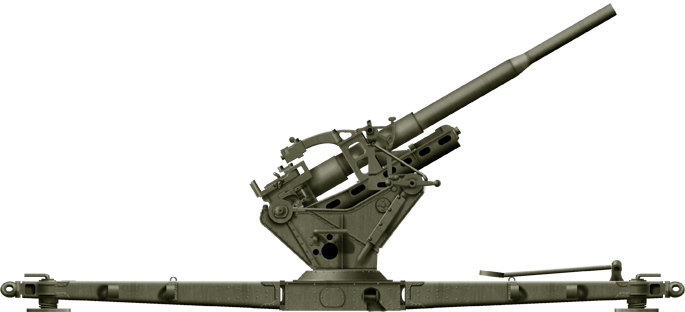
⚙ Specifications Vickers M1931 | |
| Dimensions | 3.225 m (10 ft 7 in) L/43 |
| Mass | 2,825 kg (6,228 lb) |
| Crew | c5-6 |
| Elevation/traverse | 0° to +90°, 360° |
| Rate of fire | 12 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 750 m/s (2,500 ft/s) |
| Range/ceiling | 5 effective, 10 km max (33,000 ft) |
| Shell | 76.2 x 505mm R 6.5 kg (14 lb 5 oz) |
| Carriage/sights | Optical, FCS data |
 37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 (61-K)
37 mm automatic air defense gun M1939 (61-K)
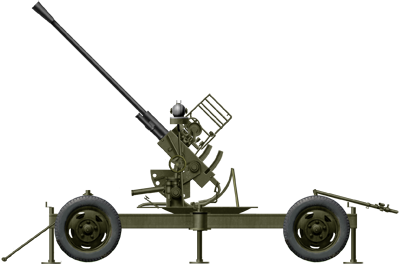

⚙ Specifications 37 mm (1.5 in) M1939 AA Gun | |
| Dimensions | 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) L/67 |
| Mass | 2,100 kg (4,600 lb) |
| Crew | 8 |
| Load/recoil | Hydro-spring |
| Elevation/traverse | −5° to 85° 360° |
| Rate of fire | 160-170 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 880 m/s (2,900 ft/s) |
| Range | 5 km (16,000 ft) |
| Shell | 730 g (1.61 lb) Frag-T 37 or 770 g (1.70 lb) AP-T × 252 mmSR |
| Carriage | Four-wheeled with twin outriggers |
 ZPU-1 (1949)
ZPU-1 (1949)
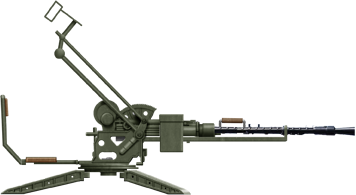
⚙ Specifications 14.5 mm ZPU-1 | |
| Dimensions | 3.44 x 1.62 x 1.34m (11 ft 3 in, 5 ft 4 in, 4 ft 5 in) |
| Mass | 413 kg (910 lb) |
| Crew | 4 (Cdr, Gunner, 2 loaders) |
| Load/recoil | Short recoil operation |
| Elevation/traverse | −8° to 88° 360° |
| Rate of fire | 600 rpm, 150 round belt each, 1200 total |
| Muzzle velocity | 880 m/s (2,900 ft/s) |
| Range | 1.4km (0.87 miles) effective, 8 km (5 miles) max |
| Shell | See notes, API-T (BZT) 59.56 g (2.101 oz) |
| Carriage | Tripod, 2-wheeled carriage |
 ZPU-2
ZPU-2
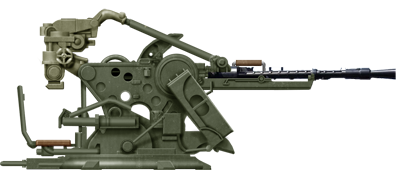
⚙ Specs. ZPU-2 Gun | |
| Dimensions | 11.6 x 6.3 x 6 ft (3.5 x 1.92 x 1.83m) |
| Mass | 639 kgs (1409 Ib) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Load/recoil | Manual, belt fed |
| Elevation/traverse | 360° traverse, +90° elevation |
| Rate of fire | 600 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 1006 m/s |
| Range | 3000 m effective, see notes |
| Shell | 14.5x114mm 60-66.5g |
| Carriage/sights | Optical, 2-wheeled carriage, towed or fixed |
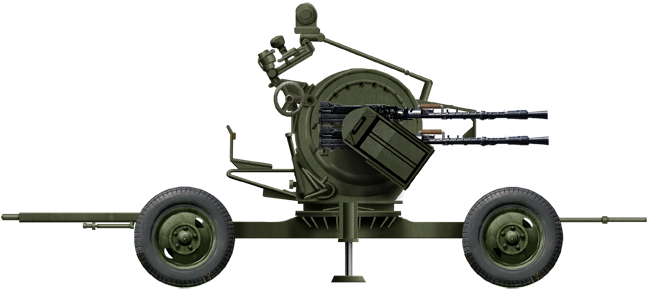
 ZPU-4
ZPU-4
⚙ Specs. | |
| Dimensions | 4.53 x 1.72 x 2.13 m (14 ft 10 in x 5 ft 8 in x 7 ft) |
| Mass | 1,810 kg(3,990 lb) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Load/recoil | Drum fed, recuperating piston |
| Elevation/traverse | +90°/−10°, 360° |
| Rate of fire | 600 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 1000 mps |
| Range | Max 8km, practical 1.5 km |
| Shell | 14.5x114mm HE 60-65g |
| Carriage/sights | Quad wheeled platform, Optical |

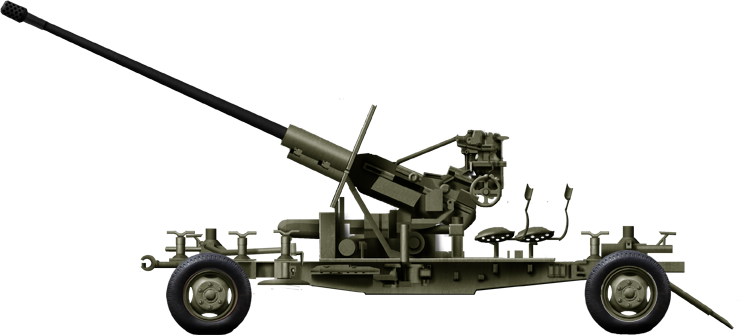
 AZP S60
AZP S60
⚙ Specs. S60 | |
| Dimensions | 8.5 m (27 ft 11 in) x 2.054 m (6 ft 9 in) x 2.37 m (7 ft 9 in) |
| Mass | 4,660 kg (10,273 lbs) |
| Crew | 7 |
| Load/recoil | Recoil operated |
| Elevation/traverse | −4° to +85°, 360° |
| Rate of fire | 105–120 rpm (cyclic), 70 rpm (sustained) |
| Muzzle velocity | 1000 mps (3,281 ft/s) |
| Range | 4,000 m (13,000 ft) (optically guided) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 57×347mmSR |
| Carriage/sights | Four wheels with outriggers |

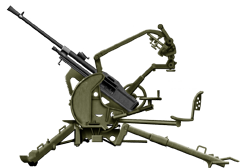
 Cannone da 20/65 M35
Cannone da 20/65 M35⚙ Specs. | |
| Dimensions | 1870 mm |
| Mass | 40.8 kg, 330 kg tail, 370 kg wheeled carriage |
| Crew | 3 |
| Load/recoil | Gas Operated, gravity feed, 12 rounds clips |
| Elevation/traverse | -10° to +80°, 360° on tails carriage |
| Rate of fire | 240 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 830 m/s |
| Range | 1,500 m (4,900 ft) optimal, max. 5.5 km (3.4 mi) |
| Shell | 20 x 138 mm R Long Solothurn |
| Carriage/sights | Variable, tripod, wheeled. |


 17 cm Kanone 18
17 cm Kanone 18
⚙ Specifications 17 cm Kanone 18 | |
| Dimensions | Bore 8.625 m (28 ft 3.6 in) L/50 |
| Mass | Transport 23.375t, action 17.520t |
| Crew | 10 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal-block Breech, Dual-recoil hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | Elevation +50°, traverse 16° wheels, 360° platform |
| Rate of fire | 3 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 925 m/s (3,030 ft/s) |
| Range | 29.6 km (18.4 mi) |
| Shell | 172.5 mm (6.79 in) separate-loading HE 62.8 kg (138 lb) |
| Carriage/sights | Box trail |
 21 cm Morser 18 (1939)
21 cm Morser 18 (1939)
⚙ Specifications 21 cm Morser 18 (210 mm/8.30 in) | |
| Dimensions | 6.51 m (21 ft 4 in) L/30 |
| Mass | 16,700 kg (36,817 lbs) |
| Crew | 6+ |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-block, Dual-recoil hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -6° to +70°; 16° wheels/360° platform |
| Rate of fire | 1 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 550–565 m/s (1,800–1,850 ft/s) |
| Range | 16,725 m (18,291 yd) effective |
| Shell | 113 kg (249 lb) (HE) separate loading case ammo |
| Carriage/sights | Box trail, unknown |
 7,5 cm LeIG-18
7,5 cm LeIG-18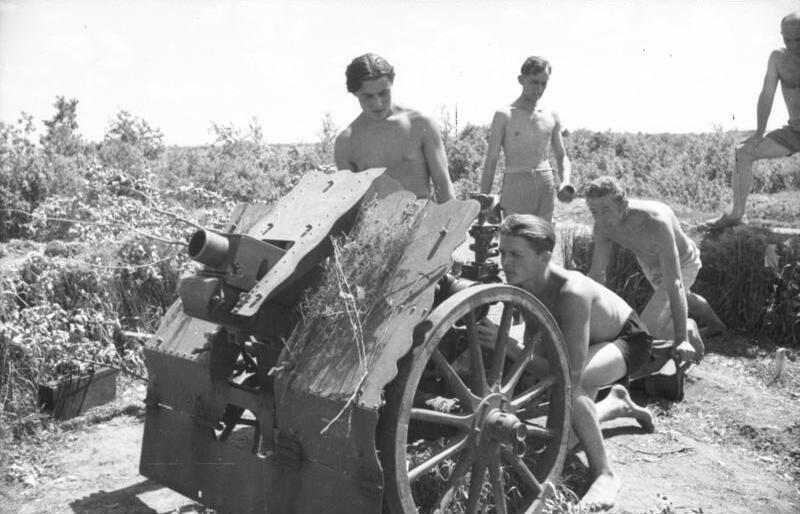
⚙ Specifications 7,5 cm LeIG-18 Howitzer | |
| Dimensions | |
| Mass | 1,560 kg (3,439 lb) Combat: 400 kg (882 lb) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Load/recoil | Top break Breech, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -10° to 73°; 12° |
| Rate of fire | 8-12 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 210 m/s (690 ft/s) |
| Range | 3,550 m (3,880 yd) |
| Shell | 75 x 89mm R Fixed QF, 6 kg (13 lb 4 oz) |
| Carriage/sights | Box trail |
 ZIS-3 76 mm divisional field Gun M1942
ZIS-3 76 mm divisional field Gun M1942

⚙ Specifications ZIS-3 field Gun | |
| Dimensions | 3.4 m (11 ft 2 in) x 1.6 m (5 ft 3 in)x 1.37 m (4 ft 6 in) |
| Mass | 1,116 kg, travel 2,150 kg |
| Crew | 7 |
| Load/recoil | Semi-automatic vertical sliding-wedge, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −5° to +37°, 54° |
| Rate of fire | 25 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | |
| Range | 13.29 km (8.25 mi) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 76.2 × 385 mm. R 76.2 mm (3 in) |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail |
 The Nebelwerfer
The Nebelwerfer

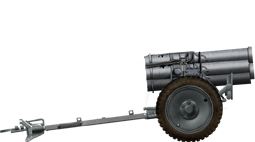
⚙ Specifications Nevelwerfer 21 cm (8.3 in) | |
| Dimensions | 3.6 x 1.6 x 1.5m (11 ft 10 in x 5 ft 3 in x 4 ft 11 in) |
| Mass | 550 kg (1,210 lb)/1,100 kg (2,400 lb) FL |
| Crew | 4 |
| Elevation/traverse | -5° to +45°, 24° |
| Warhead | 10.17[6] kg (22.4 lb) |
| Muzzle velocity | 320 m/s (1,000 ft/s) |
| Range | 7,850 m (8,580 yd) |
| Shell | 1.25 m (4 ft 1 in) 109.55 kg (241.5 lb) HE |
| Carriage/sights | split-trail, 5 barrel mount |
| Production | 2626, Donauwörth Machine Factory |
 152mm ML20 Gun-Howitzer
152mm ML20 Gun-Howitzer
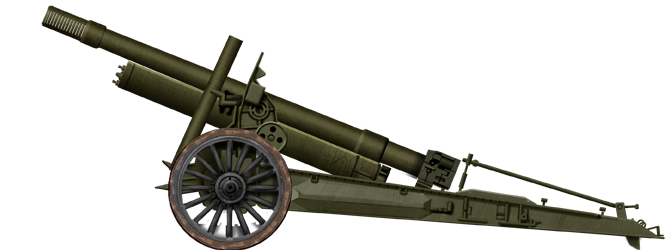

⚙ Specifications ML20 Gun-Howitzer | |
| Lenght | 8.18 m (26 ft 10 in) oa; barrel 4.24 m (13 ft 11 in) L/27.9 |
| width | 2.35 m (7 ft 9 in) |
| height | 2.27 m (7 ft 5 in) |
| Mass | combat 7,270 kg (16,027 lb, travel 7,930 kg (17,482 lb) |
| Crew | 6-8 |
| Load/recoil | Interrupted screw, hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −2° to 65°, 58° |
| Rate of fire | 3-4 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 655 m/s (2,150 ft/s) |
| Range | 17.23 km (10.7 mi) |
| Shell | 152 x 547 mm R 152.4 mm (6 in) |
| Carriage/sights | standard scope, split trail |
 105mm M119 Howitzer
105mm M119 Howitzer

⚙ Specifications 105mm M119 Howitzer | |
| Dimensions | 10 ft 6 in (3.20 m) L/30.48 x 5 ft 10 in (1.78 m) |
| Mass | 5,110 lb (2,320 kg) |
| Crew | 5 min, 7 max |
| Elevation/traverse | -5.625° +69.975°/5.625° |
| Rate of fire | 8 rpm for 3 minutes |
| Muzzle velocity | Round dependent |
| Range | 17,500 to 19,500 m (12.1 mi) |
| Shell | Semi-fixed 105 x 372 mm R (4.13 in) |
| Carriage/sights | split trail, 3× M90A2 telescope, M137A1 panoramic telescope |
 GNH N-45 Howitzer
GNH N-45 Howitzer
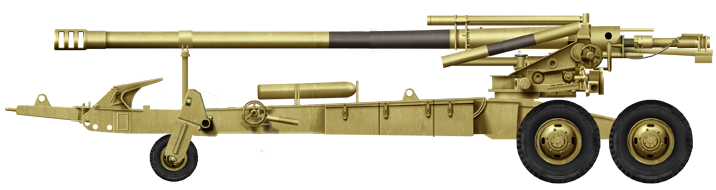
⚙ Specifications GNH N-45 | |
| Dimensions | 6.98 meters x 155 mm (6.1 in.) |
| Mass | 8,220 kg (18,120 lb) |
| Crew | 6 |
| Elevation/traverse | -89° to +128°, left 53.4°, right 71° |
| Rate of fire | 5 rpm sustained: 2 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 897 metres per second (2,940 ft/s) |
| Range | 39.6 km (24.6 mi) |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail |

 130 mm towed field gun M1954 (M-46)
130 mm towed field gun M1954 (M-46)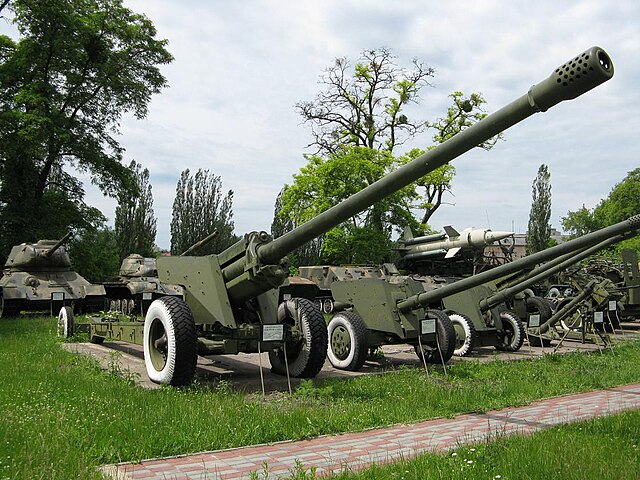

⚙ Specifications M46 | |
| Dimensions | 11.73 m (38 ft 6 in) x2.45 m (8 ft) x2.55 m (8 ft 4 in) |
| Mass | 7,700 kg (17,000 lb) |
| Crew | 8 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-wedge/hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −2.5° to 45°, 50° |
| Rate of fire | 6 rpm (normal), 8 rpm (burst), 5 rpm (sustained) |
| Muzzle velocity | 930 m/s (3,051 ft/s) |
| Range | 27 km (17 mi) unassisted, 40 km (25 mi) assisted |
| Shell | 130 x 845 mm R (R/184.6mm) separate charge and projectile |
| Carriage/sights | Split Trail |
 122m Type 83 Howitzer
122m Type 83 Howitzer
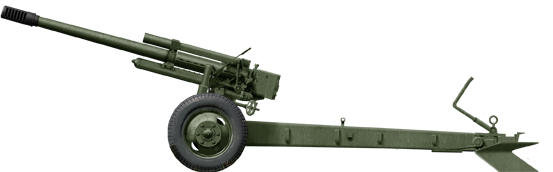
⚙ Specifications Type 83 4.8 in | |
| Dimensions | 7,862 x 2,157 x 2,088 x 1,137m. Barrel 3,634 m (30 cal.) |
| Mass | 2,7t in battle order |
| Breech | Vertical semi-automatic sliding-wedge |
| Crew | 8 |
| Load/recoil | Hydraulic buffer and hydro-pneumatic recuperator, 920-1050mm |
| Elevation/traverse | +65° |
| Rate of fire | 7-8 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | As M30 |
| Range | 15,6 km (grenade), 19 km (remote bomb). |
| Shell | 21.76 kg HE Sep. loading charge and projectile |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail |
 152mm D20 Howitzer
152mm D20 Howitzer

⚙ Specifications D20 Howitzer | |
| Dimensions | 8.69 m x 152 mm (26 calibers) |
| Mass | 5.56 t |
| Crew | 10 men |
| Elevation/traverse | -5/+45°, 58° each side |
| Rate of fire | 5-6 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | |
| Range | 17.4 km, 24 for improved modernized variants |
| Shell | Composite HE, separate ammo, 43.56 kg HE |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail |
 122mm D-74
122mm D-74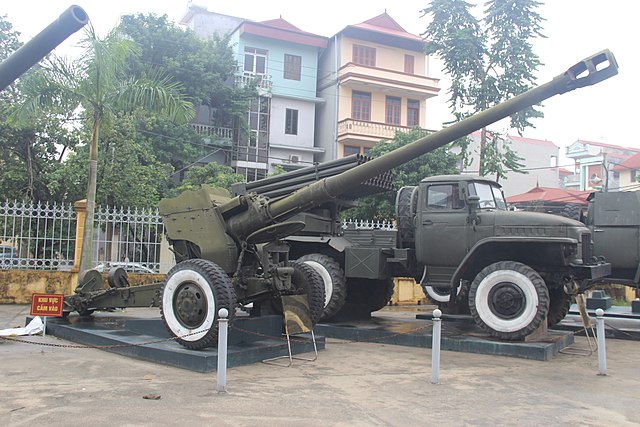

⚙ Specifications Rgt; Gun M1927 | |
| Dimensions | 9.875/6.45 x 2.35 x 2.7m (30 ft/21 ft 2 in x 7 ft 9 in x 8 ft 10 in) |
| Mass | 5,620 kg (12,390 lbs) |
| Crew | 7~9 |
| Load/recoil | Semi-auto vertical sliding-wedge, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | +45/−5°/45° |
| Rate of fire | 8–10 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 885 m/s (2,907 ft/s) |
| Range | direct 1.08 km (.67 mi)/23.9 km (15 mi) |
| Shell | 122 mm (4.8 in) Separate loading charge and projectile |
| Carriage/sights | Split-trail |
 Regimental Gun M1927
Regimental Gun M1927
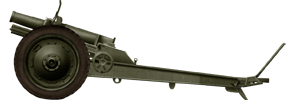
⚙ Specifications Regimental Gun M1927 | |
| Dimensions | 3.5 x 1.7 x 1.3 m (11 ft 6 in x 5 ft 7 in x 4 ft 3 in) |
| Mass | 780 kg (1,720 lb) |
| Crew | 4 - 76.2 mm (3 in) |
| Load/recoil | Interrupted screw |
| Elevation/traverse | 6°, -6° to 25° |
| Rate of fire | 10-12 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 387 m/s (1,270 ft/s) |
| Range | 4.2 km (2.6 mi) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 76.2 x 167mm R 6.2 kg (13 lb 11 oz) |
| Carriage/sights | Pole trail |

 122mm Howitzer 2A18 D30
122mm Howitzer 2A18 D30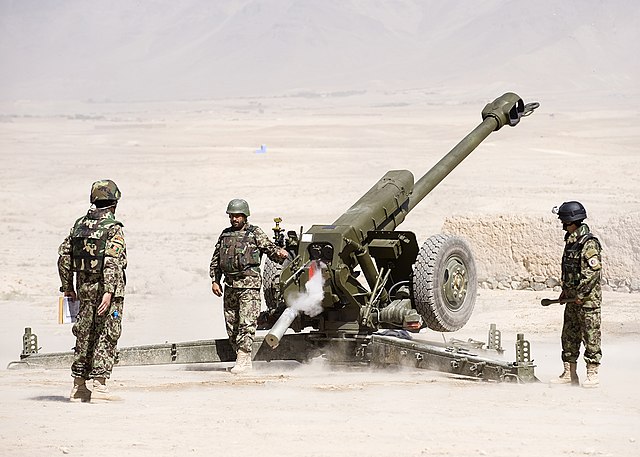


⚙ Specifications D30 (4.8 in) | |
| Dimensions | 4.66 m (15 ft 3 in) 38 calibres (5.4 x 1.9 x 1.6m transport) |
| Mass | 3,210 kg (7,080 lb) |
| Crew | 1+7 |
| Load/recoil | Semi-automatic vertical sliding-wedge, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −7° to 70°, 360° |
| Rate of fire | 10–12 rpm, sustained 5–6 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | Ammunition dependent |
| Range | 15.4 km (9.6 mi), 21.9 km (13.6 mi) assisted |
| Shell | 122 x 447mm .R |
| Carriage/sights | tripod, optical, centralized fire data |
 122mm M30 Howitzer
122mm M30 Howitzer
-web.png)
⚙ Specifications M30 | |
| Dimensions | 5.9 x 1.98 x 1.82m (19 ft 4 i x 6 ft 6 in x 6 ft) |
| Mass | Combat 2,450 kg (5,401 lbs), travel 3,100 kg (6,834 lbs) |
| Crew | 8 |
| Load/recoil | Interrupted screw, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −3° to 63.5°, 49° |
| Rate of fire | 5–6 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 431-515 mps |
| Range | 11.8 km (7.33 mi) |
| Shell | 21 Kgs. 122 x 284mm .R (121.92 mm/4.8 in) |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail |
 155mm Haubits FH77/A Howitzer (1978)
155mm Haubits FH77/A Howitzer (1978)
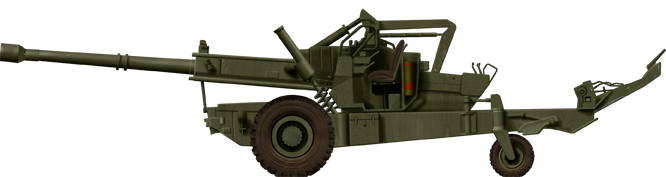
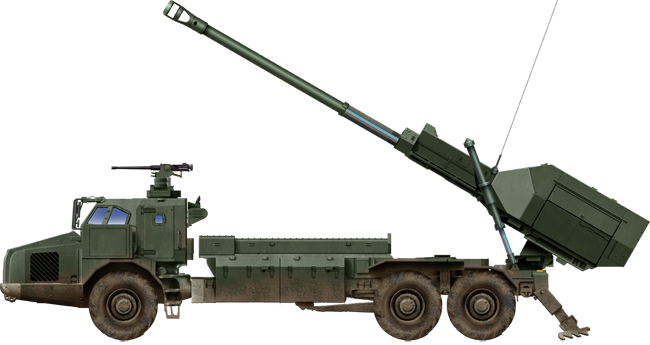
⚙ Specifications Haubits FH77 155 mm NATO | |
| Dimensions | 11.60 m/5.89 m (38 ft 1 in) |
| Engine | Volvo B20 APU 6 km/h |
| Mass | 11,500 kg (25,400 lb) |
| Crew | 9-14 |
| Load/recoil | Feed system hydraulically powered flick rammer |
| Elevation/traverse | -5°/+70°, +30° left/right |
| Rate of fire | 4 rds/9 secs., 6 rds/25 secs. |
| Muzzle velocity | 300 to 770 m/s (980 to 2,530 ft/s) |
| Range | 21 km (13 mi)/24 km (15 mi)/60 km+ Ramjet PAS |
| Shell | |
| Carriage/sights | split trail with castor wheels |
 130mm M1954 (M46) Towed Field Gun
130mm M1954 (M46) Towed Field Gun

 The 130 mm M46 was produced by China as the Type 59, Egypt (assembled), India (Karan/Sharang upgrades), Israel, updating both the M46 and Type 59 via Soltam, modified also by Serbia, Romania as the A412. It was also dapated to self propelled vehicles, such as a Cuban T-34-85 SPG and a KraZ 6x6 SPG presented in 2006. Indian of course created the SP-130 "Catapult" based on the Vijayanta hull. North Korea created the M1975, M1981 and M1991 self propelled guns, and Type 59 Tokchon or Vietnamese KrAZ based PTH130-K225B adapted from the Cuban design. The M46 fired three types of Frag-HE, a guided Shell Firn-1, smoke, chemical and illumination variants, but for direct antit-tank role, could fire the APCBC-HE-T, BR-482 and BR-482B with a useful range of just 1,140 meters. Between former and current operators, we speak of about 70 countries across the globe.
The 130 mm M46 was produced by China as the Type 59, Egypt (assembled), India (Karan/Sharang upgrades), Israel, updating both the M46 and Type 59 via Soltam, modified also by Serbia, Romania as the A412. It was also dapated to self propelled vehicles, such as a Cuban T-34-85 SPG and a KraZ 6x6 SPG presented in 2006. Indian of course created the SP-130 "Catapult" based on the Vijayanta hull. North Korea created the M1975, M1981 and M1991 self propelled guns, and Type 59 Tokchon or Vietnamese KrAZ based PTH130-K225B adapted from the Cuban design. The M46 fired three types of Frag-HE, a guided Shell Firn-1, smoke, chemical and illumination variants, but for direct antit-tank role, could fire the APCBC-HE-T, BR-482 and BR-482B with a useful range of just 1,140 meters. Between former and current operators, we speak of about 70 countries across the globe.
⚙ Specifications 130mm M46 L/55 | |
| Dimensions | 11.73 x 2.45 x 2.55 m (38 ft 6 in x 8 ft x 8 ft 4 in) |
| Mass | 7,700 kg (17,000 lb) |
| Crew | 8 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-wedge, hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −2.5° to 45° /50° |
| Rate of fire | 6 rpm (normal), 8 rpm (burst), 5 rpm (sustained) |
| Muzzle velocity | 930 m/s (3,051 ft/s) |
| Range | 27.5 km (17.1 mi)/35 km (22 mi)/42 km (26 mi) RA |
| Shell | 130 x 845 mm R, sep.-loading |
| Carriage/sights | Split-trail/optical |
 76 mm divisional gun M1939 USV
76 mm divisional gun M1939 USV

⚙ Specifications 76mm M39 USV | |
| Dimensions | 3.4 m (L/45) x 76.2 mm (3 in) |
| Mass | 1,500 kg (3,300 lb) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Load/recoil | semi-automatic breech |
| Elevation/traverse | -6°/45°, 60° |
| Rate of fire | 15–20 rounds per minute |
| Muzzle velocity | 700–713 m/s (2,297–2,339 ft/s) |
| Range | 13.3 km (8.3 mi) |
| Shell | 76.2×385 mmR HE, AP, HEAT, illum., smoke, ect. |
| Carriage/sights | split trail |

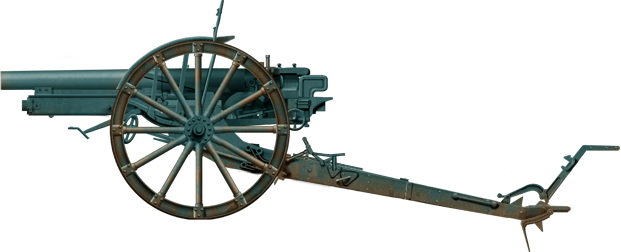
⚙ Specifications Cannone da 77/28 | |
| Dimensions | 4,23(2.285) x 1,3 x 1,61m |
| Mass | 1050 kgs |
| Crew | 4-5 |
| Load/recoil | horizontal sliding-block, hydro-spring |
| Elevation/traverse | -7° to +18° |
| Rate of fire | 10 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | c500 m/s (1600 ft/s) |
| Range | 7 km (4.3 mi) |
| Shell | 11 types Fixed QF 76.5 x 283mm R, HE 6.24-6.65 kgs |
| Carriage/sights | Dismountable, Mod.06/12/15/17 panoramic scope |
 76 mm mountain gun M1938
76 mm mountain gun M1938
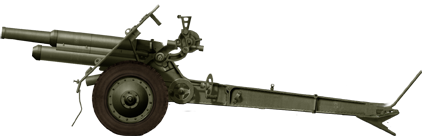
⚙ Specifications 76.2 mm mountain gun M1938 | |
| Dimensions | 4.24 m (13 ft 11 in) barrel 1.63 m (5 ft 4 in) x 1.28 m (4 ft 2 in) x 1.35 m (4 ft 5 in) |
| Mass | 785 kg (1,731 lb) |
| Crew | 4 |
| Load/recoil | Vertical sliding-block |
| Elevation/traverse | -8° to +65°, 10° |
| Rate of fire | 10-15 r.p.m. |
| Muzzle velocity | 495 m/s (1,624 ft/s) |
| Range | 10,720 m (6.66 mi) |
| Shell | 76.2 mm (3 in) 6.23 kg (13.7 lbs) |
| Carriage/sights | Box trail |
 203 mm field gun (tracked) B4
203 mm field gun (tracked) B4 The 203 mm howitzer M1931 (B-4) (cold war GRAU index 52-G-625) 8 inch Soviet high-power heavy howitzer well used in the Second World War under direct command of the Stavka's strategic reserve. "Stalin's sledgehammer" first saw combat against Finnish pillboxes at the Mannerheim Line but also later heavy German fortifications. It urban combat i destroyed buildings and bunkers, notably at the battle of Berlin. A 1944 KV-1S tank chassis was used for the self-propelled variant S-51. Heavy recoil damage led to cancellation. Between an Elevation to 60 degrees and 12 propellant loads to choose from, the B4 was all the way a success for the Red Army.
The 203 mm howitzer M1931 (B-4) (cold war GRAU index 52-G-625) 8 inch Soviet high-power heavy howitzer well used in the Second World War under direct command of the Stavka's strategic reserve. "Stalin's sledgehammer" first saw combat against Finnish pillboxes at the Mannerheim Line but also later heavy German fortifications. It urban combat i destroyed buildings and bunkers, notably at the battle of Berlin. A 1944 KV-1S tank chassis was used for the self-propelled variant S-51. Heavy recoil damage led to cancellation. Between an Elevation to 60 degrees and 12 propellant loads to choose from, the B4 was all the way a success for the Red Army.
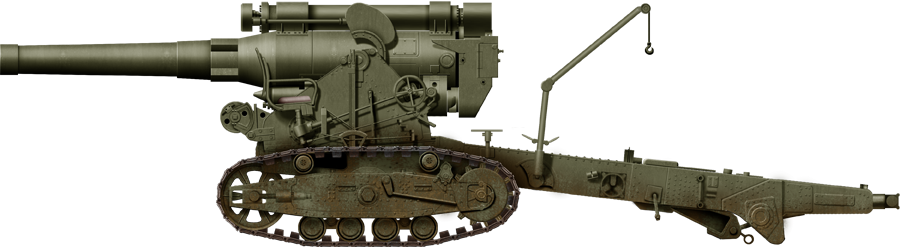
⚙ Specifications 203mm(8 in) tracked field gun | |
| Dimensions | 11.15 x 4.894 x 2.7 m (36 ft 7 in x 16 ft 1 in x 8 ft 10 in) |
| Mass | 17,700 kg (travel 19t) |
| Crew | 6 |
| Load/recoil | Interrupted screw, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | 60°/8° |
| Rate of fire | 1 round/four minutes |
| Muzzle velocity | 607 m/s (1,990 ft/s) |
| Range | 18 km (11 mi) |
| Shell | Separate loading charge/projectile HE 100 kg (220 lbs) |
| Carriage/sights | Box trail |
 240 mm Howitzer M1
240 mm Howitzer M1

⚙ Specifications 240 mm Howitzer M1 | |
| Dimensions | Barrel 27 ft 6 in (8.38 m) L/35, Width 9 ft 2 in (2.79 m) |
| Mass | 64,700 lb (29,300 kg) in action |
| Crew | 14 |
| Load/recoil | Interrupted screw, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | +15° to +65°, 22.5° either side. |
| Rate of fire | 1 rpm, 30/h sustained |
| Muzzle velocity | 2,300 ft/s (701 m/s) |
| Range | 14.3 mi (23.1 km) |
| Shell | 360 lb (160 kg) separate loading, bagged charge |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, 2 transport wagons |
 25 pdr howitzer
25 pdr howitzer
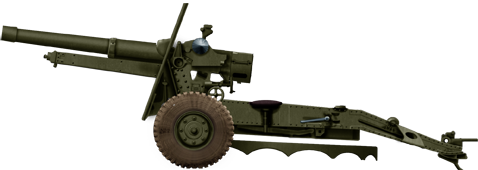
⚙ Specifications 25 pdr howitzer | |
| Dimensions | 4.6 m (15 ft 1 in) x 2.13 m (7 ft) |
| Mass | 1,633 kg (3,600 lb) |
| Crew | 6 (commander, 1 gunner, 1 pointer, 3 loaders) |
| Load/recoil | Vertical sliding-block, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -5° to 45°, 4° Left & Right traverse, 360° platform |
| Rate of fire | From 1 to 8 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 532 m/s (1,750 ft/s) AP shells |
| Range | 12,253 m (13,400 yd) (HE shell) |
| Shell | 88 x 292mm R11.5 kg (25 lb) |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, platform, Calibrating & reciprocating |
 5.5 in BL Howitzer
5.5 in BL Howitzer
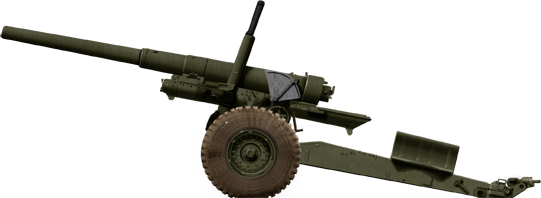

⚙ Specifications 5.5 in BL Howitzer AT Gun | |
| Dimensions | 24 ft 7 in/13 ft 9 in x 8 ft 4 in x 8 ft 6 in (7.5/4.19 m L/30 x 2.54 x 2.6 m) |
| Mass | 13,647 lbs (6,190 kg) |
| Crew | 10 |
| Load/recoil | Welin breech and Asbury mechanism, Recoil Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -5° to 45°, 30° left and right |
| Rate of fire | 2 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 100lb shell (45 kg): 1,675 ft/s (511 m/s) |
| Range | 100lb shell: 16,200 yards (14,800 m) |
| Shell | Separate loading bagged charge and projectile |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, Probert pattern reciprocating and calibrating |
 BL 7.2in Howitzer
BL 7.2in Howitzer

⚙ Specifications BL Mark I-IV 7.2in Howitzer | |
| Dimensions | 24 ft 4 in (7.42 m), barrel 14 ft 3 in (4.34 m) |
| Dimensions w/h | 9 ft (2.7 m), Height 4 ft 3 in (1.30 m) |
| Mass | 10.22 long tons (10.38 t) |
| Crew | 10 |
| Load/recoil | Welin screw & asbury mech |
| Elevation/traverse | up to 45°, 4° left & right |
| Rate of fire | Best 3 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,697 ft/s (517 m/s) |
| Range | 16,900 yd (15,500 m) |
| Shell | HE 202 pounds (92 kg) 7.2 inches (182.9 mm) |
| Carriage/sights | Split Trail |
 75mm Pack Howitzer M1 (M116)
75mm Pack Howitzer M1 (M116)

 Mounted at first on classic artillery spoked wheels it was converted to wheeled pneumatic for rapid towed deployment, it was compatible to all US trucks, down to the 1/4 ton jeep, was frequently towed by the Dodge WC or transported by plane or glider such as CG-4 Waco. It was also mounted on many vehicles: M8 Scott on the mount M7, LVT(A)-4 (same) and (A)-5 in mount M12 as well as the 75mm Howitzer Motor Carriage T30 M1A1 in mount T10, half track. It also came with an anti-tank shell, the HEAT M66 capable of penetrating 91 mm (3.6 in) of homogeneous armor.
Mounted at first on classic artillery spoked wheels it was converted to wheeled pneumatic for rapid towed deployment, it was compatible to all US trucks, down to the 1/4 ton jeep, was frequently towed by the Dodge WC or transported by plane or glider such as CG-4 Waco. It was also mounted on many vehicles: M8 Scott on the mount M7, LVT(A)-4 (same) and (A)-5 in mount M12 as well as the 75mm Howitzer Motor Carriage T30 M1A1 in mount T10, half track. It also came with an anti-tank shell, the HEAT M66 capable of penetrating 91 mm (3.6 in) of homogeneous armor.
⚙ Specifications 75mm Pack Howitzer M1 | |
| Dimensions | 3.68 x 1.19 0.94 m (12 ft 1 in x 4 ft x 3 ft 1 in) |
| Barrel | 75 mm (2.95 in), 1.38 m (4 ft 6 in) L/18.4 |
| Mass | 653 kg (1,439 lbs) |
| Crew | 6 or more |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal-block, Hydro-pneumatic, constant |
| Elevation/traverse | -5° to +45°, 6° |
| Rate of fire | 6 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 381 m/s (1,250 ft/s) |
| Range (effective) | 8.8 km (5.5 mi) |
| Shell | Fixed and Semi-fixed 75 x 272 mm R 8.27 kg (18 lb 4 oz) |
| Carriage/sights | Box trail or Split-trail depending on model |
 8-inches Howitzer M1
8-inches Howitzer M1

⚙ Specifications 8-inch gun M1 | |
| Dimensions | 40 feet (12.2 meters) overall |
| Mass | 32 tons (64,000 pounds) |
| Crew | 14 |
| Load/recoil | |
| Elevation/traverse | |
| Rate of fire | 1 round per 2-5 minutes, depending on crew efficiency and conditions |
| Muzzle velocity | |
| Range | c35,000 yards (32 km or 20 miles) |
| Shell | Average 240 pounds (108.9 kg) HE |
| Carriage/sights | |
 105 mm Howitzer M2A1
105 mm Howitzer M2A1
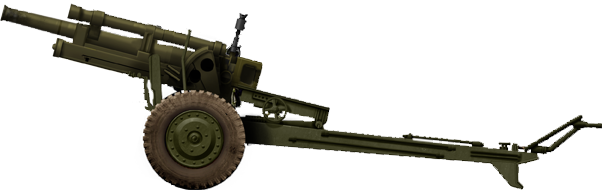

⚙ Specifications 105 mm (4.1 in) Howitzer M2 | |
| Dimensions | 19 ft 6 in x 5 ft 8 in (5.94 x 1.73 m) |
| Mass | 4,980 lb (2,260 kg) |
| Crew | 6 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal-block, Hydro-pneumatic, constant, 42 in |
| Elevation/traverse | −5° (−89 mils)-65° (1,156 mils); ±23° (±409 mils) |
| Rate of fire | 10 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 1,550 ft/s (472 m/s) |
| Range | 7.00 mi (11,270 m) |
| Shell | 105×372 mm R |
| Carriage/sights | split trail, optical |
 155 mm GIAT Howitzer M1950
155 mm GIAT Howitzer M1950

⚙ Specifications 155 mm(6.1 in) GIAT M1950 | |
| Dimensions: | 7.8 m x 2.7 x 2.5m (25 ft 7 in x 8 ft 10 in x 8 ft 2 in) |
| Barrel: | 4.65 m (15 ft 3 in) L/30 |
| Mass | 8,100 kg (17,900 lb) |
| Crew | 11 |
| Load/recoil | Interrupted screw/Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -4°/69°, 80° (40° either side of the trail) |
| Rate of fire | 3-4 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 650 m/s (2,100 ft/s) |
| Range | 18,000 m (20,000 yd)/23,300 m (25,500 yd) max |
| Shell | Separate loading charge and projectile |
| Carriage/sights | Split trail, optical |
 Canon de 75 modèle 1897
Canon de 75 modèle 1897
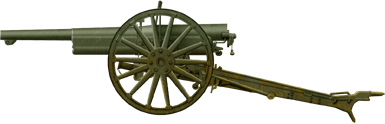
⚙ Specifications M1897, AT Variant | |
| Dimensions | |
| Mass | |
| Crew | |
| Load/recoil | |
| Elevation/traverse | |
| Rate of fire | |
| Muzzle velocity | |
| Range | |
| Shell | |
| Carriage/sights | |
 75 mm IJA Type 94 Mountain gun
75 mm IJA Type 94 Mountain gun
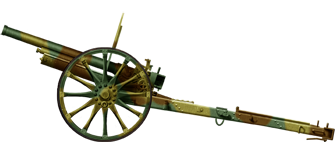
⚙ Specifications Type 94 mountain gun | |
| Dimensions | 3.81 m (12 ft 6 in) Firing trails open x 1.023 x 0.89 m |
| Mass | 544 kg (1,199 lb) Firing, 495 kg (1,091 lb) Traveling |
| Crew | 4-5 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-block, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | −10° to +45°, 40° |
| Rate of fire | 2-4 rpm, 15 rpm for 2 minutes |
| Muzzle velocity | 355 m/s (1,165 ft/s) HE |
| Range | 8 km (5.0 mi) HE |
| Shell | 75 x 294 mm R (2.95 in) HE(6 types), AP, Shrapnel, chemical... |
| Carriage/sights | Split Trail, Panoramic |
 Obice da 75/18 M34
Obice da 75/18 M34
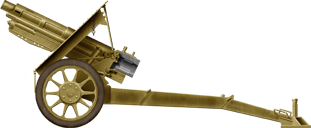
⚙ Specifications Obice da 75/18 M34 | |
| Dimensions | |
| Mass | 1,065 kg (2,348 lb) Travel, 780 kg (1,720 lb) Combat |
| Crew | 5 |
| Elevation/traverse | -10° to +45°, 50° |
| Rate of fire | c5 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 425 m/s (1,395 ft/s) |
| Range | 9,564 m (10,459 yd) |
| Shell | 75 x 232.5mmR |
| Carriage/sights | Split Trail, visual |
 105 mm Schneider M1913
105 mm Schneider M1913
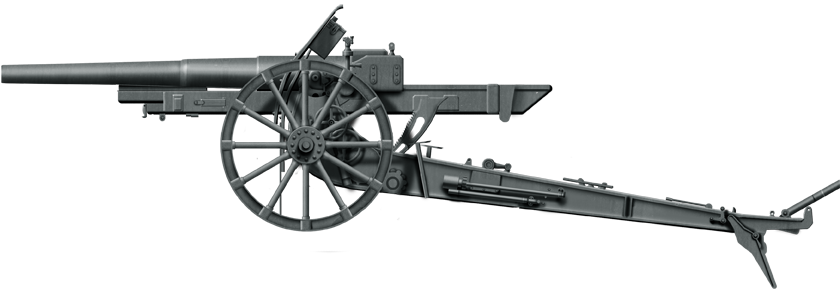
⚙ Specifications 105mm (4.1 in) Schneider | |
| Dimensions | |
| Mass | 2,300 kg (5,100 lb) combat, 2,650 kg (5,840 lb) travel |
| Crew | 6 |
| Load/recoil | Interrupted screw, Hydropneumatic |
| Elevation, traverse | -5°/+37°, traverse 6° |
| Rate of fire | 6 rounds/min |
| Muzzle velocity | 550 m/s (1,800 ft/s) |
| Range | 12 km (7.46 mi) |
| Shell | 105×390mmR, Shell weight 15.7 kg (35 lb) |
| Carriage/sights | Fixed trail |
 Cannone da 75/27 modello 11
Cannone da 75/27 modello 11
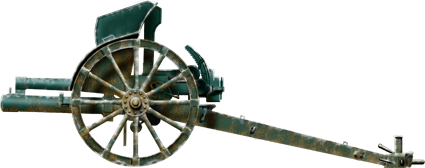
⚙ Specifications Cannone da 75/27 M11 | |
| Dimensions | 2.13 m (7 ft) L/28.4p |
| Mass | 1,076 kg (2,372 lb) travel, 1,015 kg (2,238 lb) combat |
| Crew | 5-6 (gunner, pointer, commander, 1-3 loaders) |
| Load/recoil | Nordenfelt eccentric screw/hydro spring dual recoil |
| Elevation/traverse | -15° to +65°/52° 9' |
| Rate of fire | 4-6 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 510 m/s (1,670 ft/s) base HE |
| Range | 10,240 m (11,200 yd) |
| Shell | Fixed QF 75 x 185mm R |
| Carriage/sights | Split Trail, graduated gage. |
 10 cm horská houfnice vz. 16/19
10 cm horská houfnice vz. 16/19

⚙ Spec. Skoda Vz.19 Gun 100 mm (3.9 in) | |
| Dimensions | Barrel 2.4 m (7 ft 10 in) L/24 |
| Mass | 1,350 kg (2,980 lb) |
| Crew | 5 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-wedge, Hydro-pneumatic |
| Elevation/traverse | -7° 30' to +70°, 5° 30' |
| Rate of fire | 5 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 395 m/s (1,300 ft/s) |
| Range | 9.8 km (6.1 mi) |
| Shell | 16 kg (35 lb) 100 x 183 mm R |
| Carriage/sights | Box trail |
 100 mm Skoda Field Howitzer Vz.14
100 mm Skoda Field Howitzer Vz.14
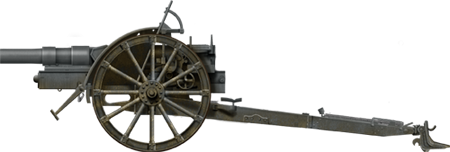
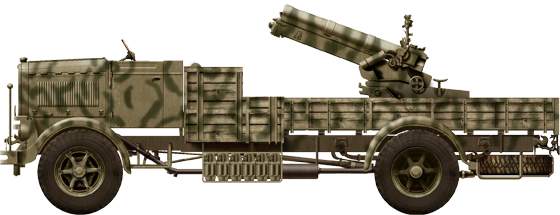
⚙ Specifications Vz.14 | |
| Dimensions | Barrel 1.93 m (6 ft 4 in) L/19. 3.93 inches |
| Mass | 1,350 kg (2,970 lbs) |
| Crew | 6 |
| Load/recoil | Horizontal sliding-block, hydro-spring variable recoil |
| Elevation/traverse | -8° to +50°, 6° |
| Rate of fire | 6-8 rpm |
| Muzzle velocity | 407 m/s (1,335 ft/s) |
| Range | 8,400 m (9,100 yards) |
| Shell | 100 x 183mm R 14 kg (31 lb), Separate loading, cased charge and projectile |
| Carriage/sights | box trail, visual |

