Introduction
AH-64 Apache: The AH-64 Apache is a renowned attack helicopter used by the United States Army and several other countries. It is armed with a 30mm M230 chain gun and can carry a combination of air-to-ground missiles, rockets, and Hellfire anti-tank missiles. The Apache is highly versatile and has proven its effectiveness in various conflicts.
Mi-24 Hind: The Mi-24 Hind is a Russian-made attack helicopter that has been widely exported and used by numerous countries. It can be equipped with a mix of rockets, anti-tank missiles, and a 12.7mm machine gun. The Hind is known for its robustness and has served in various conflicts across the globe.
Eurocopter Tiger (Airbus Tiger): As mentioned earlier, the Eurocopter Tiger (now Airbus Tiger) is a multirole attack helicopter that can perform anti-tank missions. It is armed with a range of air-to-ground missiles, rockets, and anti-tank guided missiles like the Hellfire. The Tiger has been deployed in combat situations and has demonstrated its anti-tank capabilities.
Kamov Ka-50/52 Hokum: The Kamov Ka-50 (single-seat) and Ka-52 (two-seat) Hokum helicopters are Russian attack helicopters designed for anti-armor operations. They are armed with a 30mm autocannon, guided anti-tank missiles, unguided rockets, and air-to-air missiles for self-defense. The Ka-52 is also equipped with a mast-mounted radar for enhanced target detection.
Denel Rooivalk: The Denel Rooivalk is a South African attack helicopter specifically developed for anti-armor and anti-helicopter operations. It is armed with a 20mm cannon, anti-tank guided missiles, and unguided rockets. The Rooivalk has been optimized for the challenging African battlefield and has demonstrated its capabilities in combat.
These are just a few examples of anti-tank helicopters, and there are other models and variants available around the world. Anti-tank helicopters play a crucial role in modern warfare, providing air support and firepower against armored threats on the battlefield.
Models
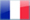
 Eurocopter Tiger
Eurocopter Tiger
➾ FF 1991, S2003, 180 Produced. Operators 



The Eurocopter Tiger, now known as the Airbus Tiger, is a multirole attack helicopter developed by Eurocopter (now Airbus Helicopters). It is a result of a collaborative effort between France and Germany. The Tiger was designed to perform a wide range of missions, including armed reconnaissance, close air support, anti-tank warfare, and escort missions. Here are some key features and information about the Eurocopter Tiger:
Design and Features:Tandem-seat cockpit (pilot in the rear, co-pilot/gunner front). Narrow fuselage with stepped tandem cockpits sleek design incorporating stealth technology to reduce its radar signature. It is armed with a chin-mounted 30mm cannon, air-to-air missiles for self-defense, and several types of air-to-ground missiles, rockets, and anti-tank guided missiles (ATGMs). It can carry its weapons on external hardpoints, as well as integrated pylons.
The Tiger is equipped with advanced avionics and mission systems to enhance its operational capabilities. It features a sophisticated electronic warfare suite, night vision compatibility, helmet-mounted displays, and a digital battlefield management system. It also has a high-performance sensor suite, including a mast-mounted sight, forward-looking infrared (FLIR) system, and a laser rangefinder/designator.
Power and Performance: The Tiger is powered by two turboshaft engines, providing it with high agility and maneuverability. It has a maximum speed of around 290 km/h (180 mph) and a range of approximately 800 kilometers (500 miles). The helicopter can operate at high altitudes and is capable of conducting operations in various environmental conditions. Service and Operators: The Tiger has been in service with the French Army and the German Army since the early 2000s. It has also been exported to other countries, including Spain and Australia. The Tiger has seen operational deployment in various conflicts and has demonstrated its effectiveness in combat situations.
German Tiger
⚙ Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 14.08 x 3.83 m (46 ft 2 in x 12 ft 7 in) |
| Rotor | 4 blades, 13 m (42 ft 8 in) 132.75 m2 |
| Weight (L/G/MTO) | 3,060 kg/5,090 kg/6,000 kg (13,228 lb) |
| Crew | 2: pilot and weapon systems officer |
| Powerplant | 2× MTR MTR390 Turbo 2x 972 kW (1,303 shp) |
| Top speed/Cruiser speed | 290-315 km/h (180 mph, 160 kn) with rotor head mast |
| Ceiling | 4,000 m (13,000 ft) |
| Climb Rate | 10.7 m/s (2,110 ft/min) |
| Range | 1,080 kg (2,381 lb) fuel, 800 km (500 mi, 430 nmi) |
| Armament | See notes |
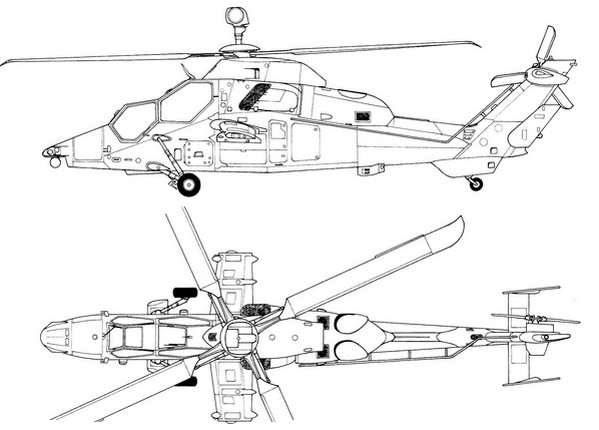
 Boeing AH-64 Apache
Boeing AH-64 Apache
➾ Produced to c2,400 machines from 1982. Operators 
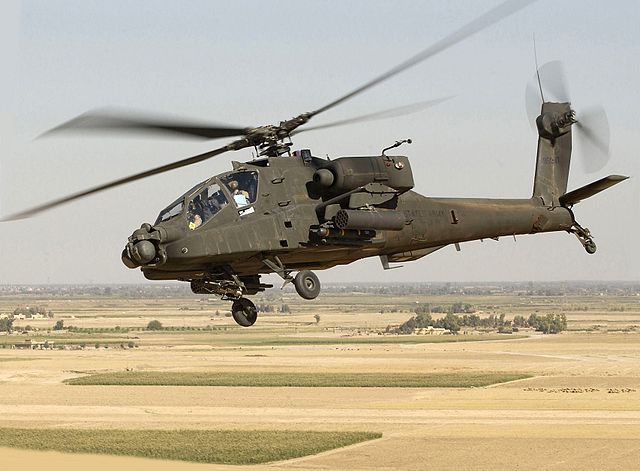


The Boeing AH-64 Apache is an attack helicopter primarily used by the United States Army, as well as several other countries. It is a versatile and heavily armed platform designed for various combat missions, including anti-armor, close air support, reconnaissance, and escort operations. Here are some key features and information about the AH-64 Apache:
Design and Features: The AH-64 Apache has a twin-engine design with a tandem-seat cockpit, accommodating a pilot and a co-pilot/gunner. Its fuselage is armored to provide protection against small arms fire and some projectiles. The helicopter incorporates stealth technology to reduce its radar signature and has advanced composite rotor blades for improved performance. Armament: The Apache is armed with a 30mm M230 chain gun mounted under the nose, capable of firing a variety of ammunition types. It can carry a combination of air-to-ground missiles, such as the AGM-114 Hellfire anti-tank missile, and Hydra 70 rockets in its stub wings. The Hellfire missile is particularly effective against armored targets, including tanks.
Avionics and Systems: The Apache is equipped with advanced avionics and targeting systems. It features a helmet-mounted display for the crew, enabling them to visually designate targets and cue the helicopter's weapons systems. The aircraft also has a Longbow fire control radar, which allows for autonomous detection, tracking, and engagement of targets. Power and Performance: The Apache is powered by two turboshaft engines, providing it with excellent maneuverability and performance. It has a maximum speed of around 293 km/h (182 mph) and a range of approximately 480 kilometers (300 miles). The helicopter can operate at high altitudes and adverse weather conditions.
Service and Operators: The AH-64 Apache has been in service with the United States Army since the early 1980s. It has also been exported to several other countries, including the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Japan, Israel, and others. The Apache has seen active duty in various conflicts worldwide and has proven its effectiveness in combat operations.
The AH-64 Apache has undergone several upgrades and modernization efforts over the years, improving its capabilities and maintaining its relevance on the modern battlefield. It remains one of the most advanced and widely used attack helicopters globally.
⚙ Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 58 ft 2 in x 49 ft 5 in x 12 ft 8 in (17.73 x 15.06 x 3.87 m) |
| Rotor | 4-blades, 48 ft (14.63 m), 1,908.5 sq ft |
| Weight (L/G/MTO) | 11,387 lb/17,650 lb/23,000 lb (10,433 kg) |
| Crew | 2: pilot and co-pilot/gunner |
| Powerplant | 2× GE T700-GE-701 turbo 1,690 shp (1,260 kW) each |
| Top speed/Cruise speed | 158 kn (182 mph, 293 km/h) |
| Ceiling | 20,000 ft (6,100 m) |
| Climb Rate | ? |
| Range | 257 nmi (296 mi, 476 km) combat 260 nmi |
| Armament | 1×30 mm M230 Chain Gun (1,200 rds), AGM-114 Hellfire/AGM-65 Maverick, see notes |
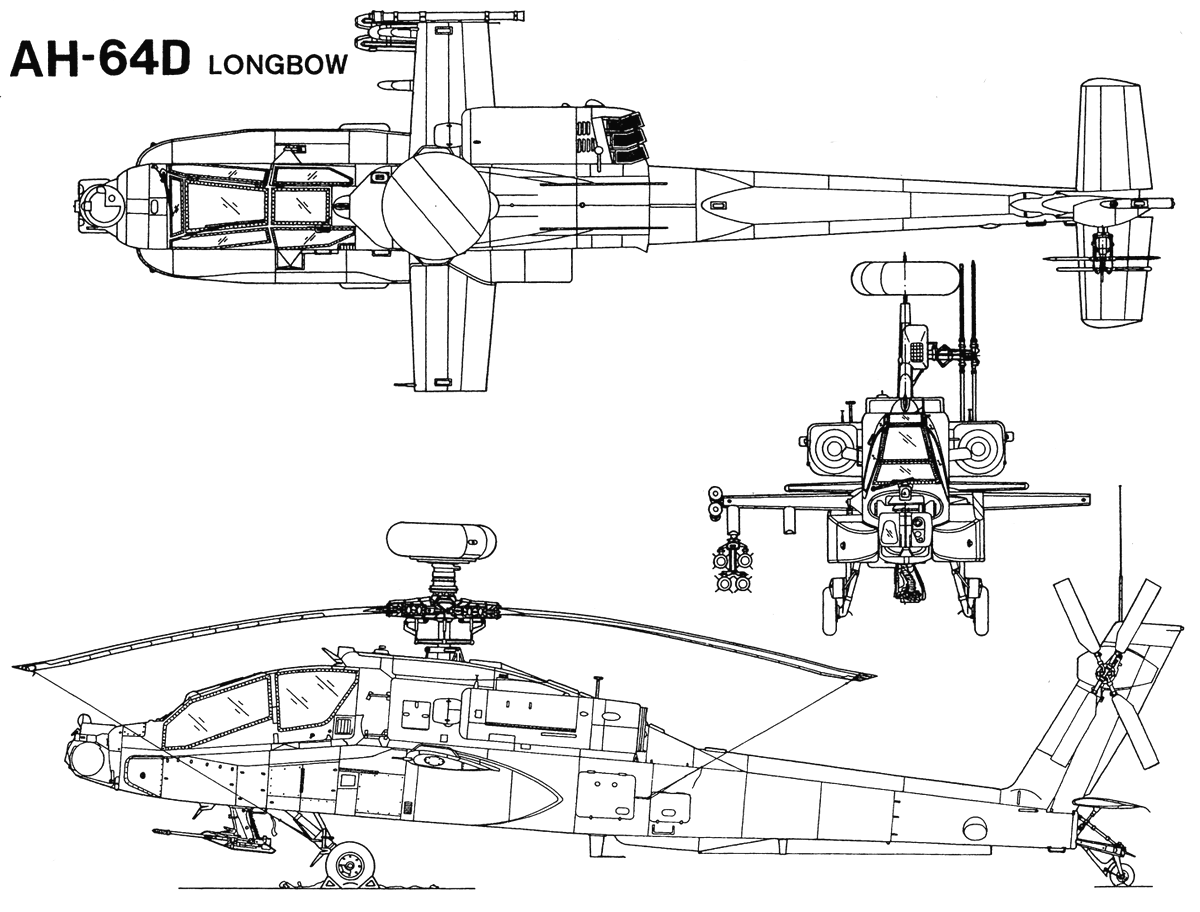
 Mil Mi-24 Hind (1969)
Mil Mi-24 Hind (1969)
➾ Produced to 2,648 machines from 1972. Still produced. 67 Operators.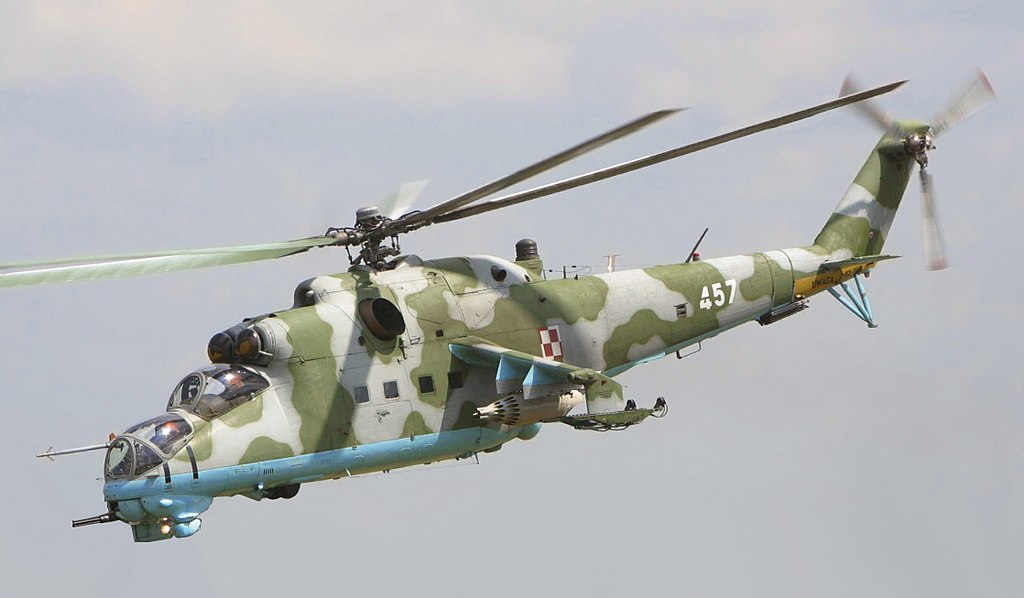
The Mil Mi-24 Hind is a large, heavily armed attack helicopter developed by the Soviet Union during the Cold War. It was designed as a multipurpose helicopter capable of performing various roles, including close air support, ground attack, and troop transport. Thus, it was also able to perform antitank missiones when needed. It was one of the most feared helicopter pof the Warsaw Pact, althought its aura somewhat shaded in the Afghan war. The Mi-24 is known for its distinctive tandem cockpit arrangement, with the pilot sitting in the rear and the weapons operator/gunner in the front.
Design and Armament: The Mi-24 features a robust, heavily armored fuselage to protect its crew and vital components. It has a tandem cockpit configuration, with the gunner/operator seated in the front and the pilot in the rear. The helicopter is equipped with various offensive weapons, including a chin-mounted turret with a 12.7mm machine gun, rocket pods, anti-tank guided missiles (ATGMs), and bombs. The armament can vary depending on the specific variant and mission requirements. Against tanks, the "Hind" possesses a large payload: UB-16 S-5 and UB-32 S-5, B-8V20 rocket launchers, S-24 240 mm rocket, and the 9M17 Fleyta and 9K114 Shturm in pairs on the outer and wingtip pylons and the always trusted UPK-23-250 gunpod for the GSh-23L firing if needed AP shells. The Mi-24 is also well protected from AA fire thanks to its armored cell.
Transport Capacity: The Mi-24 can carry up to eight fully equipped troops in its cabin or alternatively transport cargo internally. Troops can access the cabin through a large rear ramp, which can also be used for rapid deployment of troops during combat operations. This could be an antitank team, carrying it's own portable AT missile battery, adding to the helicopter own capabilities.
Performance: The Mi-24 is powered by two turboshaft engines, providing it with significant power and agility. The helicopter has a maximum speed of around 335 km/h (208 mph) and a range of approximately 450 km (280 miles) without external fuel tanks. The model saw several variants and upgrades over the years, Mi-24A, Mi-24D, Mi-24P, and Mi-24V with specific improvements in terms of avionics, weapon systems, and overall capabilities.
Service and Influence: The Mi-24 Hind has been widely exported to various countries and has seen extensive combat service in conflicts around the world. It has been used by numerous nations, including Russia, former Soviet states, and other countries in Europe, Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Fast, versatile, powerful and robust, it is still one of the very best attack helicopter ever designed.
Blueprint of the type
⚙ Mi-24D Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 17.5/ x 6.5 x (57 ft 5 in/ x 21 ft 4 in) |
| Rotor | 17.3 m (56 ft 9 in) 235.1 m2 (2,531 sq ft), with fuselage 19.79 meters oa (65 ft) |
| Weight (L/G/MTO) | 8,500 kg (18,739 lb)/12,000 kg (26,455 lb) |
| Crew | 2-3 pilot, weapons system officer and technician, 8 troops |
| Powerplant | 2x Isotov TV3-117 turboshaft 1,600 kW (2,200 shp) |
| Top speed/Cruise speed | 335 km/h (208 mph, 181 kn) |
| Ceiling | 4,900 m (16,100 ft) |
| Climb Rate | ? |
| Range | 450 km (280 mi, 240 nmi) |
| Armament | See notes |
 Leonardo AW249 Mangusta
Leonardo AW249 Mangusta
➾ Production awaited 2024+
The Leonardo Helicopters AW249 Fenice (English: Phoenix) is an attack helicopter project under development by the Italian firm Leonardo S.p.A. Development of the AW249 formally started upon receipt of a €487 million contract from the Italian Army as a replacement for the Agusta A129 Mangusta. It is to be larger, more survivable, and have greater autonomy than the Mangusta, incorporating stealth technologies and mission systems to control unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV)s. Numerous mature technologies will also be incorporated, such as the OTO Melara TM197B 20 mm chin-mounted cannon, Rafael Advanced Defense Systems Toplite targeting system and Spike missile, it is intended for the AW249 to have lower operating costs than the preceding Mangusta. Leonardo is actively seeking partners to collaborate on the AW249; a letter of intent on this matter was signed with the Polish Armaments Group during July 2018. The maiden flight of the AW249 was originally scheduled to take place during 2020, but flew for the first time on 12 August 2022 from the company’s plant in Vergiate. There are to be a single prototype and three pre-serial production rotorcraft built ahead of quantity production AW249s. As per the original timetable released in 2017, the AW249 was to be in service by 2025 to enable the retirement of the Mangusta to commence.

Leonardo Helicopters AW249
⚙ Specifications | |
| Dimensions | Unknown |
| Rotor | Unknown |
| Weight (L/G/MTO) | 7,500–8,000 kg (16,535–17,637 lb) |
| Crew | 2 |
| Powerplant | 2× GE CT7-8E6 turboshaft, 1,900 kW (2,500 shp) |
| Top speed/Cruise speed | 259 km/h (161 mph, 140 kn) |
| Ceiling | 6,100 m (20,000 ft) |
| Climb Rate | Unknown |
| Range | Three hours, |
| Armament | Payload 1,800 kg, OTO Melara TM197B cannon, RAFAEL Spike missiles |
 Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk
Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk
➾ Produced to 5,000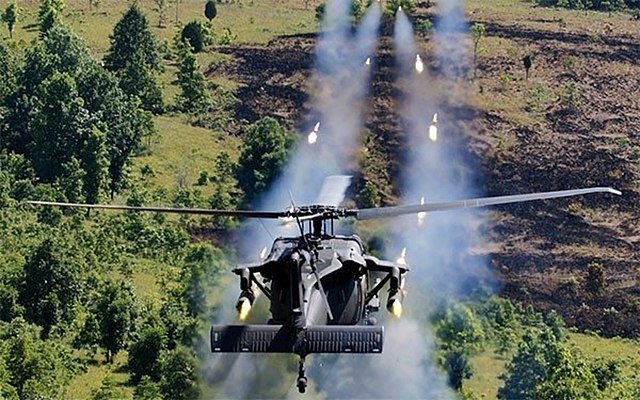
The Sikorsky UH-60 Black Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter from Sikorsky Aircraft. The S-70 design was proposed to for the UTTAS competition in 1972. The YUH-60A was the winner of the program in 1976 and entered service in 1979. Among all the variants, the MH-60L DAP was developed as the "The Direct Action Penetrator", a special operations modification (MH-60L) used by the 160th Special Operations Aviation Regiment. A gunship without troops,with ESSS or ETS stub wings is armed with the M230 Chain Gun 30 mm automatic cannon, 19-shot Hydra 70 rocket pod, AGM-114 Hellfire missiles, AIM-92 Stinger air-to-air missiles, GAU-19 gun pods, and M134 minigun pods.

Profile of the MH-60L DAP
⚙ Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 64 ft 10 in x 7 ft 9 in x 16 ft 10 in |
| Rotor | 53 ft 8 in (16.36 m), 2,260 sq ft (210 m2) |
| Weight (L/G/MTO) | 12,511/22,000 Ib. Cap. 3,190 lb (1,450 kg) |
| Crew | 2 pilots+2 crew chiefs/gunners |
| Powerplant | 2× General Electric T700-GE-701C/D turboshaft engines, 1,994 shp |
| Top speed/Cruise speed | 159 kn (183 mph, 294 km/h)/152 kn (175 mph, 282 km/h) |
| Ceiling | 19,000 ft (5,800 m) |
| Climb Rate | 1,646 ft/min (8.36 m/s) |
| Range | 320 nmi (370 mi, 590 km), Ferry range 1,199 nmi |
| Armament | 4x AGM-114 Hellfire laser guided air-to-ground missiles, see notes |
 MBB Bo 105
MBB Bo 105
➾ Produced to 1500+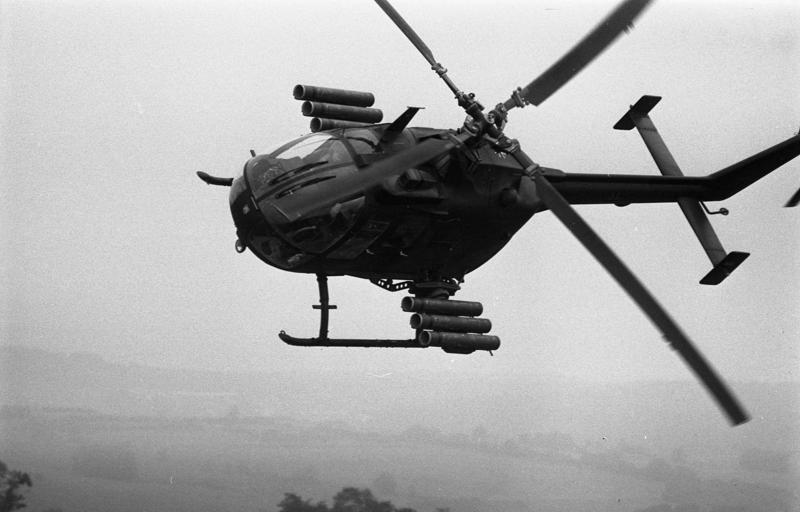
The Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm Bo 105 is a light, twin-engine, multi-purpose helicopter. Main design was started by Bölkow of Ottobrunn in West Germany by the early 1960s. The prototype first flew in 1967. It was the first light twin-engine helicopter in the world also capable of aerobatic maneuvers. It is featuring a hingeless rotor system, an innovation in helicopters back in 1970. Production was ramped up between Germany and Canada for a total of 1500+, with extensions to Spain, Indonesia, and the Philippines. MBB merged with Eurocopter in 1991 and production ceased by 2001, formally replaced by the EC135.
The MBB Bo 105 proved a remarkably adaptable helicopter, used for SAR, reconnaissance and transport, as well as ASW patrol from ships and anti-tank combat. The main version for this use was the 1975 Bo 105P/PAH-1 armed with wire-guided HOT ATGMs in service with the Bundeswehr as the Panzerabwehrhubschrauber-1. It replaced the Aerospatiale Gazelle. The Bo 105P/PAH-1A1 was an Upgraded variant of the 1980s which was ported as standard on most remaining helicopters. The Bo 105P/PAH-1 Phase 2 was a further planned upgraded version with infra-red roof mounted sight for HOT-2 missiles but it was cancelled by 1993. It was itself gradually replaced on the late 1990s by the new Eurocopter Tiger. Not scrapped ones were converted to the VBH version.

Range of armament, ancient 1980s publication
⚙ BO 105P AH1 Specifications | |
| Dimensions | 11.86 x 3 m (38 ft 11 in x 9 ft 10 in) |
| Rotor | NACA 23012, 9.84 m (32 ft 3 in), 76.05 m2 (818.6 sq ft) |
| Weight (L/G/MTO) | 1,276 kg (2,813 lb)/2,500 kg (5,512 lb) |
| Crew | 1-2 pilots, 4 passengers |
| Powerplant | 2× Allison 250-C20B 310 kW (420 shp) each |
| Top speed/Cruise speed | 242 km/h/204 km/h (127 mph, 110 kn) |
| Ceiling | 5,200 m (17,000 ft) |
| Climb Rate | 8.00 m/s (1,575 ft/min) |
| Range | 570 L (150 US gal; 130 imp gal), 657/1,112 km, 3 hr 30 min |
| Armament | 2x3 HOT or 2x4 BGM-71 TOW |
 Changhe Z-10
Changhe Z-10
➾ c250 ProducedIt is equipped with a 30mm cannon, and it can carry an array of weaponry, including HJ-10 anti-tank guided missiles, TY-90 air-to-air missiles, and other rockets. The helicopter has ballistic protection for the cockpit and engines, helping it withstand small arms fire and some level of ground-based anti-aircraft fire. The design includes some radar cross-section (RCS) reduction features, although it is not a full stealth helicopter. Originally intended to be powered by Pratt & Whitney PT6C-67C engines, it ultimately uses Chinese-made WZ-9 engines due to export restrictions and a need for domestic production, for a top speed of around 300 km/h (186 mph), combat range of approximately 800 km (497 miles). It is in service with the People’s Liberation Army Ground Force (PLAGF) since 2012 for close air support, anti-tank operations, and armed reconnaissance. It was exported to Pakistan. Albeit comparable to the American AH-64 Apache or the Russian Mi-28, though it is generally considered to be slightly lighter and less heavily armed.

 Lockheed AH-56 Cheyenne
Lockheed AH-56 Cheyenne
➾ 10 ProducedThe AH-56 Cheyenne faced a series of challenges, including mechanical issues with its pusher propeller and concerns over stability and maneuverability at high speeds. The helicopter was also seen as having limited utility in the evolving battlefield environment, as the Army began to reconsider its role in armed aviation. After several prototypes and extensive testing, the Cheyenne program was canceled in 1972 due to budget constraints, technical difficulties, and a shift in military focus toward more versatile and simpler attack helicopters. Although the Cheyenne never entered production, its development heavily influenced future attack helicopters, especially the AH-64 Apache. The compound helicopter design concept continues to be explored in modern experimental helicopters, as manufacturers and militaries look for ways to increase helicopter speeds and range.

 Bell Huey Cobra
Bell Huey Cobra
➾ 1,116 Produced until 2019It had a Slim Profile and Tandem Seating (pilot and gunner sitting one behind the other) minimized its target area, giving it a distinct advantage in combat. It was armed with a 7.62mm minigun, 40mm grenade launcher, and a 20mm M197 Gatling cannon in later versions. It could also carry rockets and anti-tank missiles such as the TOW (Tube-launched, Optically tracked, Wire-guided) missile. The Cobra uses a two-blade main rotor and tail rotor system, which contributed to its agility and allowed for faster forward speeds compared to transport helicopters. It was primarily used in close air support and armed escort missions, often flying alongside transport helicopters like the Huey to protect troops during deployment and extraction. During the Vietnam War, it proved highly effective in jungle environments, where it could provide covering fire and eliminate enemy positions before ground forces arrived. The Cobra’s role evolved over time, and it became a major anti-armor platform during the Cold War, capable of engaging tanks and armored vehicles with TOW missiles.
The AH-1 has been produced in numerous variants, including AH-1G (initial version for the U.S. Army), AH-1J SeaCobra (for the U.S. Marine Corps), AH-1W Super Cobra, and AH-1Z Viper (the most advanced version, in service with the U.S. Marine Corps). The AH-1Z Viper, the latest model, features twin engines, advanced targeting systems, a four-blade rotor, and modern avionics, making it one of the most capable attack helicopters in the world today.

 IAIO Toofan
IAIO Toofan
➾ c50? ProducedThe Toufan retains the AH-1J's basic airframe design but incorporates locally produced components, including advanced avionics, improved targeting systems, and other modernized subsystems. Like the Cobra, it has a tandem cockpit with a pilot and a gunner, allowing for a focused attack and reconnaissance role. The Toufan is armed with a 20mm cannon and can carry rockets and anti-tank missiles, similar to its American counterpart. It reportedly uses Toofan anti-tank missiles (similar to the TOW missile), though details on missile capabilities are somewhat limited due to restricted information on Iranian defense technology. The helicopter has upgraded optics, infrared cameras, and navigation systems to enhance targeting accuracy and allow for nighttime and all-weather operations.
Toufan I: The initial version of the Toufan, with upgrades to its avionics and missile systems. This version is largely based on the original AH-1J model.
Toufan II: Introduced in 2013, this variant includes further improvements to weapon systems, targeting optics, and survivability. The Toufan II has better accuracy in target acquisition and has been outfitted with modernized equipment, including enhanced communication systems.
Toufan III: Reports suggest an even more recent model, which likely includes further advancements in Iranian-built electronics and potentially increased engine performance, though specific details remain classified.
The Toufan series is primarily operated by the Islamic Republic of Iran Army and the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC). The helicopters are used for close air support, anti-armor missions, and armed reconnaissance. They are also deployed in border regions and have likely been tested in combat, given Iran’s involvement in regional conflicts. Panha, officially known as the Iran Helicopter Support and Renewal Company, specializes in the maintenance, overhaul, and manufacturing of helicopters. Established to support Iran's helicopter fleet, Panha has developed several helicopter models, including the Shabaviz 2-75 and the Saba-248. In summary, the Panha 2091 "Toufan" represents Iran's efforts to modernize its attack helicopter capabilities through domestic innovation and upgrades of existing platforms.

 Kamov Ka-50 Black Shark
Kamov Ka-50 Black Shark
➾ 19 ProducedThe Ka-50 uses a 30mm 2A42 Autocannon on the side of the fuselage,fixed, aimed by the pilot and carries a variety of anti-tank guided missiles, including the 9K121 Vikhr (AT-16 Scallion) missile, capable of penetrating heavily armored vehicles or 80mm or 122mm rockets and other ordnance, with pylons for mounting other weaponry. It was the first production helicopter to feature an ejection seat with its rotor blades jettisoned prior to. Designed for anti-armor and close air support it was superseded in the Russian Federation by the Ka-52 "Alligator" two-seat variant (196 made).

 Kawasaki OH-1
Kawasaki OH-1
➾ 38 ProducedIt has a compact, lightweight airframe with a tandem cockpit (pilot and co-pilot sitting one behind the other), giving it a narrow profile to minimize its target area and reduce radar visibility. It is powered by two Mitsubishi TS1-M-10 turboshaft engines, which offer enhanced reliability, redundancy, and safety, especially important for operations over mountainous terrain or coastal areas. The exhaust ducts on the OH-1 are designed to reduce the infrared signature, helping it evade heat-seeking missiles and enhancing its survivability. The OH-1 is equipped with an array of sensors, including an infrared targeting pod, optical sensors, and laser rangefinders. This suite enables effective reconnaissance, target acquisition, and identification. The OH-1 features a helmet-mounted display for the pilot, allowing for hands-free display of targeting information and flight data, which increases situational awareness. The cockpit is equipped with multi-functional displays (MFDs) and a digital avionics suite that enables better coordination with ground forces and other aircraft.
The OH-1 is primarily designed for reconnaissance and therefore does not carry heavy weaponry like attack helicopters. However, it has two stub wings with hardpoints, allowing it to carry Type 91 air-to-air missiles for self-defense. Future plans included potential upgrades to give the OH-1 a greater offensive capability, but for now, it remains primarily an observation and reconnaissance platform, with 250 planned, only 38 completed. The OH-1 is highly maneuverable, designed to operate effectively in mountainous terrain and urban environments. It can reach speeds up to 277 km/h (172 mph) and has a range of approximately 550 km (342 miles), allowing it to cover extensive areas in support of ground forces. Special attention was paid to reduce rotor noise, making the OH-1 more challenging to detect acoustically, an asset in covert operations or stealthy reconnaissance missions.

 Bell AH-1W Super Cobra
Bell AH-1W Super Cobra
➾ 1271 ProducedThe AH-1W has a maximum speed of approximately 282 km/h (175 mph) and is known for its agility, which makes it effective in close air support and maneuverable in close-quarters combat and combat radius of about 240 kilometers (150 miles). It saw extensive use in Operation Desert Storm, Operation Iraqi Freedom, Operation Enduring Freedom in Afghanistan, and various other conflicts. It proved effective in harsh environments, from deserts to urban combat zones, delivering precision firepower and close support to ground forces. It replaced in U.S. Marine Corps service by the Bell AH-1Z Viper but remained with Turkey and Taiwan.

 Mil Mi-28
Mil Mi-28
➾ 126 Produced 1982-2020The Mi-28 is armed with the 30mm Shipunov 2A42 Cannon mounted on a chin turret, capable of firing high-explosive and armor-piercing rounds. This cannon is effective against both armored vehicles and infantry. It is typically equipped with 9M120 Ataka (AT-9 Spiral) anti-tank guided missiles but could also carry 80mm or 122mm unguided rockets and bombs as well as having an Air-to-Air Capability with Igla or Strela mounted under pod. It is powered by two Klimov TV3-117 turboshaft engines, giving it a high degree of reliability and power, particularly in challenging terrain and hot climates, top speed 300 km/h (186 mph), range 435 km (270 miles). To the Mi-28A initial variant with day combat capability only, succeeded the Mi-28N "Night Hunter" (most common variant) alongside the training Mi-28UB (dual-control) and latest Mi-28NM with improved radar, new sensors, updated engines, and additional avionics for better survivability and combat effectiveness. It was deployed so far in Syria and more recently in Ukraine. It was exported also to Iraq and Algeria.

 HAL Prachand
HAL Prachand
➾ 15 Produced (156 ordered)The Prachand has a Lightweight and Agile Frame, Stealth and Armor Features, High-Altitude Performance (6,500 meters or 21,300 feet), a full Avionics and Sensor Suite with All-Weather, Day-Night Capability, Advanced Targeting and Display Systems, Electronic Warfare and Self-Protection with RWR and MAWS, CMDS. It is armed with a 20mm M621 Cannon, nose-mounted, turreted and Helina (a variant of the Nag) anti-armor missiles, or 70mm rockets, even the MBDA Mistral air-to-air missile. Powered by two Shakti turboshaft engines, co-developed by HAL and Safran of France optimized for high-altitude performance, procures it a top speed of about 268 km/h (167 mph), range of approximately 550 kilometers (340 miles).

 Denel Roiivalk (1990)
Denel Roiivalk (1990)
➾ 15 Produced
 Bell AH1J Super Cobra (1970)
Bell AH1J Super Cobra (1970)
➾ c1270+ ProducedIts twin-engine configuration gave it greater reliability and power than the AH-1G (20% lost in Vietnam), a slender fuselage for greater speed and agilit, modified to handle saltwater operations on Navy ships, basic night-fighting capability, improved targeting. It took part in the last operations in Vietnam and was also last seen in Operation Desert Storm, later replaced by the AH-1W Super Cobra and AH-1Z Viper and also Iran (pre-1979) which reverse-engineered it and created the Panha 2091. The Bell 309 King Cobra was a one-off 1971 prototype developed to combine features of the AH-1G Cobra and AH-1J Super Cobra for the Army, but never entered production.

 T129 Atak
T129 Atak
➾ ProducedIt us powered by two LHTEC CTS800-4A turboshaft engines (license-produced in Turkey) powering a 5-bladed main rotor, 2-blade tail rotor. Optimized for high-altitude, hot-weather performance, it was was setup for Turkey’s mountainous regions. Its Cockpit was given modern digital displays, advanced mission computers and it was capable of Asymmetrical payload capability. The Aselsan ASELFLIR-300T is its central Electro-optical targeting and laser designation system. It has a Including radar warning receivers, laser warning receivers, chaff/flare dispensers, Helmet-mounted cueing system and Ballistic protection for the crew.
The T129 Atak is armed with a 20mm three-barreled M197 Gatling gun in a nose-mounted turret, and four underwings hardpoints for Umtas or L-UMTAS: Long-range anti-tank missiles, Cirit 70mm laser-guided rockets, Stinger air-to-air missiles on stub wings and unguided 70mm rockets for area suppression. It was exported to the Philippines from 2022, Pakistan (delayed due to U.S. export license) while Bangladesh, Qatar, and others have shown interest. It was used in anti-terror and counter-insurgency operations along its borders.

 Bell AH-1Z Viper (2010)
Bell AH-1Z Viper (2010)
➾ 195 Produced
 Antitank Helicopters
Antitank Helicopters