The Tiran series were basically the reuse and modifications by the Israeli Defense Forces of captured T-54/55 from the 1967 and 1973 wars, repurposed. Gradually, the IDF replaced many of the original Soviet components with Western systems to improve compatibility with their logistics and operational needs. Later models obtained the 105mm M68 rifled gun with improved targeting optics, night vision, new communication systems, upgraded engines for better reliability, IDF storage bins and smoke grenade launchers, and other external fittings. They were mainly used in Lebanon and some given to the South Lebanese Army, phased out as more Merkava entered IDF service.
Some of these tanks were in pristine conditions, just captured, others had been damaged or just broke down in place and left there due to the absence of retrieving vehicles (it was not even in Soviet doctrine). A few also ran of diesel and were abandoned. And many of the tanks left on the battlefield, battle damaged were still usable, notably by crossing what was still working, cannibalizing them to have at least a few running. The main issue there as the absence of Soviet spare parts for maintenance after extinguishing the park of captured vehicles.
The end result was the gradual upgrade of these tanks, keeping in the end only the "envelope", and even the protection was enhanced between add-on plating, ERA boxes, and smoke dischargers. New Western guns, new HMG and LMGs, and even new engines, plus scores of Western equipments transformed these recoignisable medium tanks into something else entirely. And when they reached the end of their useful life, many were recycled and turned into new vehicles such as the Achzarit. On the grand total of c300 Tiran, only a fraction were of the final Ti-67 which shared practically nothing with the original T-55, apart the appearance.
Syria started taking delivery of the Russian T-54 Medium tank in during the 1950’s and its upgraded version the T-55 in the 1960’s. Egypt also took delivery of the same tanks in the 1960’s and both countries operated them during the 1967 Six-Day War and 1973 Yom Kippur War fighting Israel. Israel eventually came out victorious in both wars and captured hundreds of T-54 and T-55 from both countries. Prior to the development of the Merkava Main Battle Tank, Israel excelled at the communalisation of various international tanks with the same 105mm main gun, tracks, ERA armour and engines and renaming them, for example: The British Centurion became the Sho’t and both the American M48 Patton and M60 Patton became the Magach series. This was continued with the captured T-54/T-55, which became the Tiran Series.

In the Six Day War the Israeli managed to captured a world record of 860 enemy tanks. Among these were 280 T-54/5 tanks. 146 couldbe repaired and return into service as Tiran 4/5, 4 for the T-54, 5 for T-55. They were however, not an ideal solution, as they did not really suited the IDF’s needs with engineers trying to take advantage what this crude soviet tank could offer. It was considered at best as a reserve tank for wartime, usable by reservists, and second line reinforcements, but also for missions such as mine-clearing tank and other special operations. There was one variant also to guide the SA-3 anti-air missile batteries.
Many modifications later, these were incorporated in a single mixed Tiran 4/5 brigade. The IDF found a way to integrated these in a special tactical task force for surprise armor thurst in the Egyptian flank counting on their likeness to friendly tanks to cause confusion.
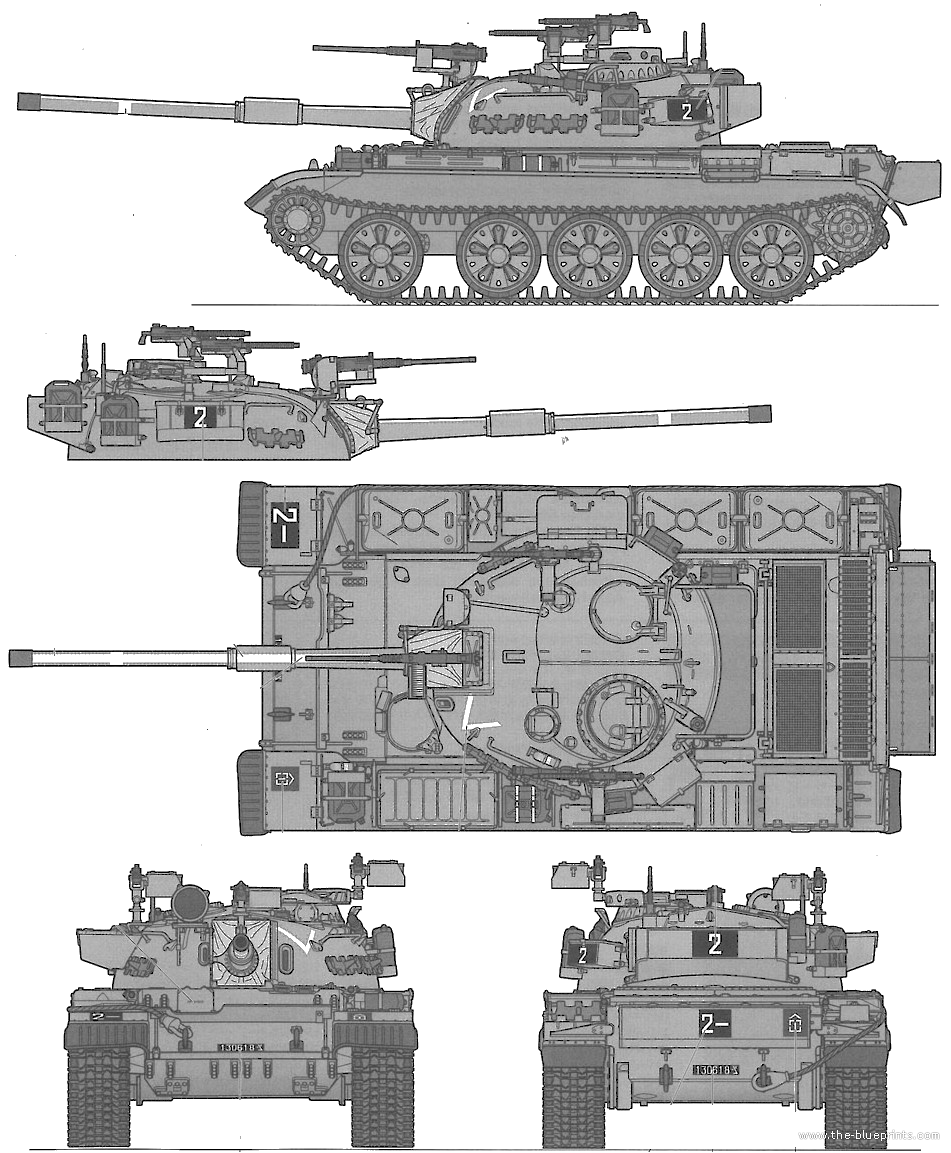

Israel beng probably the country which reused the most of military equipment obtained in combat managed to obtained some 150 T-54 and T-55 main battle taks mostly from Egypt, from the Yom Kippur War, later renamed Tiran 4 and 5 and with many subversions which are only separable via photos. They shared a lot of common elements, notably their add-on caracteristic storage bins. These additions were performed sometimes on a ad hoc basis so that many of these were unique in their configuration. Basically the early 4 and 5 kept their original gun and engine but received a lot of equipments to US/Western and IDF standards, notably their machine guns.
The Tiran 4 and 5 later evolved further (after the 1973 war) and had their original 100 mm gun barrel D-10T replced by a rifled L7 105mm used for the M48 and Centurion, spares or taken from those destroyed during the 1973 war. This was compounded by a change of main power plant, a US one, greatly improving reliability and also ensuring maintenance commonality. Still, the ergonomics were poor and the larger gun breech of the L7 had a hard time fitting inside.

The oriignal 12,7mm DShK gun and coaxial KPT were als replaced by the standard IFG M1 and M2 Browning machine gun, with at minima a single roof mounted cal.30 M1919A4 and an extra arm mount closer to the gun barrel with a Browning M2HB heavy machine gun, remotelly fired. The headlights guard was also modified and new front fenders fitted, with rubber parts. The turrets saw the most changes with many welded hooks and holders for two Jerry fuel cans, 5 of them with two on either side and three on the back of the turret. They also received fixation hooks for two spare track links on either side, whith could act as add-on protection, but also new storage/tool boxes on the rear sides and a lare utility basket at the turret back, the safest giveraway these were Tirans, outside the gun. The standard night IR illuminiaton projector atop and aside the gun mantlet was removed but an additional projectors or two were fitted close to the commander’s hatch. Several fire extinguishers were akso added in different places and some received also extra smoke dischargers (Tiran 6 notably).
The Tiran 5 conversion, in addition to what was said above, led to cast in the hollow cast turret numerous IDF details. The most obvi empty bustle cast to the turret, IDF modified loaders and drivers hatch, 105mm gun tube. 60mm mortar and spare round box, commanders and loaders m.g. mounts, correct machine guns, .30 caliber and correct ammo boxes. Turret side storage box, four IDF jerry can racks molded empty, five IDF jerry cans, separate, rear hull storage bin with medical box attached, IDF infantry comm. box. Late pattern fuel cells, accurate pattern oil storage box, two fender storage boxes, IDF Pattern driving lights and IDF pattern mud flaps with "rubber" dust guards molded separately.
-Additional stowage boxes and jerrycans strapped onto the turret's sides and rear.
-Black rubber half fenders instead of solid metal front fenders.
-Loader's hatch replaced by a new one opening rearwards
-Pintle-mounted .30 cal Browning Machine Gun fwd of the new loaders hatch -New antenna mount added at the rear of the turret
1st version: 2 brackets Jerrycans back, new radio, rest original.
First standard: New rear mud guards, a cal.30 loader, rear chassis box.
Second standard: New antennas door and turret headlights, spare tracks one turret and new 105 mm M-68 gun.
-Half black rubber fenders.
-New rear opening Loader's hatch
-Pintle-mounted .30 cal Browning MG at his position
-New antenna mount at the turret rear.
 The name "Ti-67" is referring to the ultimate evolution of the Tiran 4/5 in IDF service, with the “s” denoting an upgrade in firepower assisted by a new computerized fire control system, completed by a new night vision equipment and adapted gun stabilization system. The second major change and missing piece in this final upgrade, is the replacement of the Soviet diesel by a Detroit Diesel 8V-71T and its associated transmission. But also improved suspension, and anew dashboard and levers in the driver's station to reflect the engine's swap. Protection is enhanced by fixation points for Blazer explosive reactive armour (ERA) similar to the Magach series, plus additional external stowage. They were the ultimate evolution for the remaining Tiran 4/5 still serviceable and they were converted to The Achzarit heavy APC from 1988.
The name "Ti-67" is referring to the ultimate evolution of the Tiran 4/5 in IDF service, with the “s” denoting an upgrade in firepower assisted by a new computerized fire control system, completed by a new night vision equipment and adapted gun stabilization system. The second major change and missing piece in this final upgrade, is the replacement of the Soviet diesel by a Detroit Diesel 8V-71T and its associated transmission. But also improved suspension, and anew dashboard and levers in the driver's station to reflect the engine's swap. Protection is enhanced by fixation points for Blazer explosive reactive armour (ERA) similar to the Magach series, plus additional external stowage. They were the ultimate evolution for the remaining Tiran 4/5 still serviceable and they were converted to The Achzarit heavy APC from 1988.
Samovar 1, integrated Merkava standard equiplent, with the Merkava II maing fun, side wire-mesh basket, small short skirts and reactive bricks.
Samovar 2: More austere variant but modified turret back and new engine and reworked, taller deck.
Tiran Blazer: Proto with a ful suite of ERA bricks,different from those on the Magach and Shot.
First combat use of Tirans, were for operation "Raviv" on 8-9 September 1969, so just two years after the 6 days war, leading an amphibious raid across the Suez channel to confuse Egyptian defenders. Three T-54 tanks and six BTR-50s were used. Later Tirans found use to patrol Israel's borders, Suez front. Their first major actionw as at the 1973 Yom Kippur war. They were deployed on southern front pitted against T-54/55 created confusion. This was also the occasion to capture the T-62, but ocnversion to the Tiran-6 never bore fruition, notably due to the availability in numbers of the M-60, US-supplied until this plug was pulled.
The early 1980s marjed the withdrawal of the oldest models from active duty, some sold back to Iran and to Israel's allies fighting in Lebanon while the remainder were converted into the Achzarit APC. Tirans supplied to the South Lebanon Army militia were captured and resued by the Hezbollah after the IDF withdrawal in June 2000. Also were used in the 1980s in Lebano, the Nohcri Gimel, a Tiran 5 modified to clear mines. It was used notably by the SLA, Lebanese army or Hezbollah after the dissolution of the South Lebanon Army on May 24, 2000. Used like the Tiran 5 dozers which as the name indicates had a toothed dozer blade added at the front used on the same gear.
Introduction
The number of T-54/55 deployed by Arab countries in, the war of 1967 especially, but also in 1973, was colossal, with entire armoured divisions thrown against the young state of Israel. Despite the odds, equipped notably with a motley collection of modernized Shermans, M48 Pattons, modified Centurions and AMX-13s, the IDF did better than just resist. This was a David vs. Goliath existential combat, and yet, Israeli tank crews prevailed, leaving, notably in the valley of tears, litterally hundreds of T-54/55 wrecks, ex-Egyptian and ex-Syrian in particular. Having no surplus tank, especially after their own losses, the Israeli were looking at taking advantage of this bonanza of armour.Some of these tanks were in pristine conditions, just captured, others had been damaged or just broke down in place and left there due to the absence of retrieving vehicles (it was not even in Soviet doctrine). A few also ran of diesel and were abandoned. And many of the tanks left on the battlefield, battle damaged were still usable, notably by crossing what was still working, cannibalizing them to have at least a few running. The main issue there as the absence of Soviet spare parts for maintenance after extinguishing the park of captured vehicles.
The end result was the gradual upgrade of these tanks, keeping in the end only the "envelope", and even the protection was enhanced between add-on plating, ERA boxes, and smoke dischargers. New Western guns, new HMG and LMGs, and even new engines, plus scores of Western equipments transformed these recoignisable medium tanks into something else entirely. And when they reached the end of their useful life, many were recycled and turned into new vehicles such as the Achzarit. On the grand total of c300 Tiran, only a fraction were of the final Ti-67 which shared practically nothing with the original T-55, apart the appearance.
The Tiran in Brief
The Tiran 4 (lit. "Tyrant", in other sources, named after the Tiran strait, but in reality the meaning in Hebrew is "beginner". This was a essentially a captured and slightly-modified Arabic T-54, in IDF service. Reusing still repairable or refurbishable T-54s would also allow to disguise them as coming from an Arabic armoured corps and perform a surprise attack at close range. The Tiran serie which started at 1, represented different modifications stages, and the 4 was the modified most heavily T-54.Syria started taking delivery of the Russian T-54 Medium tank in during the 1950’s and its upgraded version the T-55 in the 1960’s. Egypt also took delivery of the same tanks in the 1960’s and both countries operated them during the 1967 Six-Day War and 1973 Yom Kippur War fighting Israel. Israel eventually came out victorious in both wars and captured hundreds of T-54 and T-55 from both countries. Prior to the development of the Merkava Main Battle Tank, Israel excelled at the communalisation of various international tanks with the same 105mm main gun, tracks, ERA armour and engines and renaming them, for example: The British Centurion became the Sho’t and both the American M48 Patton and M60 Patton became the Magach series. This was continued with the captured T-54/T-55, which became the Tiran Series.

In the Six Day War the Israeli managed to captured a world record of 860 enemy tanks. Among these were 280 T-54/5 tanks. 146 couldbe repaired and return into service as Tiran 4/5, 4 for the T-54, 5 for T-55. They were however, not an ideal solution, as they did not really suited the IDF’s needs with engineers trying to take advantage what this crude soviet tank could offer. It was considered at best as a reserve tank for wartime, usable by reservists, and second line reinforcements, but also for missions such as mine-clearing tank and other special operations. There was one variant also to guide the SA-3 anti-air missile batteries.
Many modifications later, these were incorporated in a single mixed Tiran 4/5 brigade. The IDF found a way to integrated these in a special tactical task force for surprise armor thurst in the Egyptian flank counting on their likeness to friendly tanks to cause confusion.

Development and design of the Tiran

Israel beng probably the country which reused the most of military equipment obtained in combat managed to obtained some 150 T-54 and T-55 main battle taks mostly from Egypt, from the Yom Kippur War, later renamed Tiran 4 and 5 and with many subversions which are only separable via photos. They shared a lot of common elements, notably their add-on caracteristic storage bins. These additions were performed sometimes on a ad hoc basis so that many of these were unique in their configuration. Basically the early 4 and 5 kept their original gun and engine but received a lot of equipments to US/Western and IDF standards, notably their machine guns.
The Tiran 4 and 5 later evolved further (after the 1973 war) and had their original 100 mm gun barrel D-10T replced by a rifled L7 105mm used for the M48 and Centurion, spares or taken from those destroyed during the 1973 war. This was compounded by a change of main power plant, a US one, greatly improving reliability and also ensuring maintenance commonality. Still, the ergonomics were poor and the larger gun breech of the L7 had a hard time fitting inside.

The oriignal 12,7mm DShK gun and coaxial KPT were als replaced by the standard IFG M1 and M2 Browning machine gun, with at minima a single roof mounted cal.30 M1919A4 and an extra arm mount closer to the gun barrel with a Browning M2HB heavy machine gun, remotelly fired. The headlights guard was also modified and new front fenders fitted, with rubber parts. The turrets saw the most changes with many welded hooks and holders for two Jerry fuel cans, 5 of them with two on either side and three on the back of the turret. They also received fixation hooks for two spare track links on either side, whith could act as add-on protection, but also new storage/tool boxes on the rear sides and a lare utility basket at the turret back, the safest giveraway these were Tirans, outside the gun. The standard night IR illuminiaton projector atop and aside the gun mantlet was removed but an additional projectors or two were fitted close to the commander’s hatch. Several fire extinguishers were akso added in different places and some received also extra smoke dischargers (Tiran 6 notably).
Development
The standardization of these captured vehicles was decided for it armor corps, this led the IDF to initiate an unprecedented conversion program from this mass of captured tanks. It was done in several phases, which are detailed below. Basically, they started their career between two wars (1967 and 1973) with minmal modifications, keeping their original engine and gun, but many new features to IDF standards. Their likeness to the original was appreciated but the crews complained of poor ergonomics. It took two iterations to lead to the re-engined and re-gunned late version, after the 1973 war, to reach the standard 105mm gun used in the Centurion and Patton MBT. The Tiran 4 (T-54) and Tiran 5 (T-55) after all possible upgrades became the unique Ti-67 (Tank Israeli-1967) in the west. The Tiran 4 eventually kept its 100 mm main gun but the Tiran 5 went to 105 mm main gun, in addition of being based on the T-55.The Tiran 5 conversion, in addition to what was said above, led to cast in the hollow cast turret numerous IDF details. The most obvi empty bustle cast to the turret, IDF modified loaders and drivers hatch, 105mm gun tube. 60mm mortar and spare round box, commanders and loaders m.g. mounts, correct machine guns, .30 caliber and correct ammo boxes. Turret side storage box, four IDF jerry can racks molded empty, five IDF jerry cans, separate, rear hull storage bin with medical box attached, IDF infantry comm. box. Late pattern fuel cells, accurate pattern oil storage box, two fender storage boxes, IDF Pattern driving lights and IDF pattern mud flaps with "rubber" dust guards molded separately.
Variants
Tiran 1
Designation for captured non-modified T-54 in early IDF service.Tiran 2
Designation for captured non-modified T-55 in early IDF service.Tiran 4 (1972)
First major modification, starting with:-Additional stowage boxes and jerrycans strapped onto the turret's sides and rear.
-Black rubber half fenders instead of solid metal front fenders.
-Loader's hatch replaced by a new one opening rearwards
-Pintle-mounted .30 cal Browning Machine Gun fwd of the new loaders hatch -New antenna mount added at the rear of the turret
1st version: 2 brackets Jerrycans back, new radio, rest original.
First standard: New rear mud guards, a cal.30 loader, rear chassis box.
Second standard: New antennas door and turret headlights, spare tracks one turret and new 105 mm M-68 gun.
Tiran 5 (1973)
It consisted of a mostly similar suite: -Additional stowage boxes and jerrycans on turret-Half black rubber fenders.
-New rear opening Loader's hatch
-Pintle-mounted .30 cal Browning MG at his position
-New antenna mount at the turret rear.
Late Tiran 5:
Modified as Tiran 4 late, with a M-68 105mm tank gun. Addition of stowage bins and cases on the back of the hull and sides of the turret.Tiran 5 Nochri
Also called KMT for Nochri Gimel, same as above but with front mounted mine clearing rig (limited numbers).Tiran 4Sh (c1976)
Introduced in the later 1970s, it's the generic denomination for the rearmed 105mm rifled license built M68 gun (late Tiran 4), derived itself from the British L7 commong to the late M48 and M60 Patton tanks, and Centurion among others. The breach had to be extenbsively modified in order to fit in the turret and loaded from the right as well as changed in the internal ammunition stowage. The coaxial Machine Gun is replaced with an IDF 7.62mm GMPG. Up to two .30 MGs and a single Browning .50 are mounted close to the commander/loader's hatches and/or top of the main gun. Fire Control Systems are now western style, with a new small Infared lamp with its aiming device from former IDF Shermans and other regonomics change in the fighting compartment. This also included all former modification range.Tiran 5Sh (c1976)
Like the late Tiran 5, they are rearmed with the 105mm rifled M68 and all modifications decribed for the 4Sh plus a mew communications system.Ti-67 (c1982)
 The name "Ti-67" is referring to the ultimate evolution of the Tiran 4/5 in IDF service, with the “s” denoting an upgrade in firepower assisted by a new computerized fire control system, completed by a new night vision equipment and adapted gun stabilization system. The second major change and missing piece in this final upgrade, is the replacement of the Soviet diesel by a Detroit Diesel 8V-71T and its associated transmission. But also improved suspension, and anew dashboard and levers in the driver's station to reflect the engine's swap. Protection is enhanced by fixation points for Blazer explosive reactive armour (ERA) similar to the Magach series, plus additional external stowage. They were the ultimate evolution for the remaining Tiran 4/5 still serviceable and they were converted to The Achzarit heavy APC from 1988.
The name "Ti-67" is referring to the ultimate evolution of the Tiran 4/5 in IDF service, with the “s” denoting an upgrade in firepower assisted by a new computerized fire control system, completed by a new night vision equipment and adapted gun stabilization system. The second major change and missing piece in this final upgrade, is the replacement of the Soviet diesel by a Detroit Diesel 8V-71T and its associated transmission. But also improved suspension, and anew dashboard and levers in the driver's station to reflect the engine's swap. Protection is enhanced by fixation points for Blazer explosive reactive armour (ERA) similar to the Magach series, plus additional external stowage. They were the ultimate evolution for the remaining Tiran 4/5 still serviceable and they were converted to The Achzarit heavy APC from 1988.
Tiran 6
The Tiran 6 is noted here albeit not part of the Tiran 4/5 family because it's based on captured T-62s. The turret being larger it is fitted with the same fictures found on the Iran 4/5, including details of mudguards, extra stowage, jerrycans, spare track links, and caracterized by the addition of a 60mm mortar plus large oil boxes at the rear sides. Not much information is available and they were not up-gunned or having a new engine installed, joining the reserve in the 1980s.Tiran 7
The T-72 was seemingly not being captured in suffcient numbers to justify such transformation, alsbeit there are reports of destroyed Syrian T-72s, towed and transformed, but there are rumored. The problem is the availability of these to spent R&D time into any meaningful transformation. Instead most were studied and spent as targets.Conversions
By the late 1980s the "stock" tiran 4/5 were evaluated as base for new vehicles, leading to design two prototypes:Samovar 1, integrated Merkava standard equiplent, with the Merkava II maing fun, side wire-mesh basket, small short skirts and reactive bricks.
Samovar 2: More austere variant but modified turret back and new engine and reworked, taller deck.
Tiran Blazer: Proto with a ful suite of ERA bricks,different from those on the Magach and Shot.
Active Service

First combat use of Tirans, were for operation "Raviv" on 8-9 September 1969, so just two years after the 6 days war, leading an amphibious raid across the Suez channel to confuse Egyptian defenders. Three T-54 tanks and six BTR-50s were used. Later Tirans found use to patrol Israel's borders, Suez front. Their first major actionw as at the 1973 Yom Kippur war. They were deployed on southern front pitted against T-54/55 created confusion. This was also the occasion to capture the T-62, but ocnversion to the Tiran-6 never bore fruition, notably due to the availability in numbers of the M-60, US-supplied until this plug was pulled.
The early 1980s marjed the withdrawal of the oldest models from active duty, some sold back to Iran and to Israel's allies fighting in Lebanon while the remainder were converted into the Achzarit APC. Tirans supplied to the South Lebanon Army militia were captured and resued by the Hezbollah after the IDF withdrawal in June 2000. Also were used in the 1980s in Lebano, the Nohcri Gimel, a Tiran 5 modified to clear mines. It was used notably by the SLA, Lebanese army or Hezbollah after the dissolution of the South Lebanon Army on May 24, 2000. Used like the Tiran 5 dozers which as the name indicates had a toothed dozer blade added at the front used on the same gear.
Tiran specifications 5Sh | |
| Dimensions (l-w-h): | As original T-54/55 |
| Total weight, battle ready: | 44 Tons (88,000 ibs) |
| Crew : | 4 (Driver, Gunner, Commander, loader) |
| Propulsion: | Detroit Diesel 850 hp (630 kW) 19 hp/tonne |
| Suspensions: | Torsion arms |
| Top Speed | 65 kph (40 mph) 40-45 kph off-road |
| Range (road)/Fuel consumption | 600 km (372 mi) |
| Armament (see notes) | 105 mm M68, 2x 0.3 in LMGs, .5 in HMG |
| Armour | Same as original |
| Total Production | c150 |

Tiran 2, unmodified T-55

Tiran 4 Sh early type 274th Tank Brigade Sinai, October 1973

Tiran 4, IDF Training Unit Lebanon Tankmen Negev 1980s

Tiran 5, South Lebanon Army Operation "Peace in Galilee", June 1982

Olive Green Ti-67, 1988. More to come.
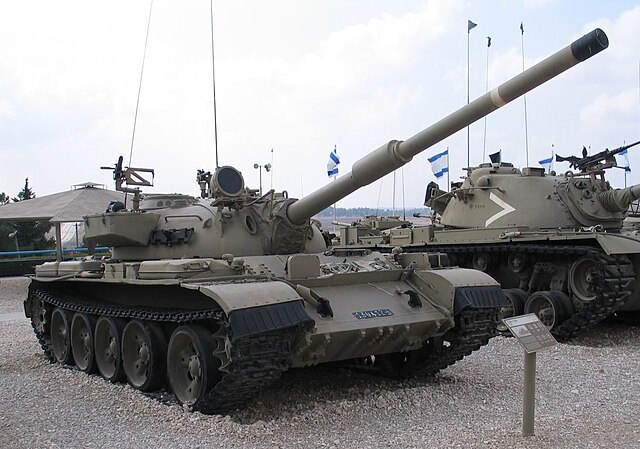














Uruguayan model
Links
tsahal-miniature.comisraeli-weapons.com
en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Operation_Raviv
globalsecurity.org
Tiran 5sh in uruguayan service
scalemates.com
ak-interactive.com
tanknutdave.com

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

