The Chinese replacement for the Type 63 APC
The Type 63 AFV was China's top armored personnel carrier for most of the Cold War. However, it was plagued by many deficiencies which needed addressing. In the early 1980s, several Chinese technical research departments, in close connection with NORINCO, designed an improved version, later to be accepted into Chinese service as the Type 89. It was longer, with an extra roadwheel, a modernized engine, an improved transmission, additional firing ports and periscopes, and most importantly full Nuclear Biological and Chemical (NBC) protection. The Type 89 is the version made for the Chinese People's Liberation Army Ground Forces. Some 1000-1200 were built since entering production in 1990. It was preceded by the Type 85 was the export only version. It was quite successful, being sold to countries like Bangladesh, Burma, Sri Lanka and Thailand.
The YW531 command variant The Type 89 differs from the Type 85 by being slightly longer and larger. The engine was the same licence-built Deutz 320 hp turbodiesel. It could carry 15 soldiers plus crew. The main armament of the basic APC version was a QJC88 12.7 mm (0.5 in) anti-aircraft machine gun, protected by a cradle-type shield/open turret. Four 76 mm (3 in) smoke grenade dischargers were mounted. It had all-around armor protection from rounds up to 12.7 mm. It had a full NBC lining. Twelve variants were built. The Type 89 was also exported to Ethiopia, Sri Lanka and Zimbabwe. The Type 90 APC (YW535) was derived from the Type 89.
Design of the Type 85
Overall, the Type 85 seems to have kept the Type 63 hull, slightly elongated, with five roadwheels instead of four. Two fuel tanks are placed externally at the rear of the tank, on each side of the rear exit door. Technical profiles and side photos also show the roof slope is more gentle. The hull nose has become more angular, probably in order to improve its amphibian capabilities. More pistol ports and sights were added, bringing the total to three pistol ports and 4 sights on each side. Two were fitted on the rear.The ports have ball and socket type mountings for the infantrymen's rifles. The front section houses the engine (right), the driver (left) and the commander (behind). Both crew members have their own hatch. Behind them is the troop compartment, which is large enough for 13 fully equipped infantrymen. One is seated in the central turret, holding a Type 54 12.7 mm anti-aircraft machine gun, protected by a half-turret open shield. A few Type 85's have been photographed showing the shield removed. The infantry can use the oblong roof hatches and rear door in order to exit the vehicle.

The Type 85 APC
Protection
The vehicle is made of welded steel, with a maximum thickness of 14 mm. It is highly probably that it is entirely protected against heavy MG rounds on the frontal arc and small arms fire from other angles. There are a few photos showing some add-on armor, but they seem to be only experiments. The most important feature is the full NBC lining, offering western-standard level of collective protection. For active concealment, two banks of two smoke dischargers are fitted each side of the hull, towards the nose (YW-534).Mobility
Compared to the Type 63's 8-cylinder air-cooled, turbo-charged diesel KHD BF8L 413F which gave 320 hp, the Type 85 has a new, German-licensed Deutz BF8L 413F 4-stroke air-cooled diesel which develops a similar figure of 320 hp at 2500 rpm (240 kW). This gives a power-to-weight ratio of 22 hp/t. It is coupled with a manual gearbox that has four forward and one reverse gear. The range is similar to the previous vehicles (500 km according to official data). The top speed is about 65 km/h (40 mph), probably on road. The vehicle is amphibious and the nose supports a two-fold trim vane to extend the water guard when swimming in rough waters.Type 85/YW 531H
The ground clearance is 0.48 m, ground pressure is an average 0.59kg/cm2.
The track has a contact length of 342.5 cm and a width of 36 cm. The vehicle rests on five dual rubber-tired road wheels on each side, connected to torsion bars. The wheels are smaller than those on the previous design, with a diameter of 560 mm vs. 760mm. The running gear is completed by front drive sprockets, rear idlers and 3 return rollers. Other equipment used also comprises a Type 889 radio set and Type 803 intercom.
Armament
The basic armored personnel carrier (APC), designated Type YW531H, mounted a standard-issue Type 14 12.7 mm heavy machine gun which fires AP/incendiary rounds. The ammunition provision 1120 rounds. The armament is apparently meant to be replaced with the new QJC88 12.7mm anti-aircraft machine gun in a later modernization. It can traverse a full 360°, with almost 90° of elevation, allowing efficient AA fire. The gunner's "open turret" shield is most probably standard issue. The same HMG is also used by most of the versions and variants except for the Infantry Fighting Vehicles (IFV).Variants
Type YW307 IFV
The YW307 is the standard Infantry Fighting Vehicle version, armed with a remotely operated turret also used on the Type 86 IFV and Type 90 wheeled APC. The turret is armed with a 25 mm (0.98 in) automatic cannon with 400 rounds, coupled with a 7.62 mm (0.3 in) coaxial machine gun with 1,000 rounds. The crew is reduced to 3+7 infantrymen. A similar version was later produced using the Type 89 and the Type 90 chassis.Type YW309 IFV
Another IFV version seems to use the turret of the WZ501 (Type 86 IFV), a copy of the BMP-1, armed with the 73 mm gun. The crew comprises three men (including the gunner) and 8 infantrymen. A Red Arrow 73 ATGW launcher is mounted above the main gun. There is also a coaxial 7.62 mm (0.3 in) machine gun.
The APC version of the Type 89 in service in Sri Lanka
Command Vehicles
The Armored Command Vehicle uses the basic hull but without the shielded heavy machine gun (HMG). Other omissions include two pistol ports, periscopes and possibly the roof hatches at the rear. The interior is fitted with Type 889 (or VRC-83) and Type 892 (or VRC-84) radio sets and a Type 70-2B (or SR119) receiver, plus a generator.The Armored Command Post has a roomier, higher roofline with the same radio equipment. The same hull was also used by Norinco for the GLC-45 battery reconnaissance vehicle, ZSY-45 battalion command post vehicle and ZCL-45 battery command post vehicle.
Tracked Armoured Ambulance
The WZ 751 Tracked Armored Ambulance has a raised superstructure at the rear. This is to make room enough for medical personnel, patients and supplies. This version also has a larger commander's cupola fitted with an HMG, but no shield.Other specialized vehicles
- Maintenance Engineering Vehicle (CEV): High roofline (rear) and fitted with a light crane and generator.
- Recovery Vehicle (ARV): Wider hull, 1-tonne crane, generator and welding equipment.
- YW323 Self-Propelled Howitzer 122 mm with 40 rounds, open compartment.
- YW306 Self-Propelled Artillery Rocket Launcher: 30x130 mm launchers mounted over the hull, 30 reloads
- YW381 Self-Propelled Mortar 120 mm: Large circular opening, 40 rounds
- YW304 Self-Propelled Mortar 82 mm: Large circular opening, 120 rounds
- PLZ-45 155 mm self-propelled gun howitzer
 Type 85 Armored Ambulance
Type 85 Armored Ambulance
Export variants
The Type 85 was exported to Bangladesh, Burma, Sri Lanka (including the YW309 IFV) and Thailand (4 variants, 1400 in all*). The Type 85 was also built by North Korea and derived into the M-1977 100 mm SPH and the "Susang" (Susang-Po) ATGM tank hunter variant. In addition, the following versions were proposed by Norinco:- NVH-1 export IFV, armed with a 2-man Vickers turret and 30 mm RARDEN gun
- NVH-4, the same as the NVH-1, but armed with a 25 mm Bushmaster gun
- A 100 mm tank hunter
- A 30 mm RWS IFV
Type 89 AFV
In general appearance, the two vehicles are closely related. They share the same prismatic hull, placement of the machine gun shielding and spacing of the roadwheels. However, there were several differences, one of which is the overall length of the hull. The rear of the vehicle is lengthened and much roomier, the front of the vehicle was also extended and became sharper (possibly a correction for seaworthiness). The Type 89 is also wider. It seems that the Sri Lankan export version is even longer, with an extra rear pair of roadwheels.
Type 85 HJ-8 ATGM tank hunter
The Type 89 was converted into the YW307 or ZSD-89-II Infantry Fighting Vehicle (25 mm automatic cannon), an Armored Command Vehicle, a Tracked Armored Ambulance, a Refuelling Vehicle, a Recovery Vehicle, a Supply Vehicle, a Reconnaissance Vehicle, a Reconnaissance Radar Carrier, a Missile Tank Destroyer, a Mine-Laying Vehicle and an Obstacle-Removing Vehicle.
The Type 89 entered service in the late 1990s (first shown publicly in 1999). About 1,000 are in service today. The industrial index is WZ534 for PLA, but an export version was also developed and received the same designation. Ultimately, it led to the all-improved Type 90 AFV or YW535. Ethiopia, Sri Lanka and Zimbabwe are customers of the YW-534.

YW306 MLRS
Type 85 (YW531H) specifications |
|
| Dimensions (L-W-H) | 6.02 m x 3.06 m x 2.16 m (17ft x 7ft 4in x 5ft 5in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 13.3 tons (266 000 Ibs) |
| Crew | 3 (driver, cdr, gunner)+8 infantrymen |
| Propulsion | Type 6V-150 diesel, 298 hp |
| Suspension | Torsion Bars |
| Speed (road/water) | 65/8 km/h (40/5 mph) |
| Range | 500 km (310 miles) |
| Armament (APC) | QJC88 12.7 mm (0.5 in) AA HMG |
| Armor | Unknown, 8-14 mm range |
| Total production | 1000+ (current) |

The regular Type 85 APC

YW-309 IFV

ZDS-90 IFV

Type 85 missile tank destroyer armed with 4 HJ-8 ATGMs

Type 85 Command Vehicle
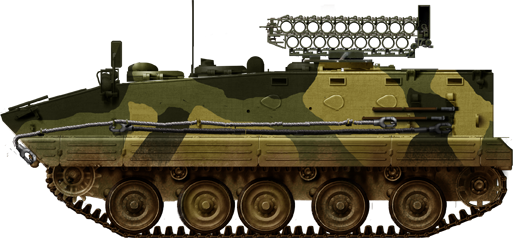
YW-306 self propelled rocker launcher

Type 85 Armored Ambulance
Gallery




Sources/Links
On globalsecurity.orgAbout the YW534/ZDS89 on army-guide
The Type 85 and variants on FAS.org
Wikipedia Type 85 AFV page

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army

