Schwerer Ladungsträger Borgward B IV
Introduction
During World War II, the Wehrmacht had under its disposal three remotely operated demolition tanks, the small Goliath (Sd.Kfz. 302/303a/303b), medium Springer (Sd.Kfz. 304) and heavy Borgward IV (Sd.Kfz. 301). The latter was not only the largest of the three, it was also capable of being manned directly, and was not "disposable" unlike the two others, it could released its explosives before taking distance and detonat e the charge, keeping thnot only the remote operators safe but also the vehicle was reusable unlike the Goliath and Springer, which were both destroyed with their own charge. That made the Borgward IV an ad hoc utility all-terrain tractor, usable for other missions and various uses, especially after 1944 when Germany was on the defensive.
B IV in Munster museum, Germany
Origins of the Borgward Tractor
Borgward is a famous automotive german brand (see ww2 german trucks) based in Bremen, Germany and founded by Carl F. W. Borgward (1890–1963). The modern company found its origin in the Hansa Automobilgesellschaft and NAMAG, maker of the Lloyd car. In WWI it manufactured trucks and cars under the name Hansa-Lloyd-Werke A.G. but faced bankrupcy in 1920. In 1929 the company bounced back with the mergeer of Goliath-Werke Borgward & Co. with Hansa-Lloyd. But the comany soon explored other markets that small cars, and created a berline, the Konsul, followed in February 1937, by the Hansa Borgward 2000 and in 1939 Borgward 2000 and the Borgward 2300 in production until 1942. Its main medium truck, rival to the Opel Blitz was the Borgward B 3000 which occupied its factories with 30,000 made until 1945.
Borgward Sonderschlepper BIII, the predecessor to the Borgward IV.
But the company also looked after lucrative the military market, closer to the Heer, and notably answered a specification in 1936 for a tracked munition carrier. In September 1937 In. 6 placed a contract to Borgward to further developed its gepanzerter Munitionsschlepper capable of carrying 1t of ammunition, 500 kg in the vehicle, 500 kg in a trailer. 20 preserie vehicles (pilot) was called the Vk. 3.01. They were delivered in 1940. From October 1941 to February 1942, 28 improved Vk. 3.02 or Sonderschlepper BIII were delivered (On 100 ordered, but later cancelled), 5 cm broader with a higher driver’s compartment and straight mudguards. It was developed as the Panzer Selbstfahrlafette 1a 5cm PaK38 auf Gepanzerte Munitionsschlepper, an impromptu, experimental tank hunter armed with a 50 mm high velocity gun.
It was tested in the summer of 1940 but the Panzerjäger I was preferred. Meanwhile, Hanomag provided in the interwar the unarmoured tractor W.D. Raupenschlepper, Rheinmetall the Versorgungsfahrzeug auf leichttraktor fahrgestell, Krupp the Leichttraktor Krupp Nachschubfahrzeug and the Austro-Daimler ADMK Motorkarrette Mulus was also integrated into service for mountain supply. However Steyr provided the bulk of German tractors as the RSO (Raupenschlepper Ost), mass produced in three variants. But the Wehrmacht used also a lot of captured tractors, starting with the French UE-Schlepper 630(f), and Soviet tanks repurposed as tractors after the offensive of the summer 1941.
Development of the Borgward BIV
Besides the B.III, the company also produced mine clearing vehicles, the Sd.Kfz.300 Minenräumpanzer Borgward B I in 1939 with a track drive assembly and three road wheels, a hull made of concrete radio controled. It towed a trailer with three rollers for mine cleaning and 50 were made from January to May 1940. Next was the Minenräumwagen B II with 100 made from July 1940 (cancelled, 2 prototypes made) as a successor to the B II, a bit larger with track drive assembly comprising four road wheels and towing a trailer with three rollers as well. There was even an amphibious variant known as the Sd.Kfz.300 Borgward BII "Ente" (tested, not produced).Work on parts and components alongside the B.III provided a wealth of experieence to produce a more elaborated vehicle. This was the Schwere Ladungsträger Sd.Kfz.301 Borgward IV developed in the summer of 1940 to destroyer French blockhaus. First tests were initially made by a modified PzKpfw. I Ausf. B chassis with a tailored equipment, to place explosive, but the vehicle was not remote controlled. Tests were relatively successful, as by October 1941, Borgward was ask to develop a much simplifed and cheaper version with the same equipment. It soon received the identified Sd.Kfz.301 by the Wehrmacht.
Design of the Borgward B.IV
 At first indeed, Borgward simply adapted its B.III schlepper for the task, but it proved ill-suited and a new vehicle was designed. The B IV was also tested as a remote minesweeper, but it was found not only too vulnerable to mines, but also too expensive to be "disposable". It's really the work by German pioneers (engineers) from the 1st Panzer Division in the Battle of France that was instrumental to design the right type of solution. They converted 10 Panzer I Ausf Bs into demolition and mine clearing vehicles. They just advanced towards enemy lines under fire, closed to meet the weak point of the enemy structure and places here timed charges. This was usabled on minefields as well, and allowed not to lose the vehicle. The Waffenamt like the idea enough to mobilize B IV after its work on the B.III to develop a remote-controlled variant usable as a demolition vehicle. The first were delivered in 1942.
At first indeed, Borgward simply adapted its B.III schlepper for the task, but it proved ill-suited and a new vehicle was designed. The B IV was also tested as a remote minesweeper, but it was found not only too vulnerable to mines, but also too expensive to be "disposable". It's really the work by German pioneers (engineers) from the 1st Panzer Division in the Battle of France that was instrumental to design the right type of solution. They converted 10 Panzer I Ausf Bs into demolition and mine clearing vehicles. They just advanced towards enemy lines under fire, closed to meet the weak point of the enemy structure and places here timed charges. This was usabled on minefields as well, and allowed not to lose the vehicle. The Waffenamt like the idea enough to mobilize B IV after its work on the B.III to develop a remote-controlled variant usable as a demolition vehicle. The first were delivered in 1942.

The Borgward IV was much heavier than the Goliath and had a larger payload. It was not wire-operated, but by radio. The force of detonation indeed required the operator to be far more remotelly placed compared t the vehicle. The Borgward IV in a backup was equipped for a driver to be would brough independently to its destination, before dismounting. However this method was exposing the latter to enemy fire. Later some variants had extra armoured panels to at least protect the driver from front and side infantry fire. Whatever the case, the detonation was radio-commanded from a distance. It was generally an organic unit armored fighting vehicle. This command vehicle was a modified Panzer III tank at first, then it became a StuG III/G and eventually a Tiger IE for heavy units.
The radio equipment onnboard and and controllers could act directly inb the controls were setup in remote driving mode. Otherwide the unusual way was to drive the vehocle to the target, drop the payload carried at the nose, and then retire at a safe distance. The charge looked like a cake slice, being almost 500 kgs filled with TNT. It had a simple readio receptor for the fuse activation, albeit it could be affected by the surroundings and radiomagnetic environment.
The move towards the target was always, risky, albeit even the dropping charge was at the front, it's detonation system made it in principle relatively safe. The Borgward IV was lightly armored, only 8mm on the Ausfürung A and B versions, and eventually 20mm in the Ausfürung C version. From protection against small arms and splinters but the vehicle was vulnerable to anti-tank rifles or light anti-tank guns. Plus when driven directly, the latter had its head exposed out in the open. That's why when the Ausf C started to take other roles outside demolition, it was up-armoured, including folding panels to better protect the driver. Being larger than the Goliath, the Borgward IV was much easier to spot and target. Besides, in order to be remotelly driven, the operator still needed to see both the target and the carrier, exposing him to sniper fire.
Production
12 experimental vehicles were built in April 1942, tested and approved fir production by the Waffenamst as Sd.Kfz.301. Production started in May 1942 and in total, 616 Borgward IV Ausf.A were manufactured until June 1943 and then 260 Ausf.B until November 1943, and finally 305 Ausf.C from December 1943 to September 1944. The Ausf B was heavier and had its radio antennas rearranged for better transmission, the radio set was an improved model. The Borgward IV Ausf.C was the heaviest notably due to the extra armour, and used for other roles than demolition. Also its driver station was shifted from the right to left and it had a better engine to deal with the greater weight, top speed probably around 35-36 kph.Variants
B IV Ausf A: Standard vehicle (616 made) with optional remote control and 8 mm armour folding panels.B IV Ausf B: Improved vehicle (260 made) same layout and options, 400 kgs heavier and different radios.
B IV Ausf C: Left driver, 20 mm armour, new tracks (305 made), total weight 4.85 tons for 4.1 m x 1.83 x 1.25, 78 hp engine.
B IV Ausf B/C mit 8.8cm Raketenpanzerbüchse 43: Conversion into a rocket launcher version, 6 tubes carried on the left, driver on the right. 56 converted by the panzerjäger Wanze, deployed in the Battle of Berlin, 1945, skirmishing with advancing Soviet forces.
Sd.Kfz.301 Schwimmfähiges: A prototype Ausf B conversion as amphibious tractor, with a television camera for observation.
B IV specifications | |
| Dimensions | 3.35 x 1.80 x 1.25m (11 ft x 5 ft 11 in x 4 ft 1 in) |
| Total weight | 3.45 tonnes (3.40 long tons; 3.80 short tons) |
| Crew | 1 driver/operator |
| Propulsion | Borgward water-cooled 4-cyl. gasoline, 14.2 PS/tonne |
| Suspension | Torsion bar |
| Maximum speed | 40 km/h (25 mph) road |
| Range | 108 L (28.5 US gal), 120 km (75 mi) |
| Armament | 450 kg (990 lb) explosive charge |
| Armor | 20 mm (0.79 in) all angles |
| Total production | 1181 |
Combat Deployment
Borgward IV vehicles were operated with Funklenk units, a group of three commanded by a single Pz.Kpfw. III 5 cm gun variant command vehicle. Then this was the Panzer III Ausf.N 7.5 cm howitzer variant. They were replaced in turn in 1944 by a StuG III Ausf. F/G. Also from 1943, schwere Panzer Abteilungen were constituted to operate with Tigertanks, with a proportion of 14 Tigers for 45 Borgward IV. The 56 converted "tank hunter" vehicles fought Russian tanks in the street of Berlin in April 1945. There were some surviving vehicles: One is at the Heeresgeschichtliches Museum in Vienna, another at the Russian Kubinka Tank Museum, at the American Heritage Museum in Greater Boston and German Tank Museum in Munster as well as at the Overlord Museum in Colleville-sur-Mer, Normandy. one was discovered in the rubble during a demolition on 31 March 2010, at Wien Südbahnhof, retrieved and restored for display at the Heeresgeschichtliches Museum.Links/Src
Thomas Ilming: Die „Wunderwaffe“ unter dem Südbahnhof: Borgward B IVc. Wien 2011Alexander Lüdeke, Waffentechnik im Zweiten Weltkrieg. Parragon Books, Bath 2007
Markus Jaugitz: Die deutsche Fernlenktruppe 1940–1943. Podzun-Pallas, Wölfersheim-Berstadt 1994
en.topwar.ru
wienerzeitung.at rediscovered B IV
achtungpanzer.com wanze bordgward rocket conversion
achtungpanzer.com Borgward IV
Wiki Borgward IV
wardrawings.be, Special purpose vehicles, Goliath, Springer and Borgwards.
wardrawings.be generic german vehicles
Gallery
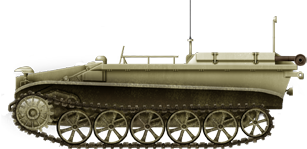
Borgward IV Schwere Ladungsträger Ausf A in standard Livery, Sevastopol summer 1942

Borgward IV Ausf A camouflaged
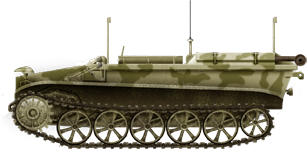
Bordgward IV Ausf A Funkpanzer in Libya 1942

Borgward IV Ausf C 1944

Bordgward IV Ausf B mit 8.8cm Raketenpanzerbüchse 43, Berlin, Brandenburg Gate March 1945.







WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

