The "mobile slit trench"
An almost forgotten vehicle of WWII, 240 Rover light armored cars were nevertheless produced with parts from Ford Canada and locally assembled at Rover Australia, based in Melbourne. It appeared just six month after the "Rhino" prototype built by Ruskin Motor Bodies Pty Ltd. Like the Dingo, it was a stopgap vehicle made with great urge after the beginning of the war and accelerated with the Japanese offensive in the Pacific, knowing that no matériel could be sent from the UK at that time. Based on a sturdy chassis with well-sloped armor, this vehicle had some unique specifics.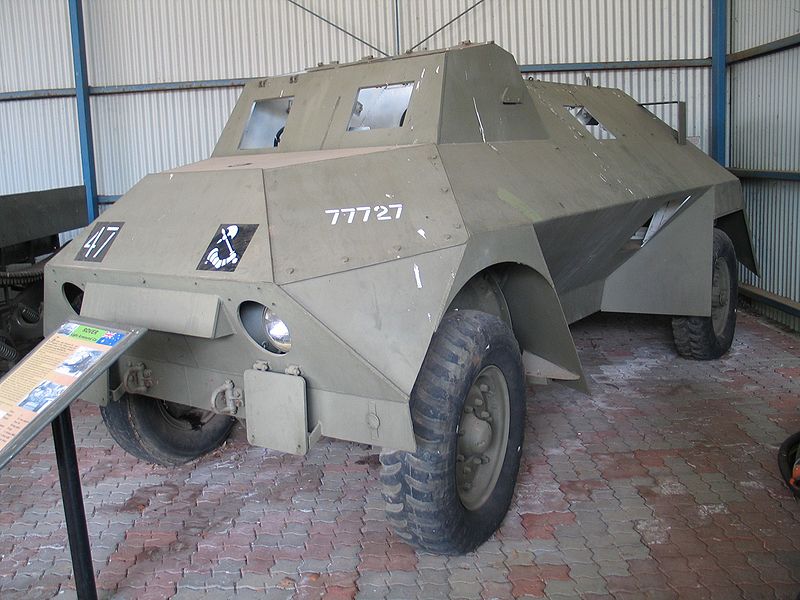
Design
Designing started at Rover on government specifications in 1941. Quite rapidly, Ford 3-ton Canadian Military Pattern truck chassis were ordered and shipped to Australia. These were either of the 158 1\4" F60L (for "long") type, which were used for the Mark I, or the shorter 134 1\4" F60S type, with a 50 cm (20 in) difference in wheelbase. Therefore, the Mark I was heavier (5.2 tons versus 5 tons). These trucks had all wheel drive (4x4) with independent leaf spring suspensions, which allowed acceptable off-road performance, although the large wheelbase made it difficult to cope with mud. The engine, a Ford V8 which gave 95 hp (71 kW) and a power/weight ratio of 19 hp/tonne, could propel the vehicle to an estimated top speed of around 80 km/h (50 mph). The body armor was made of flat steel plates welded on a frame, ranging from 4 to 16 mm (0.16-0.62 in) at the front. Compartmentalization was straightforward, with a front driving compartment behind the engine, feuturing two windows topped by folding windscreens and armored shutters, with side vision slits and roof hatches. One could receive a 0.303 (7.7 mm) Vickers machine gun manned by the commander. Access was assured through the rear "slug" between the rear axle mudguards.
Parade in the streets of Sydney in December 1942 - Credits: Royal Australian Museum Collection.
Three more men could take place in the rear compartment. The two gunners with Bren light machine guns (one mounted on a AA pintle) had two-piece folding firing hatches on each side when firing seated. The radio operator was equipped with a wireless emitter/receiver. Due to the unique shape of the hull, which was very well sloped, the rear compartment walls went as far as the front compartment roof, and presented a narrow "trench" on top, hence the nickname. From this "trench", the two gunners could fire while standing. It was covered by a tarpaulin in normal use. The headlights were well encased in the front mudguards and could be closed and protected by folding panels. Apart for their length, the two versions were similar, but there were some changes in toolbox locations and size of the lower part of the body.
.jpg)

Service
The Rovers were accepted in service in 1942, as the Light Armoured Car, Rover. Production took place until 1943, 40 long versions being produced and 198 of the short Mk.II, giving a total of 238 vehicles. They were part of the 1st Australian Armoured Division, but none of them took part in hostilities. They were used only for security purposes and training of the crews for the duration of the war. Indeed, US-made armored cars were received in large numbers by mid-1943, which were used in external operations of the Australian Army. By the autumn of 1945, the Rover LAC was declared obsolete and removed from service. Most of them were purchased at an auction by the Australian subsidiary of Ford and later re-converted into civilian trucks, while the bodies were scrapped. Apparently, a few were were used by the Australian Navy. Surviving vehicles can be seen today at the Puckapunyal collection (Royal Australian Armoured Corps Tank Museum) near Victoria and at the National Military Vehicle Museum in Edinburgh Parks.Links about the Rover light AC
The Rover Light AC on Wikipedia Surviving Aussie vehicles by the Shadocks
Rover Light AC specifications |
|
| Dimensions Mk.I(Mk.II) | 6.1/5.6 x 2.3 x 2.1 m (20/18.4 x 7.7 x 6.1 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 5.2/5 tons (10,400 lbs) |
| Crew | 5 (driver, commander, wireless operator, 2 gunners) |
| Propulsion | Ford V8 95 hp (71 kW), 19 hp/t |
| Suspensions | Leaf springs, 4x4 drive |
| Maximum speed | 80 km/h (50 mph) |
| Armament (optional) | Bren LMG .303 (7.7 mm), 2500 rounds |
| Armor | From 4 to 16 mm (0.2-0.6 in) |
| Total production | 238 |

Rover LAC Mk.I "Long" built on the F60L chassis, 1942.
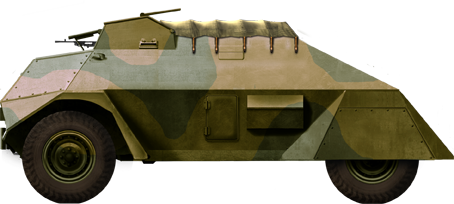
Camouflaged Rover LAC Mk.II, short F60S chassis, 1943.

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

