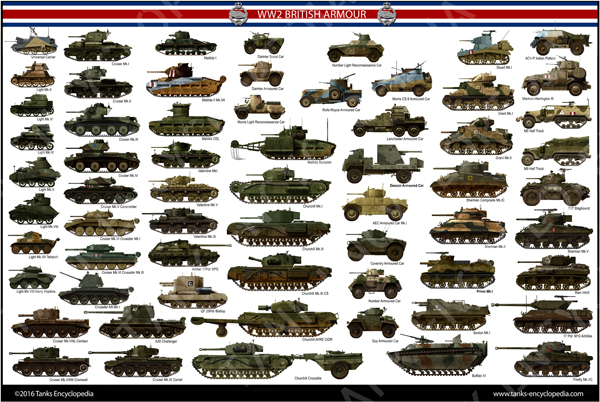
British Tanks and Armoured Cars 1930-1945
 United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (WW2) - circa 250,000
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (WW2) - circa 250,000

Introduction
While the British Empire was depending foremost on its navy to defend its interests, it also had modern and efficient aircraft, and a small army, but very well equipped and trained. Its armored forces were not at all numerically equal to France or Nazi Germany, but qualitatively of good level. This was the case mostly thanks to a booming export production in the thirties (mostly Vickers) and many tests, exercises and authorship of the idea of mechanized warfare (in fact the basis on which the Blitzkrieg was founded), with revolutionary concepts such as the Carden-Loyd tankette, or the adoption of the Christie suspension for its cruiser tanks.Articles, published and upcoming
- Cruiser I
- Cruiser II
- Cruiser III
- Cruiser IV
- Cruiser V Covenanter
- Cruiser VI Crusader
- Cruiser VII Cavalier
- Cruiser VII Centaur
- Cruiser VIII Cromwell
- Cruiser IX Comet
- Matilda Mk.I
- Matilda Mk.II
- Valentine
- Churchill
- Medium Mark I/II
- Medium Mark III
- Medium Mark D
- Vickers Mark E
- Light Mk.I
- Light Mk.II
- Light Mk.III
- Light Mk.IV
- Light Mk.V
- Light Mk.VI
- Harry Hopkins
- A30 Challenger
- A30 Avenger
- Bishop
- Achilles
- Archer
- AEC
- Dingo
- Humber AC
- Lanchester 6x4
- Morris CS9
- Morris scout car
- Leyland Beaver-Eel
- AEC 4x4 ACV Dorchester
- Staghound Tulip
- Vickers M1931 LAT
- Carden Lloyd Tankette
- Universal Carrier
- Dragon Carrier
- Loyd Carrier
- Crusader II, Gun Tractor Mk I
Tank hunter/SPGs
Armored Cars
Misc.
British AFVs Doctrine
The British Armed Forces have a long history of armored warfare, dating back to World War I. Over the years, the British Army has developed a unique doctrine for the use of Armored Fighting Vehicles (AFVs) that reflects their tactical and strategic considerations.Here are some of the key principles of British AFV doctrine: Combined Arms Operations: The British doctrine emphasizes the use of AFVs in conjunction with other arms, such as infantry, artillery, and aviation. AFVs are seen as force multipliers that can provide mobility, firepower, and protection to other units.
Flexibility: British AFV doctrine emphasizes the importance of being able to quickly adapt to changing situations. This requires a high level of training and a focus on leadership, as commanders at all levels need to be able to make decisions quickly and effectively.
Concentration of Force: The British doctrine places a strong emphasis on concentrating AFVs at critical points on the battlefield, in order to achieve a decisive breakthrough. This requires careful planning and coordination, as well as effective use of intelligence and reconnaissance.
Offensive Operations: The British doctrine sees AFVs primarily as offensive weapons, to be used to seize and hold ground. This requires a willingness to take risks, as well as a deep understanding of the terrain and the enemy.
Support of Infantry: British AFV doctrine places a strong emphasis on supporting infantry units, by providing them with protection, mobility, and fire support. This requires close coordination between the two arms, and a deep understanding of the capabilities and limitations of each.
Overall, British AFV doctrine emphasizes the importance of flexibility, initiative, and adaptability, as well as the need to work closely with other arms. By doing so, the British Army aims to create a highly effective and integrated fighting force that can operate in a wide variety of environments and situations.
British Tanks in Operations 1940-45
The BEF (British Expeditionary Force) in May, 1940
In 1939, besides the colonial forces stationed around the world, mainly made up of infantry and artillery, the heavy mechanized forces were included in the British Expeditionary Force commanded by Lord Gort, formed in 1938, and landed in France soon after the declaration of war on September 3. Reduced in number (one tenth of the Allied forces, France, Belgium, Holland, Denmark included), but of very high combat value, the BEF included 158,000 men, arrived in five weeks, with 25,000 vehicles, artillery and support. Final deployment was completed in May 1940, in 10 divisions, assisted by 500 units (approximately 400,000 men). The majority of the forces were assigned to the French-Belgian border, but some units went and stood behind the Maginot Line.These forces were highly mechanized and consisted mainly of trucks and artillery tractors, armored cars and tanks, classified according to the custom of the time, in cavalry tanks (Cruisers), Scouts (Light) and Infantry. But because of the turn of events, most of this hardware was lost on the the way to the Dunkirk beaches. Only the Matilda seemed to resist the German onslaught, when counter-attacking at Amiens, but the Germans 88 mm (3.46 in) Flak guns, superior coordination and air power definitely broke this courageous but futile attempt.
Many of the models already developed or under development in 1940 entered mass-produced, with many versions and variants until the end of the war. However, some new tanks appeared due to the precious war experience gathered, which ultimately led to the awesome Centurion, perhaps the world’s first modern MBT or “Main Battle Tank”. The best suited tanks for armored offensive appeared to be of the cruiser gender. After the Cruisers III and IV, a complete redesign of the suspension, using for the first time the Christie system, led to the design of the Mark V Covenanter and the Mark VI Crusader.
The latter gained fame in the North African campaign, but it was obsolete by 1943 and new models had arrived: The Cavalier, Centaur and, most famous, Cromwell (Mark VII), all equipped with the new 6 pdr (57 mm/2.24 in) antitank gun, improved engine and armor.
North Africa 1940-43
When the African campaign started, the British armored force was left with second-rate tanks, most of nearly obsolete models, like the Light Tanks Mk.II/III, Mk.V and Mk.VI and tankettes, and the obsolete Vickers Medium Mark II. There were also a few Cruisers Mk.II/IIIs. By 1940, as the Italian threatened Egypt from their Eastern African colonies and Libya, some armored reinforcements were sent, and nearly all available tanks when, in September 1940, the Germans ceased their air offensive over Britain.At the same time, production was re-centered around a few models: The infantry tank Matilda II, the Cruiser tank Mk.IV, and the freshly arrived Valentine. Since local Italian armor was not really impressive, the bulk of the British light tanks had been based in North Africa and in the eastern colonies (Singapore, India, Burma). By the fall of 1940 and until the fall of 1941, a not well-known offensive saw these second-rate tanks, alongside many British and Australian armored cars, fighting off the Italians in Eritrea and Somaliland (East-African campaign).
But by the start of 1941, after a series of humiliating defeats, the Regio Esercito had been pushed back and even chased out from Libya. The British forces had reached Tobruk and now threatened the Italian presence in Africa itself. Hitler, unwilling to let his ally lose this precious position against British main eastern trade roads and supply lines, sent two divisions, the core of a future “Afrika Korps”, under the command of one of the most praised German generals in history, Erwin Rommel. The year 1941 was a complete reverse of the initial successes of the British army, which was pushed back all the way to Egypt. By mid-1942, several epic battles, were tanks played a vital part, contributed to slow down the Italo-German advance, until the turning point at El Alamein.
By mid-1941, the British army had received two new tanks. First wasthe brand new Crusader, with a Christie suspension which gave, on the flat battlegrounds of the North African theater, stunning performances. But speed itself was not sufficient, especially against German tactics using bait forces and ambushing antitank units. The second tank was not British but American, on insisting British request. It was a medium tank with powerful armament -but in an awkward configuration- , good armor and mobility. Nicknamed “the Iron cathedral”, the M3 served as the Lee in US service, and the Grant in British service, with distinctive modifications. Despite its shortcomings, it was dependable and contributed to stopping the German advance literally miles from the Nile, at El Alamein, a remote railroad junction. But most of all, the future “Desert Rats” were now led by a soon iconic figure, Bernard Montgomery.
By the fall of 1942, the first British M4 Shermans arrived en masse through Alexandria harbor, but the bulk of VIIIth forces still comprised M3 Grants, M3 Stuarts, Crusaders, Cruiser III-IVs, Matildas and Valentines. All these forces were patiently and carefully gathered for the great African offensive of El Alamein (second battle), planned by Montgomery in October-November 1942. At the same time, the first US Army western front commitment of the war came in French Algeria, with operation Torch. This giant pincer movement was designed to deliver the coup de grace to the Afrika Korps and the remainder of the Italian forces, now retiring to Tunisia.
The Tunisian campaign was nothing but a though and bloody affair. Tunisian muddy winter combined with a stiffened and well-ordered fighting retreat by hardened Axis troops was not what the Allies expected, and the arrival of general Kesselring with fresh reinforcements, including the brand-new Tiger tank, further increased the Allied disarray. As a response, British armor received new anti-tank guns, but to lead the assault, they also received the heavy Churchill tank, slow but extremely resilient and versatile.
The last Crusaders had been phased out, and early versions of the Valentine had been converted with success into the Bishop SPG. Now obsolete Grants were sent to the Far East. They would go on to have a brilliant fighting career in Burma, until 1945. The Cavalier, Centaur and Cromwell, all based on the same requirements and very similar, arrived in limited numbers. Their new high-velocity gun and reliable engine proved more than a match for many aging Panzer III and IVs. The Italian Campaign (1943-45)
The surrender of all Axis forces in Tunisia came in May 1943. The Allies, however, had not succeeded in completely destroying Kesselring’s army, which retreated in good order to Sicily. The Sicilian campaign, from July to August 1943, saw the extensive use of US Lend-Lease vehicles to compensate for the British losses, mainly Monty’s VIIIth army, comprising M2/M3 half-tracks, jeeps, trucks, M5 Stuarts, as well as M3 derived self-propelled artillery (US-built Priest and Canadian-built Sexton). During the previous desert operation, Lend-Lease Jeeps and Chevrolet trucks, modified and heavily armed, served with the famous LRDG (Long Range Desert Group), using effective hit-and-run tactics. The next campaign, starting in Italy in September at Salerno and Taranto saw a growing number of Canadian-built tanks, mainly Universal Carriers and the Sexton SPG. Now the mainstay of the British tank force, apart from the Shermans and Churchill, were the Cruiser VII (“C” models) and later versions of the Valentine. Soon after these landings, a new Italian government was formed, which decided to put Mussolini in arrest and quickly entered peace talks with the Allies. But, despite the defection of Italian troops, the offensive reached a standstill. General Kesserling was able to put a very sturdy resistance, helped by his hardened troops, some reinforcements and the Italian landscape. The Italian campaign dragged on until the fall of 1945.
D-Day and the European campaign (1944-45):
Before D-Day, the only attempted landing in occupied France had occurred on 19 August 1942. This was a complete failure, with a heavy price which was mostly paid by Canadian troops. This was also one of the first actions of the new Churchill tank. Already developed in 1941, the Churchill looked obsolete, and it was plagued by teething problems. At Dieppe, none of these heavy tanks made it farther than the beach, easy prey for the German artillery at point-blank range. The problem was not in the tank, but in the very stuff that composed the beach, tiny chert which clogged into the drivetrain and tracks. The Churchills were doomed. But this tank would prove its value in a matter of weeks in North Africa and especially Tunisia,. When all its defaults were corrected, it ended up as a very fine armored vehicle. It was extremely sturdy, roomy, reliable, and highly adaptable, and it could climb slopes impossible for any other Allied model. It became the staple of the Royal engineers for every duty imaginable, from D-Day to V-Day.The bulk of the British tank force during D-Day was made of US-built Sherman tanks. The British were not long to grasp the potential of this tank and quickly attempted a modification of their own, the Firefly. This was basically an up-gunned version, fitted with the long-barrel, high-velocity QF 17-pdr (76.2 mm/3 in), the British perfect “tank killer”, capable of knocking out any German tank of the day. It was used in conjunction with other models and proved really up to the task during the operations in the Normandy bocage and heavy fighting around Caen. The US devised their own upgunned version, the 76(w), which appeared not long after and became the next upgrade of all Sherman versions.
The second most important British tank deployed was the Cromwell. Derived from the long line of “cruisers” and equipped with the same engine as the legendary Spitfire (the Rolls-Royce Meteor), the Cromwell was faster than the Sherman, but also lower, and equipped with the largely available and very efficient QF 6-Pdr (57 mm/2.24 in) gun. However, it was cramped and the small hatches too often condemned the crews to burn alive inside the tank. The Cromwell was chiefly used for training, and only equipped the 7th Armored Division and other elite specialized units, like the reconnaissance units attached to the Guards Armored Division and 11th Armored Division.
Other important AFVs deployed at D-Day were the self-propelled howitzers, M7 Priest and the Canadian Sexton. Indirect fire could be provided quickly thanks to these vehicles, which turned out to also be efficient troop transports. So much so, that many other turretless vehicles were called for the task, summarily called “Kangaroo“. But these converted vehicles were all open-topped. The unique SPG designed to operate as a tank hunter was the 17-Pdr Archer, based on the Valentine chassis. Around 600 were produced in 1944, and they operated in France, Holland, Germany and Italy. These were characterized by a rearward-firing configuration.
The A.30 Challenger (Cruiser Mark VIII) made its debut in France in the summer of 1944. It was introduced with the new high-velocity 17 pdr (76.2 mm/3 in) QF AT gun, capable of dealing with German Panzer IVs and Panthers. However, its development took time, and the Firefly appeared cheaper to convert in numbers. So despite its advantages (it was faster and agiler), the costly and complex Challenger never saw action before July and August 1944, when the mulberries were operational, and only 200 were built, equipping British elite units, as well as Czech and Polish ones.
Both concepts of tank hunter and cruiser tank were reunited in a single package, the Comet, first introduced by early 1945. The Comet was basically a Cromwell re-equipped with a specially adapted version of the deadly QF-17 pdr. An impressive package of speed, armor and firepower, which represented the peak of British experience facing German tanks. But it was not the last “cruiser”. As soon as 1943, the general Staff asked for a “Heavy Cruiser” (A.41), which could withstand a direct hit from a German 88, be agile like the Comet and Cromwell, still be armed with an improved version of the QF 17-pdr and stay within the 40-tons limit to allow transport by the lorries. A mock-up was built in May 1944, with prototypes in early 1945 after many revisions. It is said that three pre-series Mk.I Centurion prototypes were sent to Germany before V-day, but the armistice was signed before they could participate in any action. However, they had a great postwar career and pioneered the “main battle tank” we know today.
British Tank Prototypes
For every tank produced in serie there were at least two or three tanks that were one-off for testings or never went long after the design phase. Tank Encyclopedia over the years had mounted a considerable database on British paper projects, see the links below marked with an arrow. For those not listed her so far, and generally prototypes which saw actual limited testing profduction beyond paper stage, they will be treated in this page, depending on the data available online...Summary
- A1E1 Independent
- TOG-I
- Vickers Medium Mk.D
- ➚ 40RBL78 MA Field Gun
- ➚ A.11E1, Infantry Tank, Matilda Prototype
- ➚ A.33, Assault Tank “Excelsior”
- ➚ A.34* (Star), Cruiser Tank, Comet
- ➚ A.38, Infantry Tank, Valiant
- ➚ A.4E3 L1E3 Vickers Amphibious Light Tank
- ➚ Arthur Janser’s 500-ton Battleship and Grasshopper Tanks
- ➚ Bechhold Tank
- ➚ Churchill Mk.III with ‘Ardeer Aggie’ Mortar
- ➚ Gerrey Machine Gun Motor Vehicle
- ➚ Heavy/Assault Tank T14
- ➚ Johnson’s Light Tropical Tank
- ➚ Kahn’s Obstacle Ball / Rolling Fortress ‘Tank’
- ➚ Morris-Martel Tankettes
- ➚ Praying Mantis
- ➚ Smeaton Sochaczewski Carrier
- ➚ TOG 300G
- ➚ TOG Amphibian
- ➚ TOG Citadel
- ➚ Vickers No.1 & No.2 Tanks
Light Patrol Tank (1923)
 This particular vehicle is the first entry of our overview. If the chassis looked like a Carden-Loyd Mk.VI "tankette" one, this is not at random. The vehicle pioneered by Major Giffard Lequesne Martel and refined, produced by Vickers was indeed a huge commercial success as it seemed a good alternative to an expensive tank. However it had a very light armament, poor protection and both could only be solved by reworking the engine and drivetrain, hence creating a more expensive model. So to solve this export issue, Vickers diligently studied on its own the "Light Patrol Tank". Engineers have it a an improved suspension while the armament was no longer fixed forward but now in a fully traversable turret with roof. But despite all its merits, this compromise only seduced one country: Denmark, for which only two were made, the third kept as prototype.
This particular vehicle is the first entry of our overview. If the chassis looked like a Carden-Loyd Mk.VI "tankette" one, this is not at random. The vehicle pioneered by Major Giffard Lequesne Martel and refined, produced by Vickers was indeed a huge commercial success as it seemed a good alternative to an expensive tank. However it had a very light armament, poor protection and both could only be solved by reworking the engine and drivetrain, hence creating a more expensive model. So to solve this export issue, Vickers diligently studied on its own the "Light Patrol Tank". Engineers have it a an improved suspension while the armament was no longer fixed forward but now in a fully traversable turret with roof. But despite all its merits, this compromise only seduced one country: Denmark, for which only two were made, the third kept as prototype.
 This all started with Lt.Col. Andersen-Høyer, Danish Army Technical Corps which in United Kingdom observed the Carden-Loyd armored carrier and was promised the loan of a light tank for just £200, to be refunded if bought after loan. It seems the idea of a turret came later. The first prototype was only completed in 1932. It was abundantly tested by the Forsøgspanservogn program, and tested the vehicle which arrived from Vickers with a trailer in the summer. It was found satisfactory but budget constraints at the time,n for political reasons only led to the purchase of two "production" vehicles. They differed from the prototype, with the turret offset to the right and transmission/engine moved to the left. However problems accumulated, and the vehicle trained personal until 1937 and after storage as beredskabskøretøjer one was scrapped, the other preserved at the Military Museum in Copenhagen, on its transport trailer.
This all started with Lt.Col. Andersen-Høyer, Danish Army Technical Corps which in United Kingdom observed the Carden-Loyd armored carrier and was promised the loan of a light tank for just £200, to be refunded if bought after loan. It seems the idea of a turret came later. The first prototype was only completed in 1932. It was abundantly tested by the Forsøgspanservogn program, and tested the vehicle which arrived from Vickers with a trailer in the summer. It was found satisfactory but budget constraints at the time,n for political reasons only led to the purchase of two "production" vehicles. They differed from the prototype, with the turret offset to the right and transmission/engine moved to the left. However problems accumulated, and the vehicle trained personal until 1937 and after storage as beredskabskøretøjer one was scrapped, the other preserved at the Military Museum in Copenhagen, on its transport trailer. Matilda Black Prince (1943)
Matilda Black Prince (1941): This alleged one-off experiment, basically presented as a Mark III chassis with an A.27 turret and 6pdr gun is less well-known than the other Tank, Infantry, A.33 Black Prince based on the Churchill. In fact data about this foggy Matilda version according to wikipedia is related to a Radio-controlled prototype produced in 1941 using A.12E2 with Wilson transmission. Planned uses included use as a mobile target, for drawing fire and so reveal hidden anti-tank guns, or for demolition missions.
Order for 60 was cancelled as it would require conversion of Rackham clutch transmission to the Wilson type. There is also mention of a Matilda with A.27 turret although, again according to wikipedia. Just one produced, no documentation other than a single photograph of it remain. Now this tank is around WOT and several other forums, not as a forgery but a simple (willful) mismatch between a name and a type that has really existed but for another purpose.
A.39, Heavy Assault Tank, Tortoise (1944)

Expecting the battlefields of World War 2 to develop as they had done in the previous great war, British tank designers set about designing a tank that could breach any fortification the enemy may erect, and shrug off incoming defensive fire. Previous studies had lead to the A.33 Excelsior, a Heavy/Assault Tank and a dead end. It was basically an up-armoured version of the Churchill, built on the Cromwell chassis. Nuffield Mechanisation & Aero Ltd. soon answered the call for a completely new project, with no less than 18 separate designs lasting until February 1944. Eventually, the AT.16 was approved by the War Office. They approved a direct pre-production run of 25 vehicles without prototypes. September 1945 was set as the deadline at which they would be available for operational service. This vehicle would be immortalized as the Tortoise. Quite why it officially received this name is unknown. The name had already been reserved for a heavy AFV in 1942, however, that never got off the drawing board. Either way, the similarity to the animal is not hard to miss...
Armoured cars
Daimler Dingo
With nearly 6,400 machines produced in several sub-versions until 1945, the Dingo was one of the best armored reconnaissance 4×4 vehicles produced in the world. About 400 served during the campaign of France in the 1st Armored Division and the Northumberland Fusiliers; and in many theaters after.
Humber Light Reconnaissance Car
About 300 of these armored armored car were produced by the Rootes Group (Humber) and served with the BEF. These vehicles had a Boys anti-tank rifle and a Bren gun. After the Fall of France, 3600 more would be produced.
Older models
-There were still ww1 vintage or 1920-24 pattern Rolls-Royce models in use in North Africa, especially in Libya and East Africa
-The rare Vickers Crossley 4×4 (model 25) was produced for Japan, whereas 100 “Indian pattern” were used by the Raj of India and the 6×6 Mark I was still during the war for training (to come). About thirteen IGA-1s 6×6 were also used by the Estonian defence Forces in WW2 and the model 26 4×4 by Argentina.
-Guy Armoured Car: Only 101 of the “pre-production” prototypes for the famous Humber were built by Sydney Guy at Wolverhampton in 1939. Only four went with the BEF, all captured, the rest were used at home for training.
-Lanchester 6×4: A rather rare 6×6 model developed in 1928 (34 built) and used overseas during ww2 (Malaya) and at home for training. Relatively similar to the Vickers-Crossley.
New ww2 models
-Humber armored car: One of the most successful ww2 armored cars. Developed from the Guy in 1940, 5400 were produced up to 1945. Armament was variable but in general a couple of a heavy Besa and light machine guns. Used as a standard for ground reconnaissance on all fronts.
-AEC Armoured Car: A 4×4 monster built during the war and sturdy enough to sport the turret of the Valentine tank. It was one of the earliest example of a wheeled tank during ww2.
-Coventry Armoured Car: A late (1943) ww2 attempt to design a standard wheeled armored car to replace previous models, only 220 built.
-Morris CS9: Morris was a prolific prewar car manufacturer, but only produced 99 of its own armored car in 1938-39, the CS9. A sturdy 4×4 lightly armed and armored, it was quickly retired from the front line.
-Morris Light Reconnaissance Car: Designed and mass-produced after Dunkirk (1940) at 2200 units, this light RC armored car was lightly armored and protected, but cheap to built and faster than the heavier CS9. However it suffered from reliability issues and had limited offroad capabilities.
-Standard Beaverette: A desperate case of improvization, these were post-Dunkirk 1940. Called “Lord Beaverbrook’s pets” (RAF) they were hastily-made armored conversions for home guards defence. They were made of Standard car vehicles, 2,800 converted in a shot time and several series. They only served at Home.
Light tanks
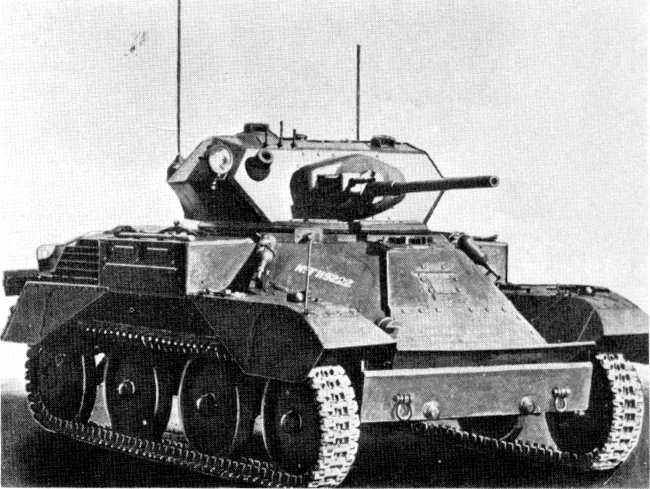
Vickers Light Mk.II-III
Mk.I (10 built), Mk.II (66 built) and Mk.III (34 built), 110 built in all. From these light tanks derived many models, including the 6-ton light tank widely sold for export. They were classified as cavalry tanks, light, fast, with a turret armed with a single gun, and a crew of two. Relegated for training until 1942.
Vickers Light Mk.IV
34 of these improved Mk.IIIs with a new hull and suspensions were delivered.
Vickers Light Mk.V
22 of these three-men crew vehicles with a redesigned hull were built.
Vickers Light Mk.VI
1682 built. By far the most common light tank of the BEF, the Mk.VI was produced until 1939, of which many were sent overseas. It used a heavy .50 cal (12.7 mm) machine gun, combined with a light machine gun (7.7 mm/0.3 in).
Tetrarch (Tank, light, Mk.VII)
177 built. The A.17 was a specific wartime version designed to be airborne. The Tetrarch served in Normandy, but, being unsatisfactory, they were quickly withdrawn. Next, was the Harry Hopkins, a disastrous model.
Tank, light, Mark VIII “Harry Hopkins”

The Tank, Light, Mk.VIII (A.25), better known as “Harry Hopkins”, was a British light tank made in just 100 vehicles by Vickers-Armstrong specifically for airborne operations. It was also the very last of the long line of British light tanks and successor to the Mk.VII Tetrarch. Compared to the latter, it was larger and had a better armour. Submitted to the War Office in late 1941, the design was accepted and an order for 1,000 was approved by the Tank Board (War Office), later increased to 2,410 in November 1941. However production only started by June 1942 and early exercises underline a great number of problems, requiring a stray of modifications of the design as production was ongoing. Complaints accumulated at the War Office from the Fighting Vehicle Proving Establishment. The issues were such that only six Hopkins tanks had been delivered by mid-1943, and the serie went on until reaching 100 in February 1945 before being cancelled.
By mid-1941 already, some in the War Office and British Army estimated that light tanks were no longer desirable, lacking armament and armour, and often foreshadow in their scout role by cheaper armoured cars. In general they performed poorly in many engagement. For the Mk.VIII this meant they were already undesirable and were in addition obsolete when the production ended. In fact none ever saw combat. Reconversion plans were made by the War Office like having reconnaissance units fielding these, attached wings tests, to be towed as gliders, but nothing really worked. By default of other ideas, they were handed over to the Royal Air Force, and used use in airfield defence. The Mk.VIII only variant was the short-lived Alecto self-propelled gun, using a howitzer for paratroopers close-support artillery in airborne operations, but only a few were produced, only tested, never fielded in active units.
Medium tanks
A.9, Cruiser Mk.I
125 built in 1938. Designed in 1937, a development of Major Giffard Le Quesne Martel’s tankettes, these medium tanks were the forerunners of the famous Crusader.
Cruiser Mk.II
175 built. Closely derived from the Mk.I, it was equipped with a 2-pounder (37 mm/1.47 in) high-velocity gun, a heavy Besa machine-gun and a coaxial Vickers machine gun.
Cruiser Mk.III
65 built. Derived from the Mk.II, this new medium tank had a Christie suspension, giving it a much better grip on rough terrain. They were built in part for the BEF, but quickly supplanted by the Mk.IV.
Cruiser Mk.IV
890 in all (225 Mk.IV and 665 Mk.IVA). Based on the Mk.III with improvements but with a far superior, sloped armor. It was widely used in North Africa .
Cruiser Mk.V Covenanter
1771 built in 1940-42. A largely improved Cruiser, built by LMS/Nuffield, which suffered from many design flaws, despite being the blueprint of the Crusader. It saw little combat and was mostly used for drilling.
Cruiser Mk.VI Crusader
5,300 in all. An all-around superior tank to the previous Cruisers, it made up the bulk of the British tank force during the African campaign. But, suffering from engine problems, relatively weak armor and armament, it was phased out in 1942.
Cruiser Mk.VII Cavalier
500 built. Also known earlier as the Cromwell I or A.24 (Nuffield), it was basically an improved Crusader with a new turret, armor and 6 pdr.
Cruiser Mk.VIII Centaur/Cromwell
4,016 built until 1945. Improved version of the Cavalier or A.27L (the Centaur was at first known as the Cromwell II) with a Liberty Engine (by Nuffield). The Cromwell proper (A.27M) was propelled by a more powerful Rolls-Royce Meteor, an adaptation of the famous Merlin propelling the Spitfire.
Cruiser Mk.VIII Challenger

This 1942 project, headed by Roy Robotham, was meant to carry the long 17-pdr gun. On paper, this was quite a formidable anti-tank gun, but incompatible with the turrets of the Crusader and Cromwell series. It was realized that the new tanks (Comet and later Centurion) would need at least two more years of development, so an interim solution was chosen with the modification of a Cromwell tailored to carry a larger turret ring for the 17-pdr.
This resulted into the A.30 design, basically a stretched-out Cromwell with an extra pair of roadwheels and many other modifications, including the removal of the bow machine gun to free space for the bigger rounds. The new turret was taller and, due to the strain added, compromise led to it having thinner armor than actually found on the Cromwell. After production started in February 1943, with 200 Challengers built by Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company, the General Staff declined any further order and canceled the project in November of that year. The few Challengers built acted as tank hunters until the end of the war. They arrived in operations in August 1944 in Normandy, then northern France and the Low Countries. Many served with the 1st Czechoslovak Armoured Brigade and 22 were found in service in the Czechoslovak army until 1951 when provisions of Soviet-built tanks made it obsolete.
Derivative: The A.30 Avenger tank hunter
The Challenger’s turret problems were later to be solved by a tank hunter, developed in 1944 by Leyland motors. It reused most of the Challenger, swapping to the Comet’s suspensions in late production (1945). This peculiar vehicle was the A.30 self-propelled gun, Avenger. just like the Achilles, a conversion with the 17-pdr of the American M10 GMC Wolwerine, the Avenger had a lower, thicker open top turret, which just a small cover for the crew. It was not very successful and of the 230 ordered, it seems only about 60 were delivered as the order was cancelled in May 1945. None was used during the war, but they made two tank hunter battalions until 1952, discarded afterwards.
Comet
1,186 built in 1944-45. A product of Leyland motors, carrying the 77 mm (3 in) gun, better known as the legendary 17-pdr, the best piece of AT ordinance in the Allied arsenal by 1943. The Comet was also designed to correct the Cromwell’s flaws (track shedding and broken suspension problems).
Infantry Tank Mk.I Matilda I
140 built. This vehicle was slow and very well protected, with a simple caliber .303 (7.62 mm) heavy machine gun, it was a testbed for the next, better known Matilda II.
Infantry Tank Mk.II Matilda II
2,987 built by 1939. Called A.12, Tank, Infantry, Mk.II, it was a major best-seller among the British models. By 1939, about 300 were produced. They were a little faster, had a powerful and economical diesel and a high-velocity 2-pounder gun (40 mm/1.57 in). It was twice as massive and overall better protected than the Matilda I. Heavy tank by the standards of 1939.
Infantry Tank Mk.III Valentine
8,300 built until 1943. Designed internally by Vickers without a specific request from the War Ministry, the Valentine infantry tank was more compact and lighter than previous tanks of the type. It was not a priority, but received the endorsement of the War Office after the Dunkirk evacuation, being produced in many versions, steadily improved until the Mk.XI of 1943.
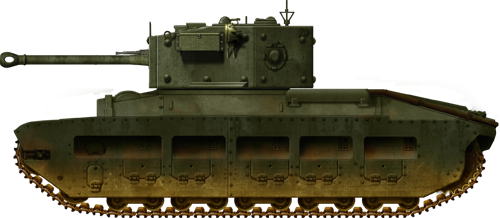
Infantry Tank Mk.IV Churchill
7,368 built. The Tank, Infantry, Mk.IV was one of the heaviest, but also most dependable Allied tanks during the war. Its sturdy chassis and well-protected hull served for many conversions and utility versions: bridge layer, minelayer/minesweeper, AVRE (Royal engineer corp), Petard (mortar), Oke and Crocodile (flamethrower), ARV (recovery), ARK (ramp).
Others
Bishop SPH support artillery
149 built in 1941. Converted Valentine with a protected QF 25-Pdr (87.6 mm/3.45 in) howitzer
Archer SPG tank hunter
660 built. Tank hunter armed with the 17 Pdr gun on the Valentine chassis, 1944.
Sherman Firefly
2,000 built. Tank hunter armed with the 17 Pdr (76.2 mm/3 in) gun on the Sherman chassis, 1944.
WW2 British Tanks more in detail
(And Tanks missing as posts for now).
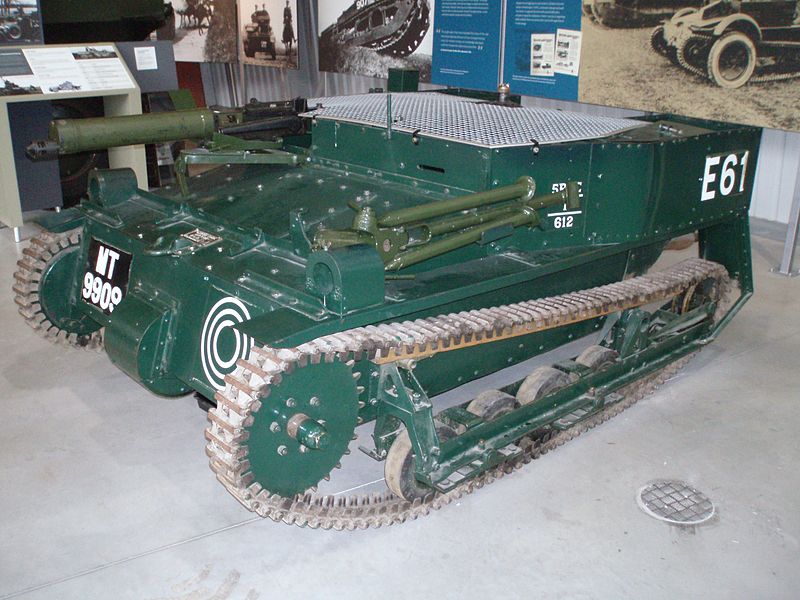

The Vickers-Carden-Loyd Mark.VI was the most exported and most produced tankette, from 1927 to 1935. Born as a concept from army engineer Major Giffard LeQuesne Martel, it reduced the armored mobility concept to its very core. 450 were built, most exported, although many served with the British armored forces. They were discarded and phased out to training duties by 1939. The tankette fad lasted until 1939. Photo credits: Flickr, dave Highbury, Bovington Tank Museum (wikimedia commons)
The Vickers 6 ton (Mark E) from 1929. With its twin turret and one turret versions, it was another one of the firm’s outstanding export successes. 13 countries bought it. The first customer, the USSR, developed the T-26 and the Polish firm Ursus developed the 7TP. Here is a Portuguese Vickers Mark E Type B (37 mm/1.46 in)

The Vickers Medium tank Mk.I was another famous interwar British tank. It belonged to the early twenties generation, fitted with a full traverse three-man turret (for the first time in the world), a new suspension system, and a quick-firing 3 pdr (47 mm/1.85 in) gun. 200 were built and phased out for training in 1938. The next Medium Mk.II was mostly similar. Production stopped in 1934. Many were reactivated and served in secondary duties during the early phases of WW2. They were slow, badly protected and their suspension too weakly built to sustain any damage.

Probably the most successful of all tankette derivatives, the famous “Universal Carrier” was mass-produced to such an extent that it became the prime scout and armored mover of all Commonwealth forces, being largely supplied to the Soviets (like in this picture), Free Polish, Free French and other allies during World War Two. It was very fast, reliable, but lightly armed and protected only against small arms fire. It was also produced and used in large numbers by the Canadian army.

The Matilda I was a new generation specialized infantry tank. But this cost-saving model was quickly replaced by the much more efficient Matilda II, which became famous during the early phase of the war (1940-42) in Africa. Although very slow, its armor could stand against everything except the deadly German 88.

Conceived as the Tank, Infantry, Mk.III, the Valentine was a compromise between the speed of the Cruiser IV and the sturdiness of the Matilda II. It was declined into eleven versions throughout the war, with a total production of 8275, the biggest British wartime tank production ever.

The Churchill was the last infantry tank. This good all-around heavy tank was at the forefront of the British armored force from 1943 to 1945. It started with teething problems in 1941, and failed miserably at Dieppe. However, in Tunisia, this model proved its superb climbing abilities and out of the ordinary sturdiness. It was used for any kind of support and genie missions imaginable.

The Cruiser I was the first of a long line of early cruiser tanks, a new breed of cavalry tanks designed to exploit a breakthrough. Unfortunately, their top speed was unsatisfactory since they had a classically sprung suspension. The up-armored Cruiser Mk.II, was too slow to operate effectively as a cruiser, but the Mk.III and Mk.IV, featuring a Christie-style suspension, were a real improvement and regained the edge.

The Cruiser Mk.IV was very similar to the Cruiser III, apart from the turret design. Very fast, it appeared ideally suited for desert warfare.

The Cruiser V Covenanter (named after the Scottish Presbyterian movement) was a much-improved evolution of the Mk.IV. Production was first ordered in April 1939, featuring innovations like an opposed-piston engine, the front placement of cooling radiators, and the wide use of welding for the hull construction. However, it was kept chiefly for training, and inspired the more famous Cruiser VI.

The Cruiser VI, better known as Crusader, was the most famous cruiser tank using the revolutionary Christie suspension. Its top speed largely compensated for its light armament and average protection. It was, however, the war horse of many operations throughout the North African campaign, and one of its most distinctive symbols.

Although similar, the Cruiser VIII Centaur and Cavalier differed by the choice of their engine. They had a new QF 6-Pdr (57 mm/2.24 in) gun and good protection, while retaining a low profile and excellent speed of previous cruisers.
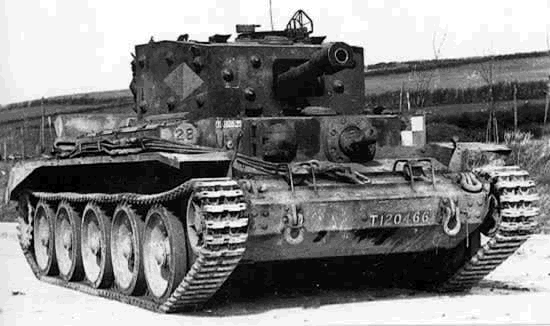
The Cruiser VIII Cromwell was the one fitted with the Rolls Royce Meteor engine, and most successful of the three. It was introduced in 1943, declined into many variants. It soldiered until the end of the war.
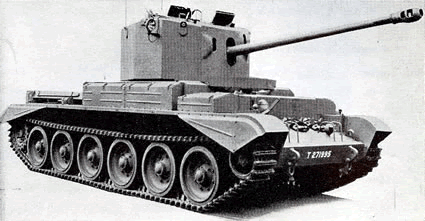
The Cruiser VIII Challenger was based on the previous Centaur/Cromwell, but fitted with a devastating 17-Pdr (76.2 mm/3 in) gun. Although promising and liked by its crews, it was dropped in favor of the Sherman Firefly.
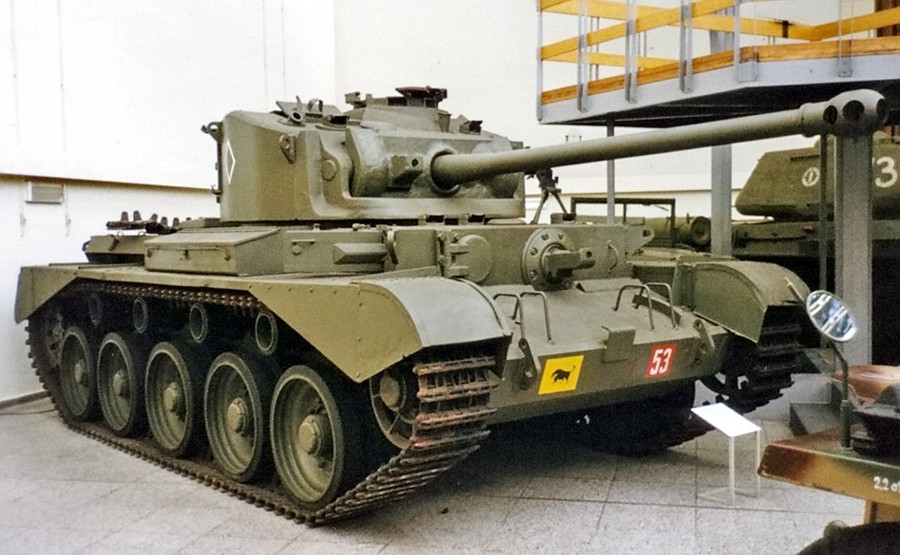

Developed after a long line of Crusader successors, the Comet was the last of this “cruiser” generation, and the best overall. It arrived in late 1944, ready for post D-Day operations in Europe, and opening the way for the postwar generation of British tanks led by the legendary Centurion.
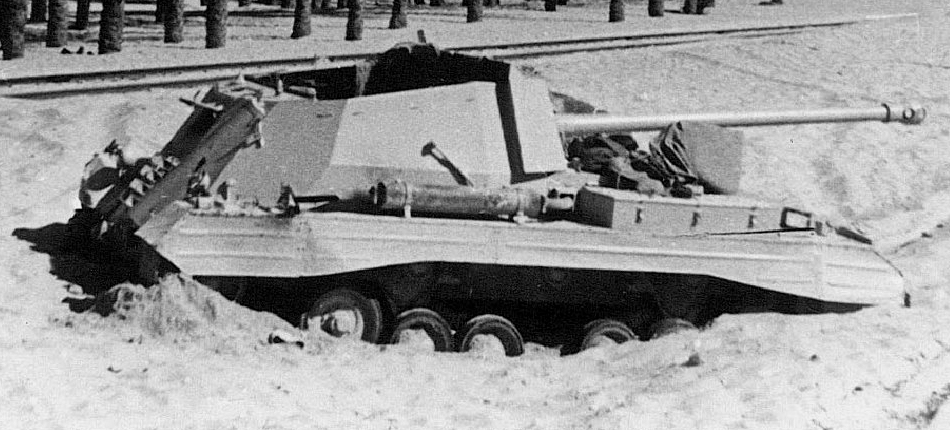

The 17 pdr (76.2 mm/3 in) Archer, built over surplus Valentine chassis, was a British SPG tank destroyer. It was designed to make use of the 17-Pdr in its original form, but had it mounted facing the rear of the tank.
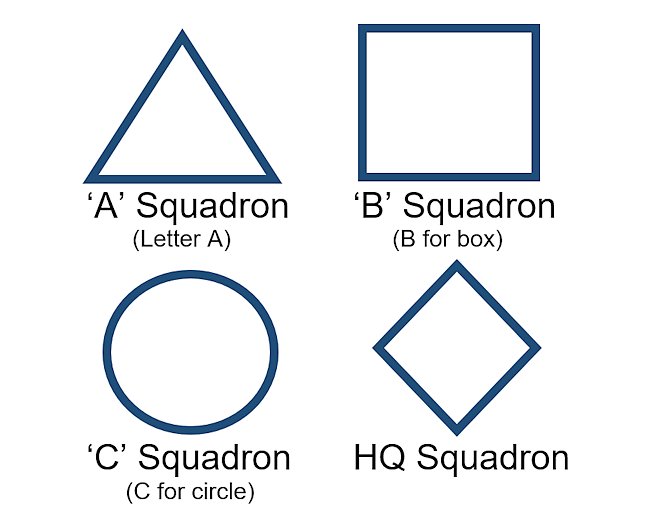
British tank squadron markings. The color changes depending on the regiment, but they normally used the same shapes.

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com


