South Korean Tanks & AFVs
 About 8,000 armored vehicles 1980 - today
About 8,000 armored vehicles 1980 - today
- K1 88
- K200
- KM-900
- M48A3K
- M48A5K
- K1 (M113)
- K1 AVLB
- K1 ARV
- K2 Black Panther*
- K-Sam Choonma*
- K30 Biho*
- K9 Thunder*
Initial situation in 1945
Just as stated in the North Korean page, both the ironclad concept and multiple rocket launchers (MRL) are proud legacies of the age-old Korean military heritage, which defeated time and again its powerful Chinese and Japanese neighbors. However, with ww2 and the Korean occupation that ended in 1945, the partition saw the country divided on the 38th parallel, recognizing de facto the Soviet occupation zone in the North, and US/UN-backed up southern zone, which both went to develop their own government, born from a trusteeship administration. The Republic of Korea Armed Forces (대한민국 육군, romanized as "Daehanminguk Yuk-gun") was established on September 5, 1948. The South Korean ground forces were equipped with locally-supplied US ww2 military equipment, from small arms to vehicles but no tanks. However, due to the nature of the terrain (70%) mountainous, the emphasis was put on artillery. Its first test would be the Korean War.The Korean War
Under its first president, Syngman Rhee as the first president, South Korea was found attacked by the North on June 25, 1950. Prior to the invasion, the North Korean Forces totaled between 150,000 and 200,000 infantry (10 infantry divisions) and one tank division, with a total of 280 tanks from ww2, most being T-34/85s (274). Opposed to that the South Koreans had 98,000 soldiers (about 1/3 were committed to support according to US doctrine), no tanks at all (which were denied), and a poor "air force" comprising 22 piston-engine recce and training planes. There were also apparently dubious loyalty within the army to the Syngman Rhee regime. Overwhelmed by numbers, lack of training (most SK infantry were conscripts) and material superiority, the South Korean defense crumbled, and the remnants were pushed back to the Pusan Perimeter while the UNC (United Nations Command) then 16-member coalition exerted its first collective action but was not ready before the situation was critical.With the assurance of the US full support (under McArthur), the perimeter held out, while the poker coup was played at Inchon, when US Forces landed and cut the back of the North Korean forces, retreating almost constantly before the winter 1950 Chinese intervention. The front stabilized on the 38th parallel and remained almost unchanged until the armistice formally signed in November 1954.
 U.S. Marines watch explosions of bombs dropped by Marine Vought F4U Corsairs during the Battle of Chosin Reservoir, Korea, in December 1950.
U.S. Marines watch explosions of bombs dropped by Marine Vought F4U Corsairs during the Battle of Chosin Reservoir, Korea, in December 1950.
The ROKA in the 1960-70s
The ROKA (Republic of Korea Army) was reformed mostly after the Park Chung-hee coup on May 16, 1961, ending the second republic (1960-61) whereas the Korean Central Intelligence Agency (KCIA) was created. The referendum ended the military junta regime in 1963, Park being elected the first president of the third republic, which lasted until 1972. Relations with Japan were formalized, while a status of forces agreement was concluded in 1966 with the US (which stationed massive forces to deter a possible new North Korean invasion attempt). The Ground Forces mostly counted M4 Shermans and M24 Chaffee as military aid, later reinforced by M47 Pattons but all were clearly insufficient against the T-54/55s and T-62s of the North Korean Army. A controversial gesture was the involvement in the Vietnam War (300,000 Korean soldiers were sent from 1964 to 1973) as support to US Forces operating in the region. Along with a spectacular economic growth, the 1st of every October was celebrated as Armed Forces Day to commemorate the first ROK Army that crossed the 38th Parallel during the SK-US-UN reconquest of the peninsula.The ROKA in the 1980s
At that time, the ground forces had received more modern M48 Patton, and the Army was reorganized into three entities, the First Army (FROKA), Third Army (TROKA) and Second Operational Command (SOC). The first was responsible for the western DMZ and capital area defense, while the TROKA was in charge of the east sector of the DMZ and the SOC was a backup force, ready to intervene to support both sectors. At the same time concerns about the aging materials of the ground forces obliged the Park administration to turn to solutions for backing-up and replace its aging tanks and after the purchased of M60s and license production of the Leopard were turned off, a program was launched with the aim of building a purely domestic force. This led to the K1 88, developed in the 1980s from the KM1, jointly developed with Chrysler Defence, the makers of the M1 Abrams. The K1 88 was the first domestic South Korean MBT, developed alongside a serie of radical modernizations for the M48A3/A5K and the armored personal carrier K200 derived from the M113. For the first time the K1 (superior o the Abrams in many ways) gave the edge over the North Korean Ch'ŏnma Ho and Pop'kung Ho (derived from the T-62 and T-72 respectively).Official Flag of the Republic of Korea Army
2007 reorganization
TROKA (second army, east) was reorganized to avoid redundancies and fused into SOC (Second Operational Command) and the FROKA or 1st Army is now the First Operations Command since 2014. As of 2014, ROK ground army forces can count on 495,000 troops, 2,400 tanks, 2,700 AFVs, 5,800 artillery pieces plus 60 guided missile systems and 600 helicopters.Equipment as of 2015
Tanks
The Main battle Tanks are classed into two main types, the first-line K1 (1027), K1A1/A2 (484) and now K2 Black Panther (390 Black Panthers planned, 40 in service) and the second-line M48A3K (381) and M48A5K (680) which were largely improved over the years to stay operational despite their half-century-old conception. Surprisingly enough, there are USSR-origin tanks also in service, 33 T-80U and 2 T-80UK all given by Russia as a partial payment of debts incurred during the Soviet era (used for training aggressors), as well as five T-62 (ex-IDF Tiran-6) and three T-72M1s. Both are a close match for the modern type MBTs in service with North Korea.- Hyundai Rotem K2 Black Panther
- Hyundai Rotem K1 88
- M48A3K/A5K
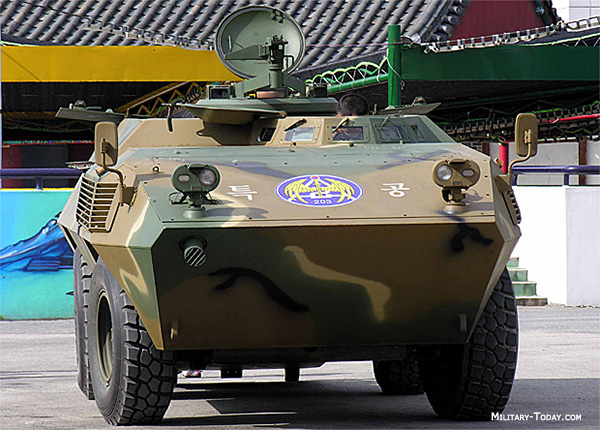 Km900 license built Fiat 6614. Credits: military today.
Km900 license built Fiat 6614. Credits: military today.
APCs/IFVs
The bulk of the AFVs comprised until this date 400 M113K1, now being retained in storage and reserve depots. Their replacement, the K200, is an intermediary APC/IFV developed by Doosan from similar 1980s modernization designs of the M113. Over 1,700 are in service today, and 800 more are in service as derivatives, an NBC reconnaissance vehicle, Smoke generating vehicle, Ammunition resupply vehicle, and a Command post vehicle. The K200 were partly succeeded by the K21 KIFV (the first Korean IFV) also developed by Doosan, and of which over 300 were built since 2009. Wheeled APCs includes the 4x4 KM900 (license-built Fiat 6614), Barracuda MRAP and the new 6x6-8x8 Hyundai Rotem KW1 Scorpion, of which 600 are planned. Also, 33 BMP-3F and 37 BMP-3M were Given by Russia in 1996 as a partial payment of debts incurred during the Soviet era. They are used for exercises, as an aggressor.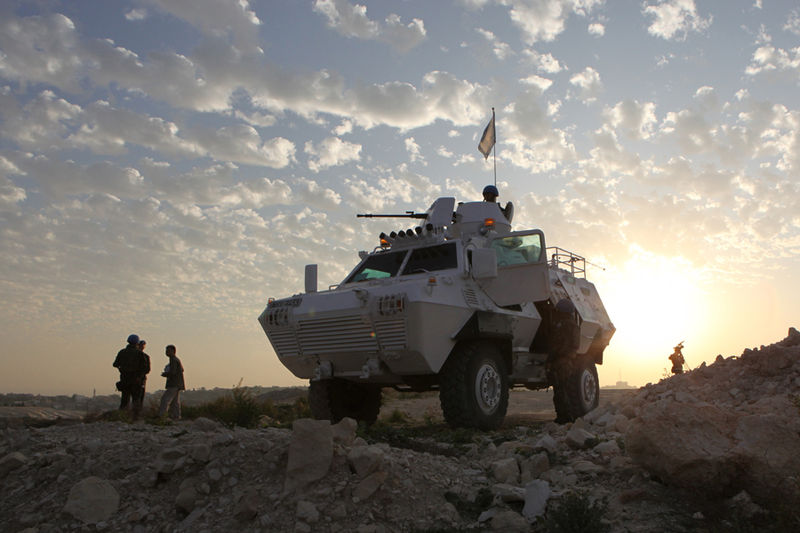
Barracuda MRAP in peace keeping operations in lebanon. MaxxPro were also used.
- Doosan K200 APC
- K21 KIFV
- KM900 Wheeled APC
- Barracuda MRAP
- KW1 Scorpion wheeled APC
SPGs
Self-propelled guns are also well represented due to the mountainous nature of operations, with the K9 Thunder as flagship. More than 850 were manufactured so far by Samsung Techwin, starting in 1999. These came in addition to 1040 K55/K55A1 (license-built M109 howitzers), K281A1 and K242A1 82 & 107 mm howitzers, and the K532 (license-built Bandvagn 206), armed with a 107 mm mortar (1994). Supply vehicles comprise 180 K10 ARVs and from 2013, 900 K56 ARV are planned. Earlier, but based on the same chassis, an undisclosed number of K77 FDCV (Fire Direction Center Vehicle) were also built.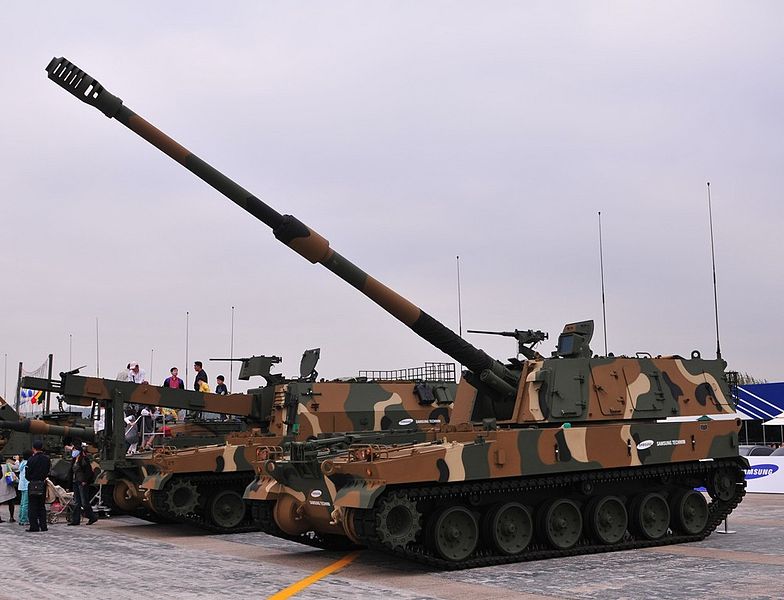
K9 Thunder SPG
- K281/241A1 SPGs
- K9 Thunder
MRLs
Complementary to the artillery fire, A variety of multiple Rocket-launchers vehicles are also used, the 130 truck-based Kooryoung (Kia) K30/33 130/131 mm and the recent tracked MLRS Chunmoo (2013, 30 planned, 130 mm rockets) and the US-licenced tracked MLRS M270/A1 firing 270 mm rockets.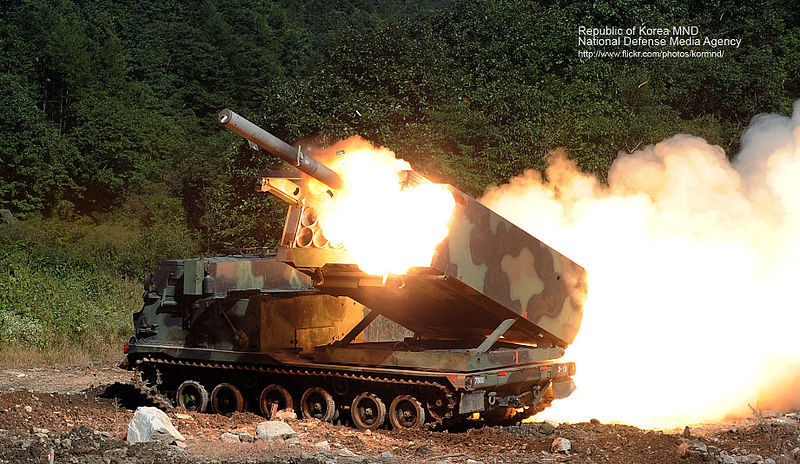
M270 MLRS
SPAAGs, SPAAMLs
Anti-aircraft cover is provided by three vehicles, the K263A1 Chungung (20 mm Vulcan) and K30 Biho (30 mm) SPAAGS, 200 and 176 respectively in service, completed by 120 K-SAM Chunma SPAAMLs equipped with Crotale missiles (short range) built by Samsung-Thales. In addition there is the addition of Manpads (Man-Portable Air Defense System) distributed to the infantry, the Javelin (UK), Mistral (Fr), Igla (Ru), Stigner (US) and the locally-manufactured Shingung (KP-SAM) designed in 2005 to replace them all.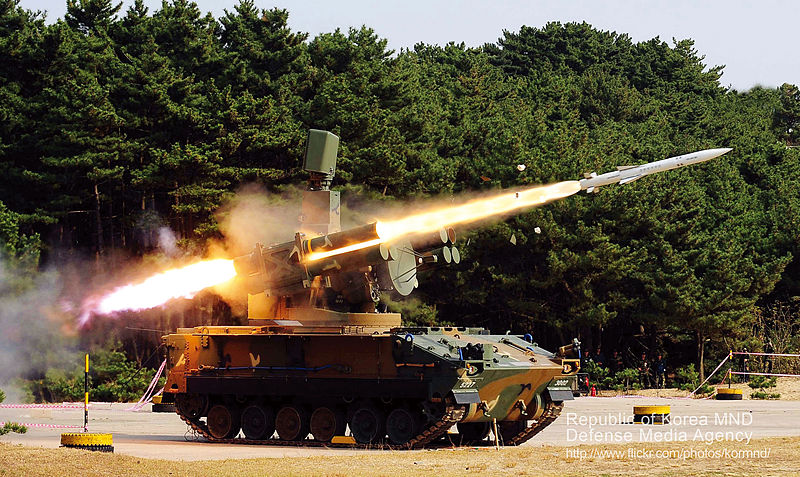
K-SAM Chunma SPAAML
- K263A1 Chungung SPAAG
- K30 Biho SPAAG
- K-SAM Chunma SPAAML
ATGMs
The APC-carried infantry is also given an extra provision of Anti Tank Guided Missile, most of US fabrication, the BGM-71 TOW (heavy ATGM), M40 106 mm (Recoilless Rifle), M67 90mm Man-Portable Recoilless Rifle, and Vietnam-era M72 LAW Man-Portable (Unguided) RPGs, plus the German modernized Panzerfaust 3.Genie and others
The genie is equipped with the K21 AVLB (70), K1, K288 and K21 ARVs (180-200 total), some 207 KM9 Armoured Combat Earthmover (dozer), 7 German and UK-built Mine Clearing Vehicles. In addition, Kia Motors delivered several tens of thousands (soft skin or lightly armoured) utility/liaison vehicles and trucks, the K131 (7,866), K311 (13,170), K511 (18,972), and K711 (10,560). Since some service in Lebanon for peace-keeping operations, the Korens used a variety of MRAPS, some of US-construction, and robots for special duties like EOD Disposal, Unmanned Ground Vehicles and even Armed Robotic Vehicle which represents the apex in Korean research and development today.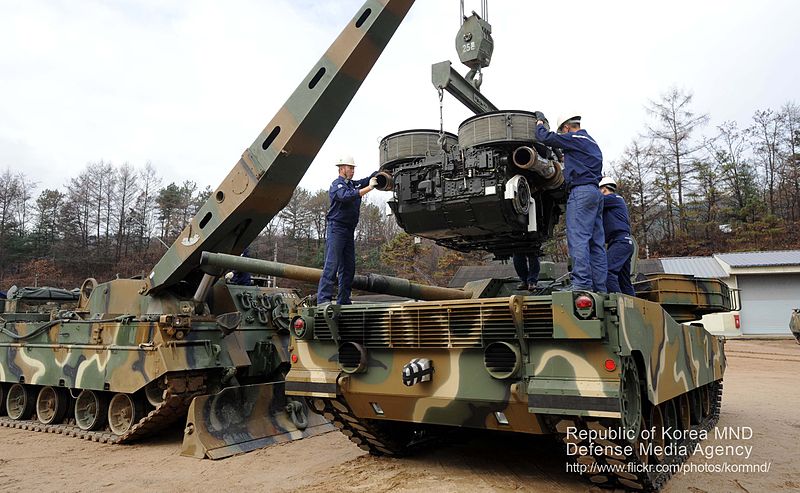
K-1 ARV from the 88th battalion in operations
- K21 AVLB
- K21 ARV
Combat helicopters
Since 1987, the ground forces are only provided with rotary-wing aircrafts. Attack helicopters (with ATMs) includes the licence-built (by Korean Air) MD-500MD (257), Bell Helicopter AH-1 Cobra (90), Messerschmitt Bo 105 (12) and most importantly the AH-64E Guardian (Apache) of which 36 are on order. Also since 2001, six drones for reconnaissance are produced, including three imported from Israel and three of local manufacture.Links
ROKA (ground forces) on WikipediaROKA Equipments (Wikipedia)
Official website (Army.mil.kr)
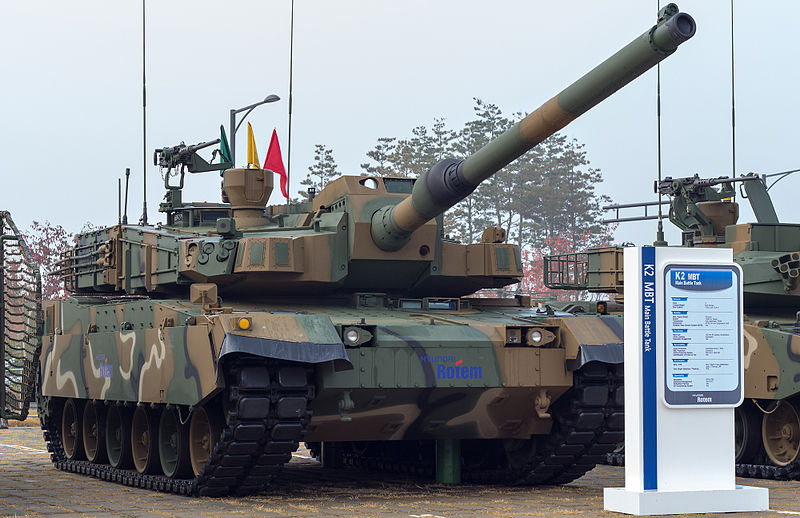

The K2 Black Panther, one of the costliest and most sophisticated MBTs today. Around 40 are in service, 390 planned in total.
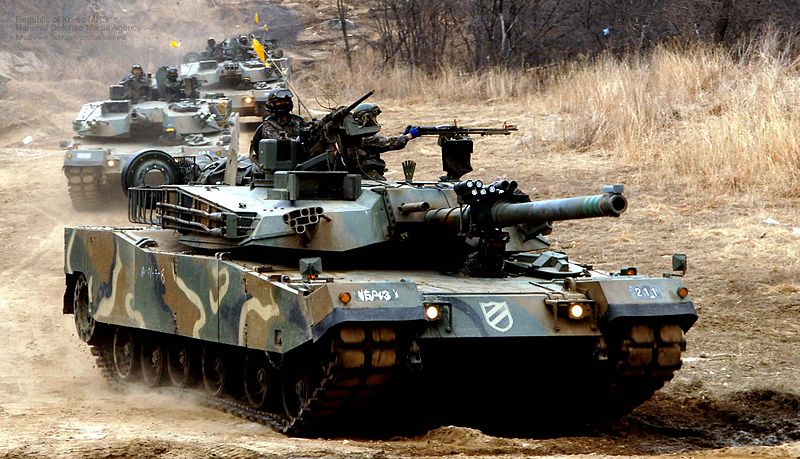

The K1A1 MBT (1997) armed with a 120 mm smoothbore gun.
K1 88, the first version, 105 mm armed, and the most prolific.

M48A5K. Upgrade of the M48A5 Patton. KM68 105 mm main gun, additional side skirts, new Korean Laser Tank Fire Control System (LTFCS).
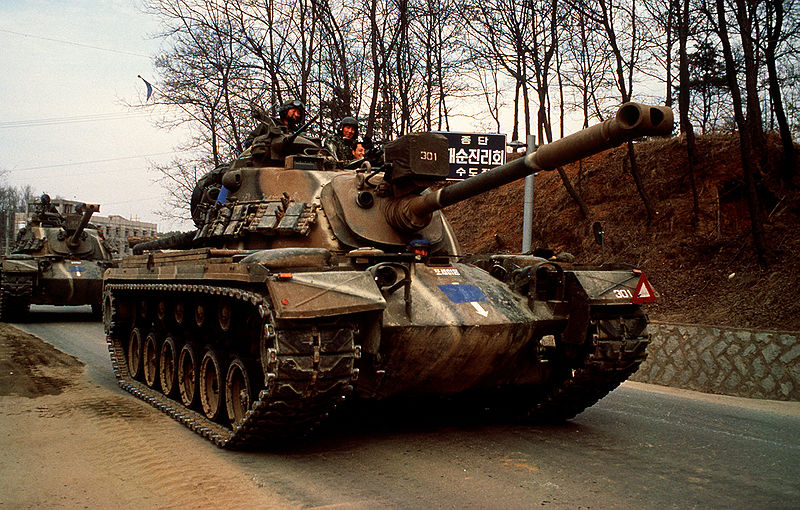

M48A3K. Upgrade: T-shaped muzzle brake, three additional tracks support wheels, new commander's periscope, smoke grenade dischargers, South Korean FCS.
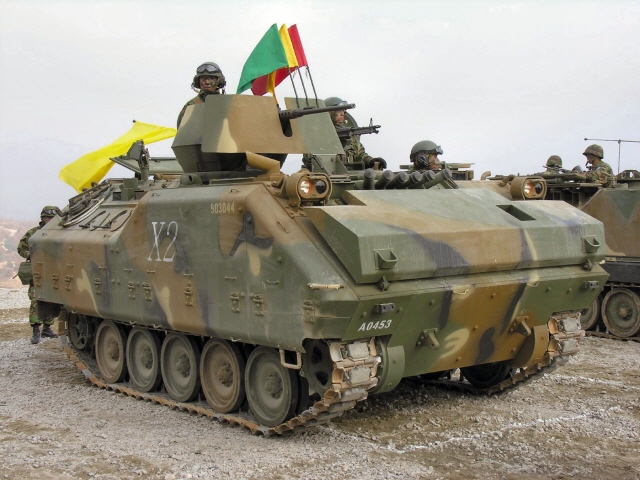

K200A1 APC
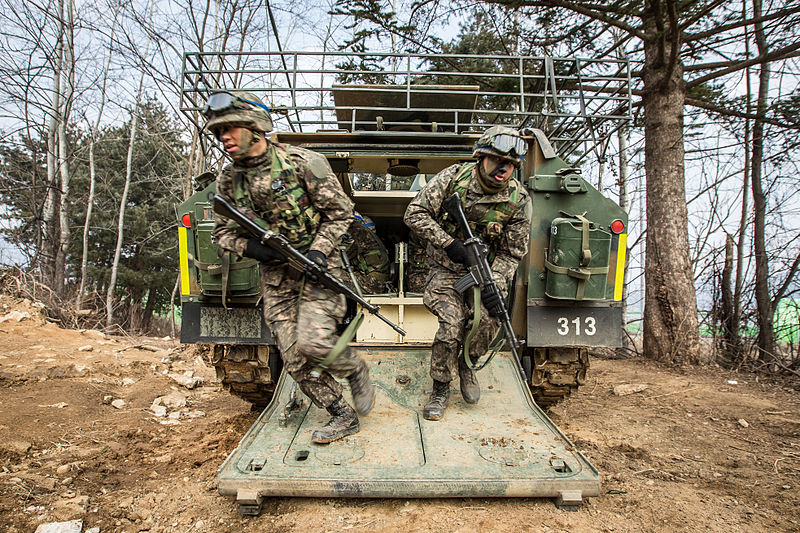

K200 (rear view) in exercises
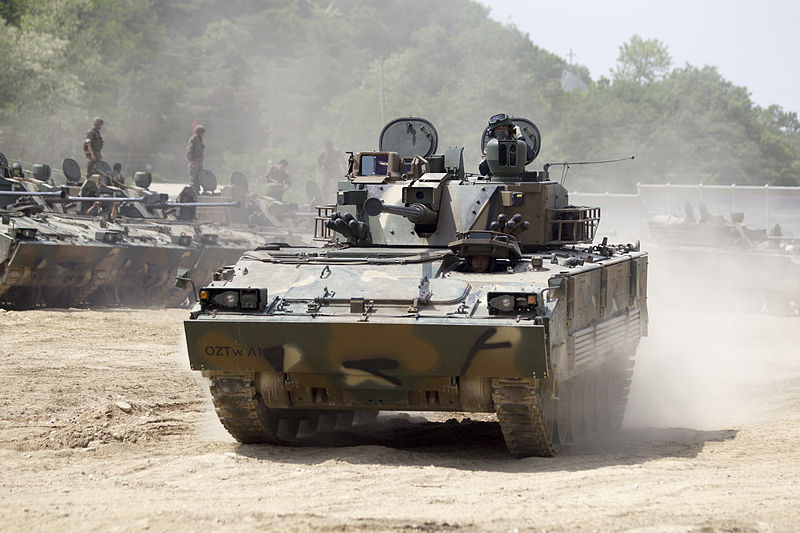

K21 KFIVF, infantry fighting vehicle

KM900 APC, licence-built version of the Fiat 6014
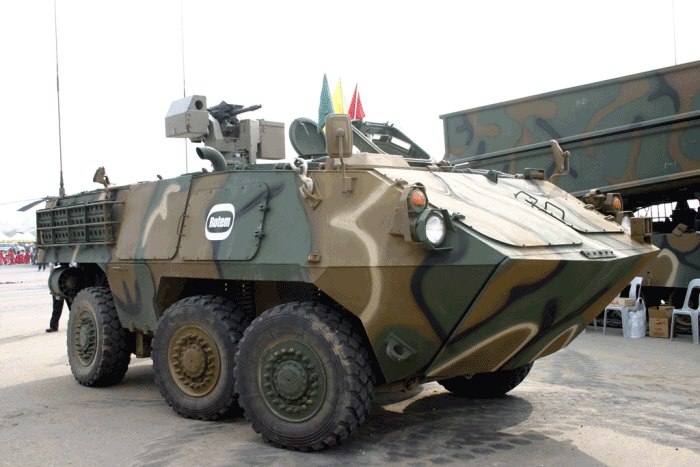

Rotem KW1 Skorpion, the latest Korean wheeled APC. credits: deagel.com
.jpg)
K55 SPG (licence-built M109 howitzer SPG)
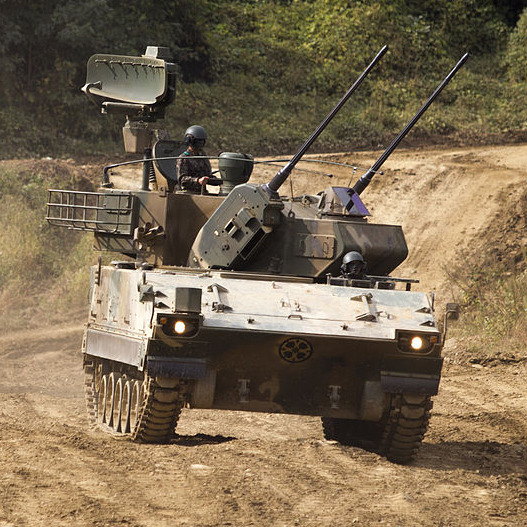

Doosan K30 Biho SPAAG

K263A1 Cheongoong, 65th anniversary of the ROKA
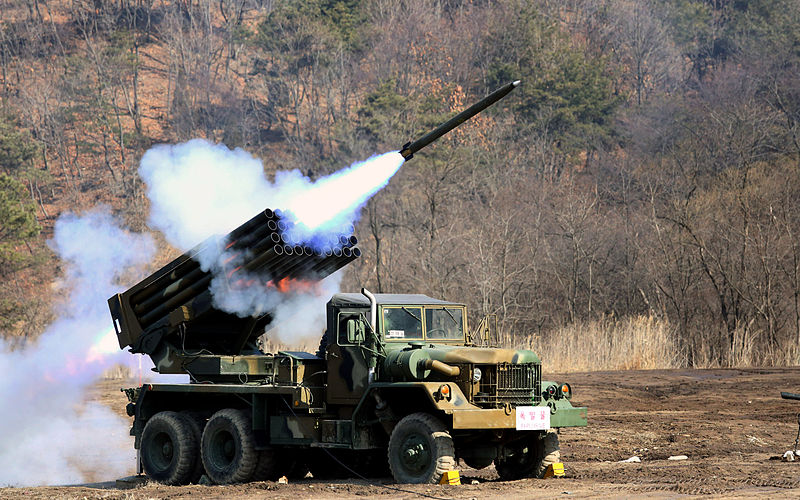

Kooryoung 130 mm MRL, 5th artillery brigade

Armed Robotic Vehicle, KOCIS 65th ROKA anniversary
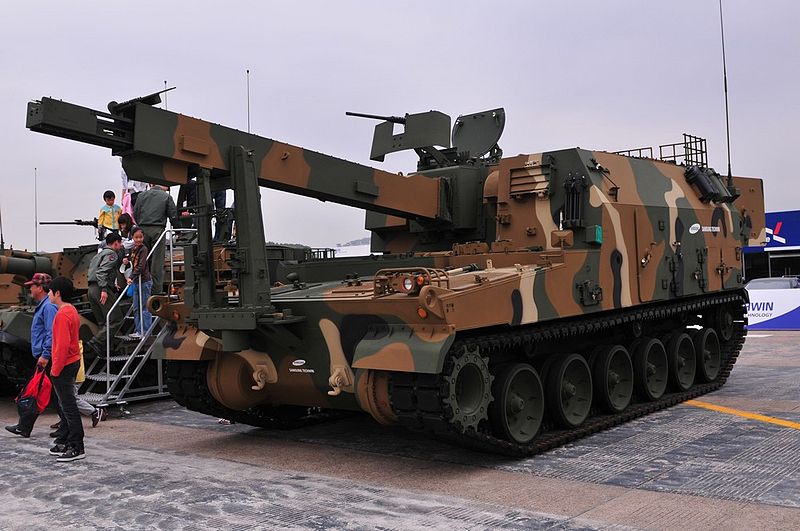

K10 ARV (Ammunition Resupply Vehicle) based on the K9 chassis by Samsung Techwin (2006).
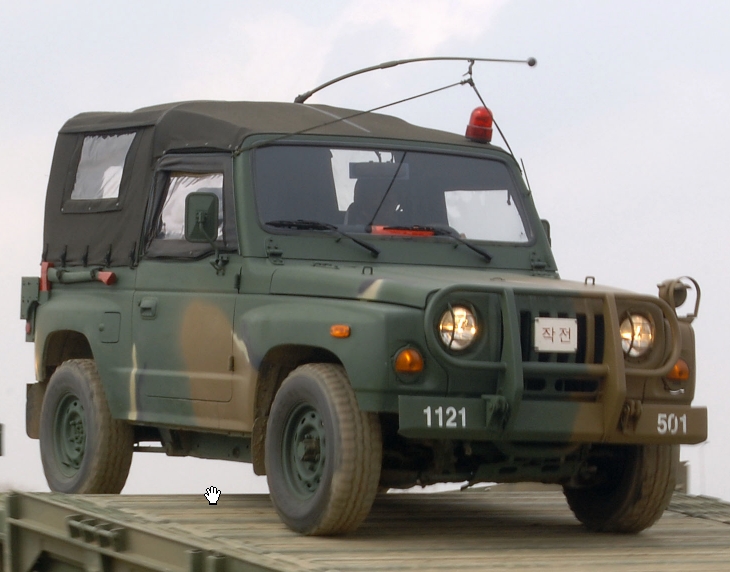

Kia 131 light utility vehicle

Samsung Techwin K77 FDVC (Fire Direction Center Vehicle) based on the K55 chassis (1990).
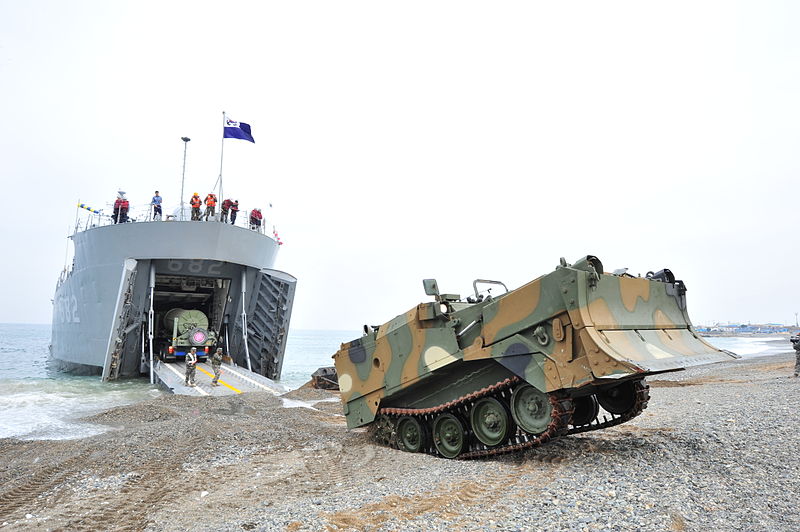

KM9 Armoured Combat Earthmover in ROKS/US Navy combined exercise 2014
Illustrations

K1 88 initial production model, 1986

Up-armoured k1 88

K1-88 late production in winter manoeuvers

Camouflaged K1A1 88 in exercises

K2 Black Panther.

K-SAM Chunma in regular livery, 2000s. To our knowledge that's the first illustration done of this vehicle, an exclusivity from Tanks Encyclopedia.

K200 KIFV, 1988.

K200A1 KIFV in UN colors, 2000s

K242 mortar carrier

K263 Cheongoong SPAAG
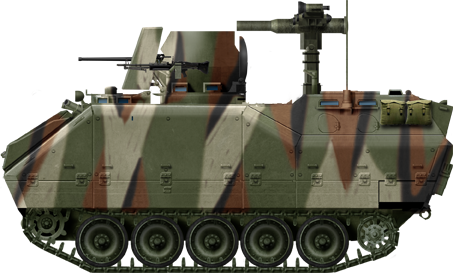
Malaysian K200 IFV
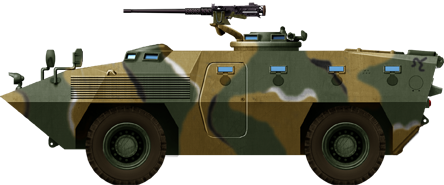
KM900 APC, 1980s.

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
