WWI France Tanks and Armored Cars
 Tanks and armoured cars -
Tanks and armoured cars - Around 4,000 armoured military vehicles by September 1918
 Archives: Schneider CA * St Chamond * Renault FT * Charron * Peugeot * Renault M1915 * Renault M1914 * White
Archives: Schneider CA * St Chamond * Renault FT * Charron * Peugeot * Renault M1915 * Renault M1914 * White
Early developments
It seems that similar conceptions of an armored tractor were shared early in the war by both allies. On the French side, Colonel Estienne, a renowned military engineer and successful gunnery officer, studied in 1914 the idea of an "armored transport" able to carry troops through no man's land. After some trials in Great Britain, he saw the new Holt tractor (largely in use for towing artillery) as an opportunity to develop his ideas.The Fouché prototype was an early forerunner, the Number 1 Type C. It was designed and tried as soon as February 2-17, 1916. This was basically a lengthened Holt chassis (1 meter with an extra bogie) wrapped into a makeshift boat-like structure. The front design was meant to cut through barb wire and possibly "surf" on mud. It was unarmed, made of wood and open-top. Trials were organized with Adjutant De Bousquet and officer Cdt Ferrus. Several other people attended as well, including Louis Renault. Most of this experience was later passed onto the CA-1.
Among other projects, the Char Frot-Turmel-Laffly was tried in March 1915 and rejected by the commission. It was a 7-meters long armored box, based on a wheeled Laffly steamroller, and propelled by a 20 hp engine. It was protected by 7 mm (0.28 in) of armor, up to four machine-guns or more, a crew of nine, and a top speed of 3-5 km/h (2-3 mph).
The same year, the Aubriot-Gabet "Cuirassé" (ironclad) was also tried. This was a Filtz farm tractor equipped with an electric engine, fed by cable, and equipped with a revolving turret housing a QF 37 mm (1.45 in) gun. By December 1915, another project by the same team (this time autonomous with a petrol engine and full tracks) was tried and also rejected.
The Schneider CA-1
Another engineer, from Schneider, Eugène Brillé, had already started work on a modified Holt chassis. After political pressure and final approval by the head of staff, Schneider Cie, by then the biggest French arsenal, started work on the Schneider CA-1. But because of administrative mismatches and Schneider reorganization for war production, the CA-1 production (then assumed by a subsidiary of the firm, SOMUA) was delayed by months. By April 1916 when the first were delivered, the British had already thrown in action their Mark Is. The surprise effect was mostly lost. Losses were enormous, but this is more due to General Nivelle's poorly coordinated plan and the lack of reliability of this first model. Many Schneider tanks simply broke down or bogged down on the way. Others were picked up by German artillery.The Saint-Chamond
The Schneider CA-1 was an arsenal-built model and the later Renault FT was a car company product. But by 1916, the Army wanted its own project, which became the Char Saint-Chamond.The St Chamond, developed in parallel to the Schneider CA, was also based on a modified Holt chassis. It has a far bigger hull, to fill the Army's requirements for better armament, in fact becoming the most heavily armed tank of the war on the Allied side, with a QF 75 mm (2.95 in) field gun and four machine-guns. But its longer hull proved to be its demise. It was more prone to being bogged down than the Schneider, and consequent operations had a huge attrition rate.
Consequently it was mostly relegated to operations on better terrains, easily found during the last stages of the war, after the stalemate was broken, or relegated to training. The Saint Chamond could have been rated as a heavy tank as well, but it was not the case in French military nomenclature. By 1918 this kind of tank was considered obsolete, although possessing some interesting innovations.
The "best-seller", Renault's miracle
The famous FT (a factory serial designation without meaning), was born from Renault's ideas for mass-production, General Estienne own concept of the "mosquito" tank fleets, and the inspired pen of Renault's chief engineer, Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier. It was really a breakthrough, an historical landmark. The vehicle was small, but not cramped (at least for the size of an average Frenchman, recruited largely from the peasantry). It was organized in a new way, now mainstream: The driver at the front, engine at the rear, long tracks and a central revolving turret housing the main armament.Light, relatively fast, easy and cheap to built, declined in gun and MG armed versions, it was turned into the thousands in 1917-18, widely exported and produced under licence for years. It was the first American tank, first Russian, first Japanese, and first of many other nations after the war. The Italian FIAT 3000 was largely inspired by this model.
Other tanks
Other projects were on their way in 1917-18, but never did it, or after the war. Saint Chamond, for example, worked on a new model largely inspired by the British rhomboid style hull, but with a fixed superstructure at the front, and later a revolving turret. It stayed a paper project. The FCM-2C (Forges et Chantiers de la Mediterranée) was another project from Estienne, a "land-cruiser" designed to operate breakthroughs in the most difficult and heavily defended sectors. It was ambitious, with several turrets and a crew of 7. Perhaps overambitious, as the Mediterranean shipyard dragged on to produce a single prototype. Eventually a serie of 10 "super-heavy tanks" were built in 1920-21, propelled by captured German Maybach engines.WWI French medium tanks
- Schneider CA-1 (1916)
400 built, one 47 mm (1.85 in) SB field gun in barbette, two Hotchkiss machine guns in sponsons.- Saint Chamond (1917)
400 built, one hull mounted 75 mm (2.95 in) field gun, 4 Hotchkiss machine guns in sponsons.WWI French light tanks
- Renault FT 17 (1917)
4500 built, one 37 mm (1.45 in) SB Puteaux gun or one Hotchkiss 8 mm (0.31 in) machine gun.WWI French heavy tanks
- Char 2C (1921)
20 built, one 75 mm (2.95 in), two 37 mm (1.45 in) guns, four Hotchkiss 8 mm (0.31 in) machine guns.WWI French armored cars
- Charron armoured car (1905)
around 16 built, one Hotchkiss 8 mm (0.31 in) M1902 machine gun.- Automitrailleuse Peugeot (1914)
270 built, one 37 mm (1.45 in) SB Puteaux gun or one Hotchkiss 8 mm (0.31 in) M1909 machine gun.- Automitrailleuse Renault (1914)
Unknown number built, one 37 mm (1.45 in) SB Puteaux gun or one Hotchkiss 8 mm (0.31 in) M1909 machine gun. The Schneider CA-1, the first French operational tank. Due to its design being closely based on the "long" Holt Chassis, the large, angular hull was prone to bog down and poor maintenance and average training proved issues as well. Like British tanks they suffered enormous casualties due to German artillery fire and gained the nickname of "mobile crematoriums" because of the exposed fuel tank. By late 1917, all existing CA-1s had been limited to training purposes only.
The Schneider CA-1, the first French operational tank. Due to its design being closely based on the "long" Holt Chassis, the large, angular hull was prone to bog down and poor maintenance and average training proved issues as well. Like British tanks they suffered enormous casualties due to German artillery fire and gained the nickname of "mobile crematoriums" because of the exposed fuel tank. By late 1917, all existing CA-1s had been limited to training purposes only.
 The Saint Chamond, produced by the army with army specifications, was the most heavily armed and impressive tank of the Allies, but proved completely unreliable in the field.
With the same, lengthened Holt chassis and an even longer, protruding angular hull, the Saint Chamond had even poorer mobility than the CA-1 from Schneider. Serving officers, after many crew reports, even complained on this matter to the national assembly, which led to an official commission of inquiry. However, on relatively moderate ground, they proved efficient, with speed better than usual (7.45 mph / 12 km/h). Some advances features like its Crochat Collardeau electric transmission proved somewhat unreliable in real combat conditions.
The Saint Chamond, produced by the army with army specifications, was the most heavily armed and impressive tank of the Allies, but proved completely unreliable in the field.
With the same, lengthened Holt chassis and an even longer, protruding angular hull, the Saint Chamond had even poorer mobility than the CA-1 from Schneider. Serving officers, after many crew reports, even complained on this matter to the national assembly, which led to an official commission of inquiry. However, on relatively moderate ground, they proved efficient, with speed better than usual (7.45 mph / 12 km/h). Some advances features like its Crochat Collardeau electric transmission proved somewhat unreliable in real combat conditions.
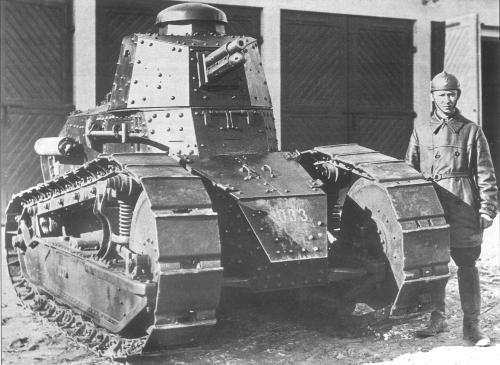 The famous Renault FT. By far the best of the three designs launched during the war, it was revolutionary, featuring many characteristics still in use on modern tanks to this day. The FT was also the most produced tank of the war, surpassing by far in this matter any contemporary tank. Marshal Joffre imagined an assault with perhaps 20,000 FTs in early 1919, which was intended to open the way towards the heart of Germany.
The famous Renault FT. By far the best of the three designs launched during the war, it was revolutionary, featuring many characteristics still in use on modern tanks to this day. The FT was also the most produced tank of the war, surpassing by far in this matter any contemporary tank. Marshal Joffre imagined an assault with perhaps 20,000 FTs in early 1919, which was intended to open the way towards the heart of Germany. Peugeot Tank (Prototype)
This little fellow was Peugot's competitive answer to Renault, a sign it would, as well, join the war production effort with the same minimalist approach took by General Estienne for his “swarms of mosquito tanks”. It was designed by Captain Oemichen, an engineer from the Special Artillery branch of the French military. The Peugeot tank was indeed a small machine at 8 tons, with the driver (right) and gunner (left) seated in échelon, side by side, in a fixed superstructure. The whole upper front section, from the engine to the roof, was one solid cast block, sloped and thick. There were access doors on the sides and rear of the superstructure. The armament consisted of a single 37 mm (1.46 in) standard short-barrel SA-18 Puteaux gun ball-mounted and offset to the left, although other sources state it was a 75 mm (2.95 in) BS howitzer.
Peugeot Tank (Prototype)
This little fellow was Peugot's competitive answer to Renault, a sign it would, as well, join the war production effort with the same minimalist approach took by General Estienne for his “swarms of mosquito tanks”. It was designed by Captain Oemichen, an engineer from the Special Artillery branch of the French military. The Peugeot tank was indeed a small machine at 8 tons, with the driver (right) and gunner (left) seated in échelon, side by side, in a fixed superstructure. The whole upper front section, from the engine to the roof, was one solid cast block, sloped and thick. There were access doors on the sides and rear of the superstructure. The armament consisted of a single 37 mm (1.46 in) standard short-barrel SA-18 Puteaux gun ball-mounted and offset to the left, although other sources state it was a 75 mm (2.95 in) BS howitzer.
The suspension comprised two pairs of bogeys, leaf and coil springs, plus an upper protection plate for the most sensitive part of the wheeltrain. The upper part of the tracks was supported by five return rollers. The engine was a current Peugeot gasoline model, probably serial 4-cylinder. Released in 1918, it successfully passed evaluations, but since it did not bring anything new the Renault FT wasn't already providing, the program was cancelled.
 Weighing nearly 70 tons, studied and developed since 1916 at Forges et Ateliers de la Méditerrannée (FCM), the Char 2C was another long wanted army project, a super-heavy tank. It was intended to be able to deal with the most fortified German positions and recapture forts of the eastern border. But the development of such an advanced model was initially so slow that the project was taken over by Renault's chief engineer Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier and General Mouret's careful and personal involvement. They were operational by 1923. The original order of 200 was cancelled after the 1918 armistice.
Weighing nearly 70 tons, studied and developed since 1916 at Forges et Ateliers de la Méditerrannée (FCM), the Char 2C was another long wanted army project, a super-heavy tank. It was intended to be able to deal with the most fortified German positions and recapture forts of the eastern border. But the development of such an advanced model was initially so slow that the project was taken over by Renault's chief engineer Rodolphe Ernst-Metzmaier and General Mouret's careful and personal involvement. They were operational by 1923. The original order of 200 was cancelled after the 1918 armistice.
Links & resources
Chars-Francais.net (French) Centennial WW1 POSTER
Illustrations
 One of the very first Saint Chamonds engaged in operations, Lauffaux plateau, May 1917. Notice the flat roof, angled vision kiosks, and the M1915 heavy field gun. The unspotted, unblended three-tone livery was usual in 1917, often featuring stripes as well.
One of the very first Saint Chamonds engaged in operations, Lauffaux plateau, May 1917. Notice the flat roof, angled vision kiosks, and the M1915 heavy field gun. The unspotted, unblended three-tone livery was usual in 1917, often featuring stripes as well.
 One of the late production char Saint Chamonds, engaged in counter-battery support in June 1918.
One of the late production char Saint Chamonds, engaged in counter-battery support in June 1918.
 One of the first Schneider CA-1 tanks engaged on the front, April 1917, at Berry-Au-Bac, part of the disastrous Nivelle offensives. The olive livery was not a standard one, but it was the standard factory paint. When the first units arrived they were put in combat in such haste that most of them appeared in this livery.
One of the first Schneider CA-1 tanks engaged on the front, April 1917, at Berry-Au-Bac, part of the disastrous Nivelle offensives. The olive livery was not a standard one, but it was the standard factory paint. When the first units arrived they were put in combat in such haste that most of them appeared in this livery.
 A late 1917 CA-1 in February 1918, in a training unit near the front, freshly camouflaged with an unusual pattern of sand, dark brow, khaki green and pale blue over a dark blue-grey basis. Later these took part in the July 1918 offensives launched by Ferdinand Foch, were 350 French tanks were committed.
A late 1917 CA-1 in February 1918, in a training unit near the front, freshly camouflaged with an unusual pattern of sand, dark brow, khaki green and pale blue over a dark blue-grey basis. Later these took part in the July 1918 offensives launched by Ferdinand Foch, were 350 French tanks were committed.
 The last Schneider CA-1s committed in action were the ones participating in the August French counter-offensive under General Gouraud's command, after the failure of the Ludendorff summer offensive. The livery is the one used in early 1918, with bright colors separated by blacks lines, creating a paving effect to disrupt shapes. But these colors made the tanks even more visible on a uniform grey-brownish battlefield. The French usage of playing card symbols to identify units by their letter stuck until WWII.
The last Schneider CA-1s committed in action were the ones participating in the August French counter-offensive under General Gouraud's command, after the failure of the Ludendorff summer offensive. The livery is the one used in early 1918, with bright colors separated by blacks lines, creating a paving effect to disrupt shapes. But these colors made the tanks even more visible on a uniform grey-brownish battlefield. The French usage of playing card symbols to identify units by their letter stuck until WWII.
 A Schneider CA "Char Ravitailleur". In mid-1918 all early production models which had survived were sent to training duties and, later, most of the late production CA-1 were converted to supply tanks. Their superstructure was altered, they gained extra armor, lost their heavy blockhaus gun which was replaced by a new hatch and also had their machine guns removed.
A Schneider CA "Char Ravitailleur". In mid-1918 all early production models which had survived were sent to training duties and, later, most of the late production CA-1 were converted to supply tanks. Their superstructure was altered, they gained extra armor, lost their heavy blockhaus gun which was replaced by a new hatch and also had their machine guns removed.
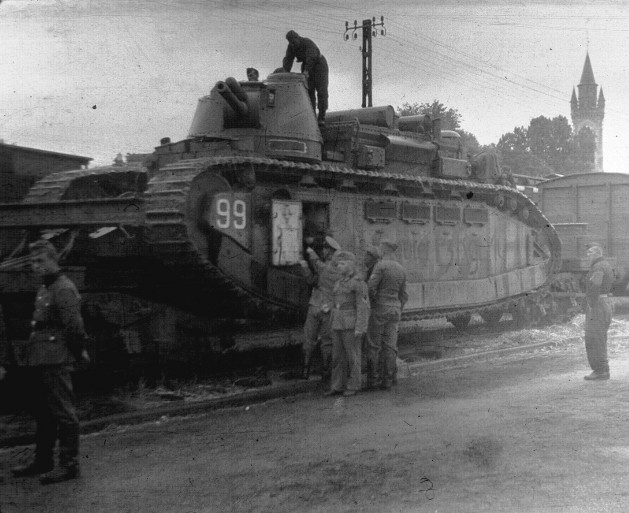
 French Charron automitrailleuse modele 1906. Russian vehicles were called "Nakashidze-Charron"
French Charron automitrailleuse modele 1906. Russian vehicles were called "Nakashidze-Charron"
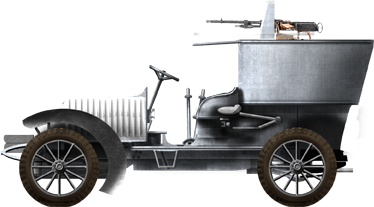 Illustration of the model in Turkish service, used for anti-riot duties. The probable color was white and not green, as it is sometimes illustrated.
Illustration of the model in Turkish service, used for anti-riot duties. The probable color was white and not green, as it is sometimes illustrated.
 Peugeot AM, armed with the Hotchkiss machine-gun. Early camouflage. Unknown cavalry unit on the Marne river, late 1914.
Peugeot AM, armed with the Hotchkiss machine-gun. Early camouflage. Unknown cavalry unit on the Marne river, late 1914.
 Peugeot armored car AC-2, with the short-barreled mle 1897 Schneider field gun and spoked wheels. Also notice the late "Japanese style" camouflage. Yser front, summer 1918. In 1916 they were rearmed with Puteaux guns, carrying 400 rounds. By 1918 they served as fast infantry support.
Peugeot armored car AC-2, with the short-barreled mle 1897 Schneider field gun and spoked wheels. Also notice the late "Japanese style" camouflage. Yser front, summer 1918. In 1916 they were rearmed with Puteaux guns, carrying 400 rounds. By 1918 they served as fast infantry support.
 Samochod Pancerny Peugeot AM in service with the Polish Border Police, 1st of September 1939. They were probably the oldest AFVs in service in Poland and fought with the German Freikorps and other advanced elements of the German army near Katowice. The six gun-armed cars (named after Lithuanian queens) received a 6+594437 mm (1.45 in) wz.18 (SA-18) Puteaux L/21 with 40 rounds. The other 8 (named after Lithuanian kings and princesses) received a 7.92 mm (0.31 in) Hotchkiss wz.25 and narrower shields. Among other modifications they received new headlights and a big searchlight, new rear sloped compartment, extra storage boxes and reinforced gear. Their chassis number was painted next to Polish blazon.
Samochod Pancerny Peugeot AM in service with the Polish Border Police, 1st of September 1939. They were probably the oldest AFVs in service in Poland and fought with the German Freikorps and other advanced elements of the German army near Katowice. The six gun-armed cars (named after Lithuanian queens) received a 6+594437 mm (1.45 in) wz.18 (SA-18) Puteaux L/21 with 40 rounds. The other 8 (named after Lithuanian kings and princesses) received a 7.92 mm (0.31 in) Hotchkiss wz.25 and narrower shields. Among other modifications they received new headlights and a big searchlight, new rear sloped compartment, extra storage boxes and reinforced gear. Their chassis number was painted next to Polish blazon.
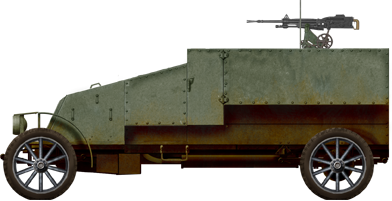 Renault automitrailleuse modèle 1914.
Renault automitrailleuse modèle 1914.
 White AC in French service, 1918, with the specific turret and armament. By the end of 1915, the first twenty armored were cars constructed in France on the White chassis. Here is the model 1917. Duplicate steering controls, for driving backwards, were apparently fitted in emergency. In total, 200 chassis of two White series were armored in France.
White AC in French service, 1918, with the specific turret and armament. By the end of 1915, the first twenty armored were cars constructed in France on the White chassis. Here is the model 1917. Duplicate steering controls, for driving backwards, were apparently fitted in emergency. In total, 200 chassis of two White series were armored in France.

The Great War
 Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary Belgium
Belgium British Empire
British Empire France
France German Empire
German Empire Italy
Italy Russia
Russia USA
USAWW1 tanks posters
