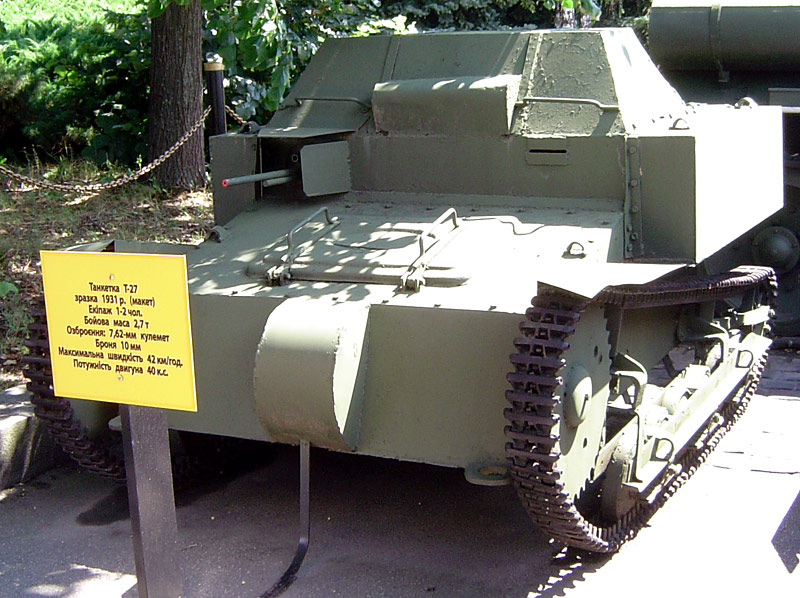
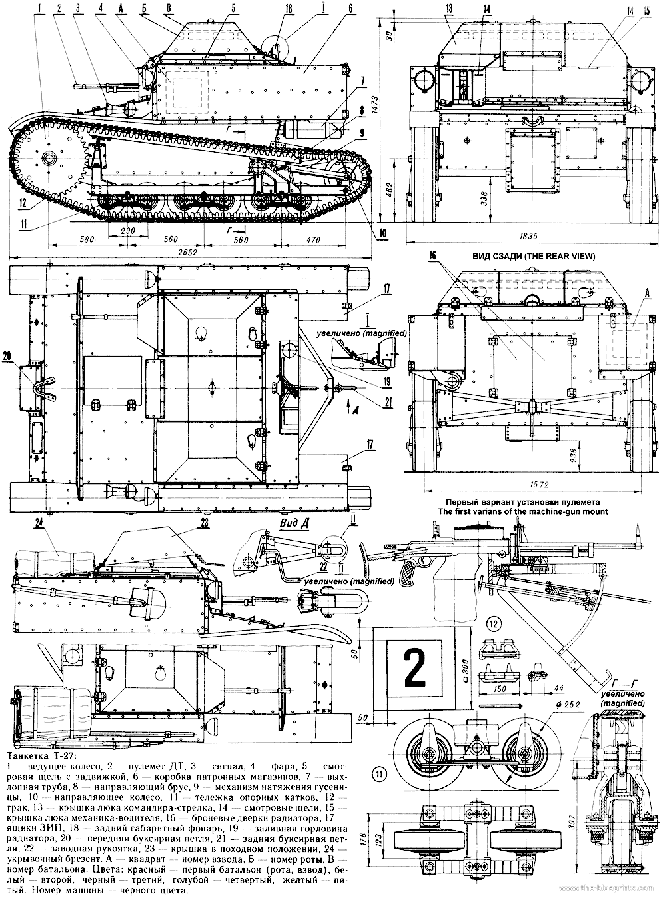
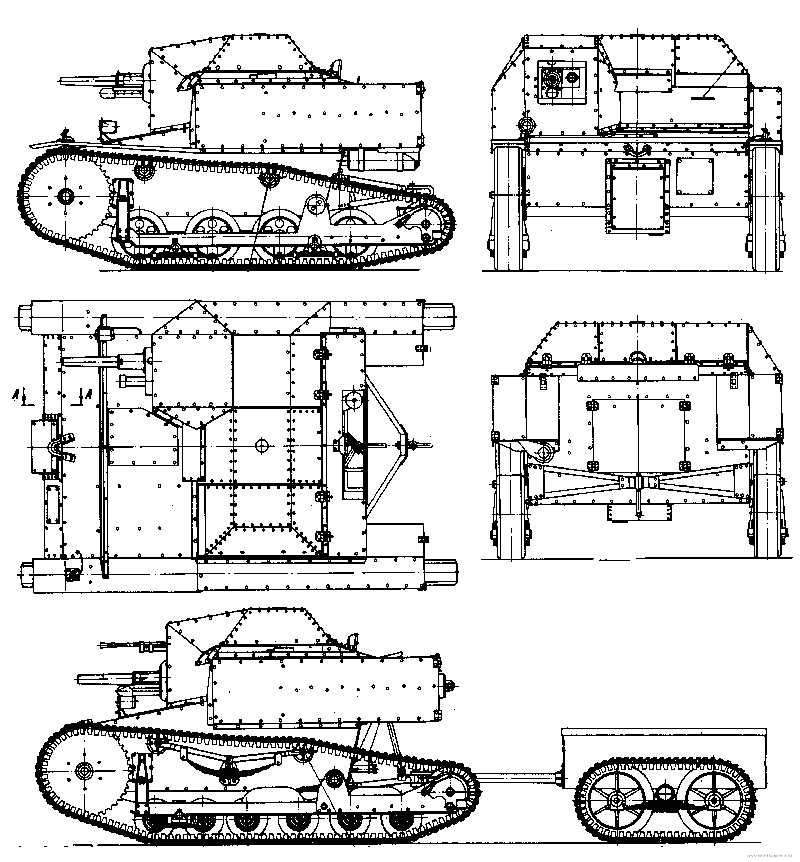
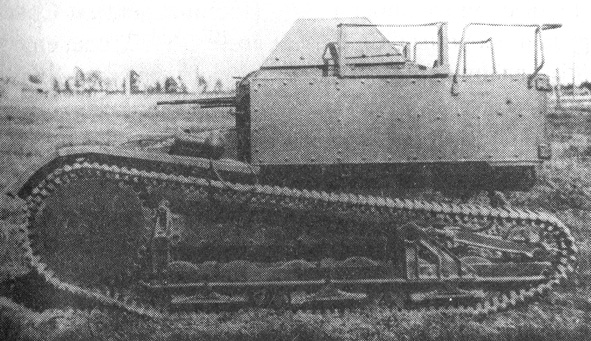
T-27 Tankette

 Tankette (1930-33) Soviet Union - 2540 built
Tankette (1930-33) Soviet Union - 2540 built
Based on the Carden-Loyd Mk.VI
Like the Vickers 6-ton and the Vickers Amphibious model acquired at the same time, the Soviet Union's UMM special commission bought the Mk.VI in 1929, already a world market success. This was the export model, characterized by a rear engine compartment and a pyramidal structure protecting the crew's heads. It corresponded to an Army requirement for a light reconnaissance tank. The vehicle undergone a series of trials but production was delayed as the general staff was displeased with it. A preseries was apparently built (unknown quantity) on the original British plans in 1930. Changes were made by Chief Engineer N. Kozyrev and chief Engineer K. Sirken at Zavod No. 37 near Moscow in 1931. They included a scaled-up hull, many reworked details to cope with the Russian climate and terrain, new engine and transmission, a new, sturdier running gear, extended rear storage and a new mount for the main machine-gun, the Soviet-built 7.62 mm (0.3 in) DT, fed with 2520 cartridges.Design & production
The hull of the main production type A of 1932 was lengthened from 2.45 to 2.60 m (8.04-8.53 ft) and enlarged. The main change was in the fighting compartment, which led to elongate the running gear with three pairs of roadwheels instead of two. Kozyrev adopted the more powerful GAZ AA (derived from a Ford licensed engine), coupled with a pair of new clutches and bigger drive sprockets, still placed between the driver and gunner. The top separate hatches for the crew were connected to the main upper body, allowing the full width to be open.But apart from these changes, the T-27 externally remained a slightly scaled-up Mk.VI, with the same advantages and limitations. The important fact about it was that it was the real start for Soviet tank mass-production, without any equivalent in Europe or the world. According to an over-optimistic five-year plan, 10,000 tanks were scheduled to be built until 1932! By 1941, the Red Army turned into the greatest armored force in existence at the time, and the T-27 started it all. Around 348 type A (1931) were built at Leningrad's Bolshevik factory plant, followed by 1683 type B in 1932 and around 500 in 1933.

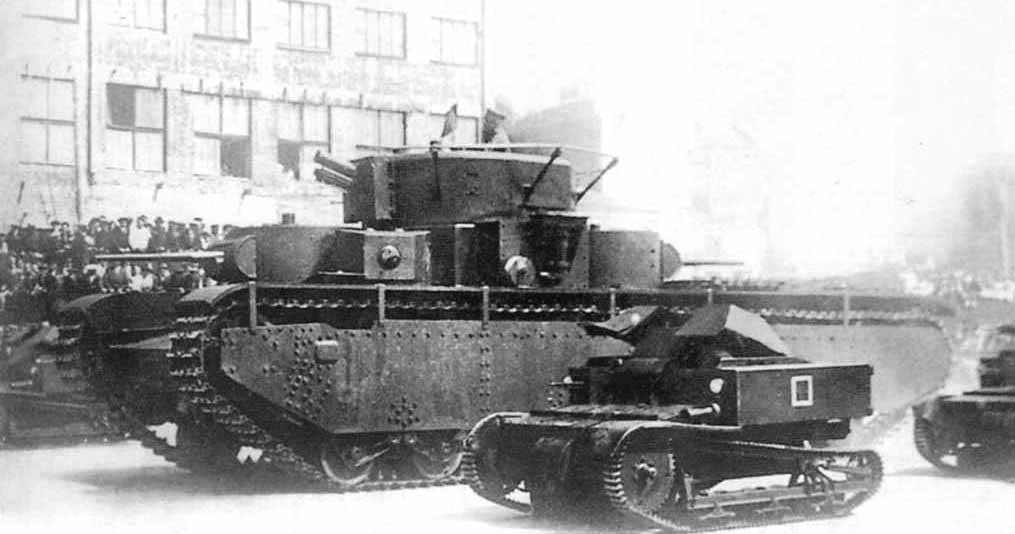
T-27s in Red Square military parade, Moscow, 1st May 1934.
However, even with the changes carried out on the original model, internal space was still very cramped and specifications for the crew asked for short men only. Plus, in the absence of compartmentation, the noise and hot environment around the engine rendered long runs unbearable. The absence of a turret made these models less versatile than other tanks. The narrow tracks and still fragile suspension proved critically weakened by the brutal, unforgiving conditions of the Russian terrain. Last, but not least, these models were deprived of radios, according to the poor state of development of the Soviet electrical industry. Signal flags were to be used during maneuvers. Moreover, a 1938 survey showed that some of the T-27 frames had been wrapped in simple cast steel plates instead of the regular chrome-nickel steel alloy required to protect against small arms fire. The T-27 had many advantages like reliability, simplicity of construction and maintenance, easy training and their speed on a flat terrain. The BTs proved much faster, but with engines ten times more powerful.
Variants
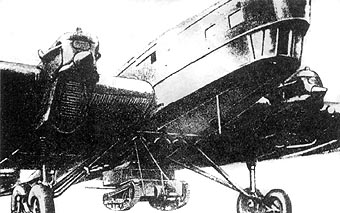
The T-27V was a rare commander's version equipped with a radio, of frame-type, fitted on the upper rear compartment. The large production figures led to many experiments, one of these being to support paratroops companies, T-27s being airlifted by TB-1 bombers, suspended under their belly. Another experiment called for a modified T-27 fitted with removable wings, the Antonov A-40. These experiments were short-lived. Rearming the T-27 was also given priority in 1932. The common 37 mm (1.46 in) gun, derived from the French Puteaux, was fitted on a modified T-27M. A small number of prototypes were extensively tested, some with 45 mm (1.77 in) guns or even 75 mm (2.95) howitzers, which proved way too heavy and even dangerous to operate for the whole structure. Recoiless guns were also tried, again without any success. Underwater tests were carried out with a pressurized hull, as well as flame-thrower and gas-thrower variants. A rocket launcher version was also tried. None received the greenlight for production.The T-27 in active service
In 1932 the T-27 formed the bulk of the Soviet light reconnaissance tank force. 65 tankette battalions, counting 50 T-27s each, were enlisted in the Red Army. The first real fighting actions arrived in 1931-32 when dealing with the eastern Basmatchis rebels on the bone dry southern steppes of Central Asia. Their participation to the Polish invasion in September 1939 or the Winter War in Finland was real but of limited value. Some were reported posted in the Far East, along the disputed Mongolo-Chinese-Russian borders. But none were reported to have see any action at Nomonanh in August 1939. Action records in Poland are unknown. With its narrow tracks, the T-27 literally "sank" in the snow or were kept trapped in springtime by the marshy terrain in Finland. Their battle records here are scarce and they were used in second line, flagged as obsolete by then.Only 1127 T-27s were left at the start of 1941 and only in second line. Their main duty was training, carrying supplies and light artillery (like the standard 45 mm/1.77 in AT gun) and mortar tractors. On June, 22, these equipped the 1st, 4th, and 9th, 10th, 15th, 18th and 24th Mechanized Corps. Their actions in combat in these desperate hours are still not well known. Many were recorded as late as in the winter of 1941, during the defense of Moscow , like the 71st Separate Naval Infantry Brigade near Lakhroma, still listed attacking German positions in December. Some were later captured by the Germans and other Axis members (in Ukraine), but their fate is unknown.
T-27A specifications |
|
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 2.60 x 1.83 x 1.44 m (8ft 6in x 6ft 03in x 4ft 8in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 2.7 tons (5600 lbs) |
| Crew | 2 |
| Propulsion | 4-cyl GAZ AA 40 bhp (30 kW) |
| Speed (land/water) | 42 km/h (26 mph) |
| Range (road/off road) | 120 km (74.5 mi) |
| Armament | 1x DT 7.62 mm (0.3 in) machine gun, 2520 rounds |
| Armor | 6 to 10 mm (0.24-0.39 in) |
| Total production | 2540 |
T-27 related links
The T-27 on WikipediaThe T-27 on wwIIvehicles.com
T-27 on aviarmor.net (in Russian), many photos

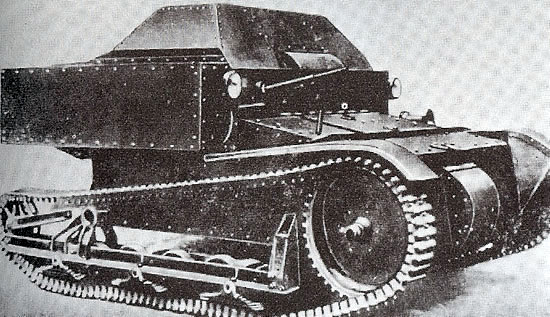
Early model, unknown unit, 1931.

Early model, Far East Asia, 1932.

Modified late T-27, 1937.

T-27 testing the PTRS-41 AT rifle during the Winter War, Finland, December 1939.

Camouflaged T-27, during exercises in 1938, with the "spotted pattern" also applied on scout amphibious tanks.

T-27 testing a rocket launcher, date unknown.

Transport vehicle during the Winter War, Finland, January 1940

T-27 in the autumn of 1941, second line training unit.
Gallery





WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
