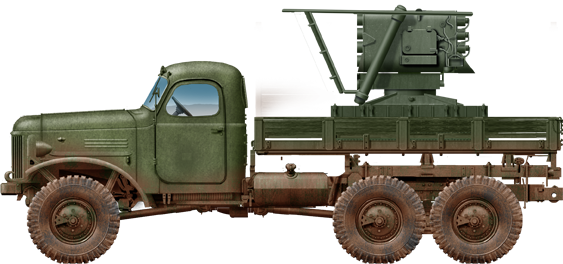
The RM-70 (Raketomet vzor 1970) multiple rocket launcher was developed in the cold war for the Czechoslovak Army as a national replacement for the Russian BM-21 Grad multiple rocket launcher. Mounted on a national 8x8 truck chassos and featuring proper protection, it was to have much enhanced performance over its parent while still being considerted as an area-saturation rocket artillery system. The RM-70 was introduced in 1971 and earned the NATO designation M1972.
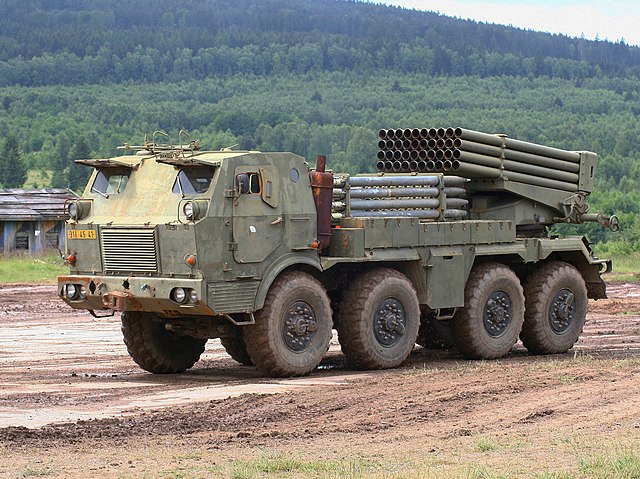

Raketomet VZ.51 that the RM-70 replaced
The RM-70 was developed in Czechoslovakia as a successor for the RM-51. The latter was developed in 1946-56 and accepted for service as the Raketomet vzor 1951 hence the acronym. It was developed as a Czechoslovak Army alternative to the BM-13 multiple rocket launcher developed in the 1950s. The latter originally based on the ZIS-6 truck as an improvised vehicle mount, towed trailer or sled in WW2, rapidly supplanted from 1944 by the more modern BM-13-16 based on US lend-leased 6x6 trucks such as the International K7 "Inter" truck, International M-5-5-31 truck, Fordson WOT8 truck, Ford/Marmon-Herrington HH6-COE4 truck, Chevrolet G-7117 truck, Studebaker US6 U3 truck, GMC CCKW-352M-13 truck. Each carried a rack of sixteen 132 mm rockets. Postwar, they were based on the Studebaker US-6 copy, the ZIL-151 and ZIL-157 from 1958.
The RM-51 could be mounted on the latter trucks, but at first the ZIL-151. The rocket launcher was more compact and highly capable in traverse and elevation. However it only fired short ranged ORNNG missiles with NZ-60V warheads. The need to fire heavier rockets led to design heavier vehicles with a better platform to handle the weight of the launcher and reload missiles as well as better absorbing the recoil and offering better proteciton overall. Initially, the Czech Army was proposed the brand new Ural 375D 6x6 trucks (manufactured 1964–1983) as a base to be built under licence and carry the new JROF 122.4 mm rockets. The Czech army instead preferred its own national Tatra T813 "Kolos" 8x8 truck as more promising as a carrier platform for the 40-round launcher. The larger chassis and heavy duty axles enabled a large weight to be installed, and enough space for the 40 additional spare 122 mm rockets and the automatic reload system. After however all the necessary modifications and armoured cabin, the RM-70 performance remained comparable to the BM-21 Grad in terms of speed and range. Still, the RM-70 as approved as a program in 1970 reached initial operational capability in 1972.
Initially, the Czech Army was proposed the brand new Ural 375D 6x6 trucks (manufactured 1964–1983) as a base to be built under licence and carry the new JROF 122.4 mm rockets. The Czech army instead preferred its own national Tatra T813 "Kolos" 8x8 truck as more promising as a carrier platform for the 40-round launcher. The larger chassis and heavy duty axles enabled a large weight to be installed, and enough space for the 40 additional spare 122 mm rockets and the automatic reload system. After however all the necessary modifications and armoured cabin, the RM-70 performance remained comparable to the BM-21 Grad in terms of speed and range. Still, the RM-70 as approved as a program in 1970 reached initial operational capability in 1972.
Production was approved and setup at Dubnica nad Váhom in Slovakia. Originally, the vehicle was manufactured for the Czech army but soon also exported to East Germany (265 from 1975 to 1989). It's only after the Soviet Union collapse and split of Czechoslovakia (Czech Republic and Slovakia) that the vehicle was sold in export to 50 countries between Africa, America, Asia and Europe.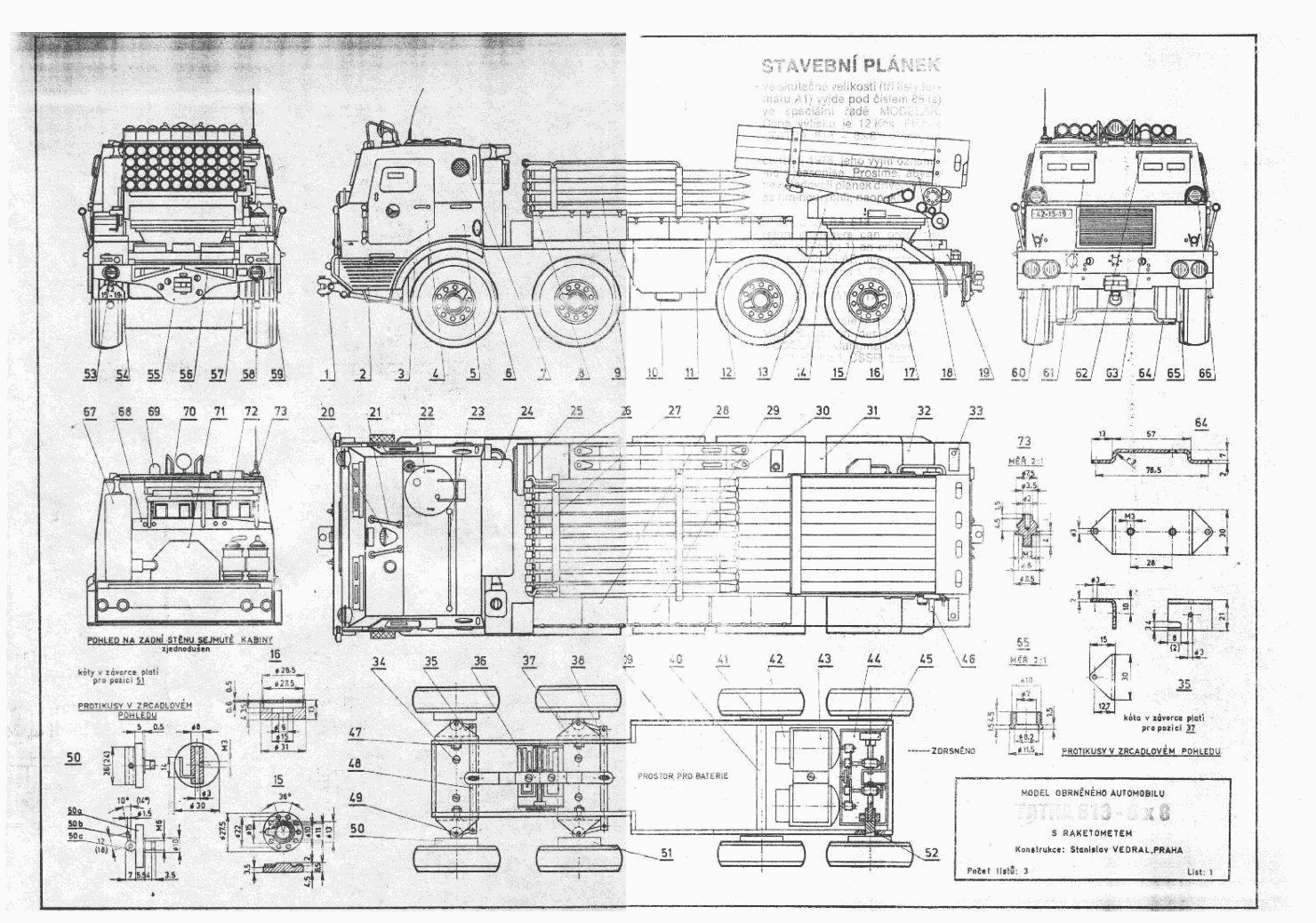
The latter provides 20 forward plus 4 reverse gears. Top speed was noted at 75 kph and range ay 1,100 km on cruise speed, road. The RM-70 had excellent cross-country capabilities and could negociate 60% slopes, climb a step 0.6m high and cross a 1.6m max. trehch, ford 1.4m of water without preparation. It is not amphibious and cannot float.
Among equipments, the RM-70 came out with the same central tire-pressure regulation system from the T-813, adjusted by the driver. There is also one spare tires behind the cab and extra storage. Some came out in option with a dozer blade mounted at the front either to prepare a hull down fire position or clearing obstacles. Also optional is a 22 ton pulling capacity but the NBC protection system is standard, helped by the armoured cabin. The latter is only protected against small arms fire.
The RM-70 rocket launcher was setup to fire individual rounds or volleys, with various indirect fire modes. It was tailored for concentrated fire over large areas, up to 3 hectares or 30,000 m2 with the warhead scalculated for cross-coverage with shrapnels in a single volley using high explosive fragmentation. A single volley was equivalent to 256 kg of explosives over 40 rockets.
The later could be the Soviet 9M22 and 9M28, or the Czech developed models:
-JROF which had a range of 20.75 km
-JROF-K with a range of 11 km
-"Trnovnik" with 63 HEAT-bomblets, range of 17.5 km
-"Kuš" with five PPMI-S1 anti-personnel mines
-"Krizhna-R" with four PTMI-D anti-tank mines, range of 19.45 km.

The other advantage of the RM-70 over the BM-21 was its included full rocket reload. Indeed, thanks to the long 8x8 chassis, the launcher is located at the rear and a full stack of 40 spare rockets could be mounted forward, just behind the cabin. During transport, the rocker launcher is angled upwards, and sit above the heads of the spare rockets as space is lacking. Once all 40 4.8 in fin-stabilized rockets are fired, the barrels can be aligned with a the rack and all rockets could be mechanically inserted into the empty barrels automatically and in one go under a minute. That too, is much faster than the usual reload process of a BM-21. This allowed the vehicle the same firepower as two BM-21, being able to deliver each two salvos with 80 rockets total in short succession in a total between 18 to 22 seconds. The vehicle also has a self-protection with a 7.62mm machine gun mounted at the right side top of the crew cabin, on a ring mount. The co-driver could stand through his open hatch and act on it.

East German Geschützwerfer RM-70
RM-70: Basic model
RM-70/85: Unarmored version of the RM-70, 26.1 t Tatra T815 VPR9 8x8 1R truck rated for 265 hp (engine T3-930-51).
RM-70/85M: New fire control and navigation and 36 km rockets, 50 upgrades ordered by Slovakia
RM-70 Modular: German-Slovak modernization for 28x 122 mm rockets, or 6x 227 mm rockets common to the M270 MLRS, NATO interoperable. Armoured cabin. 26 for Slovakia delivered from 2005.
Vz.92 "Križan": VMZ (velkokapacitní mobilní zatarasovač) Engineer vehicle based on the Tatra T815 36.265, lightly armoured cabin. 40-round rocket launcher Krizhna-R, mechanical mine layer for anti-tank mines PT Mi-U or PT Mi-Ba-III, two dispensers for anti-personnel mines PP Mi-S1.
RM-70 Vampire: Digital fire control, Tatra 817 chassis/T3C V8 engine (270 kW) and 10 TS 210 N gearbox, Norgen drive and 2nd gearbox 2.30TRS. 1,000 km (620 mi) range and 90 km/h (56 mph) with armored and NBC-protected cabin.

RM-70 Vampire Bulgaria: 12 imported in 2009, and re-exported
Bulgaria: 12 imported in 2009, and re-exported
 Czechoslovakia: c500, later Passed on to the Czech Rep. and Slovakia
Czechoslovakia: c500, later Passed on to the Czech Rep. and Slovakia
 East Germany: 265 from 1975 to 1989, 158 to Greece, 36 to Finland 1991
East Germany: 265 from 1975 to 1989, 158 to Greece, 36 to Finland 1991
 Libya: 36 Delivered between 1981 and 1982 and 100 in 2011, Libyan civil war.
Libya: 36 Delivered between 1981 and 1982 and 100 in 2011, Libyan civil war.
 Angola: 40 (2023)
Angola: 40 (2023)
 Azerbaijan: 18 RM-70 Vampir.
Azerbaijan: 18 RM-70 Vampir.
 Cambodia: 20 RM-70
Cambodia: 20 RM-70
 Czech Republic: 60 RM-70 (decommissioned late 2011)
Czech Republic: 60 RM-70 (decommissioned late 2011)
 Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo
 Ecuador: 6.
Ecuador: 6.
 Finland: 34 RM-70.
Finland: 34 RM-70.
 Georgia: 18 RM-70
Georgia: 18 RM-70
 Greece: 108 RM-70
Greece: 108 RM-70
 Indonesia: 9 RM-70 and 8 RM-70 Vampire used by the Marines.
Indonesia: 9 RM-70 and 8 RM-70 Vampire used by the Marines.
 Nigeria: 7 RM-70
Nigeria: 7 RM-70
 North Korea: Unknown number and domestically produced
North Korea: Unknown number and domestically produced
 Poland: 29 RM-70.
Poland: 29 RM-70.
 Rwanda: 5
Rwanda: 5
 Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, unknown.
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, unknown.
 Slovakia: 4 RM-70, 26 RM-70/85 Modular
Slovakia: 4 RM-70, 26 RM-70/85 Modular
 Sri Lanka: 22 RM-70
Sri Lanka: 22 RM-70
 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan
 Uganda: 6
Uganda: 6
 Ukraine: 20 RM-70 Vampire, 4 destroyed/damaged March 2024.
Ukraine: 20 RM-70 Vampire, 4 destroyed/damaged March 2024.
 Zimbabwe: 60 RM-70.
Zimbabwe: 60 RM-70.

RM-70 of the Hellenic Army (ex-East German)

Indonesian RM-70

Same, other livery RM-70
A Czech vehicle firing in exercises
If the Czech RM-70 and East German ones saw no action, the model jad been largely exported post Soviet-collapse and thus, saw plenty of action: Western Sahara War, Russo-Georgian War, Sri Lankan Civil War, First Libyan Civil War, Afghanistan conflict (1978–present), 2013 Kivu Offensive, Yemeni Civil War (2014–present), 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war, and 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. The latter received 20 of the upgraded Vampire version with long range Serbian rockets. Indeed Ukraine modified its own models to fire G-2000 rockets which had a range of 40.5 km. They were notably used to strike the city of Belgorod. So far according to Oryx, 5 were lost, 2 damaged, the rest destroyed.
Design development

Replacing the RM-51

Raketomet VZ.51 that the RM-70 replaced
The RM-70 was developed in Czechoslovakia as a successor for the RM-51. The latter was developed in 1946-56 and accepted for service as the Raketomet vzor 1951 hence the acronym. It was developed as a Czechoslovak Army alternative to the BM-13 multiple rocket launcher developed in the 1950s. The latter originally based on the ZIS-6 truck as an improvised vehicle mount, towed trailer or sled in WW2, rapidly supplanted from 1944 by the more modern BM-13-16 based on US lend-leased 6x6 trucks such as the International K7 "Inter" truck, International M-5-5-31 truck, Fordson WOT8 truck, Ford/Marmon-Herrington HH6-COE4 truck, Chevrolet G-7117 truck, Studebaker US6 U3 truck, GMC CCKW-352M-13 truck. Each carried a rack of sixteen 132 mm rockets. Postwar, they were based on the Studebaker US-6 copy, the ZIL-151 and ZIL-157 from 1958.
The RM-51 could be mounted on the latter trucks, but at first the ZIL-151. The rocket launcher was more compact and highly capable in traverse and elevation. However it only fired short ranged ORNNG missiles with NZ-60V warheads. The need to fire heavier rockets led to design heavier vehicles with a better platform to handle the weight of the launcher and reload missiles as well as better absorbing the recoil and offering better proteciton overall.
Using the Tatra T813 "Kolos" as base
 Initially, the Czech Army was proposed the brand new Ural 375D 6x6 trucks (manufactured 1964–1983) as a base to be built under licence and carry the new JROF 122.4 mm rockets. The Czech army instead preferred its own national Tatra T813 "Kolos" 8x8 truck as more promising as a carrier platform for the 40-round launcher. The larger chassis and heavy duty axles enabled a large weight to be installed, and enough space for the 40 additional spare 122 mm rockets and the automatic reload system. After however all the necessary modifications and armoured cabin, the RM-70 performance remained comparable to the BM-21 Grad in terms of speed and range. Still, the RM-70 as approved as a program in 1970 reached initial operational capability in 1972.
Initially, the Czech Army was proposed the brand new Ural 375D 6x6 trucks (manufactured 1964–1983) as a base to be built under licence and carry the new JROF 122.4 mm rockets. The Czech army instead preferred its own national Tatra T813 "Kolos" 8x8 truck as more promising as a carrier platform for the 40-round launcher. The larger chassis and heavy duty axles enabled a large weight to be installed, and enough space for the 40 additional spare 122 mm rockets and the automatic reload system. After however all the necessary modifications and armoured cabin, the RM-70 performance remained comparable to the BM-21 Grad in terms of speed and range. Still, the RM-70 as approved as a program in 1970 reached initial operational capability in 1972.
Production was approved and setup at Dubnica nad Váhom in Slovakia. Originally, the vehicle was manufactured for the Czech army but soon also exported to East Germany (265 from 1975 to 1989). It's only after the Soviet Union collapse and split of Czechoslovakia (Czech Republic and Slovakia) that the vehicle was sold in export to 50 countries between Africa, America, Asia and Europe.
Design of the RM-70

Chassis, engine and drivetrain
The chassis and powerplants are essentially the same as the original Tatra 813. The vehicle kept a central tyre pressure regulation system. There was a headlight with white light on the forward cab roof. The other frequent option is a snow plough SSP 1000 or a dozer blade BZ-T forward to create an emplacement or remove obstacles. The engine is a Tatra T-930-3 V-12 air-cooled diesel rated for 270 hp. at 2,700 rpm coupled to a dual-range 5-speed plus overdrive gearbox.The latter provides 20 forward plus 4 reverse gears. Top speed was noted at 75 kph and range ay 1,100 km on cruise speed, road. The RM-70 had excellent cross-country capabilities and could negociate 60% slopes, climb a step 0.6m high and cross a 1.6m max. trehch, ford 1.4m of water without preparation. It is not amphibious and cannot float.
Among equipments, the RM-70 came out with the same central tire-pressure regulation system from the T-813, adjusted by the driver. There is also one spare tires behind the cab and extra storage. Some came out in option with a dozer blade mounted at the front either to prepare a hull down fire position or clearing obstacles. Also optional is a 22 ton pulling capacity but the NBC protection system is standard, helped by the armoured cabin. The latter is only protected against small arms fire.
Armament and equipments

The RM-70 rocket launcher was setup to fire individual rounds or volleys, with various indirect fire modes. It was tailored for concentrated fire over large areas, up to 3 hectares or 30,000 m2 with the warhead scalculated for cross-coverage with shrapnels in a single volley using high explosive fragmentation. A single volley was equivalent to 256 kg of explosives over 40 rockets.
The later could be the Soviet 9M22 and 9M28, or the Czech developed models:
-JROF which had a range of 20.75 km
-JROF-K with a range of 11 km
-"Trnovnik" with 63 HEAT-bomblets, range of 17.5 km
-"Kuš" with five PPMI-S1 anti-personnel mines
-"Krizhna-R" with four PTMI-D anti-tank mines, range of 19.45 km.

The other advantage of the RM-70 over the BM-21 was its included full rocket reload. Indeed, thanks to the long 8x8 chassis, the launcher is located at the rear and a full stack of 40 spare rockets could be mounted forward, just behind the cabin. During transport, the rocker launcher is angled upwards, and sit above the heads of the spare rockets as space is lacking. Once all 40 4.8 in fin-stabilized rockets are fired, the barrels can be aligned with a the rack and all rockets could be mechanically inserted into the empty barrels automatically and in one go under a minute. That too, is much faster than the usual reload process of a BM-21. This allowed the vehicle the same firepower as two BM-21, being able to deliver each two salvos with 80 rockets total in short succession in a total between 18 to 22 seconds. The vehicle also has a self-protection with a 7.62mm machine gun mounted at the right side top of the crew cabin, on a ring mount. The co-driver could stand through his open hatch and act on it.
specifications RM-70 | |
| Dimensions | 8.8 m x 2.55 m x 2.96 m |
| Total weight, battle ready | 25,300 kg fully loaded |
| Crew | 2 (driver, operator) |
| Propulsion | Tatra T-930-3 V-12 AC diesel 270 hp/2,700 rpm |
| Suspension | 8x8 Torsion Bars |
| Speed (road) | 75 kph |
| Range | 1,100 km |
| Armament | 40 122mm rockets (+40), 7.62mm LMG roof pintle mount. |
| Armor | c8mm cabin armour |
| Total production | |
Variants

East German Geschützwerfer RM-70
RM-70: Basic model
RM-70/85: Unarmored version of the RM-70, 26.1 t Tatra T815 VPR9 8x8 1R truck rated for 265 hp (engine T3-930-51).
RM-70/85M: New fire control and navigation and 36 km rockets, 50 upgrades ordered by Slovakia
RM-70 Modular: German-Slovak modernization for 28x 122 mm rockets, or 6x 227 mm rockets common to the M270 MLRS, NATO interoperable. Armoured cabin. 26 for Slovakia delivered from 2005.
Vz.92 "Križan": VMZ (velkokapacitní mobilní zatarasovač) Engineer vehicle based on the Tatra T815 36.265, lightly armoured cabin. 40-round rocket launcher Krizhna-R, mechanical mine layer for anti-tank mines PT Mi-U or PT Mi-Ba-III, two dispensers for anti-personnel mines PP Mi-S1.
RM-70 Vampire: Digital fire control, Tatra 817 chassis/T3C V8 engine (270 kW) and 10 TS 210 N gearbox, Norgen drive and 2nd gearbox 2.30TRS. 1,000 km (620 mi) range and 90 km/h (56 mph) with armored and NBC-protected cabin.

RM-70 Vampire
Exports
Warsaw Pact era
 Bulgaria: 12 imported in 2009, and re-exported
Bulgaria: 12 imported in 2009, and re-exported Czechoslovakia: c500, later Passed on to the Czech Rep. and Slovakia
Czechoslovakia: c500, later Passed on to the Czech Rep. and Slovakia East Germany: 265 from 1975 to 1989, 158 to Greece, 36 to Finland 1991
East Germany: 265 from 1975 to 1989, 158 to Greece, 36 to Finland 1991 Libya: 36 Delivered between 1981 and 1982 and 100 in 2011, Libyan civil war.
Libya: 36 Delivered between 1981 and 1982 and 100 in 2011, Libyan civil war.
Post-USSR Customers
 Angola: 40 (2023)
Angola: 40 (2023) Azerbaijan: 18 RM-70 Vampir.
Azerbaijan: 18 RM-70 Vampir. Cambodia: 20 RM-70
Cambodia: 20 RM-70 Czech Republic: 60 RM-70 (decommissioned late 2011)
Czech Republic: 60 RM-70 (decommissioned late 2011) Democratic Republic of the Congo
Democratic Republic of the Congo Ecuador: 6.
Ecuador: 6. Finland: 34 RM-70.
Finland: 34 RM-70. Georgia: 18 RM-70
Georgia: 18 RM-70 Greece: 108 RM-70
Greece: 108 RM-70 Indonesia: 9 RM-70 and 8 RM-70 Vampire used by the Marines.
Indonesia: 9 RM-70 and 8 RM-70 Vampire used by the Marines. Nigeria: 7 RM-70
Nigeria: 7 RM-70 North Korea: Unknown number and domestically produced
North Korea: Unknown number and domestically produced Poland: 29 RM-70.
Poland: 29 RM-70. Rwanda: 5
Rwanda: 5 Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, unknown.
Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic, unknown. Slovakia: 4 RM-70, 26 RM-70/85 Modular
Slovakia: 4 RM-70, 26 RM-70/85 Modular Sri Lanka: 22 RM-70
Sri Lanka: 22 RM-70 Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan Uganda: 6
Uganda: 6  Ukraine: 20 RM-70 Vampire, 4 destroyed/damaged March 2024.
Ukraine: 20 RM-70 Vampire, 4 destroyed/damaged March 2024. Zimbabwe: 60 RM-70.
Zimbabwe: 60 RM-70.

RM-70 of the Hellenic Army (ex-East German)

Indonesian RM-70

Same, other livery RM-70
in action

A Czech vehicle firing in exercises
If the Czech RM-70 and East German ones saw no action, the model jad been largely exported post Soviet-collapse and thus, saw plenty of action: Western Sahara War, Russo-Georgian War, Sri Lankan Civil War, First Libyan Civil War, Afghanistan conflict (1978–present), 2013 Kivu Offensive, Yemeni Civil War (2014–present), 2020 Nagorno-Karabakh war, and 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. The latter received 20 of the upgraded Vampire version with long range Serbian rockets. Indeed Ukraine modified its own models to fire G-2000 rockets which had a range of 40.5 km. They were notably used to strike the city of Belgorod. So far according to Oryx, 5 were lost, 2 damaged, the rest destroyed.
Gallery

The original Tatra 813
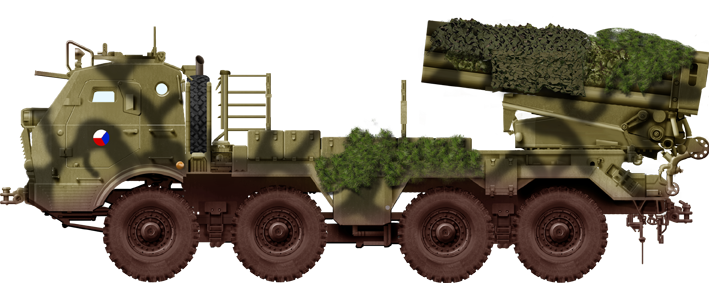
Camouflaged RM-70. This was the exception, not the rule, as olive green was standard.

Slovakian RM-70

RM-70 of the Georgian Army, dozer variant

Sri Lanka RM-70 with spare rockets

Ukrainian RM-70 today
Photos



East German

East German vehicle

RM-70 Vampir

Sources
RM-70 Vampire on armyrecoignitionRM-70 M1972 same source
kotadef.sk
armedconflicts.com RM-70 Vampire
SVK - RM 70/85M (122 mm raketomet)
army-guide.com
czdefence.com
militaryfactory.com
tatradefenceindustrial.com
On weaponsystems.net
On mocr.army.cz
The Vampire on newsweek.com, hammering Belgorod.
oryxspioenkop.com
wikipedia RM-70
wikipedia RM-51
Videos

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
