Origins: The Carden-Loyd Mk.VI tankette
The early Carden-Loyd tankettes from 1933 were the very basis for the Universal Carrier. Originally, these machines were invented by Major Giffard LeQuesne Martel, who developed a prototype privately, for potential requests from the Royal Army Corp. He was a military engineer and a daring tank strategist. After his demonstration to the War Office, the Carden-Loyd Tractors Ltd. company was requested to study practical production. They introduced a slightly enlarged vehicle for two men. Success with the prototype guaranteed their first order, with Vickers-Armstrong's business network as a backup for exports.The last production version was the Mk.VI, of which up to 450 were built in all, from 1927 to 1935. The Mk.VI was the blueprint for the Universal Carrier. A hundred or more of Mk.VI tankettes were sold abroad.
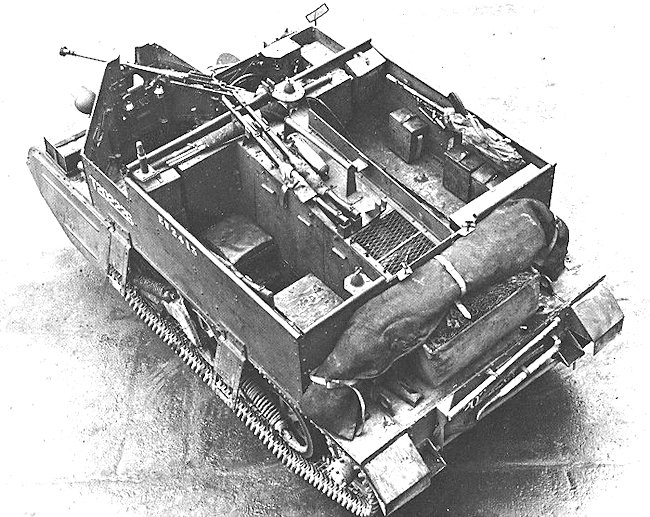
The Universal Carrier was very adaptable and was used for a multitude of different tasks during WW2
Production: The Mk.I of 1934
The Mk.VIs in service with the British army were scouts, transports, machine-gun carriers, artillery carriers, mortar carriers and smoke projector carriers. Later on, experience showed that a single model was preferable to six or more, and a larger one was conceived by Vickers and approved in 1935 for mass production as the "Medium Machine Gun Carrier", "Bren Gun Carrier", "Scout Carrier", and "Cavalry Carrier". Compared to the previous Carden-Loyd Mk.VI tankettes, they were enlarged, with the crew now at the front, driver and machine-gunner, and a large open gallery with a rounded end for all kind of loads. Up to five infantrymen or a gun crew could be deployed quickly.The suspension was a mix of the standard Vickers type and Hortsmann springs. Production was assumed by Aveling and Porter, Bedford Vehicles (British Ford), Morris, the Sentinel Wagon Works, and Thornycroft. But the real production of the definitive standard "Universal Carrier" and first deliveries (Mk.II) came in 1940, just in time for the campaign of France.
Evolution: The Mk.II
The Mk.II tankettes were the production version of the many "Carriers" which were built from 1935 to 1940. This standard version had a square gallery and was versatile enough to accommodate all kind of military payloads easily. They were always equipped with a towing device. The Mk.II was the most heavily produced, from 1940 to 1945, in Great Britain, in the Commonwealth and Canada under various licenses. Their speed and agility, but most of all, tremendous versatility, became legendary, despite their lack of armor and weaponry. Infantry battalions were given 10 to 33 of these from 1940 to 1943 and motorized artillery battalions were entirely equipped with these vehicles, each carrying an ordinance antitank QF 6pdr (2.24 in/57 mm) gun.The American T16
This was an American-built version, derived from those manufactured by Ford-motor Canada. They were sent to Great Britain and the Commonwealth under Lend-Lease. Up to 16,000 units were built with local modifications and improvements, starting in 1943. Many were rearmed with a heavy Browning cal.50 (12.7 mm) machine-guns. Most of them were used by the Canadians as artillery tractors in Europe. After the war, surviving units were sold to Switzerland and the Low Countries.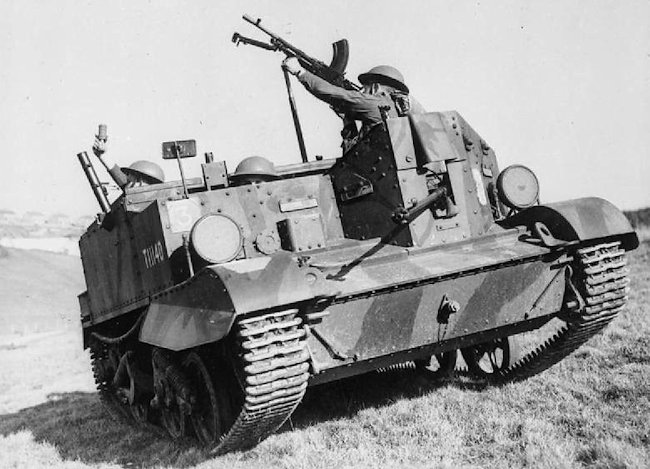
Universal carriers were armed with a number of different weapons including Mortars, Bren Guns and 0.55 inch Boys Anti-tank rifles
Other variants
The main variants were a tank-hunter equipped with a Boys 13.9 mm (0.55 in) rifle, replacing the original Bren gun, which was often relocated to an anti-air mountThere was a heavy machine gun version equipped with the .303 (7.7 mm) Vickers machine-gun, also replacing the forward Bren gun.
There was also a flame-thrower version, where a pipe exhaust replaced the Bren, called the Wasp, and carrying the "Ronson Flamethrower, Transportable, No 2". The Canadian-built ones were named Wasp Mk.IIC. A gun version was developed especially for the Homeguards, armed with a Smith 8pdr mounted in a large sponson at the front.
A prototype of the strange "Praying Mantis" was also built and tested in 1943. This very low-profile vehicle was designed to fire from above walls or hedgerows.
The Commonwealth variants
Australia built, under license, no less than 5600 LP1 and LP2 versions, essentially some slightly modified Mk.I and Mk.II. The LP2 was also produced in limited numbers (520 units) by New Zealand. An antitank version, the Carrier, Tank Attack 2-pdr (40 mm/1.58 in) was produced (200 units), and a mortar-version, with the 3-in (76.2 mm) mortar. The QF 2 pdr (40 mm/1.58 in) was fast and efficient, but its mounting required the displacement of the engine to the front. Most of them were used for training. The 400 mortar versions were sent as military aid to the Nationalist Chinese.In Wehrmacht service
A few of them were captured in Norway, but most of the Mk.Is, later used by the Wehrmacht, were captured at Dunkirk in June 1940. Other various models were captured in Crete and during Rommel's offensives in North Africa. German versions were dubbed "Fahrgestell Bren".There were many derivatives, but most were rearmed with an MG 34 or 42 instead of the Bren gun, in a standardization effort. Some antitank Boys rifle versions, called Fahrgestell Bren 731 (e), saw extensive service in the Afrikakorps, but later received, in Sicily and Italy, more efficient antitank armaments, like the 3.7 cm (1.47 in) Pak (sometimes the hull was covered with spare wooden protections), or Panzerschreck and Panzerfaust (mostly in 1944).
Another version, seen around airfields and gun positions was largely used by the end of 1944, the Fahrgestell Bren 731(e) Flak 38, with a 20 mm (0.79 in) QF anti aircraft mount.
Exports
The versatile and cheap Bren Carrier benefited from such a large production that many Allied countries were equipped with it. Exiled country armies were often equipped with it, like the Belgian, Dutch, Danish, Polish, Czechoslovakian, Norwegian, Greek and the French free forces. They received large amounts of Bren Carriers for various duties.Before the USA provided enough vehicle to make a surplus (1943), the Bren Carrier was seen everywhere, under all flags. This dependable machine had another advantage. Being so light and relatively small, it could be carried like a Jeep in gliders. Many were used by commandos and paratroopers.
After the war
Around 81,700 vehicles were built during the war in all. 31,300 were produced after the armistice. The concept was very successful, in Great Britain, but also in many other countries like the Swiss Confederation, Netherlands (mostly modernized T16s), but also Belgium.Links
The Universal Carrier on Wikipedia
Universal Carrier Mk.II specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 3.65 x 1.92 x 1.57 m (11.98 x 6.3 x 5.15 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 3.75 tons |
| Crew | 2 (Driver, machine-gunner) |
| Propulsion | Ford V8 petrol 85 bhp at 3500 rpm |
| Speed | 30 mph (48 km/h) |
| Range | 150 km at medium speed (93 mi) |
| Armament | 7.92 mm Bren machine-gun (0.31 in) |
| Armor | From 7 to 10 mm (0.28-0.39 in) |
| Total production | 57,000 from 1934 to 1945 |

A camouflaged 1942 Mk.I "Bren Carrier", here with an added anti-aerial Bren on the specially modified mount. Click for the high definition illustration.

A Universal Carrier Mk.II heavily modified for desert combat with the VIIIth army, El Alamein, June 1942. This version was capable of towing artillery like the ordinance QF 6pdr (2.24 in/57 mm). However, this vehicle was equipped with a long range radio for scouting, an anti-air Bren gun and, instead of the regular forward mount, a 13.9 mm (0.55 in) Boys anti-tank rifle. This added some anti-armor capacity, mostly against early Panzer II and III tanks and all Italian models, especially at short range, or from the rear.

An Australian LP1 Carrier in North Africa, 1942. Some of the LP1s and LP2s were used in North Africa, were their speed, sturdiness and adaptability were true assets in the desert. Others were affected to ANZAC battalions fighting from New Guinea to the Solomons.
 An Australian-built LP2 Carrier converted as a "Vickers Carrier", with a heavy Vickers cal.303 (7.62 mm) machine gun instead of the usual Bren. The Vickers machine-gun was relatively outdated but could still sustain long, punishing fire as well as endure harsh conditions, even in North Africa. The secondary Bren is mounted on a telescopic arm, here retracted.
An Australian-built LP2 Carrier converted as a "Vickers Carrier", with a heavy Vickers cal.303 (7.62 mm) machine gun instead of the usual Bren. The Vickers machine-gun was relatively outdated but could still sustain long, punishing fire as well as endure harsh conditions, even in North Africa. The secondary Bren is mounted on a telescopic arm, here retracted.

Canadian Wasp Mk.IIC. The British version of this well-produced (1000 units) flame-thrower variant, the Mk.I, was different. The Bren emplacement was replaced by the orientable projector, relatively similar to the portable infantry model, fed by two 50 gallons fuel containers at the rear, inside the protective hull. The Canadian version was called Mk.IIC, and the 75 gallons container was external, allowing an extra crew member to be carried. These models were widely used during from 1943 to 1945.

A German captured Carrier Mk.I (Fahrgestell Bren), here converted into a "Panzerjäger", or tank hunter. In fact, this was a far more convincing conversion than the usual Bren 731 (e) equipped with the original Boys rifle. In this configuration, there were three Panzerschrecks (Raketen Panzerbüchse 43) arranged on a centerline triple mount, with many spare rockets, and also six Panzerfausts. Italy, summer 1944.
Gallery
A Bren Mk.II mortar carrier at Bovington, where most of the Brens in the world are displayed - Credits: Wikipedia.

An Australian Mk.I derived 3-in (76.2 mm) Mortar Carrier. The rounded backside of the Mk.I is clearly visible - Credits: Wikipedia.
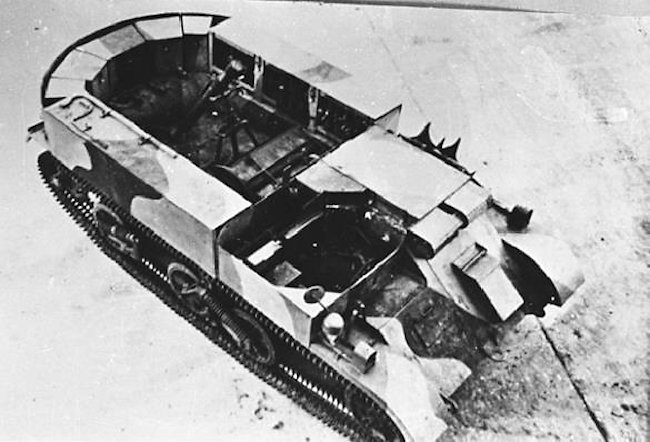
Australian Mk.I derived 3-in (76.2 mm) Mortar Carrier
The Rocket-powered Bren Gun Carrier trials
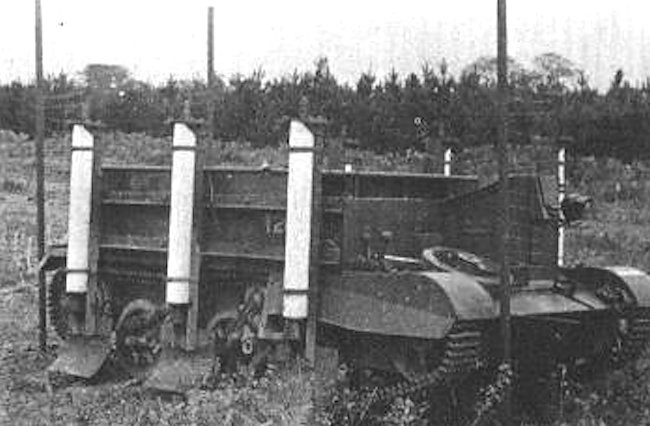

The Rocket powered gap leaping Bren Gun Carrier had three rockets attached to each side of the vehicle
A rocket powered gap leaping Bren Gun carrier prototype was also built. It was designed to cross minefields and other obstacles by firing its rockets. It got cancelled after it kept landing upside down during trials. Because of this SADE experiment and the fact that a jet engine was fitted to the back of a Valentine tank, the Valentine Gap Jumping Tank myth evolved. The Valentine SADE rocket experiment was, in fact, a mine-clearing experiment using the blast from a jet engine to detonate anti-tank and anti-personnel mines.

The rocket-powered Bren Gun Carrier trials did not end well Another SADE trial involved four rockets, two strapped together each side of a Universal Carrier. They could be set at an angle. The idea was that they would be used to help extract a vehicle that had become ditched, stuck in the mud or waterlogged ground. It was not successful.

Rocket equipped Universal Carrier experimental vehicle

British Tanks of WW2 Poster (Support Tank Encyclopedia)

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

