About Renault armored cars in WW1
Back in 1905, Renault was already a pioneer in the rapidly-growing automotive industry. Long situated at Boulogne-Billancourt, in a suburb of Paris, the company founded by Louis Renault already tested the military waters in 1909, with a Hotchkiss shield-protected machine-gun carrying vehicle. It attracted limited interest from the military, perhaps inspired by the 1908 Charron. However, shortly after the start of the war, along with Hotchkiss, Schneider, De Dion Bouton, Panhard Levassor, Gasnier, Archer and Latil and Peugeot, Renault presented in 1914 its own model, intended for AA purposes. It was followed the next year by a completely rebuilt model similar to the Peugeot, along with the conversion of the former mle 1914. Also, Renault produced a lorry armed with a 47 mm (1.85 in) "autocanon Renault" for the motorized marine infantry.Renault Autoblindée 1914
This first model was accepted and fifty units were built until early 1915, as 4x2 AA vehicles with an open air rear compartment, armed with a single 8 mm (0.31 in) St Etienne light machine gun. It was relatively lightly armored, with vertical plates between 4 and 6 mm (0.16-0.24 in) in thickness. These enclosed the closed driving compartment (with a single wide armored shutter), while the rear compartment was open, large enough for two operators (loader and gunner). Access for all crewmen provided through this open compartment. The machine gun was protected by a large frontal shield, with a mounting providing full vertical manual elevation (90°) and traverse. It had ammunition supplied in 8 mm/24 cartridge strips. This model had a ground clearance of 24 cm (9.5 in), 3.35 m wheelbase (132 in), with a 4x2 front steering with manual transmission, and a Renault water cooled petrol engine. The axles rested on leaf spring suspensions.Wartime use
Although a hundred were originally ordered, only 50 were built before their limitations were discovered. The AA mount was problematic, and the rate of fire and range were not sufficient for their intended rôle. Also, the armor was too light to protect against shrapnel and machine-gun rounds, while the open compartment left the crew vulnerable. But, probably worst of all, the front wheel drive proved ill-suited in operations. In 1916, all 50 were taken over to be rebuilt to the mle 1915 standard, which resembled the Peugeot armored car, with a short barrel 37 mm (1.46 in) gun or Hotchkiss LMG behind a shield.Links about the Renault Mle 1914
David Haugh's French ACs (pdf)Early WWI armored cars (in French) Centennial WW1 POSTER

Renault AC 1914 specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 4.5 x 1.7 x 1.7 m (180 x 66 x 66 in) |
| Total weight | 3 tons, estimated |
| Crew | 3-4 (driver, commander, gunner/loader) |
| Propulsion | 4-cyl Renault WC, gasoline, 35 bhp (26 kW) |
| Top speed (road) | 45 km/h (28 mph) |
| Range | Around 100 km (62 mi) |
| Armament | St Etienne M1907 machine gun |
| Armor | 4 to 6 mm (0.16 to 0.22 in) |
| Total production | 50 in 1914 |
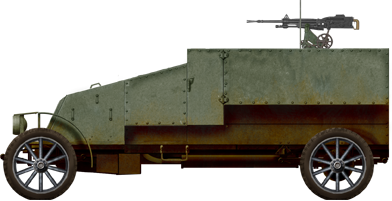
Renault automitrailleuse modèle 1914.
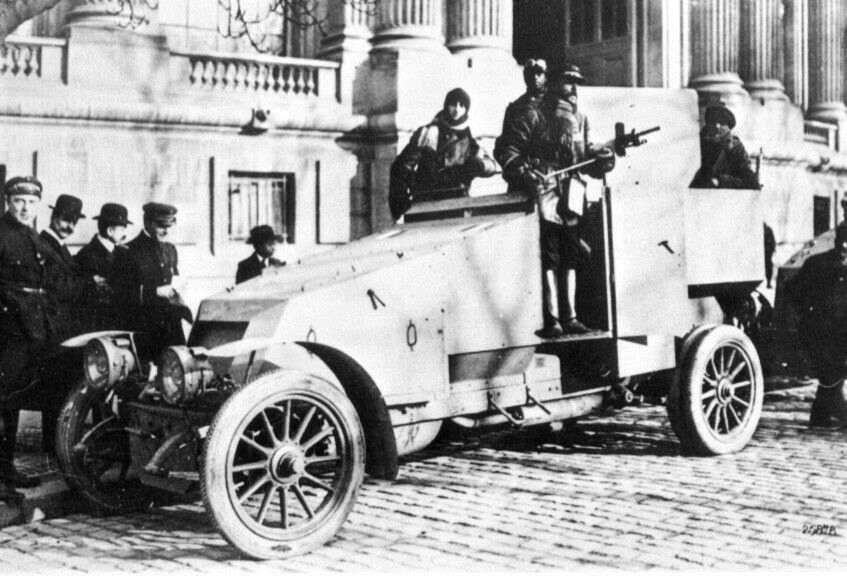

Renault mle 1914 - Credits: blindes-français.net

Renault Armored Car modèle 1915. The mle 1914s were rebuilt to this standard

The Great War
 Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary Belgium
Belgium British Empire
British Empire France
France German Empire
German Empire Italy
Italy Russia
Russia USA
USAWW1 tanks posters