Origins
The TK3 and TKS tankettes were the bulk of the Polish armored forces when war broke in September 1939. They were lightweight fast scout tanks. They were developed after a military delegation was invited at Rembertow (near Warsaw) to see the latest Vickers-Armstrong Carden-Loyd Mk. IV in action. They immediately bought the license to produce them locally, but with domestic modifications. The Polish design incorporated newer, more flexible suspension, as the original one's stiffness was very tiresome for the crewmembers. Development went along from 1929 to 1930 and ultimately the first true Polish tankette, the TK1 prototype, was delivered and widely tested, followed closely by the TK2. Both had an open roof and a single 7.92 mm (0.3 in) Hotchkiss wz. 25 or wz. 30 machine gun. They differed by the engine exhaust, location of the drive train and engine (a Ford Type A or Type T). Armor was slightly sloped and ranged from 4 to 7 mm (0.16-0.28 in), sufficient to stop or deflect 7.9 to 9 mm (0.3-0.35 in) caliber bullets. They were also slightly heavier and slower than the original Carden-Loyd tankette.
TKS Tankette
The TK3
By mid-1930, both TK prototypes successfully passed all tests at Modlin and the final, slightly simplified version was put into production at the Ursus company, near Warsaw. Production model TK3 passed all tests in June, 1931 and was officially commissioned. 300 of these machines were built by Panstwowe Zaklady Inzynierii (Ursus) until 1934. The engine was a Ford model A built under licence, the roof was closed and the frontal armor was up to 8 mm (0.31 in) thick. They were deployed in mechanized cavalry companies, able to tow 75 mm (2.95 in) guns, ammunition carriages and various trailers to carry various payloads, including soldiers. Transport to the frontline was to be made by rail and using a custom-devised Ursus "autotransport" chassis, which was fitted under the tank and propelled by its own motor via an external transmission. A few of these were built.

The TKS
From 1931 to 1933 various attempts were made to replace the light 7.92 mm (0.3 in) wz. 25 machine gun with French Hotchkiss 13.2 mm (0.52 in) or even 20 mm (0.79 in) long-barrel antitank guns. In 1938, a single TK3 prototype was equipped with Polish wz. 38 20 mm (0.79 in) high velocity antitank gun. In June 1933, a heavier TK3, with stronger, thicker, cast steel armor was successfully tested and accepted. Production started in March 1934. It was not only better protected, but also incorporated many minor improvements as well, being a faithful upgrade after three years of training and real-condition exercises. In all, 390 of these improved tankettes were built, until September 1939. Only 20 units were converted as anti-tank units, equipped with the wz. 38 cannon. The final prototype was ready in January 1939. The gun was capable of penetrating 40 mm (1.57 in) at 200 meters (660 ft).Other variants
Many variants were studied until 1939, some testing a single-man rotating turret (TKW) with various armaments, including a 20 mm (0.79 in) gun. The prototype was ready in 1933 and six were ultimately built, but the entire project was cancelled in favor of the 7TP. The 1932 TKD was a specially designed 47 mm (1.85 in) self propelled gun of which only four were built, also with variants using the Puteaux 37 mm (1.46 in) and the Vickers 47 mm (1.85 in) guns. The 1934 TKF was equipped with a new, more powerful Polksi Fiat 122AB Motor and possessed an extra 9 mm (0.35 in) anti-aircraft machine gun. 22 were built but the TKS series was favored instead. In 1937, two TKS-D were built as self-propelled guns armed with the high velocity wz. 36 Bofors 40 mm (1.57 in) anti-tank gun. None of these projects entered production until the war broke out. The original design was just too cramped for other up-gunning attempts.

TKS
The TK in action
With a total of 690 tanks, the TK family made up the bulk of the Polish armored forces. Although the TK3 was seen as obsolete, it was nevertheless thrown in action against both German and Soviet forces. Their German opponents were the Panzer II, many machine-gun armed Panzer Is, a handful of Panzer IIIs and many ex-Czech Pz. 35(t) and Pz. 38(t), which all dominated the small Polish tankette. They also faced the Soviet T-26, T-28 and the BT family. Most of them were attached to infantry units and cavalry brigades and some Polish tankettes were deployed in independent companies of 13 machines. They fought bravely but hopelessly, achieving some success, most of it attributed to the 20 mm (0.79 in) armed TKS antitank brigade. Some of the captured tankettes were later used locally by the Germans for training purposes, as armored transports or to deal with Polish insurgents.Specs |
TK3 |
TKS |
| Dimensions | 2.58 x 1.78 x 1.32 m (8.46x5.84x4.33 ft) | 2.58 x 1.78 x 1.32 m (8.46x5.84x4.33 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 2.43 tons | 2.57 to 2.65 tons |
| Crew | 2 | 2 |
| Propulsion | Ford Model A, 4-cyl, 40 hp |
Polksi Fiat 122AC/B 6 cyl, 42/46 hp |
| Speed | 46 km/h (29 mph) | 40 km/h (25 mph) |
| Range (road/off road)/consumption | 200-100 km (124-62 mi) -60 l/100 km | 60-190 km (37-118 mi) -70 l/100 km |
| Armament | Hotchkiss wz. 25 7.92 mm (0.3 in) machine-gun | Hotchkiss wz. 30 7.92 mm (0.3 in) machine-gun Variant 20 mm (0.79 in) wz. 44 |
| Armor | From 4 to 6 mm (0.16-0.24 in) | From 3 to 10 mm (0.12-0.39 in) |
| Ammunition | 1800 rounds | 2400 rounds |
| Total production | 300 | 390 |

TKS tankettes and Wz.34 armoured cars in the background
Links
derela.republika on the TK tankette developmentA project about reconstructing Polish TK3-TKS tankettes

A TK3 from a cavalry division, 1934 maneuvers. Note the operational markings and the early "Japanese style" camouflage.

A cavalry division TK3, Kielce, September 1939.
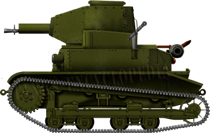
The TKW preseries conversion, sometimes called TKW-1 because of their late reconversion into antitank version. The regular machine-gun of this turret version was the Vickers, replaced later by wz.25 or wz.30 machine-guns.

The TKW 2 was a late conversion of the TK3 into an antitank version. The combination of a turret and this weapon were far more efficient than the fixed guns of the regular TKS converted in the same fashion.

The TKD was a lightweight, unprotected, self propelled gun conversion of the TK3, using the light 47 mm (1.85 in) SP Pocisk infantry gun or "bullet gun", center-mounted, with its own shield. They served at Modlin for trials and from 1938 in the 10th Motorized Cavalry Brigade. They took part in the seizure of the Czech Zaolzie province and were lost near Warsaw in September 1939.

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

