Cold War and Modern Canadian Tanks & AFVs
 Circa 2,500 armored vehicles 1947-
Circa 2,500 armored vehicles 1947-
History and Origins in World War 2
 Canadian armored history began at the outbreak of World War 2, with the rapid expansion of the army brought about by the mobilization of manpower and industrial might. The Permanent Active Militia was beefed-up and reorganized as a standing army. By the end of the war, the Canadian industry had produced thousands of Ram and Valentine tanks, Sexton self propelled guns, three types of armored cars and almost one million of the famous "Canadian Military Pattern" (CMP) trucks from Ford, GM Canada and Montréal Locomotive Works factories. After the ill-fated raid on Dieppe in 1942, Canadian tanks continued to serve from Sicily to Italy, France, the Low Countries and Germany. With this experience, the Canadian armored forces entered the Cold War.
Canadian armored history began at the outbreak of World War 2, with the rapid expansion of the army brought about by the mobilization of manpower and industrial might. The Permanent Active Militia was beefed-up and reorganized as a standing army. By the end of the war, the Canadian industry had produced thousands of Ram and Valentine tanks, Sexton self propelled guns, three types of armored cars and almost one million of the famous "Canadian Military Pattern" (CMP) trucks from Ford, GM Canada and Montréal Locomotive Works factories. After the ill-fated raid on Dieppe in 1942, Canadian tanks continued to serve from Sicily to Italy, France, the Low Countries and Germany. With this experience, the Canadian armored forces entered the Cold War.
Find more about Canadian armor at our partner museum, the Ontario Regiment Museum!

Articles done and to come
M4A HVSSM4A3 easy 8 HVSS
AVGP Cougar
AVGP Grizzly
AVGP Husky
M113 CV Lynx
2A4M CAN MBT
Coyote IFV (1990)
Bison APC (1990)
LAV UP APC
LAV ACSV Super Bison
TAPV
Arva Industries MPEV
Felix Tech. CTL
Canadian armor in the Korean War
The first Cold War test of the Canadian army came with the Korean War. In 1950, a Canadian contingent was sent under the UN banner to defend South Korea against the Northern aggression. At that time, the Canadian Army relied on existing WW2 stocks and its only modern tanks were acquired in 1946 from US WW2 surplus stocks in the form of the Sherman M4A2 (76)W HVSS. In 1952, the Canadian government purchased additional Sherman M4A3 (76)W HVSS tanks, which were immediately shipped overseas for use in the war. The government also began purchasing Centurion Mk.3 and Mk.5 tanks, and after the ceasefire, Centurion Mk.11s to replace the Shermans.Centurion

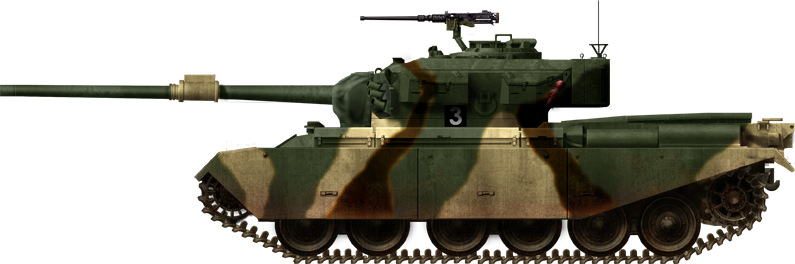 Until the early 1970s, the Centurion tanks formed the bulk of the Canadian tank force. On top is a Mark V-1 of the 8th Canadian Hussars (Princess Louise's) in Exercise Holdfast, Northern Germany, September 1960. Below, a Mark V-2 of Lord Strathcona's Horses (Royal Canadians) in Soltau, West Germany, September 1966. Some Mark 11 were also purchased. By 1979 all of the Centurions were sold to Israel, where they were modified, modernized (Sho't Kal) and kept in service until the early 1990s.
Until the early 1970s, the Centurion tanks formed the bulk of the Canadian tank force. On top is a Mark V-1 of the 8th Canadian Hussars (Princess Louise's) in Exercise Holdfast, Northern Germany, September 1960. Below, a Mark V-2 of Lord Strathcona's Horses (Royal Canadians) in Soltau, West Germany, September 1966. Some Mark 11 were also purchased. By 1979 all of the Centurions were sold to Israel, where they were modified, modernized (Sho't Kal) and kept in service until the early 1990s.
Leopard C1

Canada acquired the German Leopard main battle tank in 1978. 127 were bought in total, 114 of which were "Canadianized" with specific local requirements, based on the Leopard 1A3 standard.
AVGP Cougar (1976)

The Cougar was armed with the Scorpion light tank's turret. It was based on the Piranha II 6x6 and was a pure reconnaissance vehicle.
AVGP Grizzly (1976)

The Grizzly was similar to the Cougar, but with a Cadillac-Gage 1 meter turret. Used for reconnaissance and as an APC.
AVGP Husky (1976)
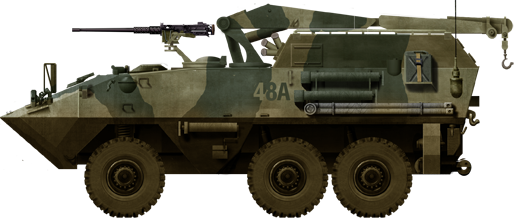
ARV version of the AVGP programme.
M113

Lynx

A reconnaissance vehicle designed in the US based on the M113 chassis.

CANADIAN ARMOR (1990-today)
Models
Post cold war reorganization
Being on the northern parallel on the route of many possible Soviet incursions from the Pacific as well as the Arctic, the Canadian Forces were quite an important defense sector for NATO, albeit far less than Germany, the most in-demand arm was the RCN or Royal Canadian Navy, because of Soviet submarines well-known incursion routes going southwards to spy or patrol off the American west coast.After the unification with the navy and air force in 1968 and a seemingly the reduced size but rationalization, Canada emerged from the cold war ready for new challenges with a variety of equipment, between the German-built Leopard and Swiss-built Piranha. Troops deployed in numerous NATO exercises, and cooperation with the British army, often training in the large expenses of Banff park with armour allowed day or week-long realistic exercises (BATUS) over 2700 km2, allowing battalion-size deployments over fictitious objectives. The most notable post-war action of the Canadian armor was of course the Gulf War in 1991 and the invasion of Afghanistan in 2001. Following these, Canadian tanks and AFVs took part in many peacekeeping operations worldwide.

Canadian intervention in Afghanistan, M113 with add-on BAR armor.
Current organization
Commander of the Canadian Army operates within the National Defence Headquarters located in Ottawa. Four divisions exists, based on geography.During the cold war, these forces's likely scenarios were to counter an amphibious landing by Soviet forces in order to destroy strategic radar and command bases, and less likely, attempt a diversion invasion action. These divisions were the:
- 2nd Canadian Division in Quebec
- 3rd Canadian Division in Western Canada
- 4th Canadian Division in Ontario
- 5th Canadian Division on the Atlantic sector

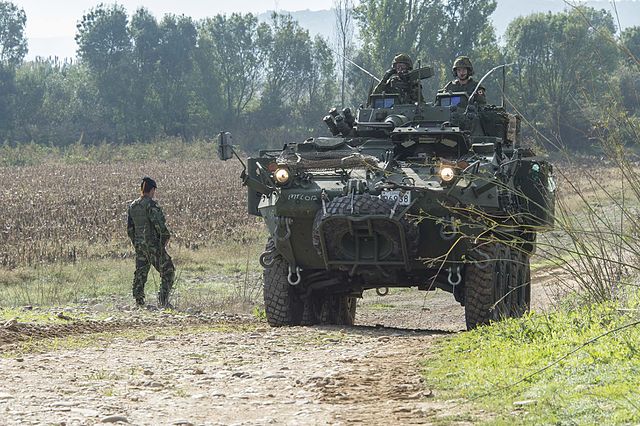
Canadian troops patrolling at Kandahar, with a LAV-3 in the background.
The Canadian Army Doctrine and Training Centre (ex-Land Force Doctrine and Training System) is headed by a major-general, based at McNaughton Barracks, CFB Kingston in Ontario. It is responsible for the definition and application of all Army training and doctrine development and includes the Combat Training Centre at CFB Gagetown, New Brunswick, and Canadian Manoeuvre Training Centre at CFB Wainwright, Alberta which is considered here for the armour component of the Canadian army.

The Canadian-modified Leopard 1A4-1e/A7 is one of these 1960s generation replaced by the 2A4M/2A6M (60 in service).
A new title for the head of staff
After the wall fell and change of regime in Russia, it was time for a reorganization and less defense spending. The senior appointment within the Canadian Army was Chief of the General Staff, which became in 1964 the Commander, Mobile Command with the gradual unification of Canada's military forces. After the cold war this title became the Chief of the Land Staff (1993). The Land Forces were versed into the Canadian Army which became in 2011 Commander of the Canadian Army.Officers recruitment sources
The Regular Officer Training Plan was the regular way, where candidates went through the Royal Military College of Canada (RMC) of from civilian Canadian universities.The continued Education Officer Training Plan, addresses the lack a degree for officers that already serves serving in the Army. There is also an University Training Plan for non-Commissioned Members and commissioning From the Ranks Plan, for officers with military experience and qualities to promote them. The Special Requirements Commissioning Plan, allows to profit from the skills and experience of senior non-commissioned members for possible Chief Warrant Officers.
Subsidized special education can include Medical Officer Training Plan or Dental Officer Training Plan also exists. Other ways includes the Officer Candidate Training Plan for commissioning serving members are now discarded.
Combat Training Centre are set up for various sub-arms like armour, artillery, infantry, electrical and mechanical engineers. They exist in parralel and support to the Canadian Armed Forces schools such as the Canadian Forces School of Administration and Logistics or Defence Public Affairs Learning Centre for officers which career skills were formed outside the army.
Find more about Canadian armour

The Canadian Armoured Forces in detail
placeholder.Soldiers and vehicles of the 12th Régiment blindé du Canada armoured reconnaissance regiment training. Based in Valcartier they are part of the 2nd division based in Québec. The 2nd division also comprises the 5 Canadian Mechanized Brigade Group, the 34 and 35 Canadian Brigade Groups (with some armour components such as this 12th regiment, or the Royal Canadian Hussars of Montreal and Sherbrooke Hussars or the Canadian Ranger Patrol Group of Richelain.
Modern Canadian Armour
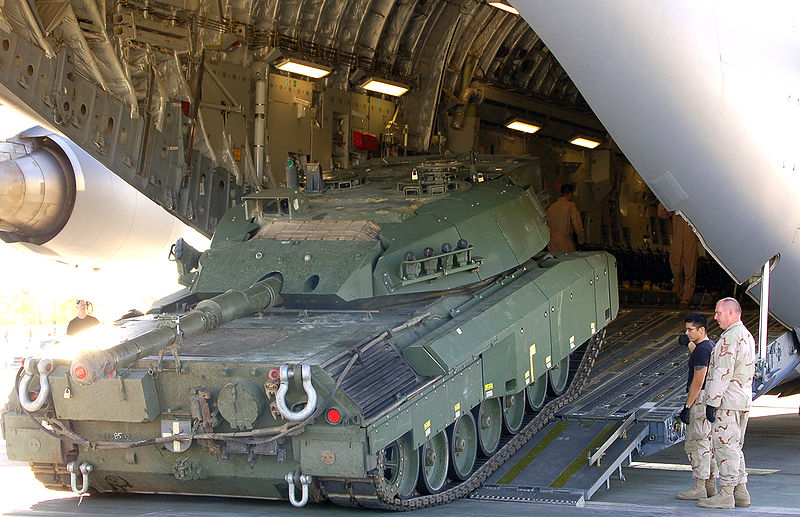
Leopard 2A6M CAN
 Entered service in 2007, 20 loaned by Germany followed by 80 purchased from the Netherlands. Here, a modified model for urban combat deployed in Afghanistan from 2008 to 2013.
Entered service in 2007, 20 loaned by Germany followed by 80 purchased from the Netherlands. Here, a modified model for urban combat deployed in Afghanistan from 2008 to 2013.Leopard C2
 Entered service in 2000. The were C1 upgraded and refitted with Leopard 1A5 turrets. 66 still in active service.
Entered service in 2000. The were C1 upgraded and refitted with Leopard 1A5 turrets. 66 still in active service.Bison APC

Coyote ARV
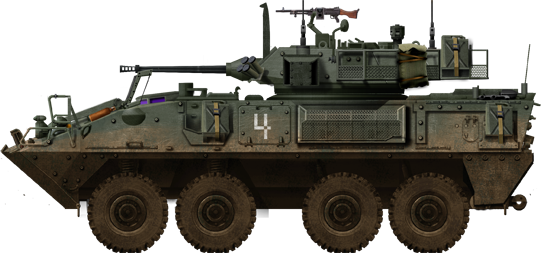
LAV-III

Textron TAPV

Text in redaction
Trucks and softskin vehicles
1,300 MSVS MilCOTS; 1,587 MSVS SMP; 6 AHSVS; 59 Western Star 4900 series.Others: M-Gator (48), MRZR-D (36), DAGOR (62), HMMWV (?), ASUV (27), LUVW MilCOTS (1,061- replaced the Bombardier Iltis), LUVW SMP (1,159), Bv206 (14)
Canadian built: LSVW (1333), HLVW (591).
Links & Sources
The Canadian Army on Wikipedia List of modern Canadian equipment (including AFVs) The full list of Canadian armament, including WW2 and Cold War AFVs

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
