Indian Tanks & AFVs today

The inheritance of the cold war
The Creation of the modern Indian Army is linked to the independence in 1947 which placed the newly formed federal state of India in an antagonistic relation with neighbouring Pakistan right away. This came after the difficult separation and tensions between muslims and Hindus. This will also translate into a serie of wars foughts since the 1940s to 1999, and the specter of a full-blown war today is not far away.As we speak, border incidents are a daily occurence around Kargyl and over the disputed region of Kashmir. Added to this a vivid, renewed tension on the northern border with China, and it's not for tomosrow India, a nuclear power since the 1980s with a spatial program, will make any defense budget cuts.
Past conflicts built this army and forged its modern doctrine, especially tailored against Pakistan: The dispute in Kashmir in 1947 and invasion of Hyderabad in 1948, the Portuguese-Indian War of 1961, the Sino-Indian war of 1962, the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, the Indo-Chinese conflict of 1967, the Naxalites uprising of 1971, the Indo-Pakistani War of 1971 (liberation of Bangladesh), and the Siachen conflict in 1984. This was a fertile ground for building and cultivate tank warfare and armoured warfare as a whole.
Main Battle Tanks
T-90 Bhishma
Arjun MBT Mk1 & Mk1A
APC/IFV (tracked)
BMP-2 Sarath
Tarmour AFV
Abhay IFV
DRDO CMTV
DRDO NBCRV
DRDO AERV
DRDO Namica
DRDO Akash
DRDO ambutank
DRDO Trishul
DRDO Rajentra
DRDO UGV Muntra
DRDO 105mm SPG K9 Vajra-T
APC/IFV (wheeled)
TATA Kestrel
Mahindra ALSV
Mahindra Straton Plus
Tata Motors LAMV
Mahindra Marksman
Kalyani Group M4
Wheeled utility, softskin
Force Gurkha 4x4 (Truck Encyclopedia)
Pinaka MBRL (Truck Encyclopedia)
Auxiliaries
T-72 BLT T-72 FWMP AERV
WZT-3M
VT-72B ARV
Arjun ARRV
Aditya MPV
Hydrema MCV

Indian Tankers had their own mystique, gained among other at the Battle of Asal Uttar (8-10 September 1965), where they destroyed more than 100 tanks, now "Patton Nagar".
Organization as of today
Recruitment is voluntary but there was at least on paper a military conscription, written in the Indian constitution. In 2010 the army is professional and 1,129,900 strong for the active personal and 960,000 reserve. Among these, 160,000 are in the Indian Territorial Army. The Indian Army is still today the world's largest standing volunteer army. Some regiments proceed from a long tradition and maintains local specificities in traditions and uniforms like the Assam Regiment, Jat Regiment, Sikh Regiments or the Raj, Ladakh, Arunachal and Sikkim Scouts. Outside thiese there are alo "national" components, like the free Indian regiments, Guards brigade and Parachute Regiment.Actual Combat doctrine combine defensive formations and attack formations. The former is tasked to stop and pin down the enemy, the second to counterattack at a precise point. Therefore, some units in the Indian Army had specialized corps affected either to the strike or defensive role. This is reflected both in their training and equipment. To this, the post-cold war era saw the creation of the Indian Special forces, which is closely modelled after its foreign counterparts in methods, training and equipment. So far, there is no Indian Marine Corps, but a marine brigade, is on its way according to newly developed amphibious capabilities. The construction of LHDs in India is also on the menu, at least to stay on par to the chinese efforts in that direction.
There are currently 63 armoured regiments in the Indian Army. The 1st Horse, 2nd Lancers, 3rd Cavalry, 4th Horse, 7th Light Cavalry, 8th Light Cavalry, 9th (Deccan) Horse, 14th (Scinde) Horse, 17th (Poona) Horse, 15th Lancers, 16th Light Cavalry, 18th Cavalry, 20th Lancers, and the 21st (Central India) Horse based on XIXth century units, with extra ones created since Independence. Their equipment, duties and training also reflect the traditions of the cavalry type, like in the British Army. There are currently eight army corps, the New Delhi HQ, Central command at Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, Eastern command at Kolkata, West Bengal, Northern command at Udhampur, Jammu and Kashmir, South Western Command at Jaipur, Rajhastan, Western command at Chandimandir, Haryana, and the Training command Shimla, Himachal Pradesh.
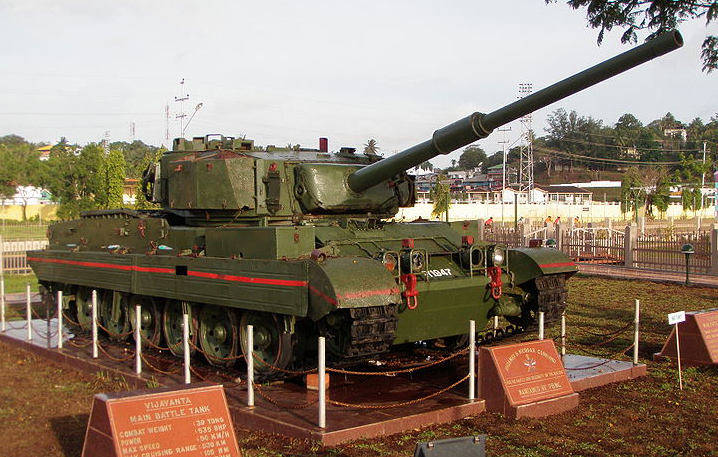

The Vijayanta, Indian first MBT, designed in the 1960s as a lighter Centurion in cooperation with Vickers (still referred as the Vickers mark 2).
Tanks and Armoured vehicles
About 2,200 armored vehicles were built by the Heavy Vehicles Factory until 1986. They were gradually upgraded, but now placed are placed into the reserve. Shortly after, the development of a new MBT started, known today as the Arjun. This development took thirty years, from 1974 until the first production tanks were out, in 2004. 250+ are now in first line service, but only counts for a small portion of the bulk of the Armoured forces equipped after a change of policy with soviet origin tanks. In reserve, there is a park of old soiet vehicles acquired in the 1960-1980s: Some 800 T-55s, PT-76, BTR-50, BTR-152, BTR-60 are likely in partial reserve. More active are a number of BTR-80 APCs, as well as BMD-1s, or specialized variants like the PRP-3. Wheeled vehicles such as the Czech OT-64 SKOT, Polish OT-62 TOPAS, and BRDM-2 are also likely to be place in reserve. All are planned for a replacement by a locally-developed 8x8 universal APC/IFV.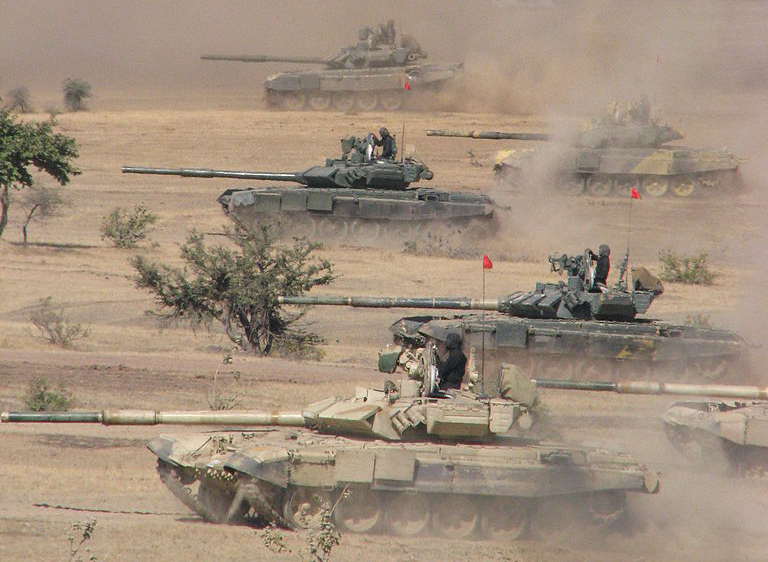 T-90S Bhishma in exercises. These forms the bulk of Indian division today and more are in service today under Indian colours than in Russia ! These are on par with the best 3rd generation MBTs today.
T-90S Bhishma in exercises. These forms the bulk of Indian division today and more are in service today under Indian colours than in Russia ! These are on par with the best 3rd generation MBTs today.
Indian AFVs as of 2020
Tanks
The bulk of the Indian MBT force today is provided by the 2,400+ T-72M1 "Ajeya" co-produced with Poland and Russia together with 1,250 T-90S "Bhishma" with Russia. The Arjun only counts for a few in this total due to a much higher price tag and are given to elite divisions. The Vijayanta are now long retired but for training and as variants.- T-90S Bhishma
- T-72M Ajeya
- Arjun
APCs and IFVs
Modern Indian IFV supplies came from co-produced BMP-1 and BMP-2 "Sarath" IFVs (1200+). In addition 900 Tarmour heavy tracked APCs (local construction, based on T-55 chassis) are still in service. Also 100+ (out of 200) BTR-50 are maintained in service. Specialized missile tank destroyers, the Namica, are built on the Sarath chassis (2013). 13 were produced out of 200+ by Ordnance Factory Medak and L&T. There is no mass-production APC in service which is a lack of mobility for the infantry divisions. The Sarath (BMP-2) has been also derived into the CMT mortar carrier version (200 on order), as well as the DRDO Armoured Ambulance, and the NBC Reconnaissance Vehicle (CRBN). Also related are a few PRP-3, or NATO BMP M1975 Battlefield surveillance systems; An undisclosed numbers of former APCs OT-62 TOPAS and OT-64 SKOT are now used as Technical support vehicles.- BMP-2 Sarath
- Tarmour APC
- Namica TD
SPGs (ported artillery)
Ported artillery is provided by 80 VAE-versions of the FV433 Abbot SPGs, 100 M-46 Catapult (based on the Vijayanta), 110 2S1 Gvozdika, 62 Smerch 9K58 MRL, 80 Indian-built Pinaka MBRL, and 150 BM-21 MRLs (rocket launchers).ATGMs

Various vehicles can be equipped or carry a large array of Indian ATGMs of various provenance: Spike (Israel), Milan/2T (France, and built under licence), Russian 9M133 Kornet, 9M113 Konkurs (licence), 9K114 Shturm, 9M120 Ataka-V, 9M119 Svir, 3UBK-Invar, and 9K121 Vikhr. Two models are Indian-built, the Nag missile used on the Namica TD (see above), and the 125 mm CLGM Missile (gun launched) for the T-90 and T-72.
SPAAGs/SPAAMLs
Outside SAM missile carriers like the 80 9K33 Osa 6x6, there are 250 SA-13 Gopher (9K35 Strela-10) in service, and SPAAGs in service are the 180 2K22 Tunguska (SA-19 Grison) and 75 ZSU-23-4M Shilka,and infantry can be equipped with 4 types of Manpads, including Stingers, SA-14, 16 and 18.Specialized vehicles
AVLBs: 34 Kartik ABL, based on the Vijayanta chassis, MT-55 (unknown) based on the T55 chassis, T-72 BLT (12), 8x8 Sarvatra VLB (unknown), and 6 CEASE or Canal Embankment Assault Equipment.ARV, CEVs: BMP-2 based AERV (unknown), 7362 BMP-2 Dozer, 39 FV180 Combat Engineer Tractors (UK import), 196 WZT-2, 352 WZT-3M and 200+ VT-72B ARV Polish/Indian ARVs, and an indisclosed numbers of Armoured Vehicle Tracked Light Repair BMP-2 based vehicles, and light ARVs as the VFJ, Yuktirath, CL-70.
MPVs and MRAPs: India also operated 255 South African Casspirs, alongside 1300+6 Aditya MPVs and 24 Hydrema mine clearing vehicles. For mine warfare, there are many T-72 FWMP kits made readily available for mine-clearing operations, as well as a robot, the DRDO Daksh for bomb disposal.
Attack helicopters

Like most ground forces in the world, the Indian Army Aviation Corps is limited to rotary-wing aircrafts, the recent attack helicopters HAL Rudra (2012) with 22 built and 150+ on order and most importantly the HAL LCH or Light Combat Helicopter, a pure, two-seats attack helicopter (2010) of which 140 are on order. This is a perfect "tank killer" with advanced detection and FCS servicing a Nexter THL 20 cannon, AP/HE rockets and ATGMs.
R&D, future developments
Future developments includes the Arjun MBT Mk.2 (Production in 2014), FMBT – The FMBT concept (50 tons), the DRDO FICV (Future Infantry Combat Vehicle program) to replace BMP-2s IFV and projects for a new MBT with an active protection system to defeat Fin Stabilized Armor Piercing Discarding Sabot (FSAPDS).Indian AFVs in action
Kargil war (1999)
Like the Siachen glacier skirmish in 1984, again upon bordering regions of Jammu and Kashmir with Pakistan, the Kargil war saw limited use of armoured vehicles due to the nature of the terrain. Artillery and aviation reigned supreme. However armoured vehicles were sent to Sri Lanka in 1987 for peace-keeping operations and actually were heavily engaged.Links
The Indian army on Wikipedia Equipment of the Indian army (Wikipedia) Official website indianarmy.nic.in Video: The three Indian MBTs today -part 1 Video: The three Indian MBTs today -part 2 Video: Documentary about the Arjun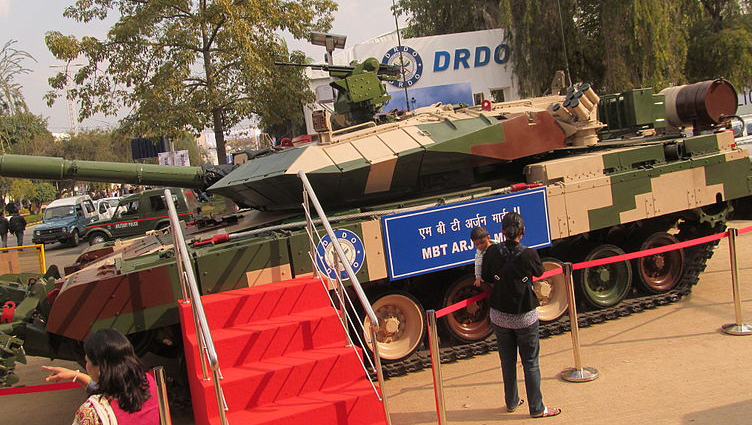
The Arjun mark 2, here in exhibition, is the latest version of the 3rd generation Indian MBT.

Arjun Mark 1 on a track test.

T72M Ajeya Mark.I, derived from the Soviet T-72 and assembled under licence with Russian and Polish components
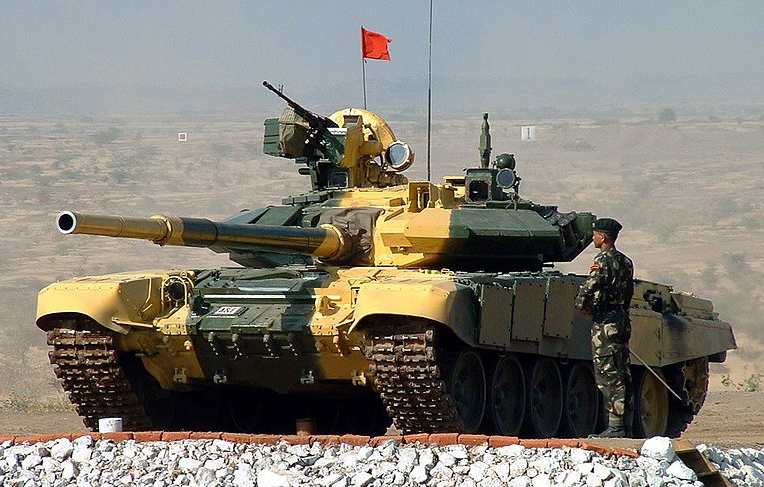

T-90S Bhishma, also licence-built. There are prospects for modernization into the "Bheesma II"
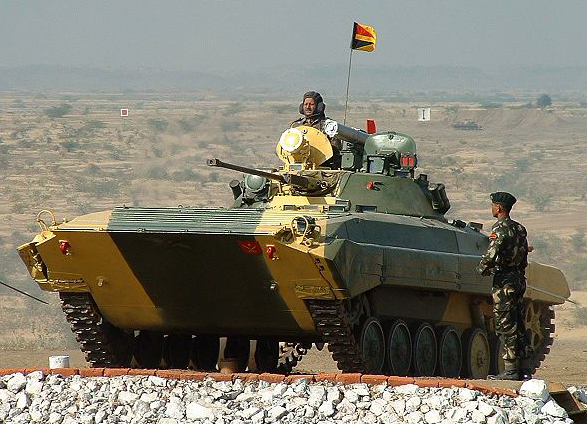

Sarath Infantry Fighting Vehicle, derived from the BMP-2

Sarath IFV upgraded
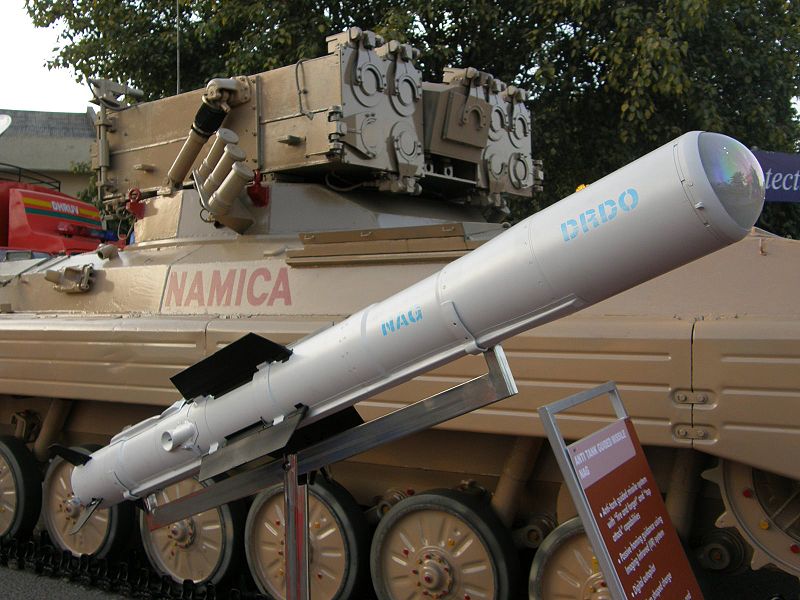

Namica tank hunter at Defexpo 2008

Tarmour heavy APC

Pinaka MBRL
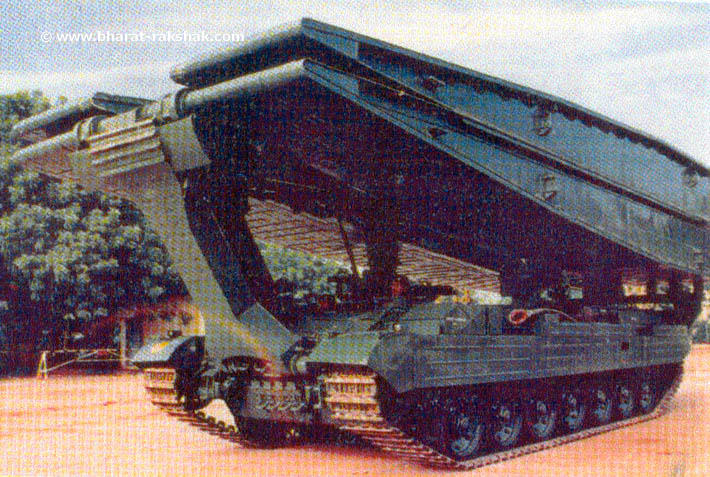

Kartik BLT AVLB (credits: www.barak-rakhsak.com)
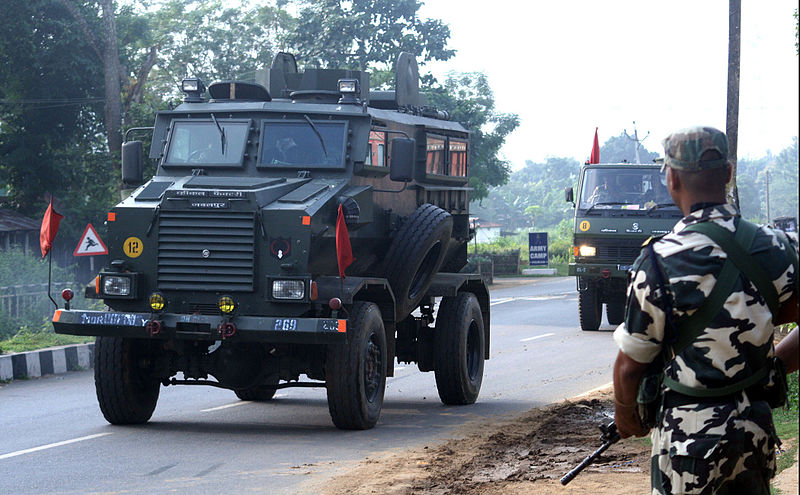

Arditya MPV

Hydremia specialized mine clearing vehicle
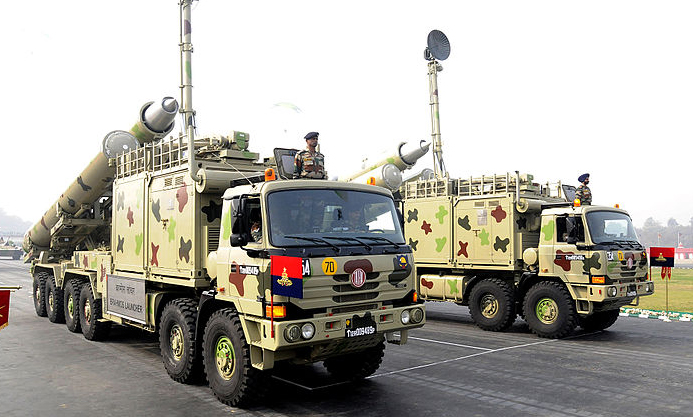

Brahmos tactical missile launcher
Current strength:

About 2410 (including 1900 T-72/M/M1) and Ajeya Mark I/II are currently in service*

1,650 T-90S Bhishsma are in service with a further 1,000 in construction to be delivered in 2020, 2011 as of 2019.
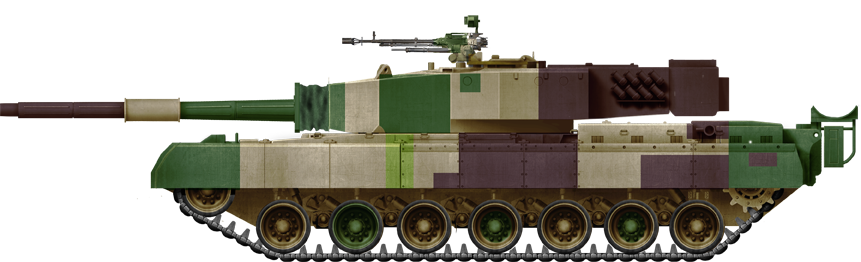
366 Arjun are in service today, as Indian native, elite MBT (248 Mark 1, 118 Mark 2).

2691 BMP-2 "Sarath" are in service today, as the new local Abhay IFV is still in development. About 12 antitank Namica variants were also delivered as well as 220 Carrier Mortar Tracked (CMT), 162 armoured ambulances developed by VRDE (DRDO) and 16 CRBN (Chemical recce vehicles) and closely related PRP-3 radar version of the venerable BMP-1 (numbers unknown).
-In addition about 200 BTR-50 are also still in service, pending replacement by the Kestrel. An undisclosed number of OT-64/64 are also in service for reconnaissance. Indeed the tracked IFV Abhay should be complemented by the brand new wheeled 8x8 IFV Tata Kestrel.
-For self-propelled guns, the most modern Indian assets are 150 K9 Thunder SPGs manufactured under licenced by Larsen & Toubro followed by 110 older 2S1 Gvodzika and about 80 FV433 Abbott, replaced by the current K9.
-For AA vehicles, India still possesses about 70 ZSU-23-4M 'Shilka' SPAAGs (pending reserve), and 66 9K22 Tunguska, complemented by 250 9K35 Strela-10 SPAAML.

Modern Tanks
Modern MBTs posters

Denel Bagder (2018)

Type 16 MCV (2016)

Gepard 1A2 last rounds 2011

SANDF

Russian AFVs

Main Battle Tanks