The Yugoslavian IFV
Under Marshal Tito's leadership and in defiance of the Warsaw Pact and USSR, Yugoslavia tried to develop a reasonably successful local armament industry, both for land vehicles and the air force. Despite its marked independence towards the Soviet bloc, some of its designs (especially for armored fighting vehicles) still had a strong eastern influence. Main Battle Tanks were Soviet-built, but instead of adopting the BMP-1 for its motorized infantry regiments, the choice was made to develop a local version early on, in 1969. Early research and development were achieved with the first completed prototype in 1974. Eventually, the BVP M-80 final prototype was ready in 1979 but only accepted for service the next year (since the "80") and fully entered service from 1982 onwards. About 800+ were manufactured (until the collapse of the country), including the upgraded M80A and several variants. All were passed onto the successor states (Serbia had the bulk of these) and saw heavy action in the 1990s civil war in all camps. BVP" means "Borbeno Vozilo Pješadije", or "Combat Infantry Vehicle".Design
The prismatic hull was made of Aluminum/Aluminum oxide and Titanium boride, over a steel structure, and in sufficient thickness to protect against heavy machine-gun rounds on the frontal arc. This was a compromise in order to get a light hull, yet still better protected than the BMP-2, in a system recalling the M2 Bradley. The shape of the hull is prismatic with a considerable glacis front. The crew comprised the driver (front left) commander behind and gunner in a small one-man turret. Behind six equipped infantry took place on benches in the rear compartment. Exit doors are provided as well as eight pistol ports to fire on the move (sides and one in the rear doors). Other protection equipment includes a collective NBC system, automatic fire extinguishers, inside heating and water ejecting system. In addition, for concealment, smoke grenade dischargers are provided and in addition, diesel could be injected on to the hot exhaust (creating a smoke screen).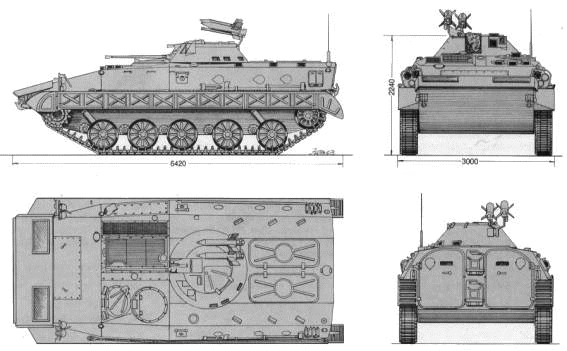
Blueprint.
Mobility was provided on the first initial serie by the French engine of 260 hp also used by the AMX-10P. It was replaced one year later on the M80A by a more powerful and reliable license-produced Daimler-Benz OM-403 which developed 320 hp engine, produced by FAMOS factories. This engine provides a 22.6 hp/tonne, which gave a top speed of 65 km/h on land. The BVP-80 is also fully amphibious, propelled by its tracks in the water at 7-8 km/h, without preparation but raising the front trim vane (folded on the glacis). The M-80A main armament consists in a Hispano-Suiza HS 804 20 mm autocannon (400 rounds) and a coaxial 7.62 mm machine gun (2000 rounds) plus launcher for two wire-guided 9M14/Malyutka AT-3 "Swagger" ATGMs at the turret's rear (licenced-manufactured). Reloads (four more inside the tank) must be performed partly on the exterior from two rear roof hatches. Above all, the M80 is relatively easy to distinguish from the BMP-1/2, as being one meter shorter with one less roadwheel, and a smaller turret.
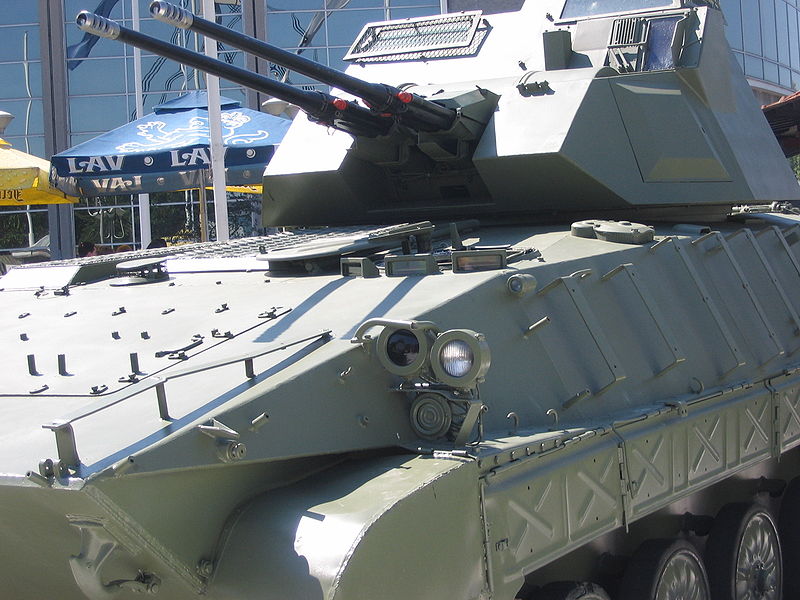

M80 SPAT 30/2 SPAAG closeup
Production and variants
The first production variant was M-80 which given a French 260 hp diesel engine, replaced next year on the upgraded BVP-M80A by a licence-built Mercedes engine. Total production estimated range from 600 to 800. Variants includes the M-80A KC (Company commander's vehicle), M-80A KB (Battalion commander's vehicle), M-80A Sn armoured ambulance without turret with a single hatch in the roof, single rear door and 4 stretcher/6 seated injured personal carried. The M-80A LT was the Tank hunter version equipped with three twin AT-3 launchers, and the SPAT 30/2 SPAAG used a twin 30 mm mounted coupled with a J-171 Motorola 6800 sight. The MOS is the minelayer version, and the M-80AK/M-98A is a late rearmed version with a 30mm M86/M89 cannon. Two prototypes were also developed, the Sava M90 SPAAML equipped with a Strela-10MJ SA-13 launcher and the M-80A1 twin-30 mm SPAAG.Active service
These vehicles served in the Yugoslavian Army until the partition in 1991 and the existing vehicles passed onto successors states according to their former garrisons. They participated in the whole operations of the Yugoslavian wars, including the War in Slovenia (1991), the Croatian War of Independence (From 1991), the Bosnian War (from 1992), and the Kosovo War (1998–1999). As of today Bosnia and Herzegovina operates 103 vehicles, Croatia 104, Serbia 550, and Slovenia 52, all M-80As still in active service.Links
The BVP-M80 on WikipediaOn the M98A conversion
Painting of a M80 in croatian service, in action during the war
BVP-80 specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 6.42 x2.90 x2.20 m |
| Total weight, battle ready | 13.850 tons |
| Crew | 3+6 (driver, gunner, Cdr, 6 infantry) |
| Propulsion | Daimler Benz OM-403 320 hp 22.6 hp/tonne |
| Suspension | Torsion bar suspensions |
| Speed (road/water) | 65/8 kmh |
| Range | 500 km (xx mi) |
| Armament | 20 mm HS 803/ coaxial 7.62 LMG |
| Armor | 10 to 30 mm est. (0.24-0.35 in) |
| Total production | 800 in 1980-1990 |

BVP-M80 in green livery, Yugoslavian Army 1980s

M80A camouflaged, Serbian Army

BVP-M980

Croatian M80A as of today.

Yugoimport modernized BVP-98A
Bosnian M80 LT (Lovac Tenkova for "Tank Hunter"), 2000.
Gallery

BVPM-80A Vidra modernized on display at Partner 2011 Military Fair










Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

