JSDGF AFVs - Cold War Japanese Tanks
 Tanks and AFVs of the JSDGF: About 5,000 armoured vehicles 1947-90.
Tanks and AFVs of the JSDGF: About 5,000 armoured vehicles 1947-90.
Articles
- Type 61 Tank
- Type 74 Tank
- Type 90 Kyu Maru
- Type 60 APC
- Type 73 APC
- Type 89
- Type 96 APC
- Type 87 AFV
- Komatsu Type 82 CV/CRV
- Hitachi Type 87 ASV
- Type 78 ARV
- Type 73 Tractor
- Type 73 Light Truck
- SX 60
- SV 60
- Komatsu NBCRV
- Komatsu LAV
- Type 92 MCV
- Hitachi Type 99 ASV
- Type 19 155 mm WSPH
- Type 99 155 mm SPH
- M110 SPH
- Type 96 120 mm SPM
- Type 11 ARV
- Type 90 ARV
- Type 91 AVLB
- Toyota HMV
From the ashes to the soviet threat
Japan emerged from world war two as from a cataclysm, in a devastated and occupied country. Mac Arthur's decision to keep Emperor Hirohito in place helped the country keep a link to its past, culture, and honour, while at the same the International Military Tribunal for the Far East judged war the criminals that do not commit Seppuku after the surrender. Prime minister Shigeru Yoshida accepted military bases on Japanese soil, now a strategic asset, facing USSR, while retaining a neutral position on foreign affairs, and with a primary objective of economic growth.It was argued that the success of radical changes in Japan was helped by the desperate situation at home, a situation that reflected the German rebirth, under new democratic principles. In 1947, a de facto alliance with the USA saw a new constitution signed on May 3, 1947, a diet with universal suffrage elected members was established, and the Treaty of Peace with Japan was signed internationally in September 1951, ratified by the congress next year, and by the Japanese diet in 1953. Full sovereignty was recognised on April 28, 1952. Left and right wing political parties were formed in 1955, but the LDP (Liberal Democratic Party) remain in the majority during the 1950s and 1960s, placing economic growth as the number one priority. Until the 1980s, Japan will enjoy a post-war economic miracle.
Foundation of the JSDF
Rearming Japan, like Germany, was a logical step in the communism containment doctrine defined in the USA. In the context of the Korean war, Japan became the number one supplier of US and allied forces in the area, while retaining a neutral position. But rearming, although encouraged by the USA was not an easy step to take. General public opinion sentiments were strongly oriented towards pacifism, while the constitution of 1947 itself stated (art.9) that Japan "forever renounces war as an instrument for settling international disputes and declares that Japan will never again maintain land, sea, or air forces or other war potential".Along the peace treaty, the Mutual Security Assistance Pact between Japan and the U.S. ratified in 1952, the latter was responsible for the defence of the archipelago, in land, sea and air. That allow Japan to maintain only a National Police Reserve (expanded to 110,000 men), the National Safety Forces, and a coast guard force equipped with ex-US navy ships, destroyers and destroyer escorts.
US supplies with Japan however decreased after the Korean war, and at the same time the soviet threat concerns pushed the new government to extend the defensive forced in 1954 split between the three traditional arms, land, air and sea. in 1960, revision of the Japan-United States Mutual Security Assistance Pact was contested and US military presence decreased to the only occupation on Okinawa, which ended in 1972 at the end of the Vietnam war.
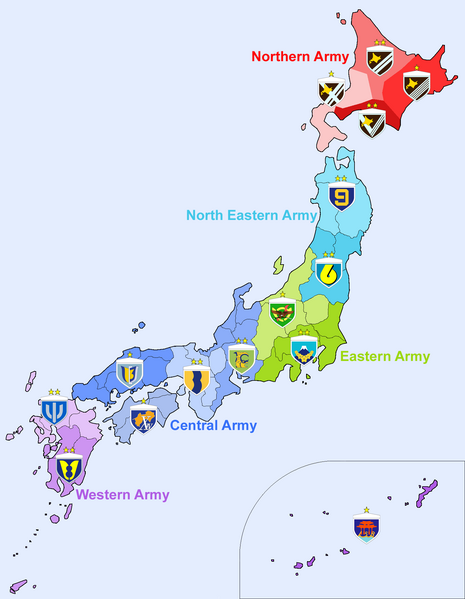
The JSDGF military districts.
The JSDGF
The Japanese Self Defence Ground Forces (陸上自衛隊; Rikujō Jieitai) was founded in July 1954. Its main original goal were to maintain internal security in Japan and counter a possible Soviet invasion of Hokkaido. JSDGF General Headquarters are based in Ichigaya, Tokyo. It is a small, but professional, well trained and well-equipped army of 148 000 men (now 170 000). NCOs came from four universities and were formed at the National Defence Academy at Yokosuka and a youth cadet program is instituted. Due to the nature of the landscape and urban density, training grounds are few in numbers, but counted in command post exercises, map manoeuvres, simulation, and overseas training at the Yakima Training Center in the United States.The JSDGF was until now divided into five military regions subdivided into fourteen districts, the Northern Army, headquartered in Sapporo, Hokkaido, the North Eastern Army, headquartered in Sendai, Miyagi, the Eastern Army, headquartered in Nerima, Tokyo, the Central Army, headquartered in Itami, Hyōgo, and the Western Army, headquartered at Kumamoto, Kumamoto. Reserves are divided into the rapid-reaction component and the main reserve. The first has a 30-days yearly training, while the second had five days of training a year. As of 2007 these counted respectively 8,425 and 22,404 men.

Japanese M41A3 Walker Bulldog. 141 were operated in the 1960s, up to the 1990s. Just one example of some of the US tanks provided to the Japanese after the Second World War.

The Type 61 was the first tankdesigned and built by the Japanese military after the Second World War. The Tank entered service in 1961 as was armed with a 90mm Cannon.

They Type 74 was designed to replace the Type 61. It was armed with a license-built copy of the NATO standard 105mm L7 main gun. It was the first of Japan's main battle tanks to incorporate hydropneumatic suspension that allowed the tank to tilt forwards, backwards, and side-to-side. The tank was designed in 1975 but didn't enter service until 1980, by which time it was quite obsolete.

The Type 87 Self-Propelled Anti-Aircraft Gun (SPAAG) was greatly inspired by the German Flakpanzer Gepard. It even features the same 35mm Oerlikon cannons. The vehicle was based on the hull of Type 74 MBT, and retained the hydropneumatic suspension. The SPAAG entered service in 1987.

The Type 60 was one of post-war Japan's first tracked Armored Personel Carriers (APCs). A number of its components were shared with the Type 61 Tank, and there was even an Anti-Tank Guided Missile (ATGM) carrying variant.
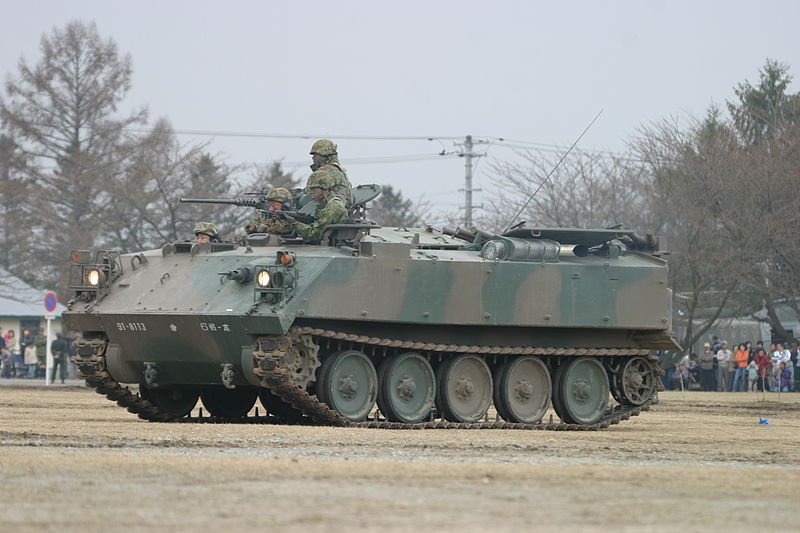

The Type 73 is today's the main Japanese tracked APC. Developed as a replacement for the Type 60 it had an aluminium hull and a mid-engined layout. Production stopped after the 338th vehicle in 2012, with a possible extra production if needed.
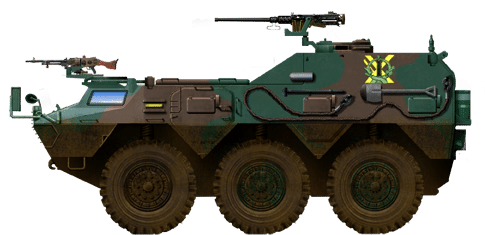
Komatsu's Type 82 wheeled Command & Communication vehicle (1982), production stopped recently, after 231 vehicles.
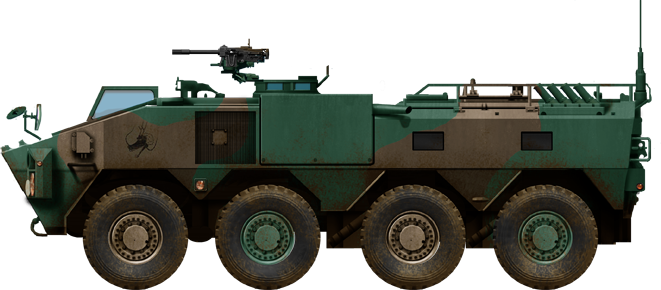
Type 96 APC at Camp Shimoshizu. This vehicle entered service with Japan in 1996 as the main wheeled aroured personal carrier. So far, 365 has been produced since 1995 until 2014. It i sechedule for replacement by the Komatsu Wheeled Armoured Vehicle (Improved) in trials in May 2019.
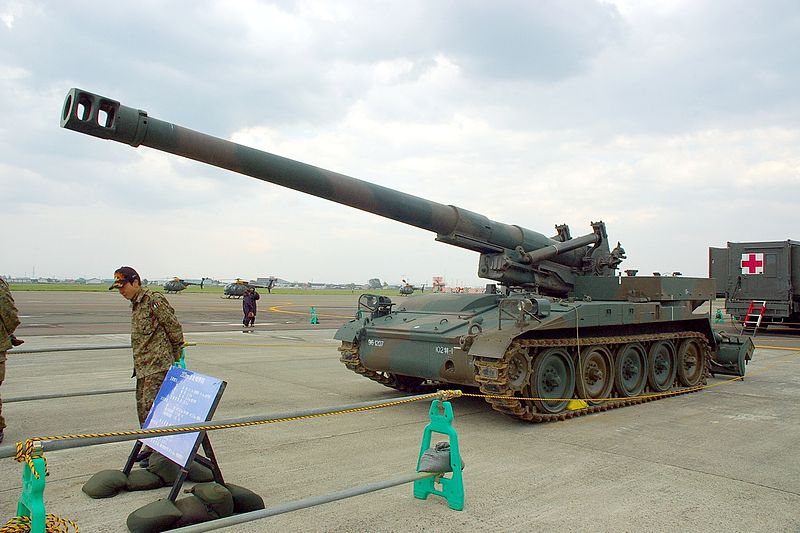

155 mm self-propelled howitzer M110A2, built under licence in the 1960s by Japan Steel Works and Komatsu (91 in service).
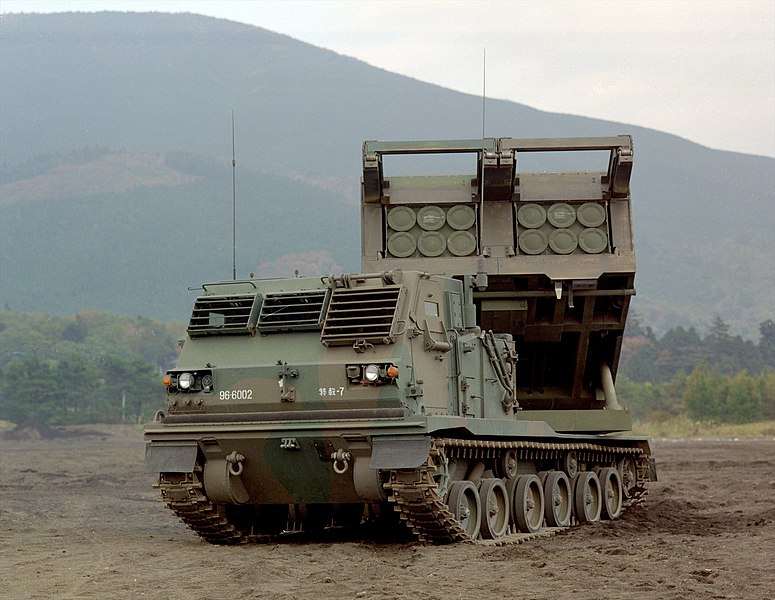

IHI Aerospace licence-built version of the
M270 self-propelled multiple rocket launcher (99 built).

Hitachi's tracked ammunition supplier.
Links
The JSDGF on Wikipedia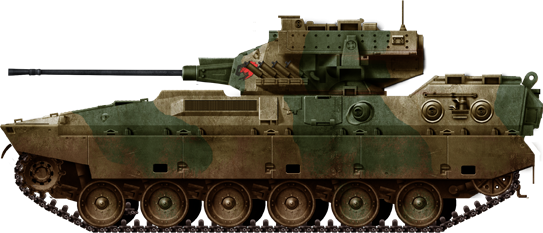
Active vehicle in the 2000s.
New Challenges (1990)
 Japan stuck to a strict non-interventionist policy, but assisted allied US Forces, in Korea and provided again support for the duration of the Vietnam War. With the end of the cold war and the Soviet menace the Northwest, there were some budget cuts, but not as severe as in the US and some European countries. In effect, the economic growth of Japan triggered an unprecedented financial boom in the whole Asian Area, from Korea to Indonesia. China military power raised in a spectacular manner, and the level of potential threats (outside terrorism, an asymmetric menace) shifted south-west, towards Beijing. Although both the Japanese and Chinese navy are mostly involved in recent territorial disputes, the growth of the Chinese Army and the ever-present threat of the conventional army of North Korea are sufficient to maintain a ground force ready to repel any invasion or intervene on a nearby disputed zone that imposes a quick reaction force...
Japan stuck to a strict non-interventionist policy, but assisted allied US Forces, in Korea and provided again support for the duration of the Vietnam War. With the end of the cold war and the Soviet menace the Northwest, there were some budget cuts, but not as severe as in the US and some European countries. In effect, the economic growth of Japan triggered an unprecedented financial boom in the whole Asian Area, from Korea to Indonesia. China military power raised in a spectacular manner, and the level of potential threats (outside terrorism, an asymmetric menace) shifted south-west, towards Beijing. Although both the Japanese and Chinese navy are mostly involved in recent territorial disputes, the growth of the Chinese Army and the ever-present threat of the conventional army of North Korea are sufficient to maintain a ground force ready to repel any invasion or intervene on a nearby disputed zone that imposes a quick reaction force...
The JSDGF today
As of today, the armored forces have 280 Type 74 MBTs, 341 Type 90, and 53 Type 10 in service (674 total). Most tracked vehicles are produced by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and their suppliers. Outside a wheeled tank destroyer similar to the Italian Centauro, the only IFV today in service with the JSDGF is the Type 89 also produced by Mitsubishi (89). The tracked APCs Type 73 provided the bulk of the type with 338 machines.Previous MBTs like the Type 61 MBTs are now discarded. Komatsu and its subcontractors usually provide the wheeled vehicles, APCs like the Type 82 Command, Type 87 armored recce, Type 96 APCs, specialized Chemical and NBC recce vehicle, a light 4x4 armored scout. Nissan Motors Aerospace was responsible for a series of MCV (mine-clearance vehicles) based on the Type 90. In total, this represents around 2870 vehicles.
The bulk of ported artillery capabilities are provided by Mitsubishi's Type 99 SPG and the license-built (by Hitachi) M110 Self-propelled Howitzer, while rocket firing tracked M270 MLRS (also license-built, by IHI Aerospace). There are also two types of ammo supply vehicles, the Type 87 and 99, both tracked. Another derived vehicle, the tracked Type 96 120mm Self-Propelled Mortar is also in service, as the only SPAAG, the Type 87 Self-Propelled Anti-Aircraft Gun. In total, around 400 artillery vehicles. The grand total as of today is around armored 3940 vehicles.
Anti-tank missiles include the Type 01 Light Anti-Tank Missile (1,073 produced), the Type 79 Anti-Landing craft and Anti-Tank Missile, and the Type 87 Anti-Tank Missile. The latter are carried by the Type 89 IFV. Anti-tank helicopters are the Fuji license-built Boeing AH-64 Apache (13) and Bell AH-1 Cobra (88), and the domestic scout Kawasaki OH-1 (38, 101 on order). The JSDGF's own airforce operates 497 aircrafts in all as of 2014, the bulk being US-licenced transport helicopters.
Post-Cold War Armoured vehicles
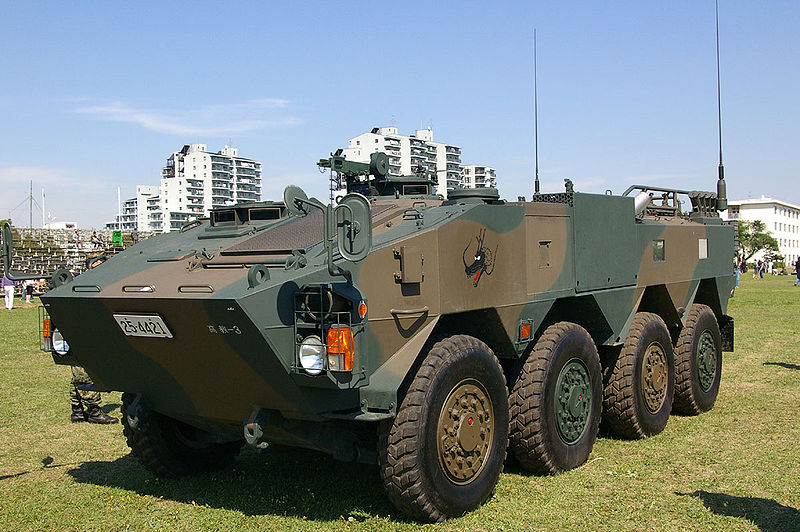

Inspired by the Swiss MOWAG Piranha and other fast wheeled APCs, Komatsu's Type 96 are still produced today. 365 are currently in service with the JSDGF.
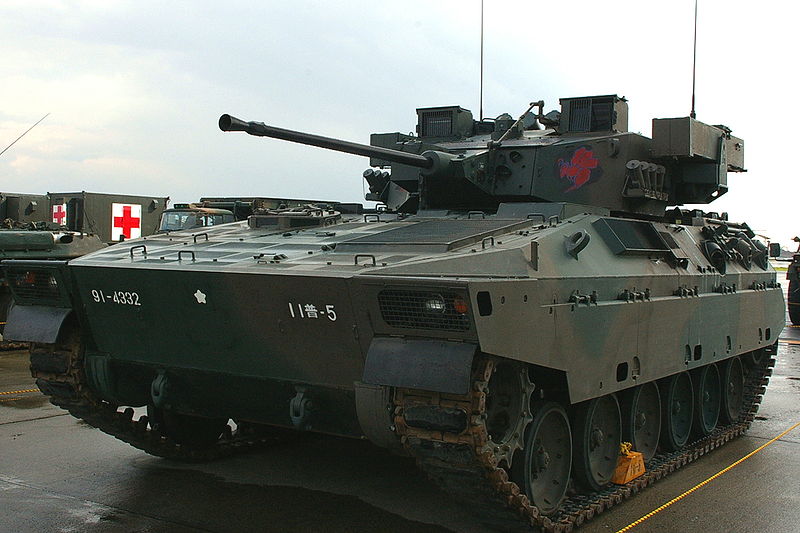

The only true Japanese IFV is the Type 89, conceived during the cold war (1980) as a Japanese "Bradley". Production is scheduled until 2018.

Komatu's LAV (2002). A versatile vehicle comparable to a lighter version of the Hummer. Actual production figures are 1855 vehicles.

Type 96 self-propelled mortar carrier or Gottohanma (24 built by Built by Hitachi and Howa).
Links
The JSDGF on WikipediaJSDGF Official webpage

The Type 90 Kyū-maru entered service in 1990, replacing the aging Type 61 and Type 74. It retained the feature of having hydropneumatic suspension and was armed with a license-built copy of the famous Rheinmetall L44 120mm Smooth-Bore Gun, as used on the German Leopard 2 and American M1 Abrams.

The Type 10 Hitomaru entered service in 2012, complimenting the still serving Type 90. It is one of the most technologically advanced main battle tanks with a connective net that allows all branches of the military to communicate together in battle. It is armed with a home-built 120mm Gun and retained the Hydropneumatic suspension of previous vehicles. It also features a modular armor system.
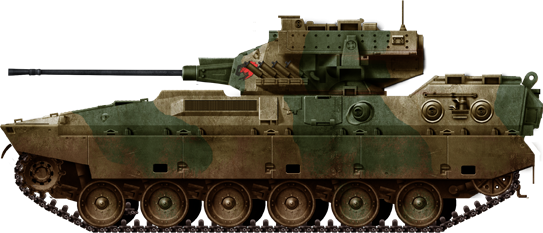
The Type 89 is the JGSDF's only true Infantry Fighting Vehicle (IFV). It entered service in 1989 and is armed with a Oerlikon Contraves 35 millimeter KDE cannon.
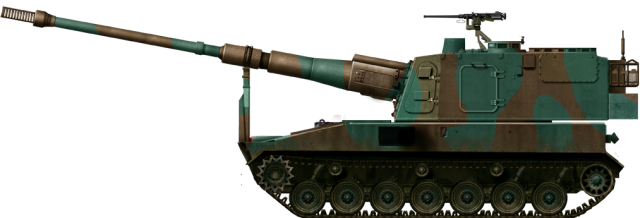
The Type 99 self-propelled howitzer entered service in 1999 as a successor to the aging Type 75. The SPH is armed with a 155mm L52 howitzer from Japan Steel Works (JSW).
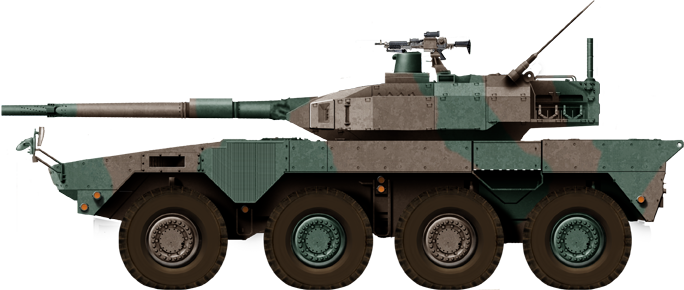 rendition of the Type 16 CMV by Tank Encyclopedia's creator. This is the next generation "wheeled tank", derived from the centauro. It's a no-compromise solution where protection is sacrified for mobility and firepower, a first-so-see, first-to-kill proposition reminiscent of the Battlecruiser concept.
rendition of the Type 16 CMV by Tank Encyclopedia's creator. This is the next generation "wheeled tank", derived from the centauro. It's a no-compromise solution where protection is sacrified for mobility and firepower, a first-so-see, first-to-kill proposition reminiscent of the Battlecruiser concept.
Illustrations

Type 90 of the early type, with the horizontal x4 type smoke dischargers.

Type 90 of the late type, with the vertical x3 type smoke dischargers.

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
