The South Korean SPAAML
The K-SAM Chunma or "Pegasus" is a self-propelled, short-range, supersonic surface-to-air missile system. Its main purpose on paper was to engage all threats flying 5,000 meters or up to 9-10 kilometers with the use of a command-to-Line-Of-Sight (CLOS) guidance. The K-SAM program was launched in 1989 and in 1999, after the prototype was delivered by Doosan and tried, the first batch of 48 vehicles (about 358m $) and deliveries scheduled to take place between 1999 and 2005. With the introduction of a modernized Crotale system, the second batch of 66 (510m $) was ordered in December 2003 and deliveries took place until 2009.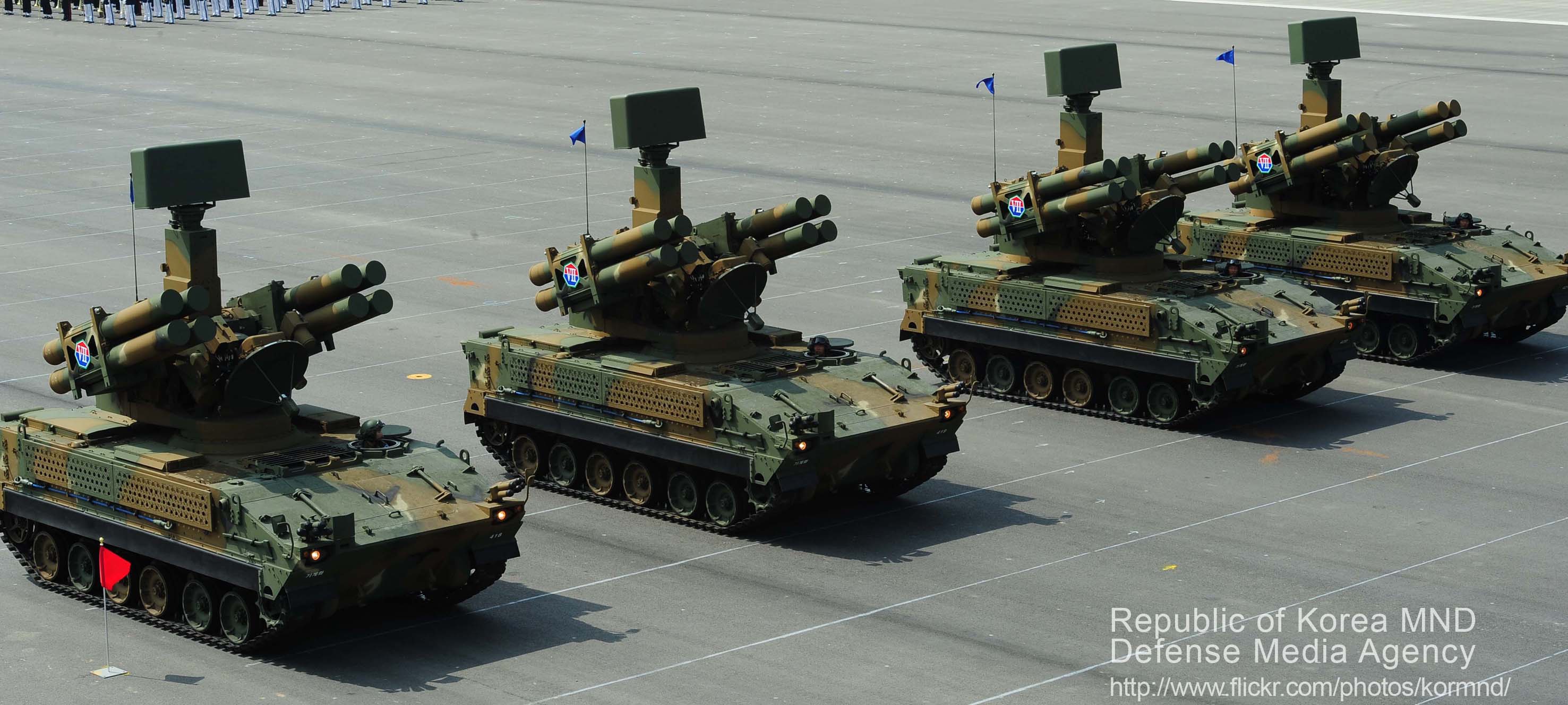
K-SAMs Pegasus at the 2013 celebration ceremony for the 35th anniversary of the ROK Armed Forces.
About the Crotale missile system
This AA missile started in 1967 as a joint venture between Rockwell International (US) and Thomson-Houston (and Mistral) in France for South Africa. At the end the French army was so impressed that it was ordered for the navy and army and these systems were also exported (Barhein, Egypt, Finland, Greece, Iran, Oman, Pakistan, S.Korea, Saudi Arabia, UAE, Portugal, South Africa), starting in 1978. France developed a 4x4 and an AMX-30 based launcher platform to provide organic defense, a tracked carrier was also used by the Saudi Shahine SPAAML, and the Korean-designed Doosan Chunma. China also uses the HQ-7 SAM 4x4 vehicle. The Crotale ("rattlesnake") is an all-weather short-range missile using InfraRed Differential Ecartometry. Its weight is 76 kg with a focused fragment warhead of 13 kg, with a length 2.35 m, the diameter of 0.165 m and a radio fuse. Range varied from 6,000 m to 9,000 m on the Thales Mark 3 (2008) and 11,000 on the NG (1990), at a top speed of 1,200 m/s (MACH 4.3). For the Pegasus, it was 5,000 km in altitude and 10,000 m for the maximal range.Design
Doosan was put in charge of the launcher which has to operate a central unit with 2x4 launchers and a central guidance system plus tracking radar. The chassis seems to be a standalone creation, although apparently with elements from the K200 AIFV. This chassis is shared also with the Biho SPAAG. The driver is located to the front left, with three vision blocks (central IR) and right-sliding hatch. The commander and operator took place in the rear section of the hull with the surveillance and tracking radar and fire control consoles. The missile system is located at the center of the vehicle. The engine compartment lays at the right side near the driver, housing a Doosan D2840L 10V turbo-intercooled diesel rated at 520-hp, for a top speed of about 60 kph for 26 tons. The welded RHA steel hull has a frontal beak, but flat sides but armor thickness is unknown, estimated to 25 mm on the frontal arc, 8-13 mm elsewhere as a standard for this kind of vehicles. There is also a collective NBC protection with overpressure, automatic fire extinguishers and 2x4 smoke dischargers are provided for concealment (installed on the glacis front). The drivetrain comprises 6 roadwheels and 5 return rollers per side suspended by torsion bars and shock absorbers, protected with the same rubber skirts shared by the K200 and M113 APCs.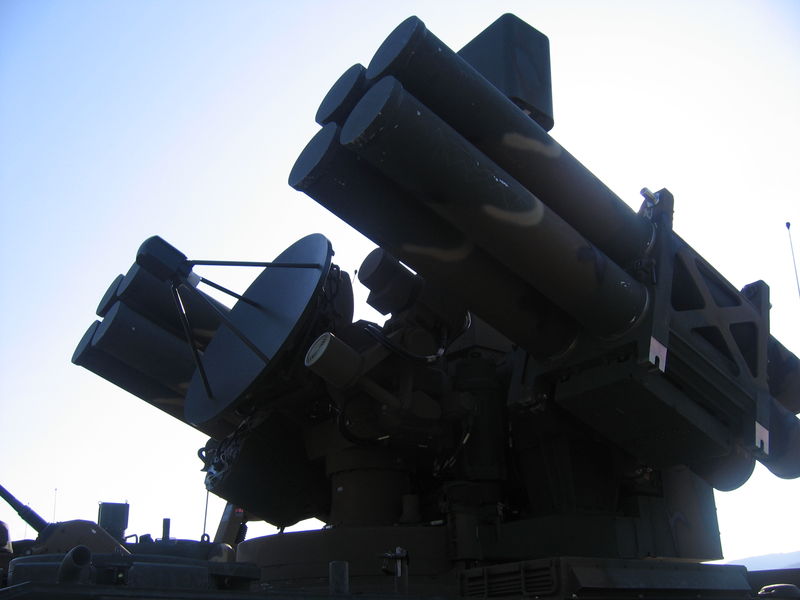
Pegasus at the 2007 Seoul air show, closeup of the radar and missiles.
Outside the 8 individual launchers which have a 90° elevation and 360° traverse, there is a surveillance radar, a tracking radar and associated electro-optics. The real-time multisensor target acquisition system combines all-weather day/night capabilities and even hostile ECM conditions, with EOTS system for surveillance (pulse-Doppler radar S-band radar tracking) and FLIR, IR Localizer and CLOS for guidance by the operator. The electro-optics counts a TWT Ku-band thermal imaging camera (detection range 19 km), a daily CCD-camera (detection range 15 km) and an infrared detector and are using the latest Korean data processing to track simultaneously 20 airborne targets at ranges up to 20 kilometers. These technologies provide also a very high first kill capability and integrate the Identification Friend or Foe (IFF). The VT-1 missile has a maximum permissible overload up to 35G, and a firing range of up to 11,000 km.
Production & service
The Pegasus was operational in 1999, and deliveries took place in two batches (the second in 2009) with the upgraded Crotale version. It is intended for front-line armoured brigades (organic short/medium range defense) in coordination with the K-30 Biho SPAAG that takes care of low flying targets at short/very short ranges (including missiles), what could have got through the second layer of aerial defense (the larger one is met by the air force). But the Pegasus was also destined to defend static but vital installations such as airfields, logistic centers and headquarters, industrial facilities or infrastructures such as ports and airports, and can operate in the most extreme environments (NBC contamination, ECM jamming, etc.).Links, sources
On Militaryparitet.comOn deagel.com
On asiafinest.com forum
Doosan K-SAM specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 7.10 x5.40 x3.40 m (23.3 x17.7 x11 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 26 tonnes (52,000 Ibs) |
| Crew | 3 (driver, cdr, operator) |
| Propulsion | Doosan D2840L 10V TID 520hp (388 kW) |
| Suspension | Torsion bars, shock dampers |
| Speed (road) | 60 km/h (37 mph) |
| Range | 500 km (310 mi) |
| Armament | 2x4 Crotale SAM, max alt 5000 km (16,404 foot) |
| Armor | Estimated 25 mm frontal arc, 8-13 mm sides rear top (0.3-0.9 in) |
| Total production | 144 in 2009 |

K-SAM Chunma in regular livery, 2000s. To our knowledge that's the first illustration done of this vehicle, an exclusivity from Tanks Encyclopedia.
Gallery
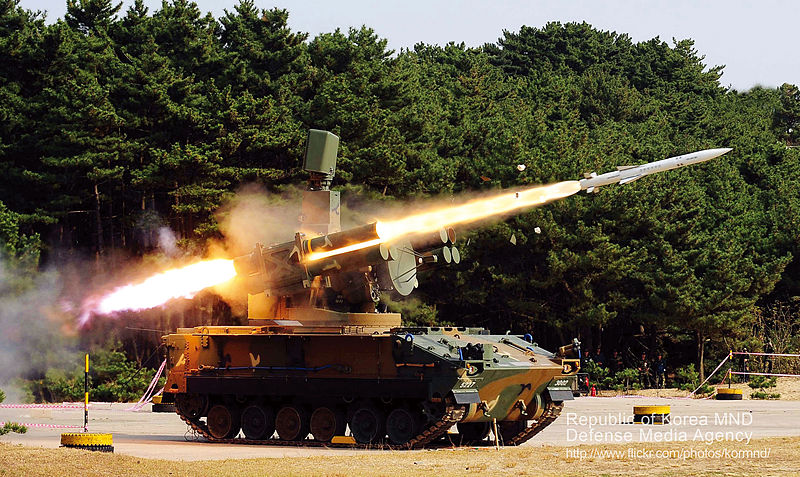

K-SAM Chunma firing (wikipedia)
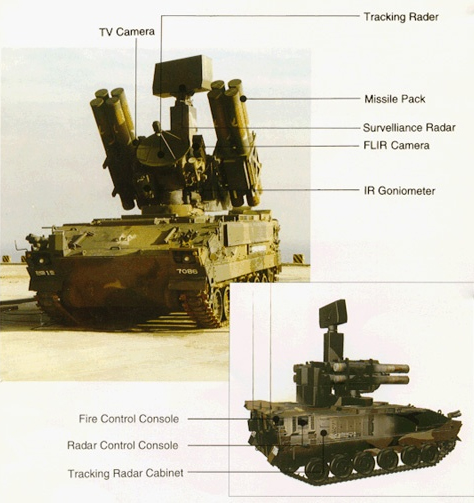
Details (from Doosan, via militaryparitet.com)
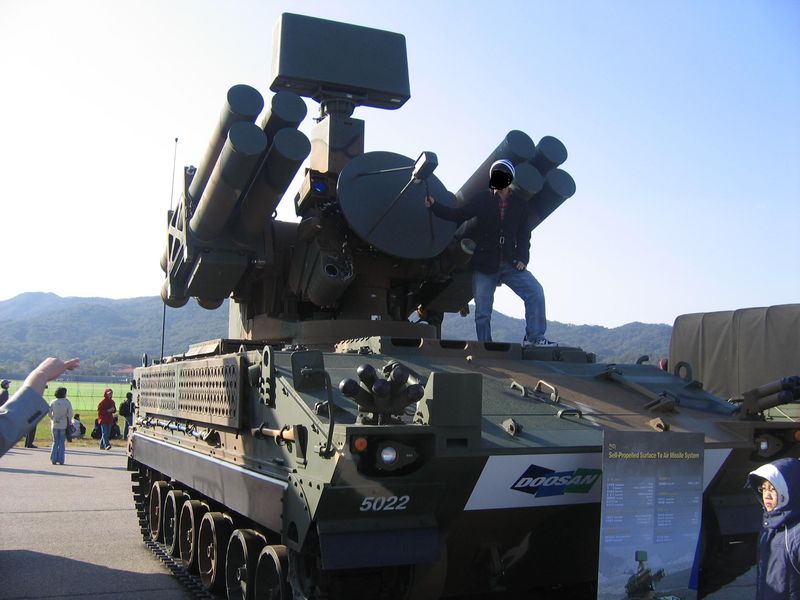

Pegasus at the 2007 Seoul air show
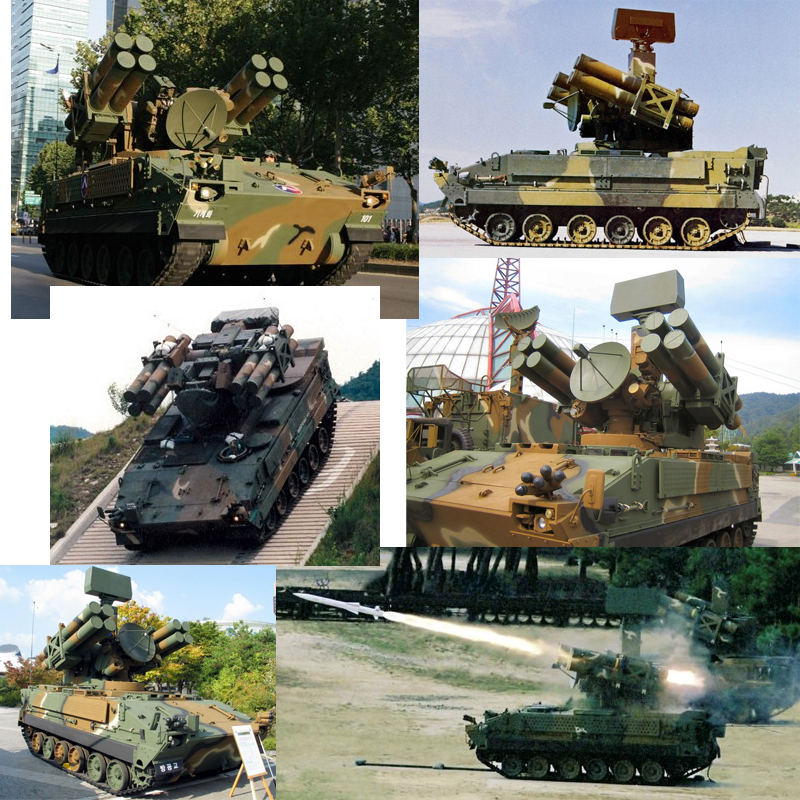

Various web references

Modern Tanks
Modern MBTs posters

Denel Bagder (2018)

Type 16 MCV (2016)

Gepard 1A2 last rounds 2011

SANDF

Russian AFVs

Main Battle Tanks
