The T-12 and the T-24 were attempts to improve the MS (T-18) tank and comprised a hard leaning curve into the shape of marely failed prototypes: T-19, T-21, and T-23. Engineers and deciders had plenty of good idea on papers, as what could be a medium tank. And this led to the T-12 and T-24 between 1925 and 1931. Both were relatively sound designs but they ended as unworkable in practice, with scores of mechanical failures.
However at the time, these failures came less from ideas or paper engineering but the fact USSR lacked skilled workers capable to tackle a relativelky complex project like this, as well generaly a problem of resources across the board. If the T-12 did not made the cut, the T-24 at least was greenlight for production with a serie on 25 built until the authorities put the plug on it. The very similar T-12/T-24 were in direct competition with "Tank Grotte-1", a German inspired prototype (by engineer Hans Grotte) and the latter was neither put into production. Just like the TG heavy tank project, these eneded by 1931 as USSR fell enamoured by the Christie tank concept, which led to the BT series, and later down the line, to the T-34. On the other hand for light tanks, the Vickers Mark E became the T-26. Soviets authorities wanted a better protected tank than the T-18 as a base. But many felt they lacked sufficient tank design experience. So a brand new tank design bureau was established at the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (KhPZ) today in Ukraine, in 1928. This prestigious bureau which spawned so many tank designs over decades, before the independence of Ukraine, was headed by I. Aleksienko, a renowned engineer and apt organizer, team leader, in cooperation with A. Morozov, the superstar of Soviet medium tank projects 1940-1970.
Soviets authorities wanted a better protected tank than the T-18 as a base. But many felt they lacked sufficient tank design experience. So a brand new tank design bureau was established at the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (KhPZ) today in Ukraine, in 1928. This prestigious bureau which spawned so many tank designs over decades, before the independence of Ukraine, was headed by I. Aleksienko, a renowned engineer and apt organizer, team leader, in cooperation with A. Morozov, the superstar of Soviet medium tank projects 1940-1970.
The first tank project emerging from KhPZ was the T-12 (also called T-1-12). It was basically and enlarged T-18 fitted with a more powerful 200 hp engine and better 45 mm (1.77 in) gun later also retofitted on the T-18M. in the 1930 budget was programmed a serie of thirty T-12s. The T-12 was largely designed base don the experience gained when designing and producting the T-18. A key idea, borrowed frol US designs, was a multi-tier weaponry arrangement, and notably it took a great deal of inspiration from the M1 Medium model 1921–1925.
The T-12 was designed with a simple hull structure between two tracks and small-bogie suspension. There was a flat sides, eight faced turret but a rounded commander’s cupola. It also had a crew of four to man all weapons. It was reasonably large for the time at 19 tons, for 7.5 m long, 3 m wide, and 2.8 m high. The main armament was the Model 32 45 mm (1.77 in) gun and a storage for ready rounds in the turrets and others in the hull, 100 rounds total. This was completed by an impressive array of light machine guns: Three 7.62mm DT MGs installed on Fedorov-Ivanov ball mount, one been placed in commander’s cupola, another coaxial to the main gun, one on the turret's side (like the T-26 later and many Japanese tanks).
The T-12 like previous T-18 and many other models had a removable "tail" to deal with large trenches. It was 69 cm long and allowed the vehicle to gap 2.65 meters. The prototype was however manufactured by hand with crude steel, a lack of special equipment or skilled labout. Still, it was assembled by working day and night, at breakneck pace so to be ready for testing on October 15, 1929. Cost was reduced by having the armored hull and turret made from construction steel, not hardened. During trials, the T-12 prototype appeard to be seriously flawed, so much a new design was needed, which will led to the T-24.
However at the time, these failures came less from ideas or paper engineering but the fact USSR lacked skilled workers capable to tackle a relativelky complex project like this, as well generaly a problem of resources across the board. If the T-12 did not made the cut, the T-24 at least was greenlight for production with a serie on 25 built until the authorities put the plug on it. The very similar T-12/T-24 were in direct competition with "Tank Grotte-1", a German inspired prototype (by engineer Hans Grotte) and the latter was neither put into production. Just like the TG heavy tank project, these eneded by 1931 as USSR fell enamoured by the Christie tank concept, which led to the BT series, and later down the line, to the T-34. On the other hand for light tanks, the Vickers Mark E became the T-26.
Development and design of the T-12
 Soviets authorities wanted a better protected tank than the T-18 as a base. But many felt they lacked sufficient tank design experience. So a brand new tank design bureau was established at the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (KhPZ) today in Ukraine, in 1928. This prestigious bureau which spawned so many tank designs over decades, before the independence of Ukraine, was headed by I. Aleksienko, a renowned engineer and apt organizer, team leader, in cooperation with A. Morozov, the superstar of Soviet medium tank projects 1940-1970.
Soviets authorities wanted a better protected tank than the T-18 as a base. But many felt they lacked sufficient tank design experience. So a brand new tank design bureau was established at the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (KhPZ) today in Ukraine, in 1928. This prestigious bureau which spawned so many tank designs over decades, before the independence of Ukraine, was headed by I. Aleksienko, a renowned engineer and apt organizer, team leader, in cooperation with A. Morozov, the superstar of Soviet medium tank projects 1940-1970.
The first tank project emerging from KhPZ was the T-12 (also called T-1-12). It was basically and enlarged T-18 fitted with a more powerful 200 hp engine and better 45 mm (1.77 in) gun later also retofitted on the T-18M. in the 1930 budget was programmed a serie of thirty T-12s. The T-12 was largely designed base don the experience gained when designing and producting the T-18. A key idea, borrowed frol US designs, was a multi-tier weaponry arrangement, and notably it took a great deal of inspiration from the M1 Medium model 1921–1925.
The T-12 was designed with a simple hull structure between two tracks and small-bogie suspension. There was a flat sides, eight faced turret but a rounded commander’s cupola. It also had a crew of four to man all weapons. It was reasonably large for the time at 19 tons, for 7.5 m long, 3 m wide, and 2.8 m high. The main armament was the Model 32 45 mm (1.77 in) gun and a storage for ready rounds in the turrets and others in the hull, 100 rounds total. This was completed by an impressive array of light machine guns: Three 7.62mm DT MGs installed on Fedorov-Ivanov ball mount, one been placed in commander’s cupola, another coaxial to the main gun, one on the turret's side (like the T-26 later and many Japanese tanks).
The T-12 like previous T-18 and many other models had a removable "tail" to deal with large trenches. It was 69 cm long and allowed the vehicle to gap 2.65 meters. The prototype was however manufactured by hand with crude steel, a lack of special equipment or skilled labout. Still, it was assembled by working day and night, at breakneck pace so to be ready for testing on October 15, 1929. Cost was reduced by having the armored hull and turret made from construction steel, not hardened. During trials, the T-12 prototype appeard to be seriously flawed, so much a new design was needed, which will led to the T-24.
T-12 specifications | |
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 7.5 x 3 x 2.8 m (21.33 x 9.84 x 9.19 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 19.8 tonnes |
| Crew | 4 (driver, commander, gunner, loader) |
| Propulsion | 200-250 hp M-6 |
| Top Speed | Estimated 25 km/h (16 mph) |
| Range | c140 km (87 miles) |
| Armament | Model 32 45 mm (1.77 in) gun, 3x DT 7.62 mm LMGs |
| Armor | 12-22 mm (0.47-0.87 in) |
| Total production | 1 prototype |
Src read more
On tank encyclopedia
T-12. Notice the eight-sided turret, the flat rear and the fact the tracks reach the top of the hull
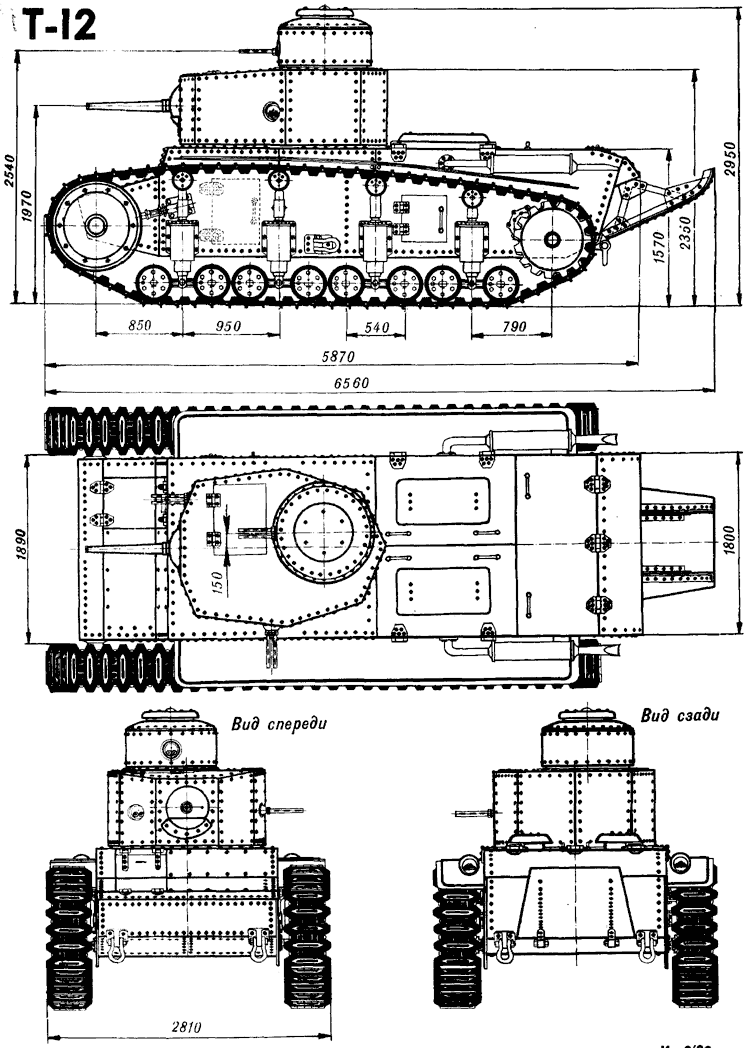
Original plans

A T-12 is posed on by workers and officers. The eight sided turret is very clear in this image

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

