A Chinese copy of the T-54A
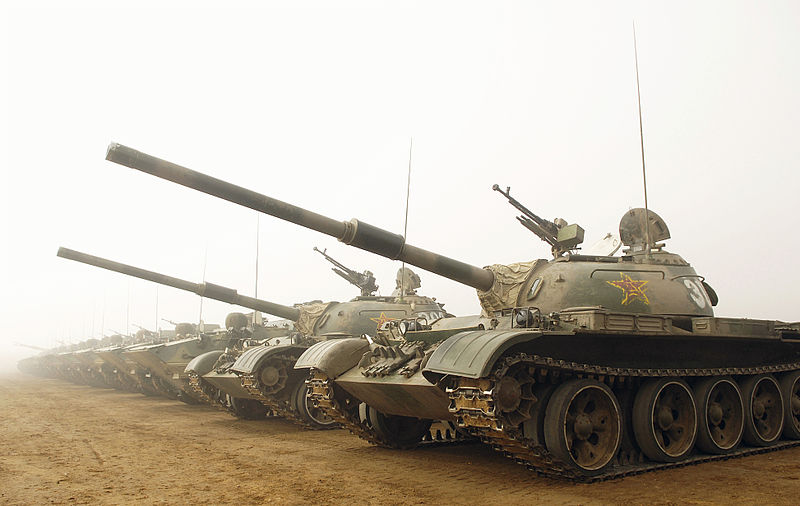
For years, the Type 59 was the backbone of the Chinese Army. Not only it was the biggest PLA tank production so far, spanning until 1985 with nearly ten thousand models and many variants, but also the very basis of several other MBTs, like the light Type 62, the Type 69 and Type 79. The Sino-Soviet Treaty of Friendship, Alliance, and Mutual Assistance helped to setup a first production facility in 1956 in the North of China, tailored to produce the T-54A. The inner Mongolia Factory 617 / Baotou Tank Plant was known later as the modern Inner-Mongolia First Machine Group Company Limited. The latter is credited to have built most of Chinese PLA MBTs as of today, now integrated as the giant Norinco (north industries) group, starting with the Type 59. This was the last Chinese tank built with some Soviet assistance, before the diplomatic relationships were severed. Internally it was called WZ-120.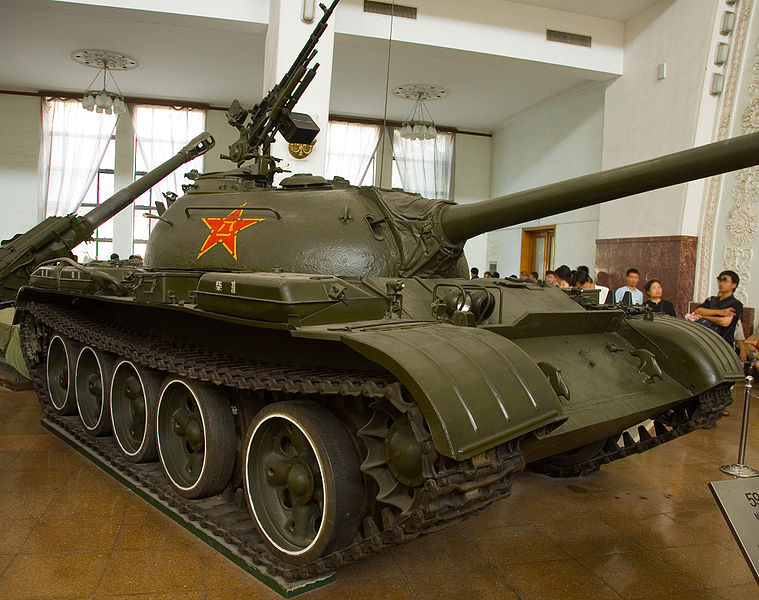
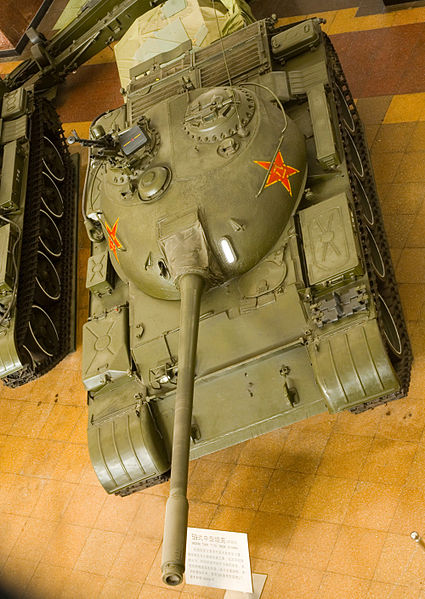
First production preserved at the Beijing Military Museum
Characteristics
Obviously, the Type 59 was a faithful Type 54A replica, internally and externally, with some modifications however. It was simplified in design, without the characteristic IR searchlight and main gun stabilization system. The hull was welded with some 99 mm of armor thickness on fht front slope, and 100 mm for the front turret armor, which had the characteristic decrease in thickness from the base to the top, according to ballistic penetration calculations. The turret floor was non-rotating. The driver, loader, commander and gunner positions were unchanged.Main armament was the 100 mm Type 59 tank gun, a copy of the original D-10TG with its characteristic muzzle fume extractor, with 34 rounds in store, mainly into the hull. Secondary armament comprised a coaxial Type 59T 7.62 mm machine gun, a bow MG manned by the driver from inside the central glacis (3500 rounds in store), and the anti-aircraft heavy machine gun Type 54 12.7 mm over the loader's hatch, apparently also a copy of the DShKM, with 200 rounds in store. The engine was the Model 12150L V-12 liquid cooled diesel, giving 520 hp @ 2000 rpm. The overall weight was also equivalent to the T-54A and road range was about 600 kilometers, with the rear external fuel tanks.
Production and derivatives:
After being developed in 1957-58, Production was geared up the same year mostly with Soviet components, and approved for service in 1959. It lasted until 1985, thanks to the upgraded versions and with Chinese parts. At the beginning the lack of IR searchlight, gun stabilization system, and NBC protection were issues, later compensated by several sets of upgrades, helped by the capture of Soviet tanks, like the T-62 during the course of the Sino-Soviet border conflict of 1969. Many improvements also made on the next Type 69 were retrofitted into the Type 59.Type 59-I
This type introduced the new Type 69-II 100 mm rifled gun, assisted by a laser rangefinder, and hydraulic servo-system and a primitive fire-control system. The engine compartment received an automatic fire suppression system, and rubber track skirt were added. Protection was also improved and apparently led to several sub-variants. Derivatives of this type includes the light Type 62 and the medium Type 69/79. The Type 73 is a turret-less derived version used as an ARV, and armed with a single 12.7 mm heavy MG.Type 59-II
The last production version, internally known as the WZ-120B was indirectly equipped with the famous OTAN L7 gun, via Austria local version, and was known as the 105 mm Type 81 rifled gun (1981). It also received a new radio and a better fire suppression system. The production lasted from 1982 to 1985. The IIA upgrade added to this a thermal sleeve of the gun, composite armor and additional equiments and protection like rubber panels (B59G). It was declined also into the BW120K command version and the ARV. The BW120K is the most ambitious upgrade of the type, with a brand new 120 mm smoothbore gun apparently based on the Leopard II's main Rheinmetall model with a muzzle velocity of 1660 m/s.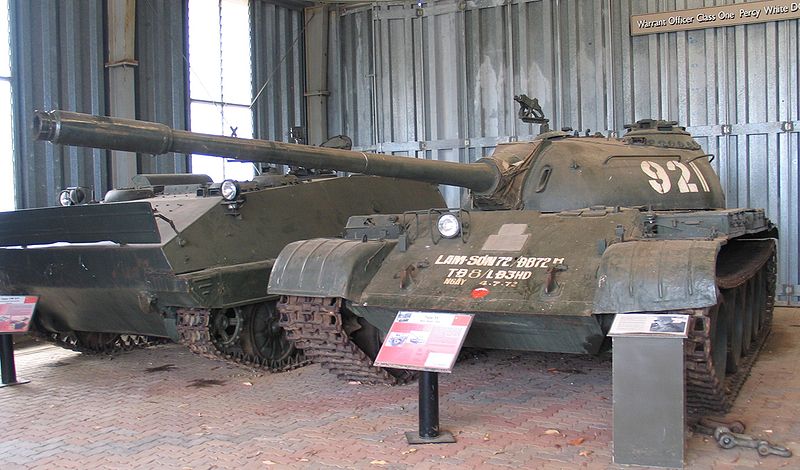
Former NVA type 59 captured by Australian troops now preserved at Puckapunyal museum in Australia
Type 59D
This enhanced version known internally as the WZ-120C was developed in the 1990s to upgrade a large part of the fleet. Part of these, of course, are secret, but includes ERA protection, new 105 mm Type 83-I/A tank gun, passive night vision, and upgraded FCS. Propulsion relies on the 580 hp 12150L7 engine. The gun could fire APFSDS and depleted uranium rounds (efficient about two miles against an equivalent of 600 mm of armor). ATGMs are apparently also carried. The Type 59P is the export version. Sudan also geared up a local production under license as the Al-Zubair 2.Type 59G
This latest upgrade is intended to upgrade the Type 59 to the 3rd generation MBT standard. This package comprises the Type 96G welded turret, redesigned armor on the rear and sides, improved side skirts, and second generation night vision equipment and brand new numeric FCS. It is propelled by a 800 or 730 hp engine. The main armament is now a smoothbore 122 mm capable of firing APFSDS, HEAT, HE-FRAG, and ATGMs through the tube.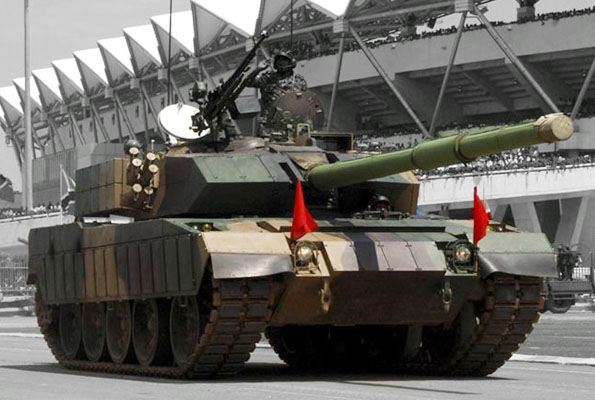
Tanzanian Type 59G, upgraded with the Type 96G turret.
Exports
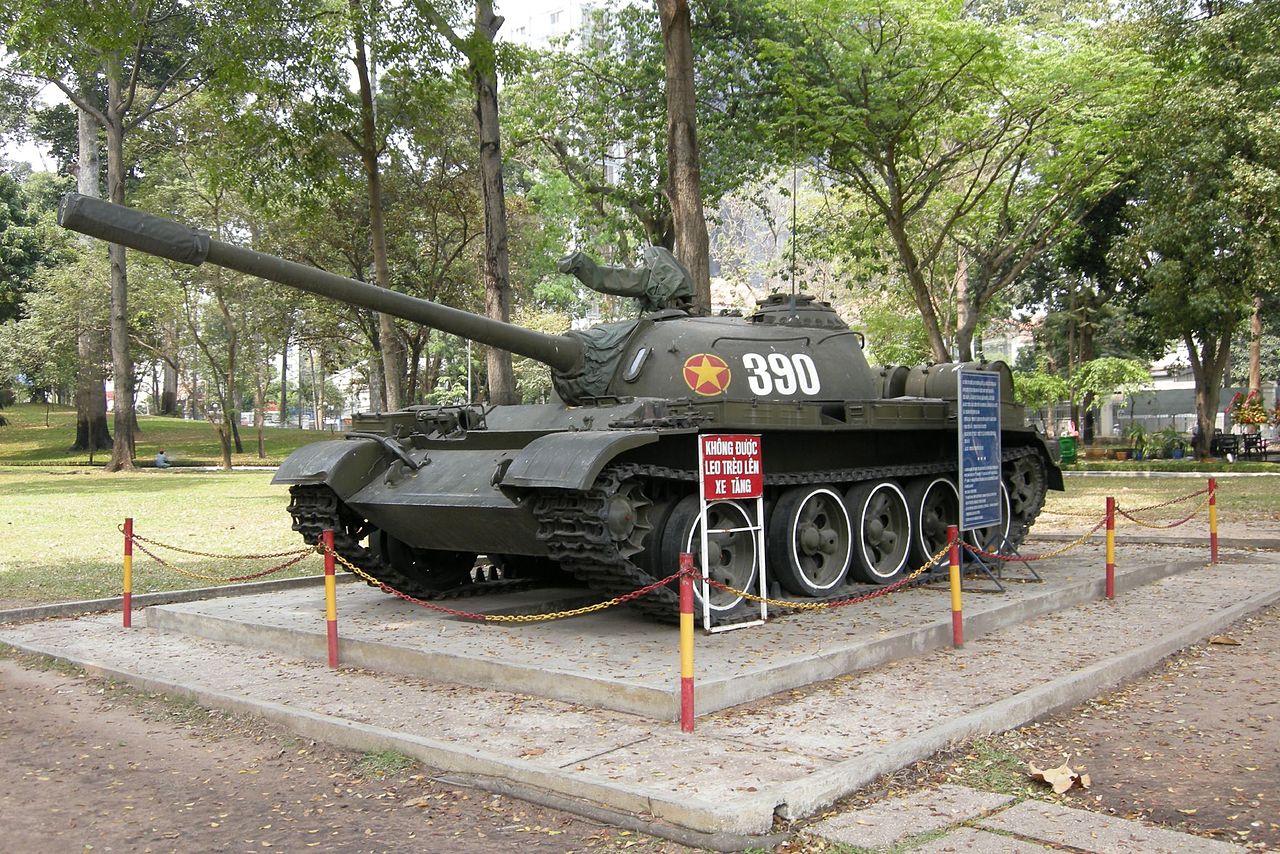
The type 59 was even cheaper than the T-54 and was helped with a strong commonality of parts with the latter. That contributed to a good success on the export market and many local variants and license productions.The most prolific user was Pakistan, which ordered several batches in 1964, 1968, 1973 and 1975 for a total of 1300 in the 1990s. A local variant was built with Chinese assistance, the Al-Zarrar MBT. Production was geared up and as of 2012, 600 are in service. Other users in Asia include Afghanistan (100), Bangladesh (264), Cambodia (200), Sri Lanka (80), Burma (160 Type 59D/D-1), North Korea (600) -which developed the Kok'san SPG, and Vietnam (350).
In Europe, Albania is the only customer of the Type-59 (around 700) now apparently mostly are deactivated. They took part actively in the Albanian-Yugoslav border incident in 1999. In Africa, the Type 59 is currently used by the Democratic Republic of the Congo (20) and Republic of Congo (15), Sudan (10), Tanzania (30 Type 59G), Zambia (20) and Zimbabwe (30).
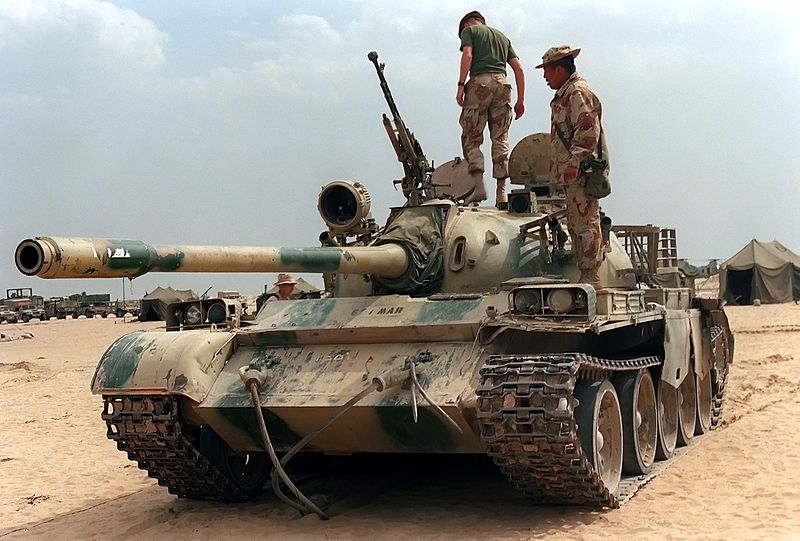
In the Middle East, Iran ordered 300 of these in 1981, delivered until 1984. Some had been modernized to the Safir-74 (T-72Z) standard. Iraq was delivered some 1500 Type 59/69 which took part in the first Gulf war of 1991.
Operational history
The Type 59 participated in the Sino-Soviet border conflict in 1969, but its only apparent active engagement was in the Sino-Vietnamese war of 1979. About 300 tanks of the PLA (with a majority of Type 59s) participated in the offensive against the mountainous north Vietnam, with heavy losses on some occurrences (like the taking of Cao Bằng). However most of the 48 tanks lost to enemy action, mostly infantry RPGs, were light Type 62s. About 5000 upgraded Type 59 are currently in service with the PLA, supplemented by other models. They still constitute the bulk of the armored forces.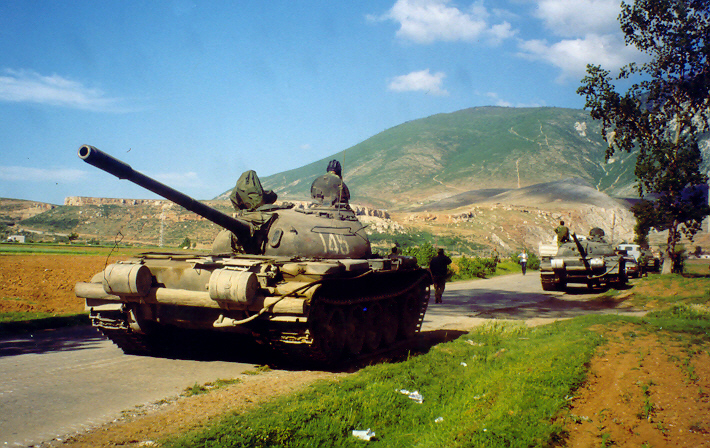
Albanian Type 59 during the Yugoslav border incident of 1999
Links on the Type 59
The Type 59 on wikipedia.
Chinese Type 59 specs. |
|
| Dimensions (L-W-H) | 9m (6.04m without gun) x 3.27m x 2.59m (29'5" (19'8") x 10'7" x 8'5" ft.in) |
| Total weight, battle ready : | 36 Tonnes (40 short tons) |
| Crew : | 4 (Cdr, driver, loader, gunner) |
| Propulsion : | M12150L V-12 diesel 520 hp (390 kW), p/w: 14.4 hp/ton |
| Top speed | 50 km/h (31mph) |
| Max Operational Range | 450 km - 600 km with external tanks |
| Suspension | Torsion bar |
| Armament | Main: 100 mm model 58 Sec: 2 x 7,62mm Type 59T, 1 AA Type 54 12,7mm Mg. |
| Armour : | Glacis front 190 mm, turret front 203 mm, others 20-100 mm. |
| Total production | Around 9500. |
Gallery







Type 59 MBT, early production, 1958.

Congolese Type 59 in operations, 1980s.

Modernized North Korean Type 59 in parade, with MANPADS "Igla" FCS, 1980s.

Chinese Type 59-I, in the 1970s. This version had an improved type 69 gun with a laser rangefinder, and other improvements.

Chinese Type 59-I, with rubber side skirts in the 1980s.

On the North Korean frontier, in winter camouflage.
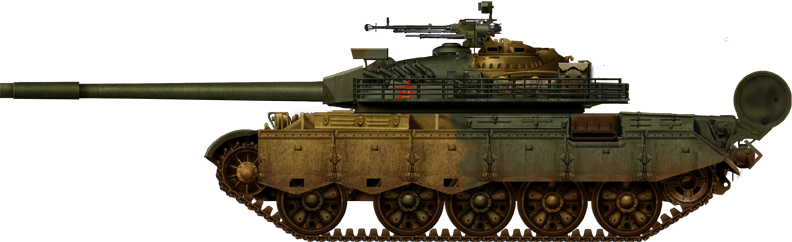
Late Type 59-I, 1990.

Type 59T with its thermal sleeve, location unknown.

Pakistani Type 59-Is stationed at the government installation in Hayatabad near tribal areas, june, 30, 2011

Possibly Iranian Zafir-74 (standard T72Z upgrade for Type 59s) with the 105 mm M68 (Royal ordnance L-7), Slovenian FCS, upgraded engine and ERA.

Type 59-II (factory designation WZ-120B) in the 1980s, equipped with the Austrian-based L7 (Royal Ordinance) 105 mm gun.

Iraqi Type 59-II, 1991 first gulf war
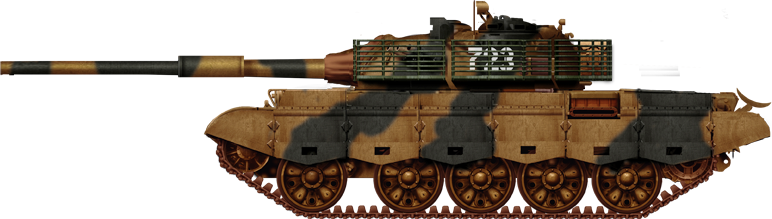
Type 59 IIA (apparently without thermal sleeves), 1980s.

Chinese Type 59-IIA upgraded in the 1990s.

Upgraded Chinese Type 59 IIA with thermal sleeves and new FCS, 2000s.

Chinese Type 59G, the very latest version of the type, here in the Tanzanian army.

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army

