Development
The German Panzerhaubitze 2000 (literally "armored howitzer 2000") or PzH-2000 is the current self-propelled howitzer of the German, Italian, Greek and Dutch armies, and one of the most potent armor system type in the world. It is built by Krauss-Maffei Wegmann (KMW) and Rheinmetall, but with a chain supply network which spans Europe. It took its root in the abandoned PzH 155-1 (SP70) NATO program, joint with Italy and the UK in 1986. The program first started in 1973, had numerous defects and was dropped after comparative trials with the M109 which was adopted instead. However, it was decided in the 1990s to give a successor to thisagingg weapons system.A new Joint Ballistics Memorandum of Understanding for a 52 calibre barrel was passed and the German industry was asked for proposals in accordance of the JBMOU specifications. Wegmann design (merged with Krauss-Maffei in 1998) was chosen in 1996 for the chassis and turret, while Rheinmetall designed the 155 mm 52-calibre JBMOU compliant gun. After trials in the late 1990s, the PzH was ordered (185) for German's rapid reaction force and 410 for the Bundeswehr, before the order was reduced. It was introduced in service in 2000, hence its name. About 345 in all were built to this day (not counting the Italian version), at US$4.5 million apiece. But this can be raised as new customers are interested in the concept, including the US Army in accordance to their tests for a replacement for the M109.
Design
Howitzer
The Rheinmetall 155 mm L52 Artillery Gun is chromium-lined for its entire 8 metre length, with a muzzle brake. Among its greatest specifics, it is using a new modular charge system with six charges (five identical), in order to be combined. This provides the optimal total charge according to the range to the target. The gun can use also a conventional bagged charge system. The primer is loaded separately with a conveyor belt, while the loading/laying/clearing process is fully automated. Maximum range is 30 km (standard L15A2 round) extended to 35 km with base bleed rounds and 40 km and more with self-propelled projectiles.In April 2006 a test featuring Denel V-Lap assisted rounds reach a target at 56 km while in maximal elevation, it can reach 60 km. In Complement, the howitzer can fire SMArt 155 artillery rounds. With 60 rounds in store, the gun could fire three rounds in 9.0 seconds (Burst) and up to 10 round a minute, or five rounds of Multiple Rounds Simultaneous Impact (MRSI). When the whole battalion (34 vehicles) fires in the auto quick-burst mode, it can put to any target 120 rounds in less than 60 seconds. This was therefore in 2010 the fastest and and perhaps longest range artillery system ever devised.
Furthermore in December 2013, Raytheon together with the German Army devised a compatible M982 Excalibur round with extended range and 10 rounds were fired, on targets distant up to 48 km. Therefore this round is about to be accepted in service also by the German Army in 2014.
 Dutch Pzh-2000 in Chura, Afghanistan, 2006
Dutch Pzh-2000 in Chura, Afghanistan, 2006
Chassis
Contrary to the former SP70, the chassis was not an adapted one, but was tailor-made by Wegmann, although sharing some components with the Leopard. Wegmann also designed the turret. Because of the use of a rebalanced drivetrain, the PzH 2000 shares the same amazing cross-country performance with the Leopard, and also armoured side skirts. The drivetrain comprised seven doubled standard rubberized roadwheels per side, and idler at the rear. There is a distinctive gap between the two series of roadwheels. The drive sprockets are at the front, according to the placement of the engine. Tracks are interchangeable with the Leopard 2.Suspensions calls a mix of torsion bars and shock absorbers on each roadwheel pair. The hull is one inch thick, providing some protection against heavy machine guns rounds, small arms fire and splinters. ERA blocks can be fitted all around the turret and part of the chassis depending on the mission. However the fire radius normally prevents the vehicle from any bad encounters with armour.
Powerplant
The engine is a MTU 881 Ka-500 diesel developing 1,000 PS (986 hp or 736 kW), with a power to weight ratio of 17.92 PS/ton. It is coupled with a four-speed Renk HSWL 284 C gearbox. Top speed, on road, is 67 km/h (41 mph) and 45 km/h (28 mph) off-road, and maximal operational range is 420 km (261 miles). There is also a small auxiliary engine that provides energy for the running systems when the diesel is off, C&C systems, turret traverse (which is electric) and crew comfort. The tank is treated NBC with a slight overpressure.Turret
The turret is a boxy structure, with a sloped roof and sides but flat front and rear, which represents approximatively 60% of the whole length of the chassis, and features a rear overhang of around 50 cm. It is fully traversable and the maximum reaches 60° (and depression -2.5°). It uses a phased array radar (placed on the front glacis) to take measurements of the muzzle velocity when firing. The laying data can be transferred in real time (via encrypted radio) from the battery fire direction centre. Coupled with GPS it is so accurate that a suppression fire on moving targets (typically a convoy) can nail down anything moving on a potential 60 to 80 km radius.The servants and crew are situated inside and below, with single piece hatches on the roof. The commander is given a general purpose MG3 roof machine gun. The turret weights 16.5 tons. The fast shell transport system needed special training though, as the system is fully automated and can causes injuries: The loader had 5 seconds to safeguard himself after the charge is loaded and the breech closed. There is a sophisticated projectile picker to shuttle rounds to the flick rammer, and rounds are stored either in tray racks of four on the hull floor or in bins in the back of the turret. There is of course a fume extractor, automatic evacuation of spent shells and an automatic fire extinguisher for the crew compartment and the engine compartment.
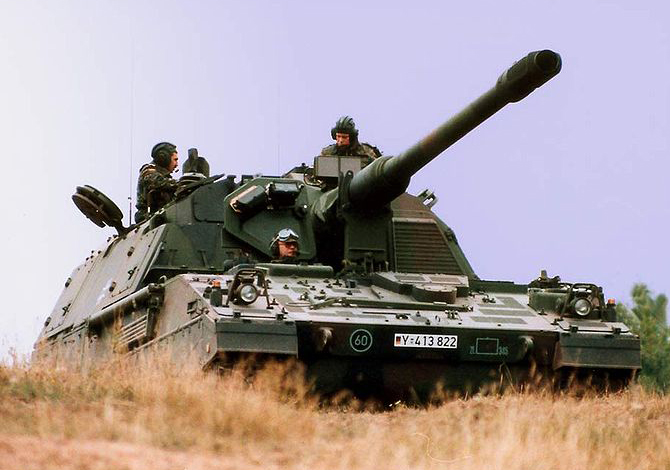

German Bundeswehr Pzh-2000.
Observation & electronics
The autonomous FCS functions are controlled by an EADS MICMOS computer and target engagements can be carried out by a crew of two, including in external remote fire. The fire control data is provided by the ballistics computer, using multiple sensors place on the turret's roof, and the gun is automatically laid and loaded with the right ammo according to the mission's objective and nature of the target, with the right charge to be manually loaded. There is also an optical mechanical backup system. The commander uses a Leica PERI-RTNL 80 panoramic periscope, used for under-armour operations and target designation in direct fire. This system comprised day and night vision channels and a laser rangefinder. The gunner has a Leica PzF TN 80 day/night direct fire sight. The driver is also provided with a night vision periscope.Variants a derivatives
Artillery Gun Module (AGM)
A lighter, air carried version using the gun in a module fitted to a lighter chassis (the M270 MLRS), was developed by Krauss-Maffei.MONARC
A module designed to fit inside German corvettes or a F124 frigate forward bridge weapons bay. It was evaluated by the Deutsche Marine but never put into production so far.DONAR
The export version of the AGM, designed to fit on the ASCOD2 Infantry Fighting Vehicle.Esercito Italiano OTO Melara Pzh-2000
Operators
Germany
The Panzerhaubitze 2000 preliminary program and development also influenced the Italian Palmaria and the British AS90. Production for the Bundeswehr began in 1998 and around 240 are planned to be in service (a first batch of 185 plus 53 others) in the Bundeswehr. The initial total German Army requirement of 450 units was reduced to 260. But the actual fleet is reduced to 185.Italy
Co-production programme with the Consorzio Iveco-Oto Melara. 70 units ordered so far for the Italian Army by KMW and delivered in 2002. The first deliveries of the remaining 68 built in Italy began in May 2007 (until 2009), and in June it entered service, fully operational in 2008.Greece
24 delivered between July 2003 and June 2004.The Netherlands
The Dutch army signed a procurement for 39 units, then 64 in all, but as of today 18 are active, 33 in reserve, and 6 kept for training. The Dutch PzH-2000 were the most tested in combat.Croatia
Croatia signed recently in 2014 an order for 12 vehicles (second-hand), complete modernization and overhaul, spare parts, and training. Delivery is expected in 2015-16.Qatar
24 ordered, deliveries expected to take place from 2014 to 2018.USA
A joint evaluation program took place in USA with the Crusader/Excalibur program but due to the gap between loading procedures and equipments, the commission concluded that too much development was needed to obtain a fully operational compatibility.Australia
The PzH 2000 was a contender in the Australian Land 17 Artillery Replacement Program IC2, but lost the bid to another system.Finland
The Finnish army tested comparatively this vehicle with the 155mm SpGH ZUZANA and the AS-90 "Braveheart" in 1998 but because of costs issues, 155 K 98 field guns were purchased instead.Sweden
Tested a single vehicle, slightly modified. However the Swedish army turned instead to the Archer Artillery system.The Panzerhaubitze 2000 in action
The Dutch Army deployed its PzH 2000 in August and September 2006 against the Talibans in the Kandahar Province, Afghanistan. This was a support mission integrated with the Canadian-led Operation Medusa. It was used afterwards quite extensively during ongoing operations in the area. The vehicles showed however that their NBC system needed to be adapted to the climate. Armour upgrades were applied to the roof to offer some extra protection against mortars shells. Later in 2010, German ISAF force used PzH 2000 extensively, first seeing action in July 2010, providing cover during a damaged armoured vehicle recovery.Sources/Links about the PzH 2000
The PzH 2000 on Wikipedia
PzH 2000 specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 11.7 x 3.6 x 3.1 m 38'5'' x 11'10'' x 10'2'' |
| Total weight, battle ready | 55.8 tons (129,000 lbs) |
| Crew | 5 (driver, commander, gunner, 2 loaders) |
| Propulsion | MTU 881 KA-500 diesel 1000 hp |
| Suspension | Independent torsion bars |
| Speed (road) | 67 km/h (40 mph) |
| Range | 420 km (260 mi) |
| Armament | Rheinmetall 152 mm L/52 gun 7.62mm MG3 machine gun |
| Total production | 345 since 1998. |
Video
Gallery
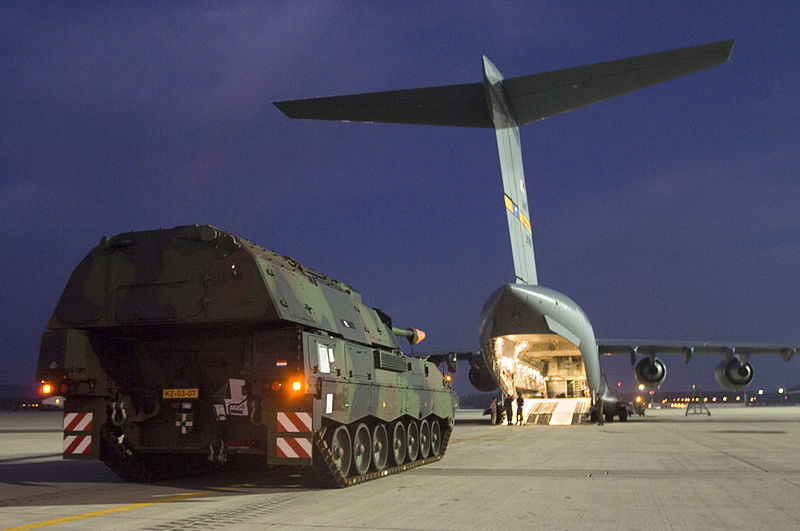
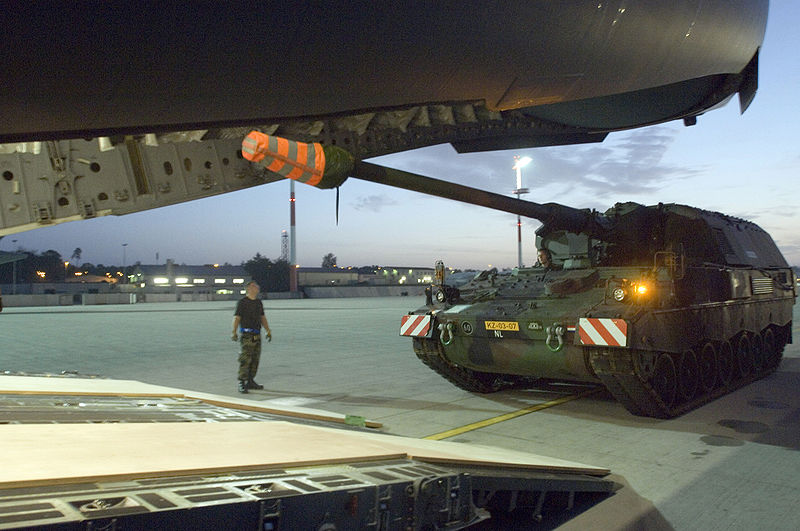
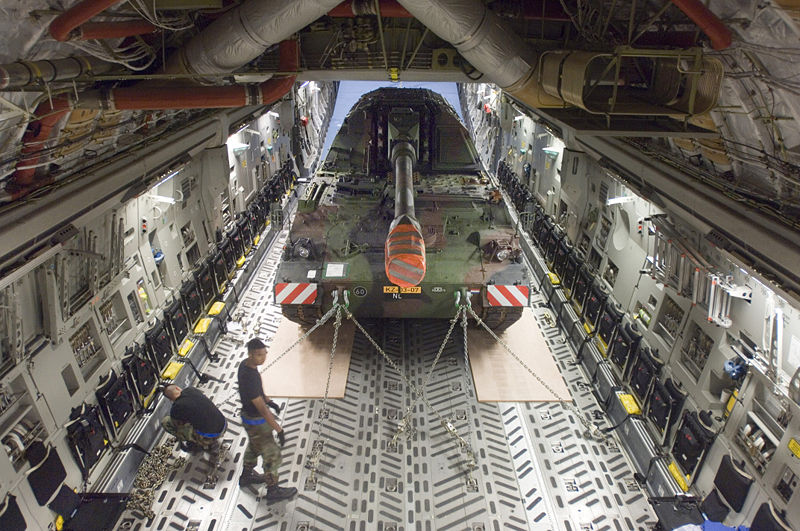
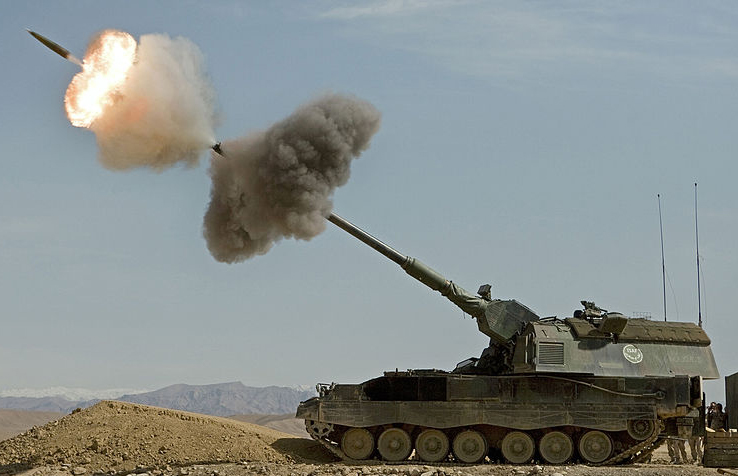
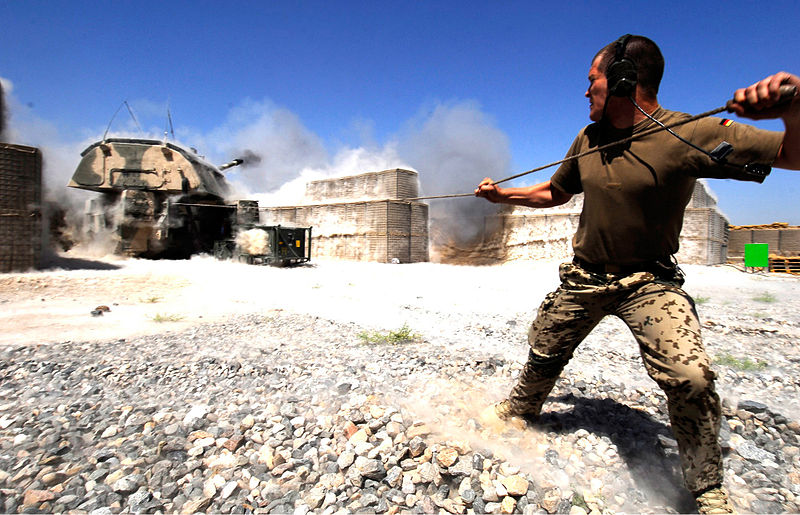
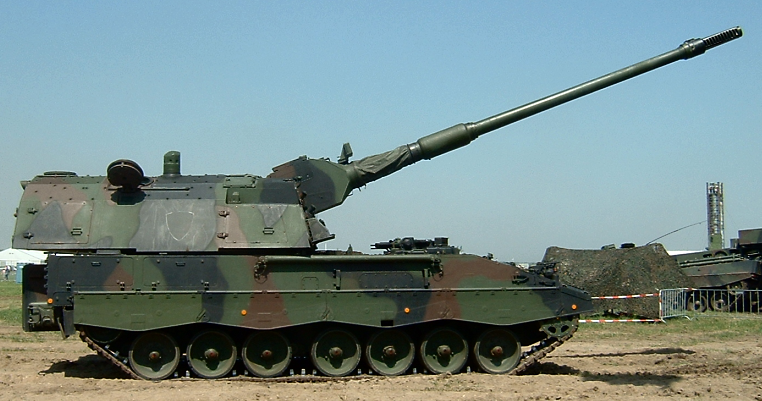
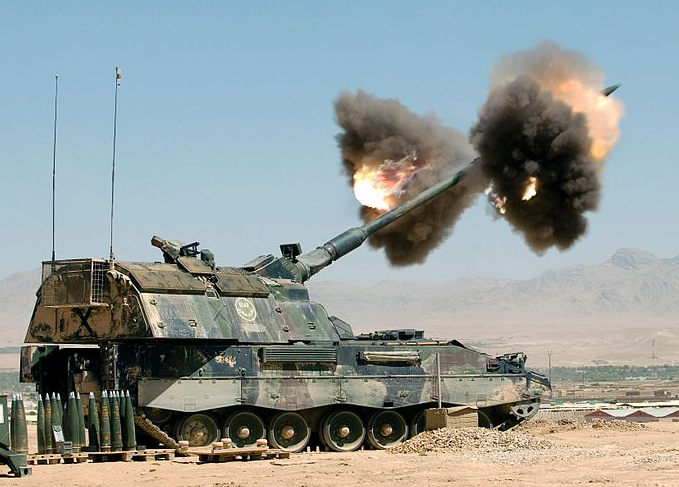
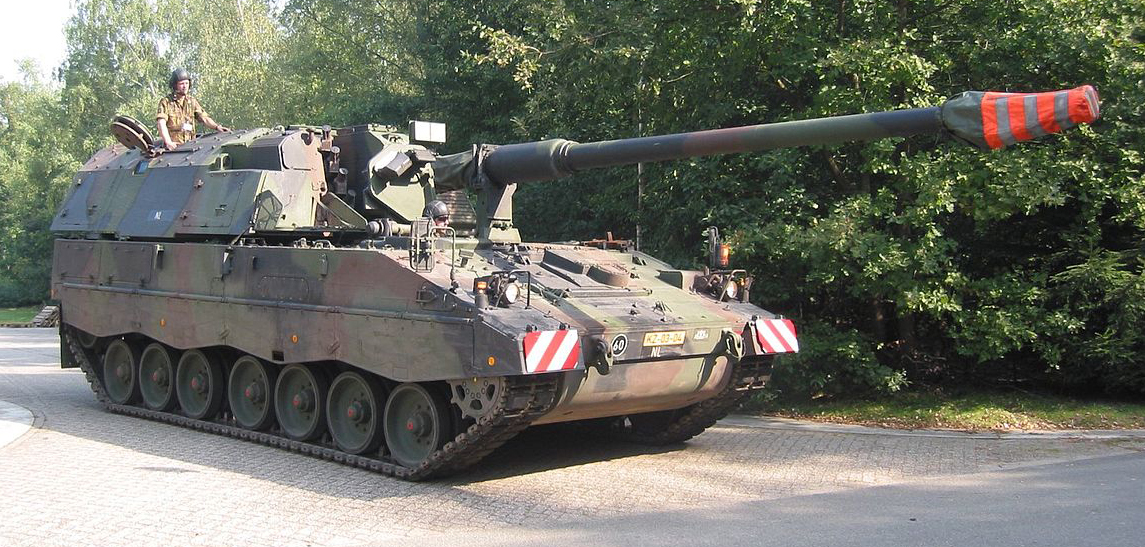
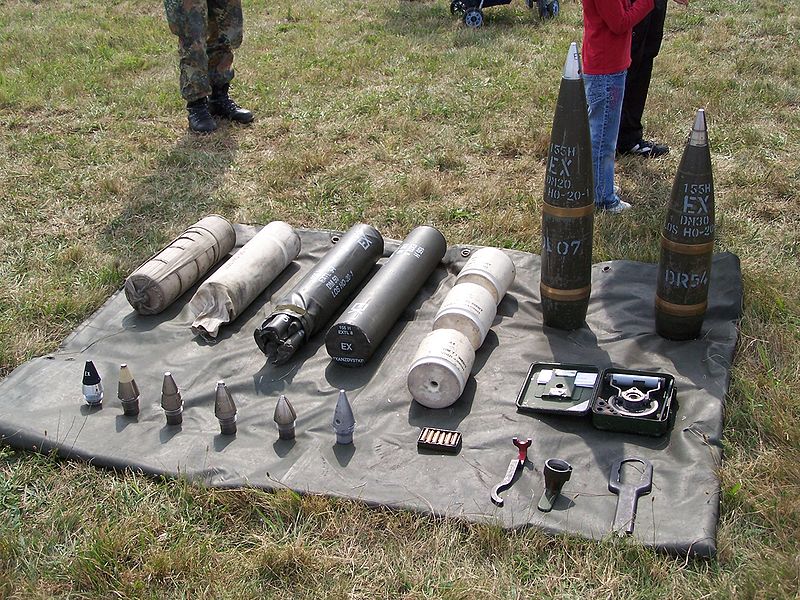
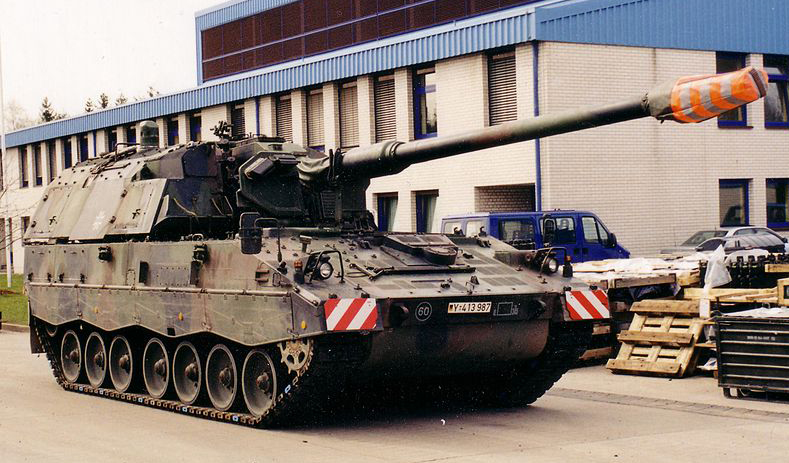














Photo credits: Wikimedia commons.

PzH 2000 from the Bundeswhehr.
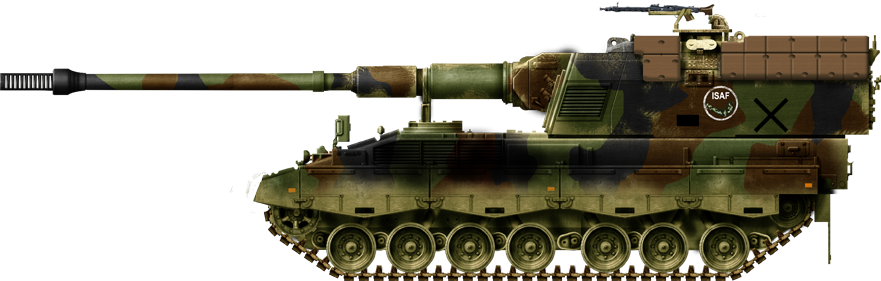
Dutch Pzh 2000, ISAF, Afghanistan, 2010
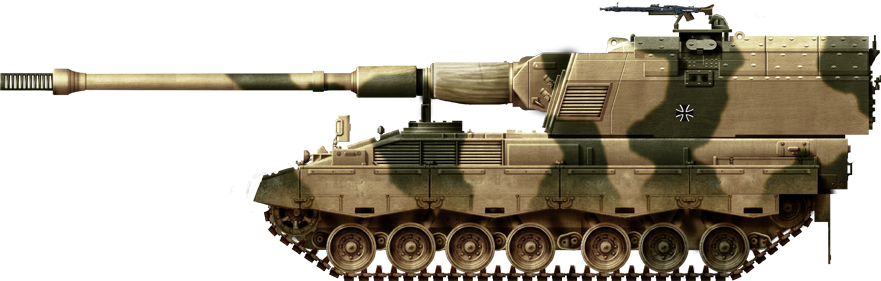
German model in the "Afghan livery", 2010. readmore.

Modern Tanks
Modern MBTs posters

Denel Bagder (2018)

Type 16 MCV (2016)

Gepard 1A2 last rounds 2011

SANDF

Russian AFVs

Main Battle Tanks
