The Flugabwehrpanzer Roland or "marder roland" (abbreviated FlaRakPz-1) was a variant of the marder infantry fighting vehicle, modified to carry roland short range ground-air missiles. The latter was a successful Franco-German missile which appeared in 1977 at the same time the first prototype of the Vehicle prototype was completed. 140 were built until 1982, in service with the Bundeswehr. They were discarded in 2003-2005 and the Brazilan army also operated four of these from 1979 to 2001.
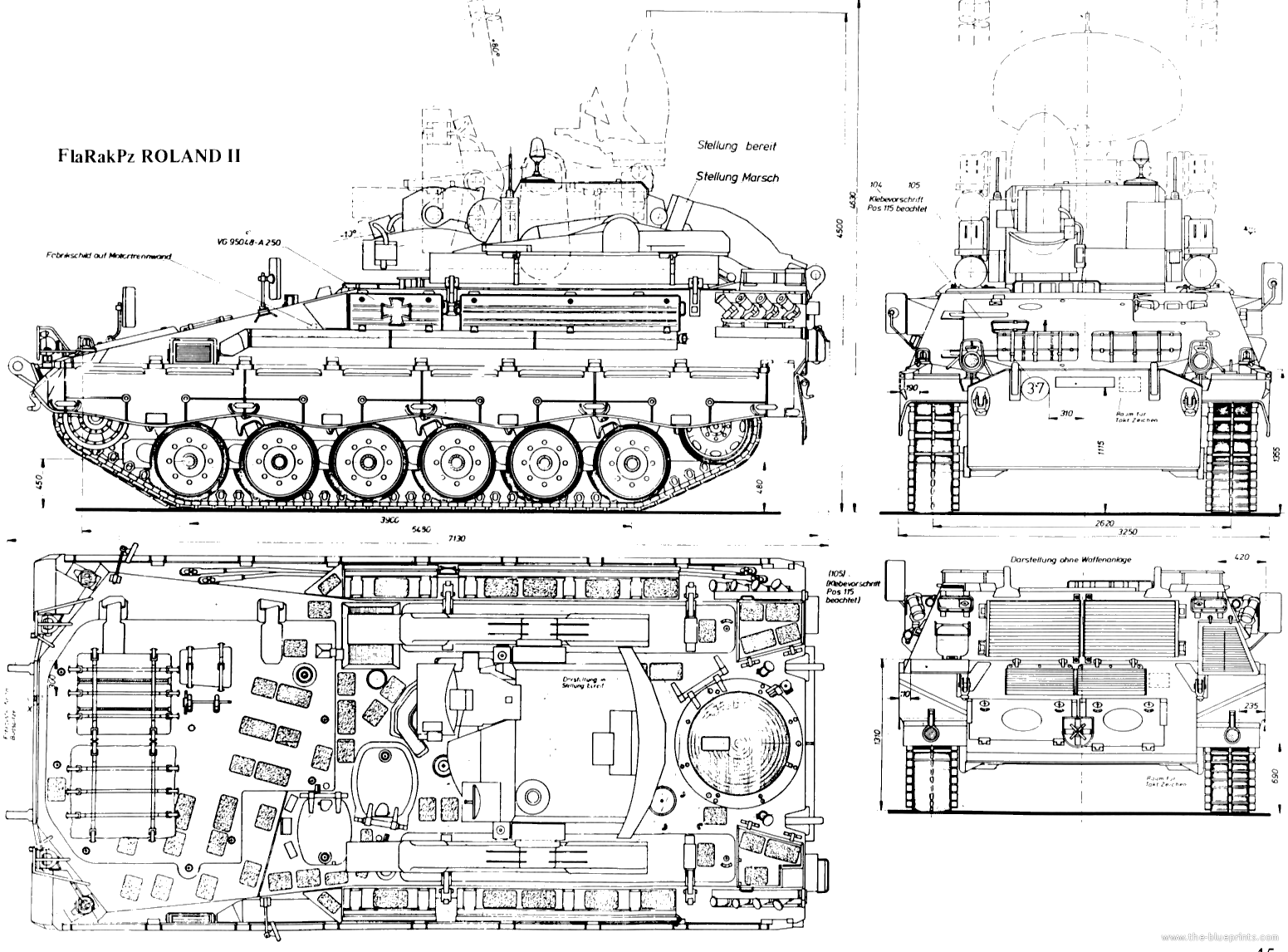
FlaRakPz 1 ROLAND II plans, 1977
The development of the Roland weapon system started to answer such a need. The name was chosen for its bi-national flavour as Roland was the most famous Paladin knight of Emperor Karl the Grosse or Charlemagne). This bilateral technology project was another major armament cooperation between Germany and France following the Elysée Treaty of 1963. The same also led to develop the Europanzer. A government contract was signed by October 1964. On the German side, Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB) in Ottobrunn was contracted to work together with French Aérospatiale, Chatillon. This joint management company became Euromissile G.I.E. based in Fontenay-aux-Roses (now Europe' major missile manufacturer). A management and steering committee was created in 1969 to pilot the project in both defense ministries, the BPFA in Rueil-Malmaison.
The program proved more complex than anticipated and more time-consuming and costly, until the USA joined the program as a partner in 1975. It happened they were also interested to provide a robust SPAAML system for its own division. More extensive trilateral testing campaigns led to modifications, many now aimed at electronic jamming measures, all time availability, repairs and maintenance, measuring and testing, and the whole training program with hit, including state of the art simulators. The final program ended with the introduction in service for the Roland 1 missile, and various platforms, mobile or fixed, were looked upon.
Roland 2 was also proposed in the early 1980s to be installed on the Leopard 1 tank chassis, as there was a similar expected Dutch army requirement. But the final vehicle carrier in France was the AMX-30R, and later in West Germany, KWM's Marder IFV was chosen as a platform.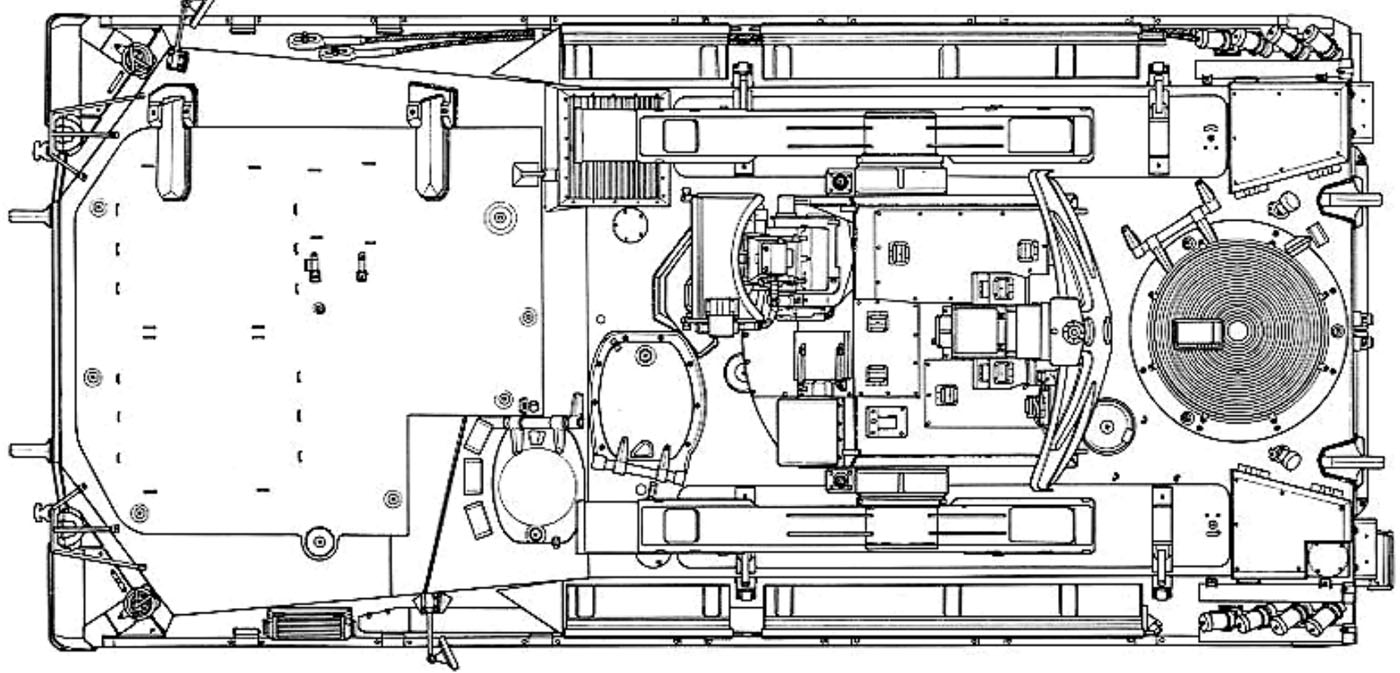
FlaRakPz 1 ROLAND II top
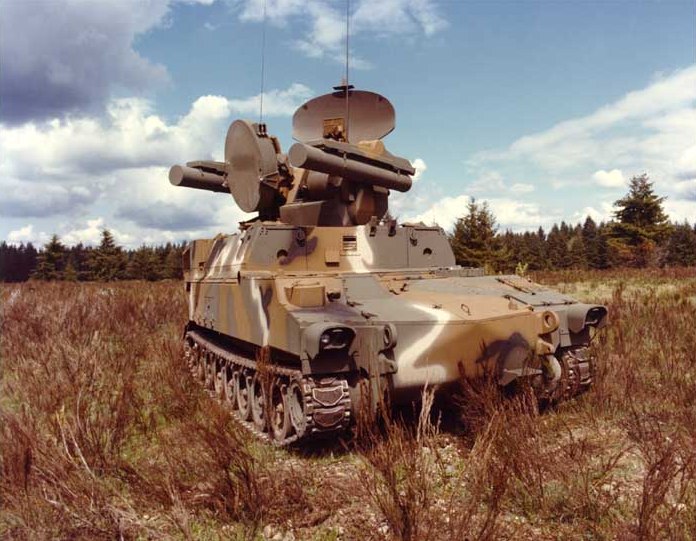
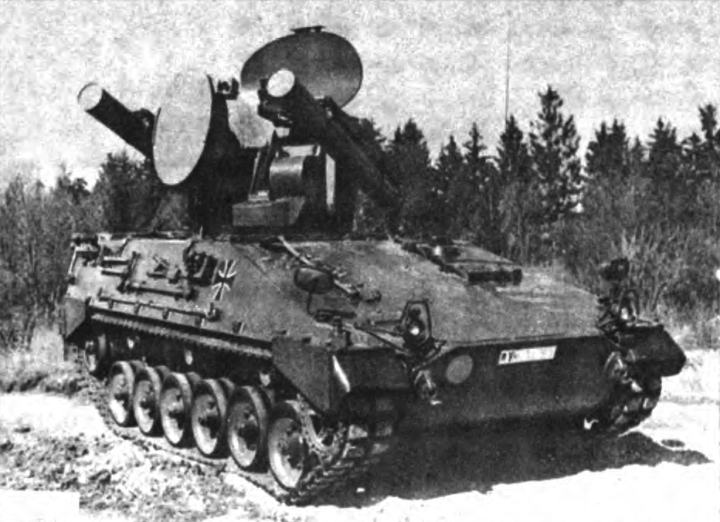
The recent Marder infantry fighting vehicle was chosen as a platform. So it kept its original configuration: Engine at the front-right, driver to the left, and main fighting compartment behind. The main difference was that the original turret was removed and replace by the Roland mount, a twin-arm turret system with foldable guidance radar. Spare missiles were in the former troop compartment.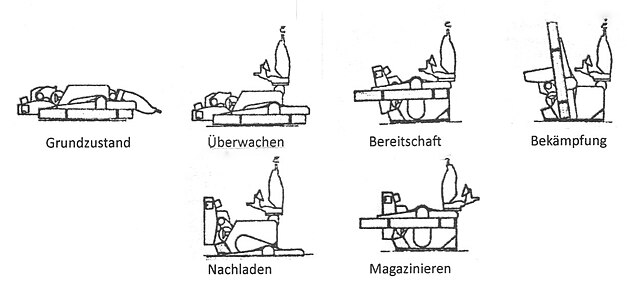
Various configurations with the popup turret, radar, launcher.
The Marder Roland is essentally a Marder chassis with its turret replaced by a tailored two-arms Roland missile launcher. The turret is unmanned, and topped with a folding guidance radar. The hull presents the exact same caracteristic as the Marder, with the drive on the right, side opening hatch and three periscopes, engine compartment and transmission at his left, main fighting compartment behind. The vehicle even kept its rear opening hatches used to load missiles. There was another access hatch behing him on the flat section for the missile operator (replacing the gunner), and the commander was located on a left side position behind the engine, with his own set of periscopes. It's not an easy position when buttoned-up, low and subect of interference by the missile launcher above and behind. The Marder Roland had the same protection level as the standard Marder machenized infantry combat vehicle, with a basic welded steel armor protecting from small arms fire and shrapnel, all around. The frontal arc was thicker in order to resist autocannon fire at a distance. The launcher, radar and guidance systems are more vulnerable than the chassis in this occurrence. No further armour package were proposed, as no Flugabwehrpanzer Roland 1A2 standard was defined. In theory, the chassis could still receive the same armour package of the Marder 1A3, with some modifications. But the launcher remains unprotected.
The Marder Roland had the same protection level as the standard Marder machenized infantry combat vehicle, with a basic welded steel armor protecting from small arms fire and shrapnel, all around. The frontal arc was thicker in order to resist autocannon fire at a distance. The launcher, radar and guidance systems are more vulnerable than the chassis in this occurrence. No further armour package were proposed, as no Flugabwehrpanzer Roland 1A2 standard was defined. In theory, the chassis could still receive the same armour package of the Marder 1A3, with some modifications. But the launcher remains unprotected.  The FlaRakPz-1 either had no smoke projectors unlike the regular Marder, and was far more vulnerable on the battlefield. However there was a collective NBC protection in standard for the crew anf automatic fire extinguishers in the driver, main combat and missile storage as well as engine compartments.
The FlaRakPz-1 either had no smoke projectors unlike the regular Marder, and was far more vulnerable on the battlefield. However there was a collective NBC protection in standard for the crew anf automatic fire extinguishers in the driver, main combat and missile storage as well as engine compartments.

Roland Missile
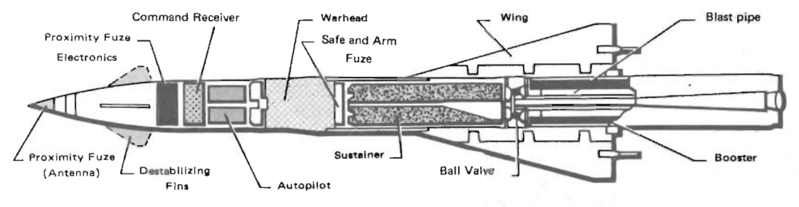
Missile diagram
The Marder Roland uses the "Roland 2" type all weather missile system. The launcher has two missiles arms ready to fire when underway in operations. Eight more missiles are carried inside the rear compartment. Targets are acquired via rotating search radar (16.5 km range) providing updates every second (full 360). The Roland missiles use radio command guidance and within, two engagement modes switchable even after launch:
-Manual guidance using an optical tracker
-Automated guidance via the fire control radar.
In addition the vehicle is given an IFF system and it is setup to alco combat helicopters and low altitude jet aircraft. The Roland 2 missile is limited to Mach 1.2 and 5.5 km cailing, its range starting as short as 500 m, up to 6.3 km. Despite having two arms, only one target can be engaged at a time. It means that the vehicle must wait before launching another missile.
There is a single channel guidance and single operator. The relaunch process is automatic, performed when the arms are lowered, horizontal, over the reloading traps, allowing two new tubes to be attached on the arms after the empty tubes had been jettisoned. This way the crew stay protected for all the engagement. For better accuracy the vehicle also was stopped when launching its missiles.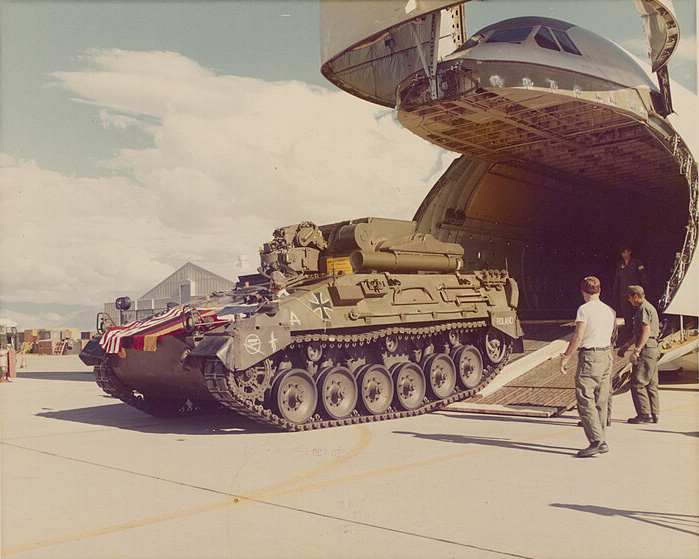
Roland SAM Offloaded from C-5A Aircraft at White Sands Missile Range 1976
After the FlaRakPz's was declared fully operational, the Bundeswehr started to received these systems from 1981 onwards. It was in parallel to remaining developments and an ad hoc logistical component. Meanwhile the Roland was also adopted for ground, mobile shelters for the Luftwaffe and fixed onboard for the navy, with an introduction delayed due to financing the Tornado procurement. The FlaRakRad program bounced again in 1987, after a cooperative procurement was done with the US and the Patriot program, with promises of integration of both systems, as agreed with the USA in 1983. This was the basis for the Roland anti-aircraft command post (FGR) introduced in 1988, resuing most of the hardware and configurations developed for the Patriot.

US XM795 Roland/M109 Paladin in trials
In 1984 also initial work started for the combat performance enhancement (KWS) and introduction of an infrared/laser sight as well a better computer, and better Roland missile. However by 1992 following security policy changes due to the end of the cold war stopped it and started the clock for the service end of the Roland Marder. It was in the end reduced to a service life extension or SLEP (NDV in Germany).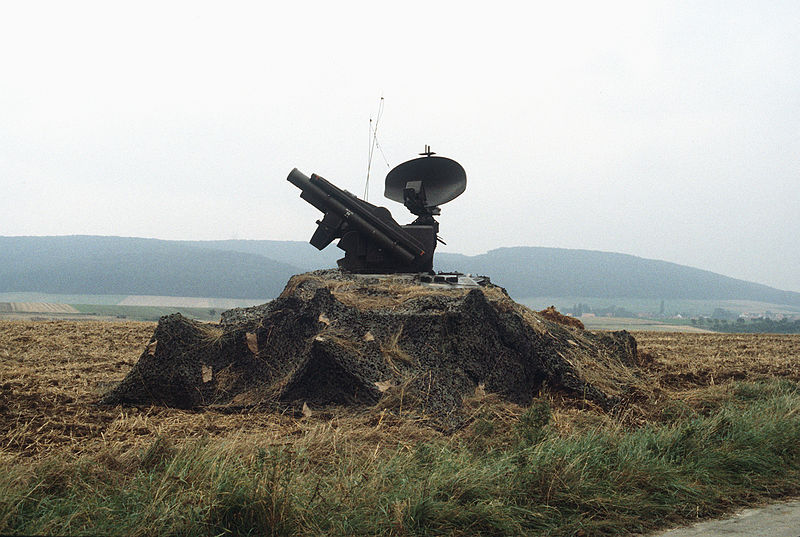
Roland II in heavy camouflage, 2003
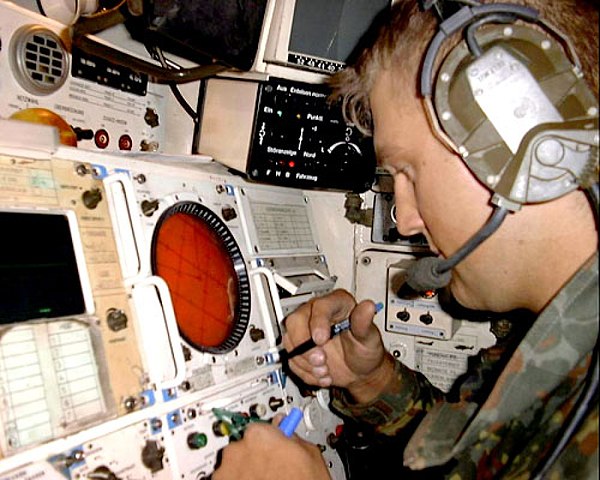

Missile Operator, 2003
140 vehicles were procured to the Bundeswehr at Corps-level air defense, and in three regiments (36 vehicles in six batteries of 6 vehicles each). One regiment assigned to each of the three army corps thus had batteries, and a single battalion had 18 vehicles, three of six for the LANDJUT Corps. The Luftwaffe required 200 Roland 2 for close-in defense of airfields and interim for the MIM-23 HAWK SAM. 95 shelter mounted Rolands were installed on MAN 8×8 trucks by the mid-1980s, 27 used by USAF airbases in Germany.
In 1998–99 ten MAN 6×6 trucks variants were made air-transportable in the Transall C-160, to be deployed with the German rapid reaction forces. The German Navy procured 20 truck-mounted shelter systems for its own naval air bases. In the spring of 1991, the FlaRakRad of FlaRakGrp 42 was relocated to Turkey, to protect NATO bases there. Issues with this led to the short-term development of a special body (FlaRakRad lvb) to be transported by a Transall C-160, introduced from 1994. There was no more need to transport the vehicle itself.
Due to the end of the cold war, new operational priorities meant upgrade programs were cancelled and SLEP was partially implemented until systems are scheduled to be phased out, in the three branches of the armed forces, from 2002. The Luftwaffe started in 2003 in anticipation to the Medium Extended Air Defense System still under development and the Roland was retired from the Bundeqwehr in 2005.
Indeed by February 2003 the Bundeswehr cancelled the planned upgrade and announced it would phase-out all of its Roland systems. The Army had planned to replace the Roland with the new and much more capable LFK NG, until it was cancelled in 2012 with the Short Range Air Defense program given to the Luftwaffe alone. A battery of shelter-mounted ROLAND 2 and its Fire Direction Centre were given to Slovenia given the tensions in 2014.
Since the 2022 invasion of Ukraine, some experts asks of the usefulness of procuring the Ukrainian with the mothballed fleet of Marder Rolands. However there are contrary arguments in Germany and no plan was made of yet. The age of the system, now 45 years old, and complete lack of transfers of the Marder to Ukraine yet, as the Bradley had priority. But this could change: Germany ordered in September 2023 forty Marder combat vehicles for Ukraine, all stock vehicle, duly overhauled and refurbished. A long process compunded by training on a vehicle quite different from the Bradley. Only future will tell.
Development
In the 1970s, the Bundeswehr depended on US systems for organic division protection. The study was initiated to fully replace the towed Bofors 40 mm guns systems and Contraves Super Fledermaus fire control systems. Already in 1962, the Bundeswehr's poor answer for its divisions anti-air protection led to devise a program in cooperation with France, the Roland program.The Roland Program

FlaRakPz 1 ROLAND II plans, 1977
The development of the Roland weapon system started to answer such a need. The name was chosen for its bi-national flavour as Roland was the most famous Paladin knight of Emperor Karl the Grosse or Charlemagne). This bilateral technology project was another major armament cooperation between Germany and France following the Elysée Treaty of 1963. The same also led to develop the Europanzer. A government contract was signed by October 1964. On the German side, Messerschmitt-Bölkow-Blohm (MBB) in Ottobrunn was contracted to work together with French Aérospatiale, Chatillon. This joint management company became Euromissile G.I.E. based in Fontenay-aux-Roses (now Europe' major missile manufacturer). A management and steering committee was created in 1969 to pilot the project in both defense ministries, the BPFA in Rueil-Malmaison.
The program proved more complex than anticipated and more time-consuming and costly, until the USA joined the program as a partner in 1975. It happened they were also interested to provide a robust SPAAML system for its own division. More extensive trilateral testing campaigns led to modifications, many now aimed at electronic jamming measures, all time availability, repairs and maintenance, measuring and testing, and the whole training program with hit, including state of the art simulators. The final program ended with the introduction in service for the Roland 1 missile, and various platforms, mobile or fixed, were looked upon.
Roland 2 was also proposed in the early 1980s to be installed on the Leopard 1 tank chassis, as there was a similar expected Dutch army requirement. But the final vehicle carrier in France was the AMX-30R, and later in West Germany, KWM's Marder IFV was chosen as a platform.
Design

FlaRakPz 1 ROLAND II top
The recent Marder infantry fighting vehicle was chosen as a platform. So it kept its original configuration: Engine at the front-right, driver to the left, and main fighting compartment behind. The main difference was that the original turret was removed and replace by the Roland mount, a twin-arm turret system with foldable guidance radar. Spare missiles were in the former troop compartment.
Hull and general layout

Various configurations with the popup turret, radar, launcher.
The Marder Roland is essentally a Marder chassis with its turret replaced by a tailored two-arms Roland missile launcher. The turret is unmanned, and topped with a folding guidance radar. The hull presents the exact same caracteristic as the Marder, with the drive on the right, side opening hatch and three periscopes, engine compartment and transmission at his left, main fighting compartment behind. The vehicle even kept its rear opening hatches used to load missiles. There was another access hatch behing him on the flat section for the missile operator (replacing the gunner), and the commander was located on a left side position behind the engine, with his own set of periscopes. It's not an easy position when buttoned-up, low and subect of interference by the missile launcher above and behind.
Protection
 The Marder Roland had the same protection level as the standard Marder machenized infantry combat vehicle, with a basic welded steel armor protecting from small arms fire and shrapnel, all around. The frontal arc was thicker in order to resist autocannon fire at a distance. The launcher, radar and guidance systems are more vulnerable than the chassis in this occurrence. No further armour package were proposed, as no Flugabwehrpanzer Roland 1A2 standard was defined. In theory, the chassis could still receive the same armour package of the Marder 1A3, with some modifications. But the launcher remains unprotected.
The Marder Roland had the same protection level as the standard Marder machenized infantry combat vehicle, with a basic welded steel armor protecting from small arms fire and shrapnel, all around. The frontal arc was thicker in order to resist autocannon fire at a distance. The launcher, radar and guidance systems are more vulnerable than the chassis in this occurrence. No further armour package were proposed, as no Flugabwehrpanzer Roland 1A2 standard was defined. In theory, the chassis could still receive the same armour package of the Marder 1A3, with some modifications. But the launcher remains unprotected.  The FlaRakPz-1 either had no smoke projectors unlike the regular Marder, and was far more vulnerable on the battlefield. However there was a collective NBC protection in standard for the crew anf automatic fire extinguishers in the driver, main combat and missile storage as well as engine compartments.
The FlaRakPz-1 either had no smoke projectors unlike the regular Marder, and was far more vulnerable on the battlefield. However there was a collective NBC protection in standard for the crew anf automatic fire extinguishers in the driver, main combat and missile storage as well as engine compartments.
Powerplant and Performances
The Propulsion is assumed by a robust MTU MB 833 Ea-500 diesel engine 441 kW (591 hp), same as the Marder, coupled with a RENK HSWL 194 transmission. The Suspension consists of Torsion bars are shock absorbers on rearmost and forward axles. There are six doubled roadhweels, the drive sprockets are forward, idler aft. Top speed would be at best 70 km/h (40 mph) and Range 520 km based on a 652 L (172 US gal) fuel capacity. It provides good all terrain mobility, but the vehicle is not amphibious and tactical mobility (air transport) quite limited to US heavy lift command assets.Armament: The Roland Missile

Roland Missile

Missile diagram
The Marder Roland uses the "Roland 2" type all weather missile system. The launcher has two missiles arms ready to fire when underway in operations. Eight more missiles are carried inside the rear compartment. Targets are acquired via rotating search radar (16.5 km range) providing updates every second (full 360). The Roland missiles use radio command guidance and within, two engagement modes switchable even after launch:
-Manual guidance using an optical tracker
-Automated guidance via the fire control radar.
In addition the vehicle is given an IFF system and it is setup to alco combat helicopters and low altitude jet aircraft. The Roland 2 missile is limited to Mach 1.2 and 5.5 km cailing, its range starting as short as 500 m, up to 6.3 km. Despite having two arms, only one target can be engaged at a time. It means that the vehicle must wait before launching another missile.
There is a single channel guidance and single operator. The relaunch process is automatic, performed when the arms are lowered, horizontal, over the reloading traps, allowing two new tubes to be attached on the arms after the empty tubes had been jettisoned. This way the crew stay protected for all the engagement. For better accuracy the vehicle also was stopped when launching its missiles.
Joint Patriot program and 1990s SLEP

Roland SAM Offloaded from C-5A Aircraft at White Sands Missile Range 1976
After the FlaRakPz's was declared fully operational, the Bundeswehr started to received these systems from 1981 onwards. It was in parallel to remaining developments and an ad hoc logistical component. Meanwhile the Roland was also adopted for ground, mobile shelters for the Luftwaffe and fixed onboard for the navy, with an introduction delayed due to financing the Tornado procurement. The FlaRakRad program bounced again in 1987, after a cooperative procurement was done with the US and the Patriot program, with promises of integration of both systems, as agreed with the USA in 1983. This was the basis for the Roland anti-aircraft command post (FGR) introduced in 1988, resuing most of the hardware and configurations developed for the Patriot.

US XM795 Roland/M109 Paladin in trials
In 1984 also initial work started for the combat performance enhancement (KWS) and introduction of an infrared/laser sight as well a better computer, and better Roland missile. However by 1992 following security policy changes due to the end of the cold war stopped it and started the clock for the service end of the Roland Marder. It was in the end reduced to a service life extension or SLEP (NDV in Germany).
Operational Service

Roland II in heavy camouflage, 2003

Missile Operator, 2003
140 vehicles were procured to the Bundeswehr at Corps-level air defense, and in three regiments (36 vehicles in six batteries of 6 vehicles each). One regiment assigned to each of the three army corps thus had batteries, and a single battalion had 18 vehicles, three of six for the LANDJUT Corps. The Luftwaffe required 200 Roland 2 for close-in defense of airfields and interim for the MIM-23 HAWK SAM. 95 shelter mounted Rolands were installed on MAN 8×8 trucks by the mid-1980s, 27 used by USAF airbases in Germany.
In 1998–99 ten MAN 6×6 trucks variants were made air-transportable in the Transall C-160, to be deployed with the German rapid reaction forces. The German Navy procured 20 truck-mounted shelter systems for its own naval air bases. In the spring of 1991, the FlaRakRad of FlaRakGrp 42 was relocated to Turkey, to protect NATO bases there. Issues with this led to the short-term development of a special body (FlaRakRad lvb) to be transported by a Transall C-160, introduced from 1994. There was no more need to transport the vehicle itself.
Due to the end of the cold war, new operational priorities meant upgrade programs were cancelled and SLEP was partially implemented until systems are scheduled to be phased out, in the three branches of the armed forces, from 2002. The Luftwaffe started in 2003 in anticipation to the Medium Extended Air Defense System still under development and the Roland was retired from the Bundeqwehr in 2005.
Indeed by February 2003 the Bundeswehr cancelled the planned upgrade and announced it would phase-out all of its Roland systems. The Army had planned to replace the Roland with the new and much more capable LFK NG, until it was cancelled in 2012 with the Short Range Air Defense program given to the Luftwaffe alone. A battery of shelter-mounted ROLAND 2 and its Fire Direction Centre were given to Slovenia given the tensions in 2014.
Since the 2022 invasion of Ukraine, some experts asks of the usefulness of procuring the Ukrainian with the mothballed fleet of Marder Rolands. However there are contrary arguments in Germany and no plan was made of yet. The age of the system, now 45 years old, and complete lack of transfers of the Marder to Ukraine yet, as the Bradley had priority. But this could change: Germany ordered in September 2023 forty Marder combat vehicles for Ukraine, all stock vehicle, duly overhauled and refurbished. A long process compunded by training on a vehicle quite different from the Bradley. Only future will tell.
Flugabwehrpanzer Roland | |
| Total weight, battle ready | c29t |
| Lenght/Width/Height | 6.79 m x 3.24 m x 2.98 m |
| Crew | 3: Driver, Cdr, Operator |
| Propulsion | MTU MB 833 Ea-500 diesel engine 441 kW (591 hp) |
| Protection | Chassis 8-25 mm protection |
| Suspension | Torsion Bars |
| Speed (road) | 70 km/h (40 mph) |
| Range | 520 km () 652 L (172 US gal) |
| Armament | 2x Roland 2 SAM, 8 reloads. |
| Production | 140 (no longer in service) |
Gallery
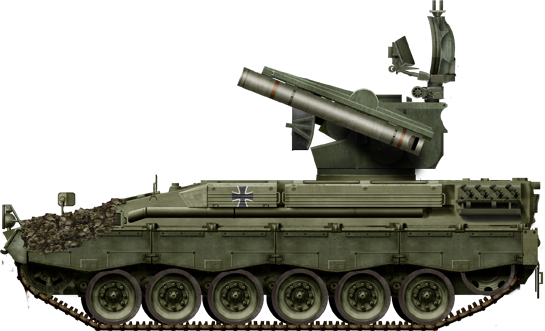
Early vehicle in plain olive green
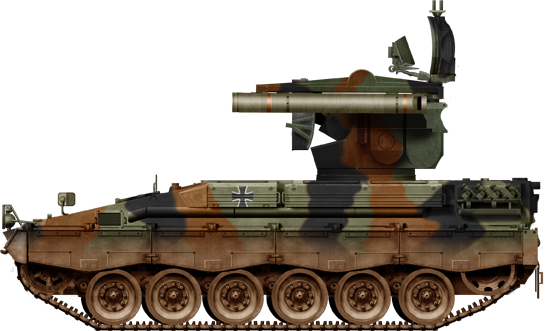
Camouflaged vehicle in the 2000s, prior to retirement
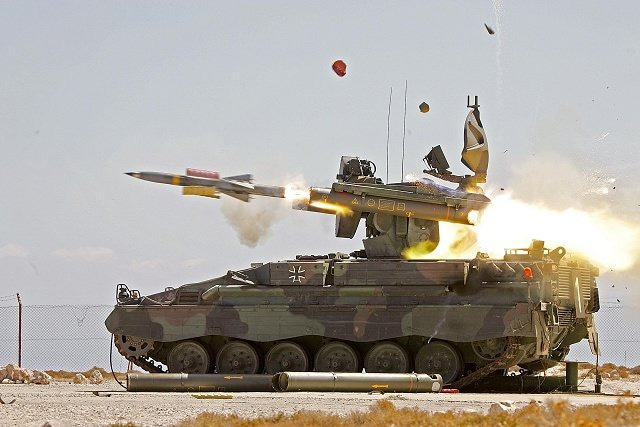

Firing
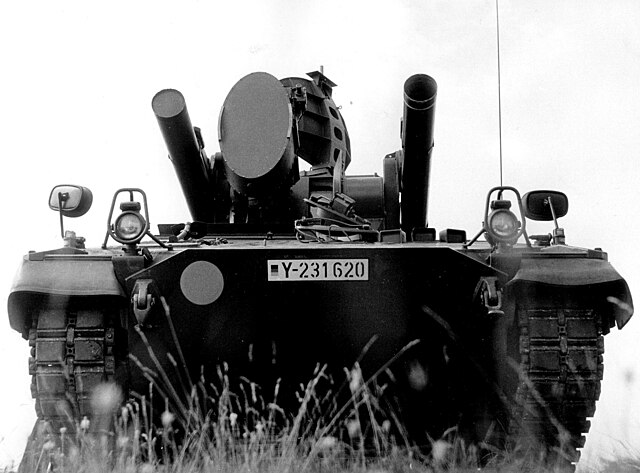

Front
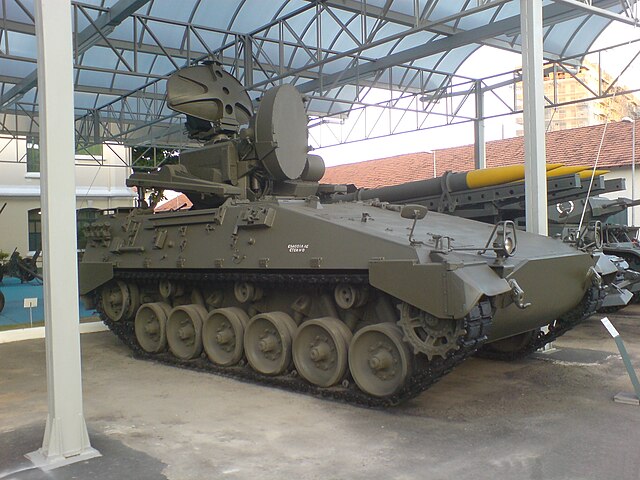

Other photo of the Marder Roland
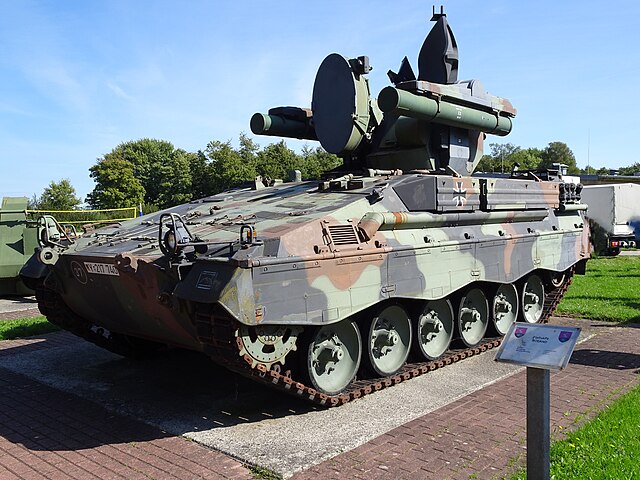

Roland in 2018
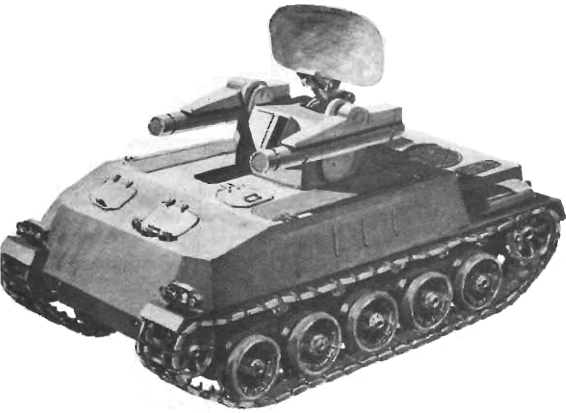

US Army artist view, US Army Roland program

Roland 2 SAM US FY1976 procurement Picture
At Panzermuseum Munster
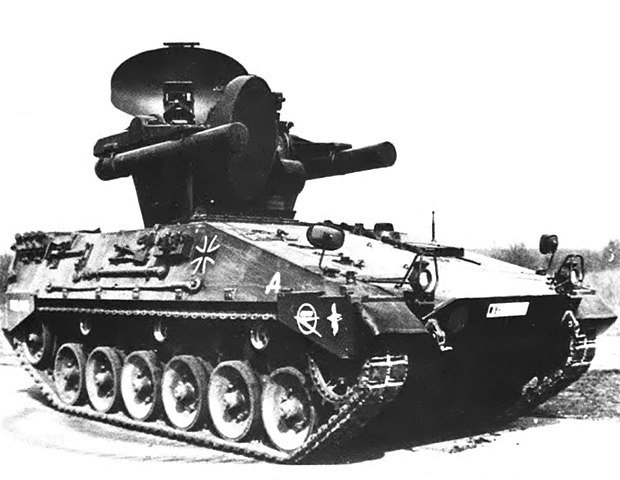

Roland 2
Brazilian Roland at the Conde de Linhares Museum
Read More
Books
Links
Roland_(Waffensystem)panzerbaer.de
panzer-modell.de
armyrecognition.com/ -
armyrecognition.com
weaponsystems.net Roland missile
weaponsystems.net Marder Roland
tankograd.com/
en.wikipedia.org
Marders to Ukraine
Videos
Model Kits/3D
On scalemates
Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

