Development and design
 Probably one of the best vehicles fielded by Canada suring WW2, the Fox was Built by General Motors, Canada, and based on the British Humber Armoured Car Mk III, which hull was obtained, but adapted to the Canadian Military Pattern truck CMP-15 chassis. It was a way to provide the Canadian Army without to deal with production bottlenecks in UK and was encouraged by British Authorities.
Probably one of the best vehicles fielded by Canada suring WW2, the Fox was Built by General Motors, Canada, and based on the British Humber Armoured Car Mk III, which hull was obtained, but adapted to the Canadian Military Pattern truck CMP-15 chassis. It was a way to provide the Canadian Army without to deal with production bottlenecks in UK and was encouraged by British Authorities.
The idea of adapting the successful Humber Armoured car MK III was probably born in 1942, and a few hulls were obtained, but tested and then adapted to be manufactured locally in Canada. The British original was based on a Karrier KT4 chassis. It was then swapped for a Canadian Military Pattern truck (CMP) chassis of the C15 type, with many modifications for the hull to fit on it. This was done relatively quickly as production was ready to start in early 1943. The exact date when the vehicle was ordered and the order figures are unknown (yet). It is likely to have been 1,500 as its pretty close to the final production figure, less prototypes and conversions. For manufacturing locations, see the article on the CMP and truck encyclopedia.

Humber Armoured Car, a sister vehicle
Main Design
The hull was similar to the original Humber AC, and was reputed simple to produce. It was already based on the earlier 1939 Guy Armoured Car, which production was limited due to he company's limited output for the British Royal Army needs. Thus it was passed onto the Rootes Group which chosed to adapt it to the Karrier KT4 all-terrain robust artillery tractor. The rest of the design was copied, including the turret and its twin Besa MG arrangement and many details. The hull was all in straight line, easy to manufacture en masse, and from the Mark I to the Mark IV some 5,400 were made, with the swap to a 37mm antitank gun from the Mark IV onwards.The base vehicle was compact and boxy, with a large sloped nose, beak, flat sides, and a compact fighting compartment, with two-man turret inspired by the one on the Mk.VI light tank. The armored body had plating up to 15mm (front) with a had a tall driver compartment. The turret and fighting compartment were at the center. There was a four man crew: Vehicle commander, driver, gunner and wireless operator seated into the hull. The changes operated the armament of Browning versus Besa machine guns was seen as advantageous since new AP rounds had been designed for the M2 HMG.
Engine and Performances
The Fox was powered by a US design GMC gasoline, 6 cylinders in line, water-cooled engine, with compensation tank and rated for 90 hp. It had a Fuel tank of 136 liters capacity with a consumption of 0.4 liters/km. Its Weight/Power Ratio was 12.9 hp/Ton. For suspension it used Laminar springs plus shock absorbers on the two axles. There was a root manual and synchronized Rootes transmission with transfer case, for four forward speeds, one reverse and two or four driving wheels with reducer. It also had “Runflat” type tires. There was an early central inflation system, with a compressor to inflate or deflate the tires depending on the terrain.Top speeds was 72 km/h, and it uusually cruised at 50 km/h, down to 40 km/h off road with a range from 340 km on flat down to 150-200 corss-country. There was also aboard an electrical system rated for 12 volts DC.
Turret and armament

There were changes to the turret. Like the original it was manually traversed, and like for the Humber Mark III, it was fitted with a couple of machine guns, albeit different; The Humber III still had a long barrel 0.59 in (15 mm) Besa machine gun coupled with a coaxial Vickers 0.303 in (7.92 mm) Besa. On the Canadian vehicle, again shortages of deliveries forced the adoption to US-pattern ordnance: This was a main 0.50 in (12.7 mm) M2 Browning machine gun and coaxial 0.3 (7.6 mm) Browning M1919A4. These were covered by long mantlets for protection, which were the same but of different lenght, showing where the HMG was. This in turn led to modify many internal details to hold different ammo boxes. The 12.7mm HMG had 2,200 rounds in reserve, and the 7.62mm LMG 2,750 rounds. Its aiming system was a simple Scope for ranges, respectively if 1,200 m and 800 m.
A long career
In Canadian and allied service
The Fox saw operations in Italy, UK and India. Practically all fighting commonwealth nations obtained some at any point, including the Poles fighting in Italy, notably the Polish 15th Pułk Ułanów Poznańskich ("Poznań Uhlans Regiment") in 1943–1944. By 1 Dec 1943, the Canadian Army overseas had 256 Foxes, 534 Lynxes and 468 Otters. Scout Cars were foundinadequate, the Otter was to be replaced by an interim, the Lynxes and the later cancelled "General Utility Project". The Fox was to be replaced by the T17E1 Staghound, far more capable at any level. In Oct 1944, the 21st Army Group requested all Foxs still in the UK (200 from the Canadian Army) be sent to North-West Europe, and they were used until V-Day for security duties as replaced by the Staghound.Other Operators
After WWII, the Canadian Government started to sell them at almost metal price. Among the customers was the the Portugese army, using them in counterinsurgency, in Angola, Guinea and Mozambique. The Netherlands lacked Humber armoured cars to be sent to retake the Dutch East Indies, and so acquired 39 Foxes of which 34 were refitted with Humber Mk. IV turrets. This hybrid was called the "Humfox". Combined with a more reliable engine they proved very successful and popular. After the departure of the Dutch and Indonesian independence, the newly formed country, already dealong with its own insurgencies, obtained these vehicles.
Dutch Humfox
Shortly after WW2, the Netherlands was trying to prevent Indonesia becoming independent. Its recently acquired es-British Humber Mk.IV Armoured Cars seemed ideal for this new theater. They soon became the backbone of the Royal Netherlands Army for its reconnaissance squadrons. However Britain ran out of Humber Mk.IVs and so 39 Foxes were acquired from Deelen dump. By October 1946 they were sent to Machinefabriek Wilton in Fijenoord (a well known Rotterdam Naval Yard, already experienced with armoured cars) to match spare Humber IV turrets to the Fox hull. Almost all of the 39 vehiocles were converted after successful trials on 7 November 1946.The main advantage of this hybrid was its Humber's 37 mm main gun, ensuring commonality with the Humbers, whereas the GMC engine was easier to maintain. They were prepared and shipped to Indonesia, used there by reconnaissance squadrons with Ford Lynx/Humber IIIs.
Indonesian Humfoxes:
After the independence of Indonesia, the RNLA handed over all its equipment, including those remaining "Humfoxes". It is however unclear if they were actively used and for how many time. It's possible that some were even shipped back to the Netherlands. On 17 March 1951 there was still a listing indeed of 14 "armoured cars, GMC, closed, with turret, Foxhound", perhaps Fox or Humfox.Portuguese Vehicles:
The Portguese acquired in 1957 thirty-eight dumped GMC Fox MKI called locally the "7-8 Ton Armored Reconnaissance Vehicle m/1957" from Canada. Apparebtly they were part of obsolete vehicles accepted to equip second-line divisions in the Pyrenees. The Portuguese Army used them from 1961 to 1975 in insurrections in their colonies of Angola, Guinea and Mozambique. When they arrived, they were assigned to Infantry Regiment No.1 and their Browning 7.62 mm coaxial changed to the Portuguese 7.92 mm standard. Not all 38 were sent to Africa.By the end of 1959, the first reconnaissance squadron of Guinea was formed with 8 Fox, transferred later to the 3rd Cavalry Regiment, subunit Reconnaissance Squadron 54. In 1960, another unit was formed in Mozambique, from the Cavalry Practical School. By late 1973, six were still in portugal (participating to the Carnation Revolution), 24 in Mozambique and 8 in Guinea. In Mozambique, a section of eight were posted to patrols along the railway between Monte Freixo and Vila Cabral. But due to their conditions they were stationed, without engines or wheels, sitting in wagon, surrounded by sandbags. These "Fox turrets" later were acquired by the Mozambican Railways after independence. Credits and more Info.
Surviving vehicles
Karl Smith Collection in Tooele, Utah.Shopland Collection, Clevedon, Somerset, UK.
Robert Gill Collection - three, one displayed in Heeresgeschichtliches Museum, Vienna)
Cavalry Tank Museum, Ahmednagar, Maharashtra, India
The Ontario Regiment RCAC Museum, Oshawa, Canada
Canada War Museum, Ottawa, Canada
Fox Mark I specifications | |
| Dimensions | 4.6 x 2.3 x 2.4m (15 ft 1 in x 7 ft 7 in x 8 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 8 tonnes |
| Crew | 3: Driver, gunner, cdr |
| Propulsion | Engine GMC 6-cylinder petrol 90-97 hp. |
| Maximum speed | 71 km/h (44 mph) |
| Transmission | Rootes Gearbox 4+1, 2/4x4 |
| Suspension | Wheel 4x4, leaf springs, schock absorbers |
| Range | 200-250 km (160 mi) |
| Armament | 12.7 mm Vickers HMG, 7.92 mm Besa machine gun* |
| Armor | Up to 15 mm (0.59 in) |
| Total production | 1,506 |
Links
facebook.comkeymilitary.com/
mapleleafup.net/
mapleleafup.nl/cmpvehicles/fox_ac
militaryimages.net
warwheels.net
quartermastersection.com
mapleleafup.net/forums/showthread
en.wikipedia.org
mapleleafup.net/vehicles/restorations/restore2
insauga.com/
blogueforanadaevaotres.blogspot.com
evaldirfalandoguerra.blogspot.com
silverhawkauthor.com/
canadiansoldiers.com
mlrsbooks.co.uk
commons.wikimedia.org
scribd.com
Gallery

Basic Canadian Fox Mark I in 1943

Polish 1st cav. Fox in Italy, 1943

Brown camouflaged Fox Mark I in Europe, late 1944.
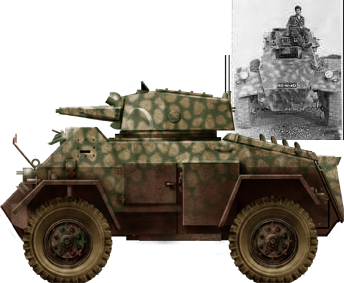
Portuguese Fox in Angola, late 1960s
More to come if references are available.


Videos

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

