The AMR-34 turned command tank
The Reconnaissance tanks of the French Army since 1933 were the AMR-33, 34 and 35. They had been distributed to cavalry units for reconnaissance, and declined each into multiple variants. Among these were a serie of command tanks equipped with radio sets, the Renault YS of which only ten were built and distributed to various units. Then, there was derived YS-2, a prototype artillery observation vehicle with an observation turret, tested in 1938-40 but not adopted either, despite the need for such vehicles.About the AMR-34
The AMR-34 (Auto Mitrailleuse de Reconnaissance Modèle 1934) was a French light reconnaissance tank developed during the interwar period and used in the early stages of World War II. It was manufactured by Renault, introduced in 1934, with 123 units manufactured total, assogned to motorized cavalry units in 1939-40. This was a small vehicle, weighting in about 5.5 tons, armoured with 9mm (0.35 inches) to 13mm (0.5 inches) light armor used mainly against small arms and it had a crew of 2, a driver and Commander/Gunner. Its main Armament consisted only in a 7.5 mm Reibel machine gun or 13.2 mm Hotchkiss heavy MG depending on the version. It was powered by a Renault 447 (84 hp) 6-cylinder air cooled engine, for a top speed up to 55 km/h on road and a range of about 200 km. Its suspensions sytem rested on Leaf spring bogie but the vehicle had a notoriously poor off-road ride.The AMR-34 was intended for cavalry units to perform reconnaissance, not front-line combat but was deployed during the Battle of France (1940) to plug holes in the French defence anyway. Its light armor and armament made it vulnerable against German anti-tank weapons and tanks and already it had been replaced in many roles by the better AMR-35. It was also declined into the AMR 34 ZT1 hoising a single 7.5 mm machine gun, the AMR 34 ZT2 armed with a 13.2 mm heavy machine gun firing AP rounds, an the experimental ZT3 featuring a 25 mm cannon in a fixed casemate. Its suspension was based on a tracked artillery tractor system, making it unreliable and uncomfortable off-road, hampering its usefulness as a reconnaissance vehicle. There were more variants, notably experimental ones such as the YS and YS 2 seen below:
Renault YS
Development
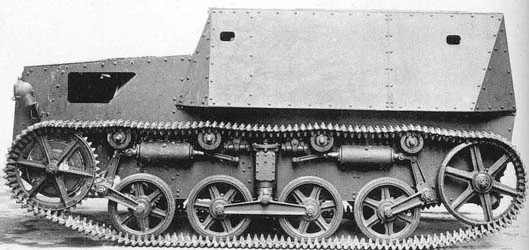
Specifications for a command tank was issued on 9 January 1931. This model was named Type M. Renault built two prototypes with boiler plate based on the AMR 33 chassis in 1933 already. General Darius Bloch at the head of the technical section of the supreme command, looked at these favourably in his trials report of September 1933. Later in a session of the Conseil Consultatif de l'Armement in January 1934, the same Bloch wanted a dozen for the Cavalry. Their goal was to coordinate platoons of AMR-33/34 in the field to the batallion and divisional HQ. On 10 April 1934, an order was signed for ten "Voitures de reconnaissance tous terrain blindés" to be delivered before 31 December 1934 but it was mentions these were command vehicles. Renault gave them the factory designation Renault YS.
The Renault YS was a completely rebuilt version with little in common with the original tank, apart the suspension and drivetrain. It had indeed a large, fixed superstructure encompassing the whole rear compartment, no turret. The comparment forced the relocation of the engine and transmission forward. The first and second prototypes, upon recommendations, were rebuilt with the AMR 35 suspension. To avoid future changes in requirements, Renault established a contract specifying that the choice of a more robust and heavier AMR 35 chassis would also garner inferior performance with a weightincrease from 3.5 to 4.3 tonnes, top speed down from 60 to 55 km/h, average road speed from 40 to 35 km/h.
Tests took place between 1 September and 22 November 1937, by the Commission de Vincennes. Ten vehicles were ordered, with chassis numbers reserved from N° 84252 to 84261 delivered from 14 to 16 December 1937. The delay of three years from 1933 was explained by several factors. Renault had to deal with different Arms with special requirements for combinations of short and long range radio sets, which had to be built in and needed many internal modifications. Plus the provider of the emitter/receiver was delayed as well, the models were still untested and required a number of fixes. The first specifications were issued in June 1935 and then for each subtype, the was a special interference suppression to be applied and tested. The original two prototypes were used for the tests, but in betwee, the requirements for the new AMR-34 chassis came in.
Renault YS deployment
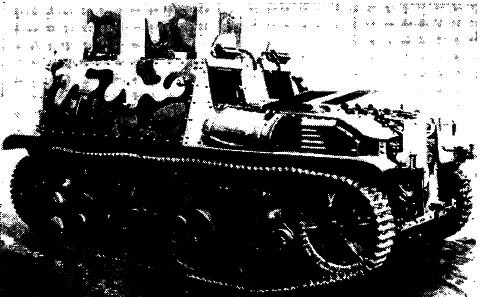
Of the ten vehicle produced, the Cavalry received four, reduced from the original allocation of six with the so-called "Type C" equipment:
-ER (Émitteur-Recepteur)26 ter and ER29.
Two were assigned to the 2nd and 3rd GAM or "Groupe de Automitrailleuses".
The Infantry received four:
-Two with the "Type G" equipment (ER51 m1935 and the R15 receiver). They were intended for army tank units, assigned to the 507e and 510e Régiment de Chars de Combat (RCC).
-Two with the "Type E" equipment (ER 26 ter and R15), assigned to mechanised infantry units, 5e and 17e BCP (Bataillon de Chasseurs Portés).
-Two more Type E were sent to the Artillery, assigned to the 1st and 42the Artillery regiments.
Renault YS Design
They differed externally in the type of antennae, frames, with configurations compared to the AMR 35 as the the raised front hosted the engine, with a right side exhaust pipes going all the way back. On the right was a strage bin instead. There was a rear superstructure. The driver was seated to the right, commander to his left of the structure under double shutters, with unseparated command post behind them with two seated radio operators, each with a double hatch for access and exit in the back. There were four top hatches as well. The main whip antenna was located in the middle.The Artillery YS variant had a single operator but carried more supplies. Calculation were wrong and their final fully lmaded weight was much higher than predicted at 5,950 kilogrammes. When fully loaded there was 0.8 tonnes of radio equipment and the weight increased to about 7.5 tonnes, 100 Kg higher than the acceptable suspension load preconized by Renault. There was a second fuel tank fitted but the final range decreased to 150 kilometres and general reliability fell. In service the road wheel axles kept breaking down. Thus, there was no incentive to produce more and the program was terminated in 1939.
Renault YS 2
The Renault YS 2 was a sub-variant asked by the Artillery corps. It was an artillery observation vehicle derived from the YS they already tested. The new vehicle was to have advanced telemetric optics and notably a rangefinder turret. Its role was to bring artillery spotter close to the target enough to transmit real time corrections. On 20 July 1936, the Artillery obtained a budget to acquire from Renault a modified YS on their own specifications. The vehicle was called the "Voiture blindée tout terrains d'observation d'artillerie" or "all terrain armoured artillery observation car".On 11 August, Renault was contacted to build a full scale wooden mock-up for it. The rear compartment was calculated to accommode the ER26 ter and R14 radio set, as well as enough room for a long telephone cable and connections plus the top an optical rangefinder turret with a 160 centimetres ring mount. The Renault tank design bureau pushed for a mock-up to be created for 6500 French franc as contracted. On 21 September Renault made a counteroffer, and proposed to rebuild one YS prototypes for ₣ 195,000, and still supplying the mock-up for ₣ 9500. but this was rejected by the ministry of defence, ordering the mock-up only by 12 October.
On 5 November, Jean Restany at the head of the Renault design bureau, still decided to rebuild the YS prototype as a private venture. On 26 January 1937, the rangefinder was received but proved, too wide for the 160 centimetres first planned, and just too wide for the YS chassis no wider than 170 centimetres. An attempt to place it in a wooden dummy turret was presented. On 2 April, a commission of artillery officers visited Renault. The saw the issue and suggested to use instead the smaller standard rangefinder used by machine-gun units, with a ring mount no more than 125 centimetres. Atelier de Rueil provided for it a steel cupola featuring a central pair of binoculars and associated diascopes at the sides and back. The cupola was also protected by armoured shutters. On 22 June, Renault offered to sell this vehicle at ₣ 150,000, mock-up included. On 31 July, the Army agreed and a contract signed on 7 October 1937.
The final prototype had the chassis N° 58993. On 8 August it was sent for field tests with the 309e RATTT (Régiment d'Artillerie de Tracteurs Tous Terrains). Atelier de Rueil meanwhile worked to integrate an improved turret, in the spring of 1938. But performances and reliability of the YS 2, which was even heavier, proved problematic, and no further YS 2s were ordered, despite a demand of all services for such vehicles. But the Renault YS 2 was just too mediocre for this, and no replacement came when the war broke out in September 1939. In many ways however, the lack of proper communication doomed the French Army.
To be more precise, the prototype presented on 30 July 1937 and assigned to 309e RATTT with a crew in Strasbourg under Captain Salaumond later took part in western manoeuvres under the 11e RA (Artillery Rgt.) with a crew in Vernon. In May 1938 it was sent to the ARL factory in Rueil and underwent repairs. Its turret was dismantled and ARL worked on a new type as well as looked to integrated more modern rangefinders. It is not known in what state the vehiucle was sent to the 71th RA, part of the 2e DLM (division légére mécanique) but the General of Artillery saw it on 4 May 1940 and judged it inadequate, confirming there would be no mass production.
Renault YS specs. | |
| Dimensions | 3.84 x 1.76 x c2 m (12 ft 7 in x 5 ft 9 in x 6 ft 8 in) |
| Weight | 7.5 tones (Orig. AMR-34 6.5 tons) |
| Crew | 2+2 |
| Propulsion | 4-cylinder petrol engine 85 hp p/w 12 hp/tonne |
| Speed | 55 km/h (34 mph) |
| Suspensions | Rubber reinforced horizontal springs |
| Range | 130 litres: c200 km |
| Armament | None. Personal pistols. |
| Armor | 6-13 mm (0.3 to 0.5 inches) |
| Total production | (10+2 YS1, 1 YS2) |

Renault YS Type M in 1939, unit unknown.

Renault YS 2 in 1940, 71st RA (2nd DLM). It was also camouflaged, albeit colors and unclear.




All sources: Pinterest.
Sources
Francois Vauvillier - The encyclopedia of French tanks and armoured vehicles 1914-1940, Histoire & Collections 2014Francois Vauvillier - Les automitrailleuses de reconnaissance, Tome 2
Links
Plans Renault YSchars-francais.net
armedconflicts.com
militaryimages.net
worldwarphotos.info
wardrawings.be
en.wikipedia.org
thelittleaviationmuseum.au
alternathistory.ru
scalemates.com
blitz-kit.fr

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

