 The Bundeswehr is the new name for the German Army recreated in 1954, signing a re-engagement towards NATO. The first phase lasted until the fall of USSR in 1991 and reunification, the second phase (1991-2020) was of a considerable decrease in size and capacity, the "dividends of peace", that is until 2022 and the war in Ukraine, prompting the vote of a 100 billion rearmament plan, but still not reaching the 2% GDP objective targeted for 2025. This second phase will be seen in its proper page in the future.
The Bundeswehr is the new name for the German Army recreated in 1954, signing a re-engagement towards NATO. The first phase lasted until the fall of USSR in 1991 and reunification, the second phase (1991-2020) was of a considerable decrease in size and capacity, the "dividends of peace", that is until 2022 and the war in Ukraine, prompting the vote of a 100 billion rearmament plan, but still not reaching the 2% GDP objective targeted for 2025. This second phase will be seen in its proper page in the future.
For the duration of the cold war, the Bundeswehr peaked to around 500,000 men until the late 1960s. It was laregly a concript army, and thanks to the reconstruction of national industries, to the the early park of MDAP (US-supplied) matériel, the 1960s saw also the reconstitution of military production, for the ground forces (with shining examples such as the Leopard and Marder), Navy (Bundesmarine, with a strong impetus on export) and the air, albeit this was spectacular in that matter.
Articles
- Leopard 1
- Leopard 2
- Marder IFV
- KjgPz-90
- RktJpz-1
- RktJpz-2
- Jaguar 1
- Jaguar 2
- Spz Lang
- Spz Kurz
- Wiesel
- Tpz Fuchs
- Spähpanzer Luchs
- KMW Daks AEV
- TM 170
- Flakpanzer Gepard
- FlaRakPz Roland SPAAML
- Panzermörser M 113 A1 G
- KMW Biber AVLB
- KMW Büffel ARV
- Minenräumer Keiler
- Kampfpanzer 70
- Spähpanzer RU 251
- Spähpanzer SPI.C.
- Kanonenjagdpanzer 1-3
- Begleitspanzer 57
- TH-301
- Leone MBT
- Indien Panzer
Tanks
Infantry Fighting Vehicles
Wheeled Combat Vehicles
Specialized Combat Vehicles
Prototypes
Deutschland Jahre Null
Germany emerged from the war in the summer of 1945 as a broken and devastated country. "Deutschland Jahre Null": As written and photographed on a ruined vestige of a wall and recalled by Rosselini's 1949 eponym movie. A country in disarray, military occupied by foreign nations, with an ongoing hunt towards Nazis on the run. The fate of Germany was kept in balance between USSR and the western allies, and the question of rearming its demobilized forces was raised as tensions rose on the Berlin question and occupation zones by some American and British officers alike, fearing the communist takeover of Europe. As these tensions crystallized with the blocus of Berlin, the question was raised once more, and eventually led to the cold war as we know it. From now on, Germany would became for NATO and the Warsaw Pact alike the object of most scenarios of a "hot" war between the two giants, a virtual battleground where most forces were deployed and multiplied excercizes.The split between the GDR (German Democratic Republic) and FRG (Federal Republic of Germany) in 1949 was in some ways, inevitable, as only a war could have persuaded Stalin to leave East Germany, but the price paid in blood for the territory made some legitimation of this occupation. As Churchill stated with his famous "iron curtain" the creation in Berlin of a wall in 1961 symbolized in itself the very nature of the tensions and drama that unfold in Germany. A people divided for 43 years.
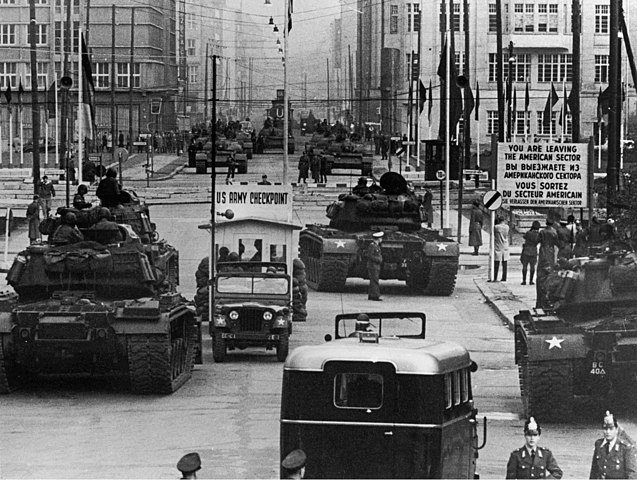 Berlin 1961: US and Soviet tanks facing off at Check Point Charlie
Berlin 1961: US and Soviet tanks facing off at Check Point Charlie
Two countries antagonized by the very fracture that divided spheres of influence and visions of the world. And on the borders were massed untold numbers of infantry and tank divisions. Military airbases and garrisons dotted the landscape, ready to get on one another's throat in the shortest notice.
Thought frightening, it was only the conventional aspect of this cold war. Over everybody in Germany loomed the dark spectre of nuclear annihilation, targeted precisely on these allied German bases. So Germany was in the very heart of the cold war, and Berlin the symbol-city of it all. In the years following the raising of the wall, entire families were divided and two countries gradually emerged, with vastly diverging way of living and cultures.
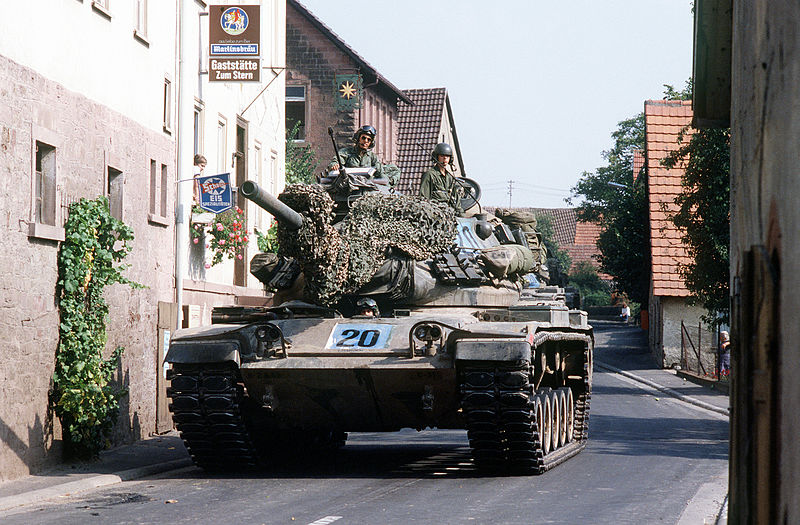

M60 Patton on the streets of a West German village, NATO exercize Reforger '82
The "Blank Bureau"
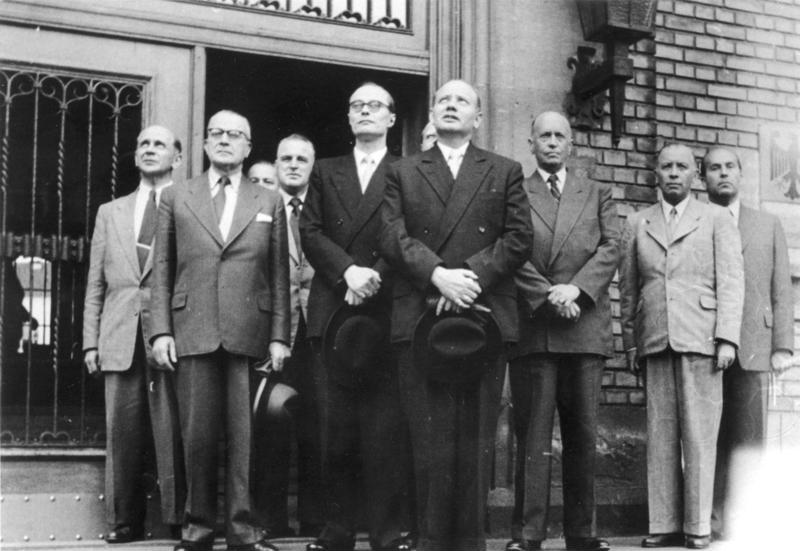

Employees of the Blank office in front of the Ermekeil barracks. From left to right: Gerhard Loosch, Ernst Wirmer, Theodor Blank*, Wolfgang Holtz, Adolf Heusinger, creating the future German MoD.
The "Amt Blank" was a follow-up of the dissolution of the Wehrmacht under Allies Control Law No. 34 on August 20, 1946. However as early as March 1949, PM Konrad Adenauer (CDU) declared that full accession of a West German state to NATO was a priority task for the first West German government. As Chancellor on November 30, 1949 he advocated for a German contingent for a European army, and associated rearmament. It was rejected however on November 24th and 25th 1949, by the Bundestag, but by the early 1950s, focus of the German government shifted to the Cold War and by March 16, 1950, Sir Winston Churchill (now in the opposition) also advocated a German defense contribution.
On May 24, 1950, Adenauer appointed former tank general Gerhard Graf von Schwerin as his adviser on technical security issues, making secret preparations for setting up a "mobile federal gendarmerie" at least to counterweight the GDR own effort to rearm the country, unofficially. The Korean War intensified these efforts and both in Western Europe and the USA voices asked to create Federal German armed forces, and it was called the "West German defense contribution". Adenauer believed this new German army was needed to protect the democratic West. High Commissioner John J. McCloy declared in Frankfurt on July 6, 1950 reaffirmed the US defence principles in Europe, taking for the two other partners, stating an attack on West Germany would mean an attack against themselves.
For Adenauer however, obtaining the means of defending the country was seen as an extension of sovereignty of the Federal Republic of Germany, still restricted occupation statute and negotiations were made under the advocacy of "rearmament against sovereignty". By July 26, 1950, the Bundestag announced at least the conclusion a European federal pact, and creation of a supranational federal authority. On August 11, 1950, the Consultative Assembly of the Council of Europe approved Churchill's proposal to create a "European army", including German contingents. An interview by the New York Times on August 18, 1950 enabled Chancellor Adenauer to push further his cause in US opinion.
By October 5-9, 1950, a commission of former high-ranking members of the Wehrmacht met in the Himmerod monastery, Eifel mountains to deliver a "Memorandum on the establishment of a West German contingent as part of an international force for the defense of Western Europe". They detailed the structures and scope of this new armed forces. This funding document was later called the "Himmerode memorandum". It also detailed the internal organization of the Bundeswehr ("Inner Leadership"). But still, part of the elected members of the Government, in the Bundestag and population were holtile to this prospect. Federal Interior Minister Gustav Heinemann (CDU) resigned on October 9, 1950; in protest.
On October 24, 1950, French Prime Minister René Pleven presented the "Pleven Plan" for a European army as prerequisite for Germany's contribution, a way to present it easier for approbation back in France, where a close majority of communists strongly opposed Germany's rearmament. On October 26, 1950, Adenauer appointed Theodor Blank as Federal Chancellor's representative in relation to Allied troops. The "Blank Office" became the embryo of the future Federal Ministry of Defence housed in the Ermekeil barracks, Bonn, the new federal capital. All that worked in the "Blank office" prepared Germany for rearmament in contradiction to the provisions of the Allies, but the latter soon had knowledge of it ans it was not only tolerated, encouraged in view of increasing tensions with the USSR.
West Germany and NATO
Soon after the signature of the treaty that led to NATO, the question of West Germany incorporated inside it was raised again. Prior to that era, the rearmament of Germany was perceived as a threat both by the Soviet Union and some in Europe, notably governments with a strong communist representation like in France and Italy. After the 1949 split, both sides started to rearm as it was seen the most logical choice. Economic boom and baby-boom were not only to provide the manpower for a new, defensive army, deeply embedded in strong constitutional and democratic principles, eradicating the old specter of German militarism, and a reborn German military industry.It was also seen as a practical way to gradually reduce the military presence of the allies (and the financial burden associated) on the territory, although local authorities alleged the financial benefits of such presence in their area. Konrad Adenauer was instrumental in leading his country resolutely on the western side rather than seeking any form of neutrality. So West Germany joined NATO on 9 May 1955 and soon the Bundeswehr was born.
In fact, negative experiences with militarism in Germany saw strong initial resistance to the establishment of new German armed forces, at first with the occupying powers and from the overwhelming majority of the population. Many voices calling for the Federal Republic of Germany to be rearmed increased however, and more in agreement between the state and NATO powers than the population. The date given for the Bundeswehr's exitence, November 12, 1955, was when the first soldiers were presented with their certificates of appointment in the Ermekeil barracks, a very precise occurence and not just signing an official document. Eventually, since the army recruited and despite full economic recovery and jobs aplenty, recruits were found.
The Bundeswehr is created (November 1955)
 The creation of the Bundeswehr was accompanied by a split between the ground forces (Heer), the Luftwaffe and Bundesmarine, but also the Streitkräftebasis (Joint Support Service) and the Joint Medical Service or Zentraler Sanitätsdienst. The symbol associated was the old Maltese cross, partly associated with the past Teutonic Knights and Prussian nobility, rather than the straight Balkan cross, still too assoviated with the WW2 Wehrmacht. Aside this, the swastika was banned from any display in any forms or shapes, under penalty.
The creation of the Bundeswehr was accompanied by a split between the ground forces (Heer), the Luftwaffe and Bundesmarine, but also the Streitkräftebasis (Joint Support Service) and the Joint Medical Service or Zentraler Sanitätsdienst. The symbol associated was the old Maltese cross, partly associated with the past Teutonic Knights and Prussian nobility, rather than the straight Balkan cross, still too assoviated with the WW2 Wehrmacht. Aside this, the swastika was banned from any display in any forms or shapes, under penalty.
This army was equipped predominantly with American equipment, soon partly produced locally under licence. To start with, the Bundeswehr were equipped with American tanks such as the M41 Walker-Bulldog light tank and the M47 Patton medium tank. The MDAP effort (Mutual Defense Assistance Act) voted in July 1950 was the military equivalent of the Marshall plan intent to rebuilt European economies to avoid them to fall under communist influence. It already helped France, Italy, the Benelux, Austria, so logically when the Bundeswehr was included, it also quickstarted a massive supply of US-built ordnance.
These "fresh" acquisitions (many however from WW2 stocks) formed the basis of most of West Germany's panzer divisions, equipped with the M41 Walker Bulldog and M47 Patton. These would be followed by the M48 Patton. Soon, West Germany had both the experience, the will and the industrial basis to design and produce a new, indigenous tank. It was decided to pursue the development of the "Europanzer" in the 1950s, together with France and later joined by Italy. The M48, however, would go through numerous upgrade programs in the Bundeswehr, ultimately culminating in the M48A2GA2, and was not removed from service until the early 1990s.
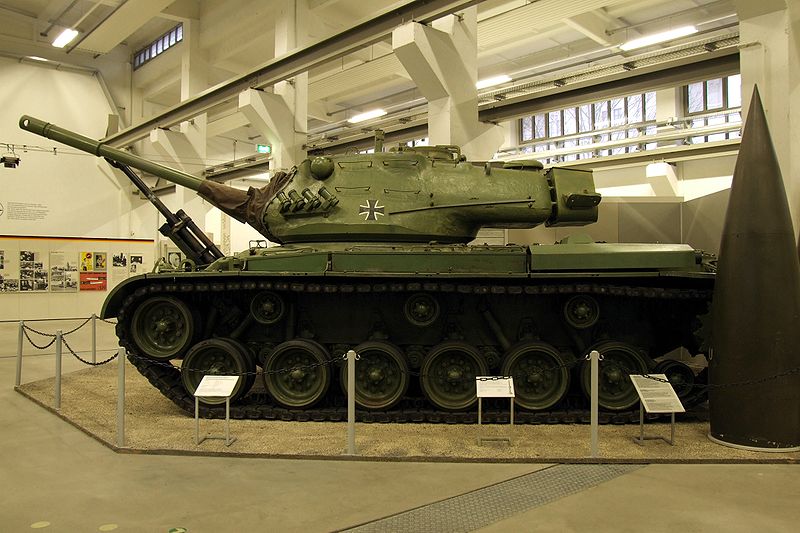 German M47 Patton now on display at the Dresden museum
German M47 Patton now on display at the Dresden museum
The "Europanzer" project
As we saw above, the impetus for the rearmament of Germany was through the constitution of a "European Army" which remained a chimera to this day, but at least pushed (under NATO guidance) towards more integration, better standards, and industrial agreements to try and create common procurement projects, chief of which were a new tank. This did not prevented Germany however to continue using US AFVs for more decades, notably M113-based vehicles or the M60 Battle Tank. The European Standard Tank was at first a joint Germans/French project started in 1955 to replace their respective US-built models and fit more precisely their collective requirements. The whole program was dubbed the "Europanzer" (but was later called the "Standard panzer") and the design emphasised mobility and firepower as both countries estimated that modern rounds rendered heavy RHA armour useless. Superior range and accuracy combined with a better speed and manoeuvrability were to compensate for a lack of protection.In June and July 1957 both Germany and France gave their the final requirements to the companies involved in the project. Officially Italy joined the project in September 1958 and contracts were signed for the production of 2 groups of German prototypes and a single French prototype. The latter began testing at Satory in march 1961, followed by the German prototypes in Meppen.
In 1963 the French prototype was evaluated in Germany. These were refined in 1963 as the Standard-Panzer and the AMX-30 when both countries eventually decided to built their own tanks due to too much specification divergences and other considerations. The Standard-Panzer became the blueprint for the following prototypes of the Leopard in 1964.

Porsche version of the Europanzer (A group), which differed from the French one by a commander's rangefinder.(credits:www.jedsite). Being an the forefront of tank design during ww2, the world saw with great attention a brand new model, especially if it renewed with the "feline" tradition of its ancestors. The name reflected agility, speed and ferocity, and also proved a marketing success.
It was tested virtually by all European nations previously equipped with American tanks, and purchased in droves, as well as former UK supplied countries like Canada and Australia. The United States themselves evaluated the vehicle in Germany, which left such an impression that in 1965, the Army decided to embark on their first joint German-American tank project ever, better known as the MBT-70.
The Leopard was armed with the standard (licence-built by Rheinmetall) 105 mm L7 main gun and featured an excellent mobility with an advanced suspension system. Protection was constantly improved in the 1970s and 1980s, until the release of the Leopard 1A5, the last version, and was one of NATO's most prolific tank. At that time the new standard gun was to be inspired the 120 mm L11 manufactured by the Royal Ordnance Factory and also purchased for licence production by Rheinmetall.
American made tanks such as this M41 Walker-Bulldog (entering service in Germany in 1955, the first tank to be adopted by the Bundeswehr, top) and M48 Patton III (also entered service in the mid-1950s, only retired in the early-1990s, bottom) formed the backbone of the Bundeswehr's armoured units after the Second World War until West Germany began producing its own tanks. The M47 Patton II was also used by the Bundeswehr.
Entering service in 1965, the Leopard 1 is one of the most famous tanks to come out of the Cold War. Thinly armoured but highly mobile, and armed with the powerful 105mm L7 gun, the tank was extremely successful. It was used by multiple countries around the world, such as Canada, Australia, Belgium and Turkey. Turkey is one of the many countries that still operates the Leopard 1. The vehicle has also spawned a number of variants, including anti-air and recovery vehicles.
The Leopard 2, like its predecessor, is one of the most successful tanks of its era. This Main Battle Tank (MBT) entered service in 1979. It is armed with the 120 mm Rheinmetall L/55 smooth bore gun, and is equipped with composite armor of high-hardness steel, tungsten, plastic filler and ceramics. Like the Leopard 1, the 2 is used by various militaries across the globe.

The Spähpanzer RU 251 was a proposed design for a light tank. It used shared the same chassis as the Kanonenjagdpanzer 90 and Raketenjagdpanzer. It also used the same 90mm main gun as the Jagdpanzer. It was only ever a prototype, however. The Bundeswehr had many of such prototypes built for various purposes over the years and procurement was always a long and protracted affait with often more than ten years before the vote of the program development and final acceptance for service.
Links
The German Heer official websiteThe bundeswehr on Wikipedia
Panzerbaer
Panzerbaer
Cold War Tank Formations
Cold War Tank Formations
Equipments of the Bundeswerr (West Germany)
Cold War Tank Formations
Bundeswehr Models in Detail
Nomenclature
Tanks
 M47 Patton II
M47 Patton II
 M41 Walker Bulldog
M41 Walker Bulldog

(section in writing)
 M48 Patton III
M48 Patton III
 The Leopard 1: True Europanzer
The Leopard 1: True Europanzer

Germany, although working for an abominable regime, proved during the war years to be capable of producing the finest and most cutting-edge tank designs ever seen. The Panther was frequently shown as an early main battle tank in the modern sense, with excellent mobility, protection and an unrivaled long-range gun, and a master standard for other countries to follow. Since the context changed dramatically in 1947, Western Germany was soon rearmed to face the Soviet threat and would produce one of the finest MBTs ever built on European soil, capitalizing on this tradition of excellence. In all, 4744 were built, between thos of the Bundewehr and at least 50% exports. In addition the chassis was used for a large number of vehicle.
 The Leopard 2: An enduring legacy
The Leopard 2: An enduring legacy
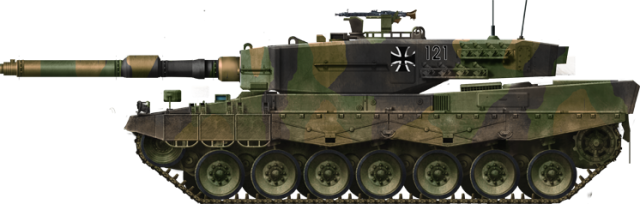
The long development of the joint MBT-70 project, revealed itself to be a failure, with the separation of both armies. Too diverging specifications on the long run and the associated costs led the Bundestag to refuse to fund the project anymore in 1969 (it reached 1.1 billion DM), but data was reused for the Keiler, code name for the future Leopard 2.
The latter reused many of the advanced technologies featured by the prototypes series, married with as many parts of the actual Leopard 1 to bring the costs down. Eventually, the Leopard 2 entered service in 1979, just one year after the M1 Abrams, also born from the MBT-70. In all, throughout all versions manufactured and exports, 3480 were built. The Leopard is recognised today as one of the very best MBT in the world, often rated #1 by military experts. Despite being thirty-six years old, it was proved modular enough to evolve with the latest technologies, and like the Abrams, is not scheduled for a replacement anytime soon.
Tank Hunters
 KanonenJägdpanzer 90 (1965)
KanonenJägdpanzer 90 (1965)

By 1960, the M47 Patton old 90 mm was still a potent weapon. Pending replacement in the Bundeswehr, it was decided to reuse it in German-made tank-hunters. General design tended to be close to the very successful ww2 era Jagdpanzer IV. Specifications were made and transmitted to three manufacturers, the German Hanomag and Henschel and Swiss MOWAG which produced prototypes. After trials, only Hanomag and Henschel were retained for pre-production. They built another pair of prototypes, equipped with the German-built Rheinmetall BK 90/L40, derived from the US patented antitank gun. Development goes on until 1965 when the Kanonenjagdpanzer (sometimes followed by 4 5 or "90"), also called Jagdpanzer Kanone 90, was accepted for service in the Bundeswehr.
 Raketenjagdpanzer-I (1958)
Raketenjagdpanzer-I (1958)

The world first missile launching tank was an experiment in 1960, based on the Hispano-Suiza HS-30 chassis, and designed the carry the French SS-11 antitank missiles produced locally under license and also used by the AMX-13. The prolific HS.30 also called Schutzenpanzer Lang SPZ 12.3 developed as an IFV had been already derivated into mortar carriers, recoilless AT gun platform, or artillery observation vehicle. Tactically the idea was sound: It was a suitable response to the problems of the threat of dozens of thousands of Soviet tanks, a massive conventional force which had no equivalent in the west. These shaped-charge missiles were able to defeat an equivalent of 600 mm of RHA, sufficient against the T-54/55.
 Raketenjagdpanzer-2 (1966)
Raketenjagdpanzer-2 (1966)

Alongside the Kanonenjagdpanzer, a standard tank hunter of the SPG type, using 1950s 90 mm guns, another contemporary vehicle shared the same chassis: The Raketenjagdpanzer-2. It was built another type of missile tank hunter, the smaller and lighter Raketenjagdpanzer-1 derived from the Spz Lang HS.30 IFV. The latter was given the same weapon, the French Nord SS-11 antitank missile. Being more powerful, far more reliable, faster, and having a better range while being better protected (50 mm of front RHA instead of 30 mm), the second RktJgPz was every bit a superior machine and was indeed upgraded to serve until the late 1980s whereas the first was quickly discarded and forgotten. Prototypes were developed and tried between 1963 and 1965 before the production was authorized and orders placed to both Henschel and Hanomag for 318 of this tank hunter.
 RktJgPz-3 Jaguar 1 (1982)
RktJgPz-3 Jaguar 1 (1982)

After the Raketenjagdpanzer missile-armed tank hunter, NATO standard HOT antitank missile appeared, requiring extensive modifications of the vehicle, leading ultimately to develop a brand new vehicle, the Raketenjagdpanzer-3, better known as the "Jaguar". The latter served until the end of the cold war and beyond after modernization, but for the most the whole park is now stored. Only the Jaguar-2 stayed semi-active for training in the 2000s.
 RktJgPz-4 Jaguar 2 (1985)
RktJgPz-4 Jaguar 2 (1985)

This was a development of the original RakJPz 1, and instead of the HOT missile it used the American BGM-71 TOW missile, and later on in its service life, the TOW-2 ATGM. The drawback which explains the abandonment of the type and the whole lineage of missile tank hunters in the Bundeswehr, was the low number of onboard TOW missiles, manually reloaded and aimed by the gunner, who has to stick out of the vehicle unlike the Jaguar 1 where the gunner can aim, fire, and reload from inside the vehicle.
Infantry Fighting Vehicles
 SPZ Kurz 11.2 IFV (1956)
SPZ Kurz 11.2 IFV (1956)

The Schützenpanzer SPz 11-2 Kurz was an early Armoured Infantry Fighting and reconnaissance vehicle developed in France (Hotchkiss SP1A). From 1959 and 1967, the Bundeswehr received some 2,374 of these light vehicle, developed as reconnaissance versions for the Panzergrenadiere, as were their WW2 equivaments, the Sd.Kfz.250 half track Cars. The SPz 11-2 served in cannon platoons of armored infantry battalions until 1974, and as a reconnaissance vehicle until 1982, replaced by the Marder and Spähpanzer Luchs.
 SPZ Lang HS.30 IFV (1958)
SPZ Lang HS.30 IFV (1958)

The Schützenpanzer Lang HS.30 (Schützenpanzer, lang, Typ 12-3) was the other, longer infantry fighting vehicle developed from 1956 to 1958. It used a Swiss Hispano-Suiza design, Rolls-Royce engine but cumulated mechanical problems. 2,176 out of the 10,680 planned were made due to a poltical scandal due to its many flaws and drawbacks. It was used by Panzergrenadier battalions in 1960 but replaced by the Marder infantry fighting vehicle from 1971, so in service for only 11 years.
 KMW Marder IFV (1968)
KMW Marder IFV (1968)

The first true German IFV: The Marder project was developed as early as September 1959 during the early phase of production of the HS 30. The aim was to develop an equivalent to the Leopard 1 as an armored infantry fighting vehicle. The ATV staff of Panzertruppenschule Munster issued specifications with the intent to create whole armored infantry vehicle family, with modular armament, ranging from AT rockets, to antitank mortars, medical armor, transport and supply, anti-aircraft and FlaRak and SPAAML. Intended for the Panzergrenadiere, this led to separate to development alleys, a cannon-armed tank hunter and an ATGM tank hunter, separately, concluded successfully in 1967. In 1969, a contract was awarded for the supply of 2136 IFVs and the first production vehicle was scheduled to be delivered on 7 May 1971. The Panzergrenadiere had their new IFV, a real step up compared to the earlier HS.30. For production, Rheinstahl AG and Maschinenbau Kiel (MaK) were contracted both. The vehicle was later declined into further versions, A1, A2, A3 until the end of the cold war.
 Flakpanzer Gepard (1968)
Flakpanzer Gepard (1968)

One of the most successful derivatives of the Leopard 1 was the Flakpanzer Gepard. Entering service in the mid-1970s, the Gepard was equipped with two 35 mm Oerlikon KDA auto-cannons with radar assisted target acquisition. The Vehicle was used by multiple countries including The Netherlands and Belgium. This Self Propelled Anti-Aircraft Gun (SPAAG) was only removed from German service in 2010, but remains active in countries such as Brazil.
 Flugabwehrpanzer Roland (1978)
Flugabwehrpanzer Roland (1978)
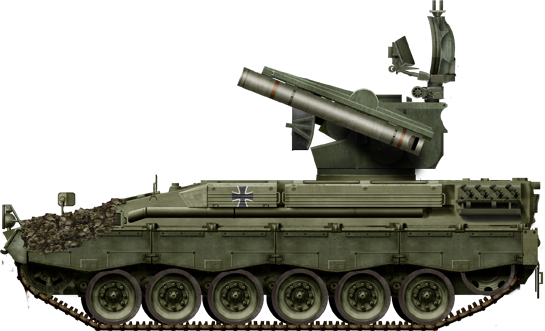
From 1980 the FlaRakPz was introduced in the army as an anti-aircraft missile tank on the modified chassis of the Marder infantry fighting vehicle. A total of 143 (including three Erp/TrVsu models) were procured. The first FlaRakPz were used for tests, troop tests and the start of training from 1979 by the 610 anti-aircraft training battalion and the army anti-aircraft school in Rendsburg and at the STTR 1/FSHT in Eschweiler. The Rolands were subordinate to the corps anti-aircraft commanders. Regiments integrated a staff battery of six anti-aircraft missile batteries (PzFlaRakBttr) and a supply battery. The vehicle has been replaced by a truck platform in 2007 where the last were retired.
 Spähpanzer SPz.2 Luchs (1975)
Spähpanzer SPz.2 Luchs (1975)

The Spähpanzer Luchs ("Lynx"), SpPz 2 A1 and A2 was a West German 8x8 amphibious reconnaissance armoured fighting vehicle (Spähpanzer), in service from 1975 to 2009. The Bundeswehr used 408 of these with the armoured reconnaissance battalions facing the "grenz" during the cold war. Developed by Daimler-Benz between 1968 and 1975 it replaced both the the M41 light tank and Schützenpanzer SPz 11-2 Kurz IFV developed in the 1960s. Very similar to more modern 8x8 AFVs, it was replaced itself by the current massive Boxer from 2009 (38 tons in battle order versus 19.5 tons). It's the perfect example on how this category grew and scaled up over the last decades.
 Spähpanzer SPz.1 Wiesel AWC (1985)
Spähpanzer SPz.1 Wiesel AWC (1985)

The Wiesel Armoured Weapons Carrier (AWC) is a German light air-transportable armoured fighting vehicle produced by Rheinmetall in the 1985-95 period (Wiesel 1 and 2), quite similar to historical scouting tankettes, it has been used with UNOSOM II, IFOR, SFOR, KFOR, TFH, ISAF.
 TPZ Fuchs (1979)
TPZ Fuchs (1979)

The TPZ Fuchs was the second wheeled vehicle to be accepted into service with the Bundeswehr. It was developed in the 1970s following the trend given by the Soviet BTR family, Swiss Piranha or French VAB. Specifications asked for a vehicle which presented the perfect balance between protection, mobility and carrying capacity. For that, engineers designed a relatively long hull, with integral 6x6 drive, amphibious, NBC protection, characterized by a single large one-piece windscreen. The primary production vehicle (APC) stopped in 1986, manufactured by Rheinmetall Landsysteme (previously Thyssen-Henschel). Later on, the production was resumed for Algeria (1,200), and a total of 2,406 with exports to the Netherlands, Saudi Arabia, USA and UK, plus Venezuela.
Future plans for the Bundeswehr section of Tank Encyclopedia
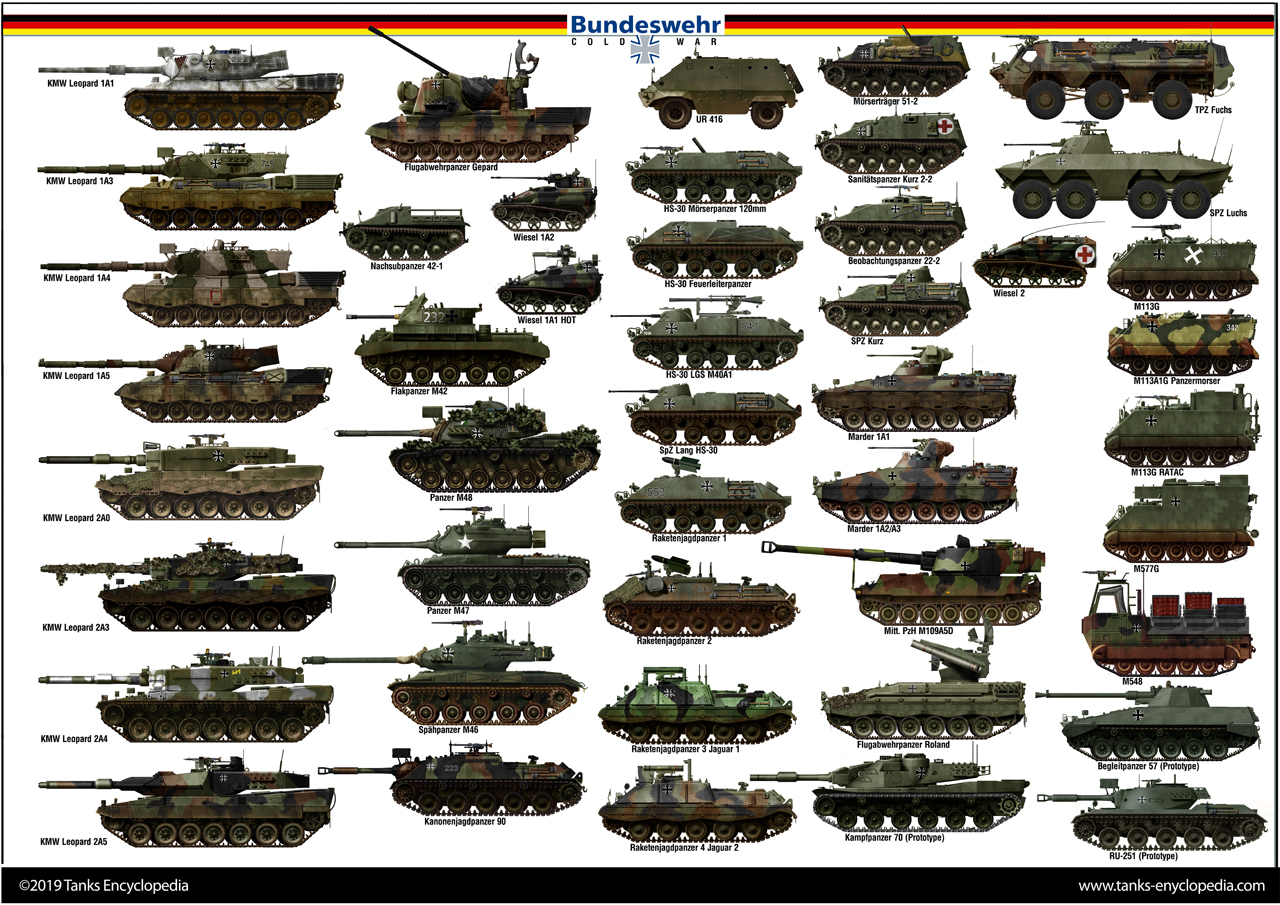 There is nothing like a good poster to show the vehicles that has been done and those which will have their own post in the future. The most next ones should be the Flugabwehrpanzer Roland
and Raketenjagdpanzer 4 Jaguar 2 to close the ban. After which, we will probably go through the M113G and the M113 variants in service with the BDW, the M48A5G, M109A5D, UR416 and other export vehicles, and individual variants. The Minenräumpanzer Keiler has been seen on tank encyclopedia.
There is nothing like a good poster to show the vehicles that has been done and those which will have their own post in the future. The most next ones should be the Flugabwehrpanzer Roland
and Raketenjagdpanzer 4 Jaguar 2 to close the ban. After which, we will probably go through the M113G and the M113 variants in service with the BDW, the M48A5G, M109A5D, UR416 and other export vehicles, and individual variants. The Minenräumpanzer Keiler has been seen on tank encyclopedia.
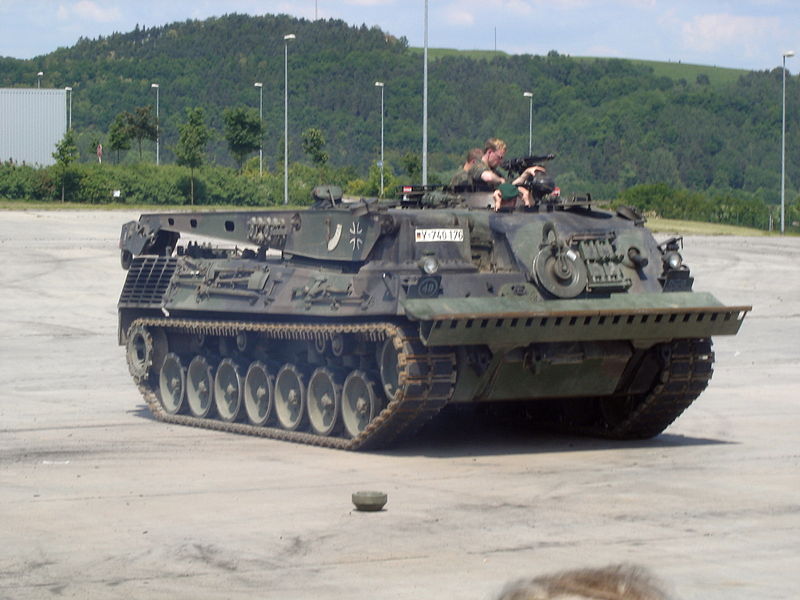

The Bergepanzer II ARV, based on the Leopard I chassis.

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

