Dingo Scout Car

 About 4,545 AFVs produced locally and 5,000+ provided
About 4,545 AFVs produced locally and 5,000+ provided
Rover Light Armoured CarDingo Scout Car
AC I Sentinel Cruiser Tank
➲ Matilda Dozer
➲ Matilda Frog and ‘Murray FT’ Flame Tank
➲ Matilda II in Australian Service
➲ Prototypes:AC II Cruiser Tank * AC III Thunderbolt Cruiser Tank * AC IV 17-pdr Armed Sentinel Cruiser Tank * Cossor Land Cruiser * G. Crowther’s ‘Land Fortress Tank’ * Gerrey Machine Gun Motor Vehicle * Grasshopper Light Tank * Melvaine’s Mobile Pill Box * Modra Revolving Light Tank * Puckridge’s Land Battleship * Wales-Whitehead Amphibian Tank * Wentworth Cruiser Tank
Prologue
The roots of the Australian armored service can be traced back to the latter part of the First World War. Australian troops were indeed committed in action with British tanks, working on close cooperation tactics, notably at the Battle of Hamel (June 1918) and Amiens (August 1918). After WWI, the idea of integrating mechanized elements in traditional cavalry units was constantly on the minds of military men. By 1927, two independent tank sections were raised with four Vickers Medium Mark II tanks provided by the UK. The first was based in New South Wales as a part-time militia unit. However, the great depression of 1930 stopped all development on the matter, whereas a regular tank cadre at least maintained some basic instruction. The 1st Tank Section was disbanded and replaced by the 1st Light Tank Company (Randwick, New South Wales) and the 2nd Light Tank Company (Caulfield, Victoria) in 1937. In 1939, ten Light Tank Mark VIa were obtained from Great Britain and completed the units. In the meantime, the 1st Royal New South Wales Lancers were fully motorized. It became the 1st Armoured Regiment, entirely re-equipped with Matilda tanks.Situation in 1939
After the start of the war in 1939, the government saw itself capped by limitations of the Defence Act (1903), which imposed only local militias, which could not leave the territory. An all-volunteer force to serve overseas was therefore raised, known as the Second Australian Imperial Force (2nd AIF), as well as the 2/2nd Machine Gun Battalion, composed of elements of the 1st Light Horse (Machine Gun). By 1940, although there was a sizable infantry force, the armor available was scarce, counting only the ten Mark VIs and four Mark IIs previously delivered. The first were only armed with a machine-gun, while the last were obsolete.Australian forces in Africa and the Middle East
A commission was raised to investigate deliveries from Great Britain and the USA. While the latter provided thirteen M3 light tanks, which arrived in September 1941 (and 400 in total until mid-1942), the delivery of 140 Matilda IIs only started in July 1942. Part of the 1st Armoured Division (1st and 2nd Light Tank Companies) was disbanded or used to create the 3rd Armoured Regiment and the tanks were reaffected to the AFV School at Puckapunyal (Seymour, Victoria). At the same time, the four infantry divisions of the 2nd AIF received a core of light tanks and scout carriers for reconnaissance, but only three divisional cavalry regiment were formed actually, excluding the 8th Division fighting in the Malayan jungles.These recce units were equipped primarily with Universal Carriers (Light Tanks were supplied later) and operated in North Africa. They captured Tobruk on 22 January and were part of Operation Compass, and the 6th Division Cavalry Regiment bolstered its own ranks with many captured Italian M11/39 tanks. Large kangaroos were painted for easier recognition. The same units were later deployed against Vichy French in Syria, involved notably in the "mad mile" battle. The 7th Division Cavalry Regiment operated in Cyprus in May 1941, and the 9th Division Cavalry Regiment also operated in Syria, receiving for the first time Crusader Mark IIs and M3 Stuart light tanks. Some of the captured French Renault R35s were also used. However, starting in mid-1942 and up to 1944, these regiments were converted to commandos and sent to the Pacific Theater as dismounted infantry.
The 1st Armoured Division, part of the 2nd AIF, was provisionally equipped with Universal Carriers for basic instruction, until the awaited deliveries. In April-May 1942, it received M3 Grant medium tanks and M3 Stuart light tanks, concentrated in the New South Wales to complete their training and extended exercised in Narrabi.
ANZAC's in the Pacific and South-eastern Asia
The 2/6th Armoured Regiment from the 1st Armoured Division was deployed in Port Moresby and Milne bay in New Guinea, against the Japanese, in September 1942. By December, two squadrons were dispatched to Buna (north coast of Papua), to try to bring to a conclusion the difficult Buna-Gona campaign. In January 1943, the remainder of the 1st Armoured division was dispatched to the Western Australian defense sector, between Perth and Geraldton. It was disbanded in September, after the threat seemed no longer relevant. The 1st Light Horse Regiment or Royal New South Wales Lancers was renamed 1st Tank Battalion equipped with Matilda tanks, taking part in the battles of Sattelberg and Lakona, New Guinea, August 1943. It was withdrawn eventually in mid-1944. It was later renamed and involved in the Balikpapan and Borneo campaigns in 1944-45.The 2nd Armoured Division was created in February 1942 from the 2nd Motor Division (former 2nd Cavalry). It comprised of three armoured regiments and one brigade, equipped with M3 Grant and M3 Stuart tanks. It only served in Australia. The 3rd Armoured Division was created in November 1943 from the 1st Motor Division (1st Cavalry.). Both were short-lived and eventually disbanded in Queensland, due to shortages in manpower. The 4th Armoured Brigade was formed in January 1943 to provide a "pool" of armored units, that could have been shipped on demand in the whole South West Pacific Area. Units from the brigade served at the Huon Peninsula campaign and the Aitape-Wewak campaign.
Although the bulk of the armored units were equipped with Allied tanks and armored vehicles, there was both the will and some industrial capabilities to produce a tank domestically, and even more easily armored cars. This need was exacerbated, at the beginning of the Pacific campaign, by the need to compensate for the UK's incapacity to provide adequate supplies of tanks, which could have been crucial in repelling any invasion of the Australian mainland by Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) forces. The program soon included the Sentinel tank, its support version, the Thunderbolt, as well as attempts of up-gunning the tank when large supplies of US tanks were available. However, from late 1943 to mid-1944, emphasis was put on jungle warfare conversion, which concerned first and foremost the old Matilda. The scope of modifications included wire mesh screens or metal protecting both the engine and air louvres against magnetic mines, turret ring protection, an infantry telephone for better coordination, waterproofing equipment both for deep wading and to cope with the extreme wetness of the climate. Other conversions included the fitting of a tank dozer blade, the Matilda Hedgehog (mortar conversion) and the Matlida Frog (flamethrowing tank). Some of these modifications were also passed on the M3 Grant.
Australian Tanks
- AC-1 Sentinel About 65 were built. Conceived as a cruiser, 1943, never deployed in combat. - AC-3 Thunderbolt 25 built, close support version with a 25 pdr howitzer (90 mm/3.54 in). Never deployed in combat. - AC-4 Prototype; tested the British 17-pdr (3 in/76.2 mm) on the AC-1 chassis, 1944.Others
- Bren carrier LP2 & LP2A Built in Australia under licence, with local parts, after a first series of Carrier, MG (Aust) No.1 or LP1.Australian armored cars
- Dingo scout car An estimated 200 vehicles were built in Australia, and used in the North African theater.Allied models used by Australian forces during WW2
- M3 Grant Alongside the Matilda II, the M3 Grant was the mainstay of the Australian armored forces during the war. By December 1942, 757 M3 Medium tanks had been delivered to Australia (and 20 more lost in transit). By June 1944, this force comprised 266 petrol Grants, 232 diesel and 239 Lees (petrol). A single M3A2 (over 12 built) with a Wright radial petrol engine and welded hull fitted with a Grant turret was sent to Australia. Many vehicles kept their factory olive drab livery, while others were camouflaged using an olive-green/beige pattern.- M3/M5 Stuart - M4 Sherman - M7 Priest - Universal Carrier (Bren carrier) and variants - Matilda II - Valentine - Sherman Firefly - M3 Half-Track - Daimler Dingo - Daimler armored car - Kangaroo APCs
Links about Australian armor in WW2
- The Australian effort in WW2 (Wikipedia)
- Australian armored units in WW2 (Wikipedia)
- Puckapunyal museum

Australian M3 Grant from the 1st troop, C Squadron, 2/4th Armoured Regiment training in Australia, Murgon, Queensland 1942 - Credits : Collection Database of the Australian War Memorial.

Australian Cavalry Regiment, Syria 1941, inspected after a successful action. We can see Universal Carriers and Mark VI light tanks - Credits : Collection Database of the Australian War Memorial.
.jpg)
Bren Carriers of the 13/33rd infantry battalion training in 1943, NSW Australia - Credits : Collection Database of the Australian War Memorial.

The 2-10 Armored Regiment training with M3 Grants, for night movement formations. Mingenew, WA, 1943 - Credits : Collection Database of the Australian War Memorial.
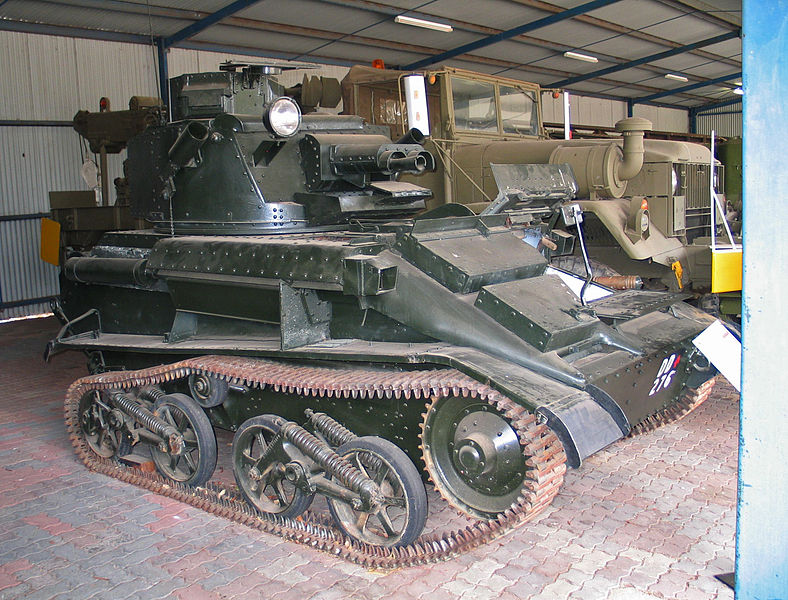

Light Mark VI at the Puckapunyal museum - Credits: Wikipedia commons.

Australian-built Bren Carrier LP2, 1942 (offscale). The glacis plate is at a much steeper angle than that seen on British-produced ones.

Australian Matilda IICS, ANZACS 1st Tank Battalion, battle of Huon (New Guinea), January 1944.
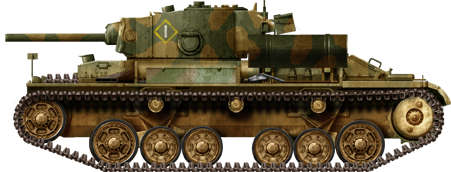
Valentine Mark V CS, 3rd Special Tank Squadron, Green Island, Pacific, February 1944.

Stuart Mark 3 from an Australian cavalry unit at the first battle of El Alamein, June 1942.

Australian M3 Grant, 2/9th Armoured Regiment, 1942.

Camouflaged Dingo, 1943
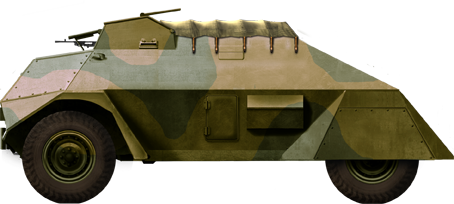
Camouflaged Rover LAC Mk.II, short F60S chassis, 1943.

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
