Predecessor: The Walid APC
The land of the Pharaohs had both the wealth and the ambition to compete with Saudi Arabia for the title of the leader of the Arabic world, a movement that started with Gamal Nasser in the 1950s. In 1975, the Arab Organization for Industrialization was founded in Cairo and represented a step towards self-sufficiency for regional defense industries (also endorsed by the UAE, Saudi Arabia, and Qatar). The AOI helped, for example, to build the first Egyptian APC, the Walid/Waleed.It was based on a German Unimog chassis which had excellent 4x4 capabilities, and Deutz AG diesel mated to a hull inspired by the BTR-40 and BTR-152. It was a mid-sized vehicle between the two, proved versatile and was exported to 8 other countries. By the early 1980s however it appeared obsolete with its open top configuration, no NBC protection nor amphibious capabilities, and the lack of night vision. A new APC was ordered by the Army staff to the Kader AOI factory in Cairo, which started sourcing a chassis and engine abroad. It was intended to replace not only the Waleed but also the BTR-40 and BTR-152 in service with the Egyptian Army.
Design of the Fahd
Army specifications called for a versatile and modular vehicle able to perform military as well as internal security duties, which was fast, manoeuvrable, had long range and excellent off-road capabilities. At least seven variants were planned. The base was a Mercedes-Benz LAP 1117/32 truck (4 × 4) chassis. Although it was assembled in the Kader factory, the general design was from Thyssen Henschel (now Rheinmetall Landsysteme). The hull was relatively slab-sided, with sloped sides but an almost flat front which gave an excellent driving forward position. It was made of welded steel RHA 8 mm thick, protecting against small arms fire and shell splinters. Both the driver (left) and commander sat in the front section. Both had bulletproof glasses protected by armored shutters hinged on top. Access was granted by two side doors, with windows that can be also protected by an armored shutter. The driver had a roof-mounted day periscope that can be swapped for a night vision device.They are separated from the rear section which could hold 10 passengers seated on removable bucket seats down the center facing outwards and can access through a rear door folding in two parts, the lower one acting as a step. The compartment also had ten pistol ports with bulletproof vision blocks, four on each side and two on the back, on each side of the door. On top were two rectangular roof hatches hinged in the center, that can be locked vertically and serve as standing fire shields, with pintle mounts for LMGs. Armament was variable depending on the configuration.
Mobility is provided by a Mercedes Benz Diesel OM 366 LA 4-Stroke turbocharged water-cooled diesel engine, giving 280 hp @ 2,200 rpm. It is light in its standard configuration (10.9 tons) fast on flat (100 kph) but also off-road (60 kph) with a range of 450 km without extension. Field performances in 1985 showed it can climb 80% slopes and negotiate 30% side slopes, cross 0.8 m trenches, climb over 0.5 m vertical obstacles, and have a steering radius of 8 m.
Variants of the Fahd
Fahd 240
The Fahd 240 APC used a modern Mercedes Benz LAP 1424/32 chassis, and have an increase in frontal armored thickness. It is one ton heavier (11.6 ton) but kept the same engine. It is now an upgrade for previous vehicles. It could be equipped with three machine-guns, one in a mount above the commander's seat and two on each end of the infantry roof hatches, facing outward down the center. These could be PK machine guns (1,500 7.62 mm rounds each) or GMPG or FN MAGs. There is also a 20 mm autocannon turret option. A special mount could be adapted to the roof for a MILAN ATGM capable also to target low flying aircrafts.Fahd 280/BTM-208
The Fahd 280 is relatively similar to the 240 with the exception of the dual French SAMM licence-built BTM-208 turret housing a 12.7 mm HMG and light coaxial 7.62 mm (100 & 200 rounds). It is air-tight, providing full collective NBC protection, had six vision blocks, allows a -8 and +45 dep./elevation, and top cupola hatch and electric traverse with a 24V DC supply.Fahd 280-30 (1990)
The most heavily armed version is the Fahd 280-30 used as an infantry fighting vehicle (IFV), and equipped with a 30 mm 2A42 autocannon and AT-5 Spandrel or AT-4 Spigot ATGM with SACLOS guidance (max. range 4 km), plus a coaxial 7.62 mm PK. The turret was similar to the one on the Russian BMP-2 and locally assembled. This version had appliqué armor but only six firing ports and is the heaviest at 12.5 tons. Compared to the armament, this is still one of the lightest IFV on the market.Other versions
The Fahd 240 ARV had a heavily modified rear compartment fitted with a roof-mounted 2.5 ton turntable-mounted hydraulic crane, and ground hydraulic stabilizers. There is a water-cannon armed Anti-Riot variant, with smoke grenade launcher. The minelaying variant use a four-bank Nather-2 launching tube system, controlled by a computer for the right dissemination. Up to 1,500 to 3,000 m x 25-30 m could be covered by a single vehicle with a density of 0.2 to 1 mines per m2.Service & exports
The Fahd was produced to an extent of more than 1900 throughout the late 1980s and 1990s is used also as a command post vehicle, ambulance, light ARV, anti-riot vehicle, mine laying and dispensing vehicle. This vehicle is currently in service with Egypt (1400 vehicles), Kuwait (200), Bangladesh (66), Algeria (200), Oman (31). A former operator was Iraq that captured in 1990 and reused most Kuwaiti vehicles. These were scrapped or destroyed. Use by Sudan and Congo is also confirmed but with no details.
Fahd 280 specifications |
|
| Dimensions : | 10.9 x 11.48 x 9.51 ft (10.8 oa/7.5 m x 3.5 m x 2.9 m) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 10.9 to 11.3 tons |
| Crew | 2+10 (commander, driver, 10 infantry). |
| Propulsion | Mercedes Benz Diesel OM 366 LA TD 275 hp @2,300 rpm |
| Speed on/off-road | 100 km/h/60 km/h ( mph) |
| Range/consumption | Range 700 km/450 km (road/cross country) |
| Armament | 1-3 7.62 mm machine guns. See notes. |
| Armor | Welded steel RHA 8 mm |
| Total Production (Fahd 280) | 900 |
Links
The Fahd APC on WikipediaAdditional pics and data on tanknutdave.com

Fahd 240 APC.

Kuwaiti Fahd 240 command. This vehicle have a three-four wireless antennas communication set, six terminals intercom system, 10-line telephone exchange and two field telephones fed by a 1.5 kW electrical generator.

Malian Fahd 240

Fahd 240 IFOR

Fahd 240 BMT-208 turret. This French licence-built version by SAMM has a 12.7 mm machine gun and a 7.62 mm machine gun. It is NBC proof and it is fitted with a fume and gas extractor.
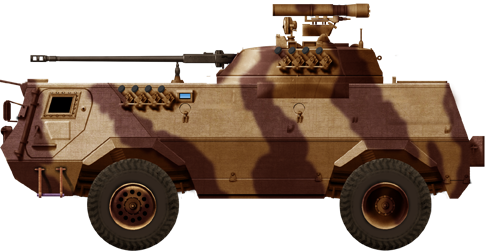
Egyptian Fahd-280-30. This IFV version had a 2A42 30 mm autocannon with a dual rate of fire of 200-300 or 550 rpm or rapid fire burst at 800 rds. It can engage other armoured vehicles but also low flying aircrafts, helicopters and dismounted infantry. With a muzzle velocity of 960 m/s it can engage armoured targets at 1,500 meters, up to 4000 for softskin targets and has maximal operational range of 2,500 meters against helicopters and planes.
Gallery




Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

