Foreword: NATO's main battletank
 Germany, although working for an abominable regime, proved during the war years to be capable of producing the finest and most cutting-edge tank designs ever seen. The Panther was frequently shown as an early main battle tank in the modern sense, with excellent mobility, protection and an unrivaled long-range gun, and a master standard for other countries to follow. Since the context changed dramatically in 1947, Western Germany was soon rearmed to face the Soviet threat and would produce one of the finest MBTs ever built on European soil, capitalizing on this tradition of excellence.
Germany, although working for an abominable regime, proved during the war years to be capable of producing the finest and most cutting-edge tank designs ever seen. The Panther was frequently shown as an early main battle tank in the modern sense, with excellent mobility, protection and an unrivaled long-range gun, and a master standard for other countries to follow. Since the context changed dramatically in 1947, Western Germany was soon rearmed to face the Soviet threat and would produce one of the finest MBTs ever built on European soil, capitalizing on this tradition of excellence.Numbers speak for themselves. The Leopard equipped nearly all European countries with the exception of France and Great Britain, and many others abroad. It is now replaced by the Leopard II, seen by many experts as one of the very best, if not, arguably, the best MBT to date. Total production was about 4744 MBTs, but adding all derivatives built on the same chassis, reaches some 6485 Leopards.

Early development: The Europanzer
The early development of the Leopard could trace its origins back in the mid-1950s, when Western Germany's fast industrial recovery allowed it to rebuild (with NATO's blessing) a powerful, locally-built defensive force to face the Soviet threat. A main battle tank was part of this plan, and at the time Franco-German relationships were at the highest. So a project of common MBT was envisioned since both countries had similar specifications on paper (in France the AMX-50 medium tank project had just been dropped). The project was known later as the "Europanzer" and would have equipped most western European countries to complement or replace US-supplied tanks like the M47 and M48.The Standard-Panzer project, as it was known in Germany, started in November 1956, and the final specs were known in July 1957. These requested 30 metric tons weight, a P/W ratio of 30 hp/ton, armor capable of resisting rapid-fire 20 mm (0.79 in) hits, had to be treated NBC and amphibious, and to be equipped with the British L7 105 mm (4.13 in) rifled gun, recently selected. Since new hollow charges were now available, protection was seen secondary over mobility and firepower. Arbeitsgruppe A, B and C started work on the German side, with the target of delivering two prototypes each. In 1958, Italy joined in.
The prototypes

In 1959 it was decided to start Phase II prototypes, with a raised weight limit. By 1960, the six prototypes of phase I were tested on the German side. Team A was led by Porsche, which shown its Model 734, while Team B (Rheinmetall) unveiled a higher cast turret. Team C (Borgward) featured a futuristic design somewhat reminiscent of the French AMX-13 with a highly automated gun, but failed to produce prototypes in time. Team A was assigned to built 26 pre-series prototypes and Team B, 6. Porsche was soon presented as the competition winner since the Bundeswehr ordered 50 pre-series vehicles, and this was officialized in 1963. At that time, specifications diverged enough for France to decide a separate development which led to the AMX-30.
Porsche "Phase II" prototype design
The Porsche pre-production design was also known as the "0-series", sporting a new cast turret and several hull changes, like the raised rear engine deck to make room for future engine developments and relocation of the radiators on the upper sides of the hull. A better optical range-finding system was mounted to improve accuracy as well as long-range and indirect fire, and this led to the modification of the turret and integration of some "bumps" to mount the optics for triangulation.This series was quickly named "Leopard" to keep the tradition began during WW2 with feline races, and stuck well with the focus given on mobility. The pre-series production was set up at the Krauss-Maffei complex in Munich in 1964 and the deliveries took place between September 1965 and July 1966. Further tests were followed by a Bundeswher order for more, followed quickly by other European nations and foreign countries.
Design
Hull & turret

The Leopard had well-sloped, electrically welded, rolled homogeneous armor (RHA), not especially thick. It was only 19 to 21.7 mm (0.75-0.85 in) thick and up to 70 mm (2.76 in) on the turret front and mantlet. Since new hollow-charge projectiles could pierce through a theoretical 250 mm (9.84 in) of armor, this was useless. This RHA enabled characteristics like a uniform, tougher and elongated grain structure, which diminished or spread the stress of an impact. However, with the improved ammunition, it was envisioned an evolution towards add-on composite armor, achieved on following versions.
The turret was cast at first, with a distinctive rear overhang, and built around the British L7 Royal Ordinance 105 mm (4.13 in) gun, then a standard inside NATO, also adopted by the new generation of US tanks, like the M60. On the definitive version, the turret was welded, with extra external and internal equipment. This turret was mounted on a large ring, whose diameter was superior to the lower hull width. In fact it reached the half-width of the tracks, thanks to extended sloped sides, which replaced the catwalks. Mudguards were short and limited to the frontal sloped section. All external equipment, like the towing cable, bars, schnorkel tube and others, were carried much like on the wartime Panther and Tiger II.
The turret top was dotted with two cupolas, one for the commander and one for the gunner, rotatable, and fitted with prismatic vision blocks. Both had night vision/magnification periscopes installed in front of them. A characteristic of the turret were the two frontal telemetric "bumps" on each side, for long-range gunnery. The turret housed the radio, 13 ready-made rounds of various types, and there was a small basket at the rear surrounded by a storage cage. The hull and turret were sealed and tested to be water-proof in case of submerged crossing and treated NBC (nuclear, bacteriologic, chemical) from the start. This turret was completely modified in later versions.
Armament

From the start, the "Leo" adopted the British-built Royal Ordinance L7A3 105 mm (4.13 in) gun, largely used inside NATO, including by US models like the M60. It featured a 52-caliber, rifled, 5.89 m long (19ft 4in) barrel and weighed 1282 kg (2826 lbs). It had a rate of fire of 10 rounds per minute (tested, with good training), and fired standard 610 or 617 long ammunition of every type available in the NATO, namely HEAT, HE rounds (1700 m/s or 1860 yd/s), HESH rounds, APERS-T (antipersonnel), dummy, canister, training rounds and, for antitank purpose, APDS and APFSDS ("sabot"), reaching 1475 m/s (1613 yd/s) muzzle velocity with these.
The L7A3 was purpose-built in Germany, with the particular of having the corner of the breech block reduced in size so the gun could be depressed more without obstruction from the roof. 13 rounds were stored inside the turret and 42 into the hull. The L7 was well-known and well-proven as very accurate even at very long range (up to 3000 m/3300 yd).
In addition, there was a coaxial MG 3 or FN MAG for the gunner and a secondary one for the commander, mounted on a circular ring around his cupola. 5500 rounds were in store for these. There were not many modifications to the gun apart adding thermal sleeves and upgrading the laser rangefinder and fire control system (FCS).
Engine & transmission
The heart of the Leopard was a MTU (Motoren- und Turbinenunion) MB 838 CaM 500, ten-cylinder, 37.4 liters, multi-fuel engine. It could take either diesel or gasoline, even aviation gasoline if needed. It gave 830 PS (819 hp, 610 kW) at 2200 RPM, and 19.6 PS per tonne. This gave the relatively lightweight hull excellent performances. The transmission was a ZF 4HP250 (Zahnradfabrik Friedrichshafen) model with 4 forward and 2 reverse gears. Engine and transmission were designed to be lifted and replaced in less than 20 minutes in the field by well-trained crews.Drivetrain

The torsion bar suspension consisted of seven roadwheels, drive sprocket at the rear and idler at the front. In addition to the torsion bars, there were shock absorbers on the three front and two rear roadwheels on each side. This combination gave them a very smooth ride and was highly tested and refined for optimal cross-country performances. It stands for one of the most efficient combination ever created and influenced many foreign designs. The Leopard, when fitted with a deep wading kit, could ford rivers up to 4 m (13 ft) deep. Field test performances showed it could reach 65 km/h (40.39 mph) on road, climb a 60% gradient, 40% side slope, 1.15 m (3.77 m) vertical step, cross a 3 meter (9.84 ft) trench and ford (without preparation) 2.25 m (7.38 ft) deep rivers.
Variants & evolution

The Leopard 1A1
The 1A1 was fitted with a new gun stabilization system (developed from Cadillac-Gage), allowing to fire on the move, and additional side skirts, new thermal sleeve on the barrel and other improvements like rectangular rubber blocks, single-pin, fastened to the treads to decrease the link wearing, which could be replaced by "X"-shaped crampons for running in snow or mud. Four batches were produced in the 1960s. By 1974-1977 upgrades came with the new Leopard 1A1A1 standard with a remodeled thermal sleeve, additional turret armor bolted onto the turret (creating air space and manufactured by Blohm & Voss.) and image-intensifier night sights developed for the Leopard II. By 1980 a second upgrade (1A1A2) added a PZB 200 image intensification system (passive low light level television or LLLTV) camera with internal monitor. Later, in the 1980s, the 1A1A3 had new SEM80/90 VHF digital radios, but retained the XSW-30-U infrared/white searchlight and stereoscopic sights of the 1A1A1.The Leopard 1A2
The fifth batch came in 1972, and production stopped in 1974, with 232 tanks built. These were immediately identified by a redesigned, heavier turret, with better protection, and received the 1A1 upgrades, creating the sub-types 1A2A1, 1A2A2 and 1A2A3s.The Leopard 1A3
The next 110 vehicles had their turret modified once more, incorporating two spaced steel plates, and a distinctive wedge-shaped gun mantlet. This new, roomier turret saw its internal space augmented by 1.2 m³, and the level of protection was almost doubled. The commander cupola received a TRP 2A independent sight. These also received the 1A1A1, A2, and A3 upgrades in the 1980s.The Leopard 1A4
This sixth batch was produced between 1974 and 1978, counting 250 vehicles. This included a new computerized FCS coupled with the new EMES 12A1 sighting system. The commander cupola also received its own night sighting system PERI R12. Ammo storage was reduced from 55 to 42.The Leopard 1A5
A full modernization program studied in the early 1980s targeted better night vision and more modern FCS. The 1225 1A1/1A2 were chosen as basis for this upgrade, which was easy to spot because of the totally redesigned turret, even roomier than before. These tanks had a new Krupp-Atlas Elektronik EMES 18 fire control system installed with thermal sights or imaging system inside an armored housing located on the top right side of the turret, in front of the commander's hatch.These eliminated the need for the turret "bumps". A ballistic computer inside the turret and a redesigned laser collimator on the 105 mm (4.13 in) barrel extreme end was fitted for rapid sight adjustment and barrel warpage detection. However, the PZB 200 LLLTV camera was removed and there were improved stereoscopic sights (welded shut). This final version weighted 42.4 tonnes, with maximum speed of 65 km/h (40.4 mph), a driving range (1/3 cross-country, 2/3 street) of around 600 km (373 mi) and a practical gunnery range in direct fire up to 2500 m (1.55 mi). Moreover it could fire now APFSDS rounds. Bolt-on lexan armor panels were also tested with success. This started in 1987 and was really geared up in the 1990s.
The Leopard 1A6
This short-lived project objective was to fit a 120 mm (4.72 in) gun to the Leopard, with added armor, back in 1985. The cost of the upgrade, compared to the 1A5 and the widespread use of the Leopard II led to the cancellation of the project in 1987.Modifications
Gepard (SPAAG)
The "Cheetah" was developed as a private venture in 1966, with the first prototypes built in 1968. This was basically a Leopard I chassis equipped with a turret mounting twin 35 mm (1.38 in) GDF Oerlikon AA guns, assisted by a radar-guided FCS. After modifications, it entered service in 1976 and 420 were built for the Bundeswehr. Other users included Brazil, Chile, Jordan, Romania, Belgium and the Netherlands. A British-built version was also offered for export, called the Leopard Marksman. The Dutch version features a different radar and fire control system.Biber (armored bridgelayer)
The "Beaver" mounted an impressive scissors-type folded bridge, almost twice as long as the chassis, with a 22 m (72 ft) span unfolded. Also called Bruckenlegepanzer or BRP-1 Bieber, it was built by the Leopard manufacturer to answer a Bundeswehr specification back in 1965. It entered service in 1975 and 105 were built. The Italian army also received 65 more built under license by OTO-Melara.Leguan AVLB (armored bridgelayer)
A Norwegian bridgelayer version made by Kraus Maffei and MAN. Deliveries started in 1997. The bridge is longer, reaching 26 m, compared to the 22 of the Biber. Belgium is another user of this version.Bergepanzer (armored engineering vehicle)

In the 1960s, this role was taken by the Bergepanzer I derived from US-built M4 Shermans. However the Bundeswehr favored the Leopard. In 1963 the development of an engineering vehicle based on the Leopard I started at Porsche under a request from the Bundesamt für Wehrtechnik und Beschaffung (BWB), but was assumed by Atlas MaK Maschinenbau and Jung Jungenthal. Deliveries started in 1966 and 444 vehicles would be built for the Bundeswehr, followed by improved versions. Outside Germany, Australia, Belgium, Brazil, Chile, Denmark, Greece, Italy, Canada, the Netherlands, Norway, Poland and Turkey also use them.
Fahrschulpanzer (Driver training)
The Bundeswehr also bought 60 driver training tanks based on the Leopard. The turret was replaced with a cab with clear windows. The trainee would sit in the driver's position, while the instructor sat in the cab, with another set of controls at his disposal. The cabin had space for two more persons, usually other drivers in training. The cabin had a mock-gun.Users and operational engagements
Australia
90 Leopard 1A3s, locally designated AS1, were delivered. They were later upgraded with various local modifications. 70 remain in service, the others being replaced by US-built M1A1 Abrams.Belgium
The Leopard was for years the Belgian main battle tank, with a total of 334 1A5s(BE) delivered in 1968-71. They were upgraded with the AVLS FCS by SABCA, By 1993-1997, 132 were upgraded to the 1A5 standard, 90 sold to Brazil, and the rest gradually put in reserve, mostly due to budget cuts. Some are to be replaced by the MOWAG Piranha III, and only 40 are left in active service.Brazil
Brazil ordered 128 Leopard 1A1s and 250 Leopard 1A5s, which are still frontline today.Canada
Canada purchased 127 Leopard 1A3s in 1978-79 as C1s, with a local laser rangefinder. Most were based in Germany, but some were shipped and stationed at the Canadian Forces Base Gagetown (New Brunswick) for training. In the 1980s there were some armor upgrades, including the radical MEXAS appliqué armor for 6 of these. They served in Kosovo with the Lord Strathcona's Horse unit. Another squadron from the same unit also served in Afghanistan in 2006. In 2000, 66 of the original 114 C1s underwent a massive upgrade to the C2 standard, equivalent to the German 1A5. Surplus turrets were also purchased to accelerate the modernization. This included the fitting of new thermal sights and EMES 18 FCS. Although gradually replaced by Leopard IIs, their final withdrawal is scheduled for 2015. Canada also used specialized versions as the local Beaver Bridgelayer and Taurus & Badger Armored Engineering Vehicles.Chile
The Chilean Army possessed 202 Leopard 1V surplus donated by the Dutch Army, gradually reduced to 150, and now 100. Leopard 2A4CHL now forms the bulk of the Armoured Forces.Denmark
Danish Leopards 1A3s were purchased in 1976, 120 in all which were renamed Leopard 1DK, delivered until 1978. 110 more were acquired in 1993 and all were gradually upgraded to the 1A5 standard. These 230 modernized Leopard 1A5 DK are now retired, replaced by the Leopard II. They also took part in one of the rare military engagement of this tank to date, successfully engaging Serbian tanks in Kosovo during Operation Bøllebank and Operation Amanda, in 1994.Ecuador
This country acquired 60 Leopards (of the 1A5 and 1 V standards) from Chile.Germany
Of the original batches of 2,437 vehicles, now replaced by the Leopard II, a substantial portion remains in storage for resale and parts. Specialized versions are still partly in service or in storage, being replaced by upgraded vehicles based on the Leo II chassis.Greece

The Leopard was -and remains- the Greek main battle tank for more than 30 years. The first batch was purchased in 1983-84: 104 1A3 GR, upgraded with local modifications like the EMES 12A3 FCS. A further 75 Leopard 1A5s were acquired through a trade agreement in 1993, plus 170 1-V more and two 1A5 from the Royal Netherlands army the same year. From 1998 to 2000, 195 Leopard 1A5s were purchased from Germany, and later on, a passive upgrade program was canceled in favor of 150 more Leopard 1A5s along with the newly built Leopard 2A6 HEL. This did not include numerous specialized versions (many converted), also based on the same chassis. This makes the Greek army the most proficient user of Leopard tanks in the world today, although budget cuts will reduce this number.
Italy

Italy was the second largest user of Leopards outside Germany, having purchased its first 200 vehicles back in 1971, replacing the obsolete M47 Patton. By 1974 a further 400 1A2s were produced locally by OTO Melara under license in 1974-79, followed by a further 120 1A5s in 1980-83. This made for a total of 720 (600 A2s, 120 A5s). As of the early 1990s 120 1A5 turrets were purchased and fitted to 1A2s. These were retired by the end of 2008 (replaced by the Ariete MBT), but served in the Balkans for peacekeeping missions. AEVs (Pionerleopard), ARVs (Bergeleopard) and ABLVs (Biber) specialized versions remain in service, most produced by OTO Melara. The upgraded Leopards 1A2s are now kept in reserve due to budgetary cuts.
Lebanon
Lebanon recently acquired 43 former Belgian 1A5 tanks along with many APCs.Netherlands

The Netherlands purchased the Leopard-1 in 1968 as a partial replacement for their aging fleet of Centurions. After this purchase the Royal Netherlands Army possessed 942 tanks, of which 468 were Leopard-1A1 (4th batch). The Leopard-1s were delivered from late 1969 to 1972 and calls for upgrading already came as soon as 1974. In 1978, when the T-72 was shown publicly for the first time, the Dutch Leopard-1 tanks were formally labelled as obsolete.
Around 1979 the order was finally given to modernise all Dutch Leopard-1s. Modernised tanks were named Leopard-1V (Verbeterd/ Improved), and the initial goal was to bring them up to the Leopard-1A1A1 standard. However, during the process the Dutch military changed its requirements numerous times and the adaptation failed hopelessly. It took too long, costed much more than expected and a series of decisions (or lack of decisions) critically impacted any true modernisation proposals on the Dutch Leopard-1 tanks.
By 1989, when the Berlin Wall fell, modernisation of the Leopard-1 was still incomplete. This year marked the beginning of the end of the Leopard-1 battle tank in Dutch service and all were phased out of service by 1995. The Netherlands gave 170 Leopard-1Vs to Greece and sold another 200 to Chile. Of the remaining tanks 14 have been used as target, 4 have been converted to a BARV (Beach Armoured Recovery Vehicle), 1 was converted to a driver trainer, 1 hull was used for EW-purposes. The remainder ended up as monument or museum piece. While in Dutch service none where operationally used.
The Dutch also used derivate versions of the Leopard-1:
The Dutch operated 52x Leopard-1 ARV (Bergepanzer-2), 14x AEV (Bergepanzer-2A1), 14x AVLB (Biber) and 95x Cheetah PRTL (Dutch version of the Flak-Panzer Gepard). Of these only a few ARVs and 5 AVLBs are currently still in service within the Royal Dutch Army. Updated 22/02/23
Norway
The Norwegian army acquired 172 Leopard Is of various models, including the later 1A5s. They were decommissioned in 2011 and are now all replaced by the Leopard II, but the specialized versions are still in service, as in many other armies.Turkey
The Turkish army purchased some 337 Leopard I in total, making the bulk of its armored force, alongside US-built models like the M60. They have been upgraded as Leopard 1Ts with local-built Volkan FCS from Aselsan. It is an all-weather night/day operating system of detection, management and fire on the move.
Leopard 1A5 specifications |
|
| Dimensions (L-W-H) | 9.54m (7.09m without gun) x 3.25m x 2.61m (31'3" (23'3") x 10'7" x 8'6" ft.in) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 42.2 tons (84,400 lbs) |
| Crew | 4 (driver, commander, gunner, loader/radio) |
| Propulsion | MTU MB 838 10-cyl 37.4 L, 830 PS (610 kW) |
| Suspension | Independent torsion bars |
| Speed (road) | 65 km/h (40.4 mph) |
| Range (road/cross-country) | 600/450 km (373/280 mi) |
| Armament | Main: L7A3/52 105 mm (4.13 in) rifled gun Secondary: 2 x 7.62 mm (0.3 in) MG3/FN MAG machine guns |
| Armor | 19-21 mm steel plus 10-70 mm RHA (0.75-0.83 + 0.39-2.76 in) |
| Total production (all MBT versions) | 4,744 in 1965-85 |
Gallery

 Prototype B (Rheinmetall), 1962.
Prototype B (Rheinmetall), 1962.
 Leopard I of the first production version, 1965.
Leopard I of the first production version, 1965.
 Leopard I, 193rd C2 Panzer-Battalion, Kampftruppenschule 2 Munster, winter 1965-66.
Leopard I, 193rd C2 Panzer-Battalion, Kampftruppenschule 2 Munster, winter 1965-66.
 Leopard I (Norway) Stridsvogneskadron, 6th Division, NATO winter exercises of 1988.
Leopard I (Norway) Stridsvogneskadron, 6th Division, NATO winter exercises of 1988.
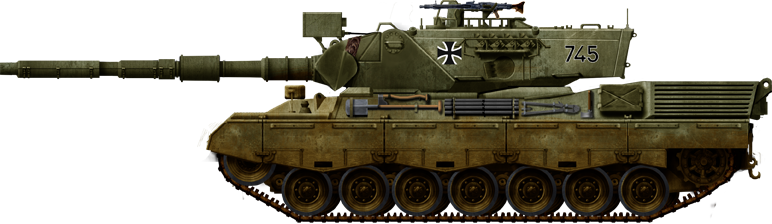 Bundeswehr Leopard 1A3, 1980s.
Bundeswehr Leopard 1A3, 1980s.
 Norwegian Leopard 1A3, 1990s.
Norwegian Leopard 1A3, 1990s.
 Danish Leopard 1A3.
Danish Leopard 1A3.
 Australian Leopard 1A3, 1990s.
Australian Leopard 1A3, 1990s.
 Australian Leopard 1A4, 4th Trp. Cmdr, B-Squadron, 1st Armoured Regiment.
Australian Leopard 1A4, 4th Trp. Cmdr, B-Squadron, 1st Armoured Regiment.
 Danish Leopard 1A5, UNPROFOR, Tuzla, Bosnia, January 1995.
Danish Leopard 1A5, UNPROFOR, Tuzla, Bosnia, January 1995.
 Greek Leopard 1A4, 1990s.
Greek Leopard 1A4, 1990s.
 Leopard 1A4, AS-1 "Assassin", 1st Australian armoured regiment, Puckapunyal, Victoria.
Leopard 1A4, AS-1 "Assassin", 1st Australian armoured regiment, Puckapunyal, Victoria.
 Leopard 1A3 (C1 late) from "A" Squadron, 8th Canadian Hussars, stationed at Lahr, March 1990s.
Leopard 1A3 (C1 late) from "A" Squadron, 8th Canadian Hussars, stationed at Lahr, March 1990s.
 Turkish Leopard 1A5, 1990s
Turkish Leopard 1A5, 1990s
 Leopard 1A5, 2nd Panzer Division, 354 Kompanie, 2nd Battalion, Exercise REFORGER FTX "Certain Challenge", September 1988.
Leopard 1A5, 2nd Panzer Division, 354 Kompanie, 2nd Battalion, Exercise REFORGER FTX "Certain Challenge", September 1988.
 Netherlands Army Leopard 1-V, 2nd tank battalion, 13th Panzer brigade FTX, Operation "Field Lion" September 1988.
Netherlands Army Leopard 1-V, 2nd tank battalion, 13th Panzer brigade FTX, Operation "Field Lion" September 1988.
 Leopard 1A5, 2nd Kompanie, Panzer Battalion 14, 1st PanzerGrenadier Brigade, FTX "Sharfer Bohrer" March 1990.
Leopard 1A5, 2nd Kompanie, Panzer Battalion 14, 1st PanzerGrenadier Brigade, FTX "Sharfer Bohrer" March 1990.
 Flakpanzer Gepard or Flugabwehrkanonenpanzer Gepard SPAAG (1969).
Flakpanzer Gepard or Flugabwehrkanonenpanzer Gepard SPAAG (1969).
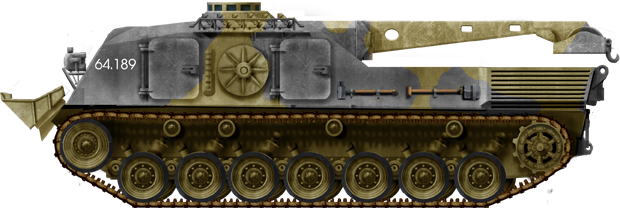
Danish 1A5 ARV, 1st Gulf War, 1991.
First written back in June 2014.

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

