Armoured Carrier Wheeled Indian Pattern
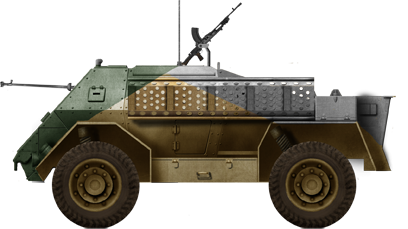
 Armoured car (1941). India. 4655 built total
Armoured car (1941). India. 4655 built total
The ww2 Indian Armoured Car
Today's Indian Ground Army could be proud of an industry taking its roots right into the 1940s, during ww2. By then, the "Tatanagar" was by far its most famous accomplishment. Built by the thousands, this reliable -yet unusual- armoured car was generously supplied to the Commonwealth nations at War. If the Indian divisions had their own fair share of this vehicle, New Zealand forces also operated many of a modified type. These were found in Africa but also Italy and the East Indies, therefore fighting the Germans, Italians and Japanese.Development
Due to the lack of skills and technical resources to built a proper tank (Australia and Canada were the only Commonwealth members to succeed in this difficult exercise) India like South Africa choosed to built an armoured car, based a similar imported Canadian chassis, the Ford/GMC truck universal Canadian Military Pattern. The armoured hulls were given to the East Indian Railway and Tata Iron & Steel Company. The standard armament was the British Bren light machine gun. Production started in late 1940, and stopped in 1944 with overall 4,655 units. Many were assembled by Tata Locomotives, hence their local name of "Tatanagar" but the full official name was Armoured Carrier, Wheeled, Indian Pattern or abbreviated into ACV-IP when accepted into service by the British Authorities.
Design
Starting from the Mark II (the MkI was quite different), and apart the Ford/GMC CO11QRF/C191QRF/C291QR and GMC CMP truck chassis that helped distinguish between versions, the hull was overall relatively similar between versions. It was made of a central frame attached to the chassis, wrapped into 8 mm thick riveted armour plates, 14 mm to the front. The sloped shapes in addition offered full protection against small arms fire and the front was immune against heavy machine gun fire. The great singularity of the model was offer an open-top front compartment, the Ford V-8/GMC petrol engine being relegated at the rear.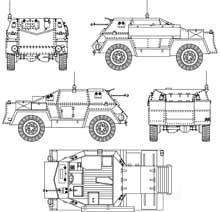
This arrangement provided better driving and general awareness, but the crew was found more vulnerable from the front due to the absence of the extra protection offered by the engine; The rear position also caused some cooling concerns. In the front section, behind the glacis were seated the driver (right hand side) and commander/gunner. The former had a rectangular armoured shutter, and there was a narrow opening, also covered by a shutter, for the Bren LMG, or a 13 mm BOYS AT rifle. The compartment allowed a raised position for observation, and could accommodate optics and telemetric instruments, while on the rear corners of the compartment there provision for pintle-mounted Brens used for AA defence. The Ford or GMC engine developed 90 hp, which combined to the nimble 2.5 tons provided a top speed of 80 kph on flat. The steering was 4 x 4 and the wheels were suspended by leaf spring.


Variants
- Mk I: Ford model 1940 truck chassis, motor in front, Marmon-Herrington all wheel drive kit.
- Mk II: Ford CO11QRF chassis, rear engine, local 4x4 steering, right hand drive (bulk of the production).
- Mk IIA: modified armoured hull.
- Mk IIB: Modified hull with thicker armour.
- Mk IIC: Ford C191QRF chassis, enclosed compartment with a roof and small turret (Bren armed).
- Mk III: Mk IIC with slightly modified hull.
- Mk IV: Ford C291QR chassis and open top hull
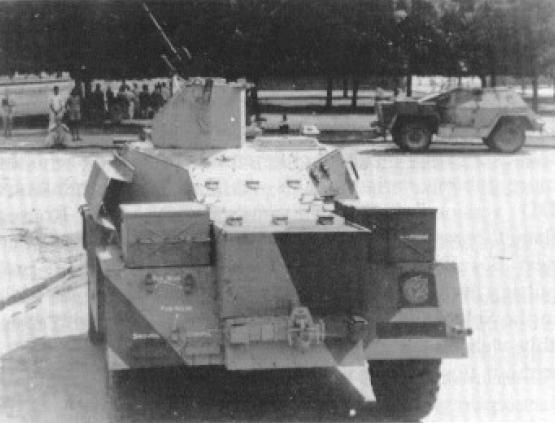
The ACV-IP in action

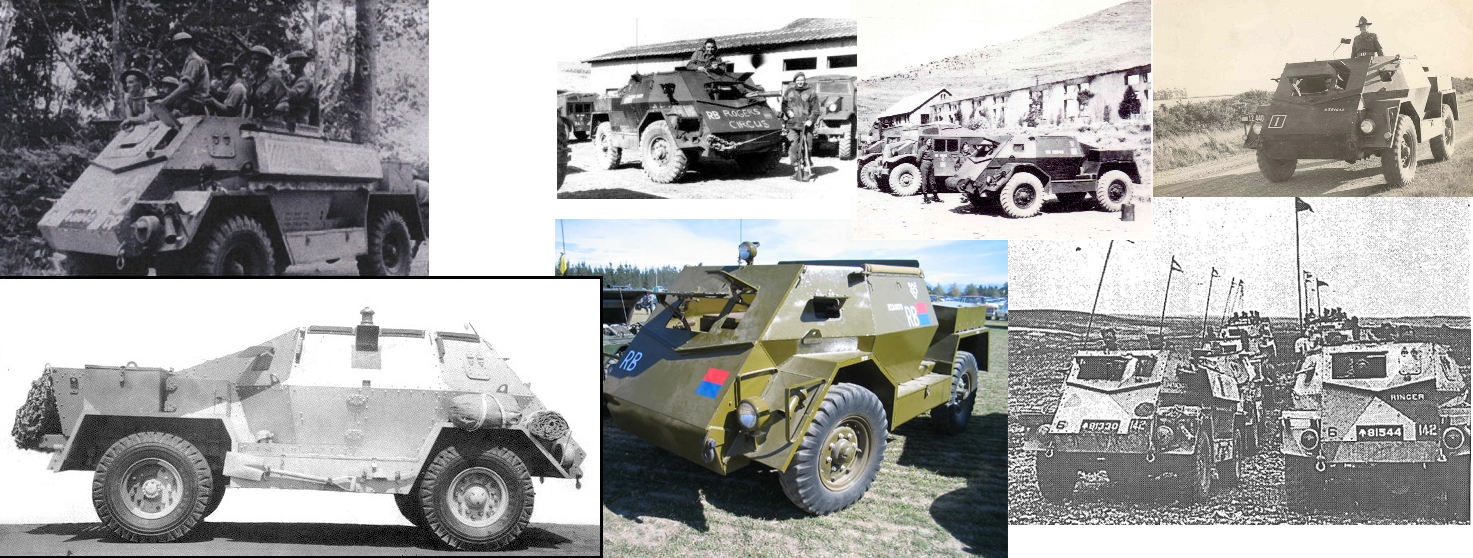
The primary rôles of the ACV-IP were reconnaissance and liaison missions. They operated in divisional reconnaissance regiments, but also personnel carriers, AA weapons carriers or Forward Observation vehicles. The Mark I and Mark II were issued to the 4th and 5th Indian Infantry Divisions operating in North Africa 1941-42 and Mk IIs only to the 10th Indian Infantry Division operating in Syria in 1941. Indian Infantry divisions operating in Italy 1943-45 only used Mark IIs and later models. In the Far Eastern fronts, the ACV-IP served in India, Malaya and Burma from 1942 to the Indian Independence, but also by the Royal New Zealand Artillery in Korea.
Links about the ACV-IP
The shadocks -pdf rare British armoured carsArticle on the ACV in 1942 Malaya

ACV-IP specifications | |
| Dimensions (l-w-h) | 4.72 x 2.26 x 1.98 m (15.6 x 7.5 x 6.6 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 2,626 kg (2.585 long tons) or 4,000 ibs |
| Crew | 3-4 (driver, commander, gunner, radio) |
| Propulsion | Ford V-8 petrol 95 hp (71 kW), pw ratio 29hp/ton |
| Suspension | 4x4 independent leaf springs |
| Speed (road) | 90 km/h (50 mph) |
| Range | 360 km (220 mi) |
| Armament | 0.303 in (7.7 mm) Bren MG or 0.55 (13.97 mm) in Boys Antitank rifle |
| Armor | 14 mm front, 8 mm sides, rear (0.5-0.3 in) |
| Total production | 4655 in 1939-1945 |

Armoured Carrier Wheeled Indian Pattern Mark II.

Unknown Mark II in North Africa 1942
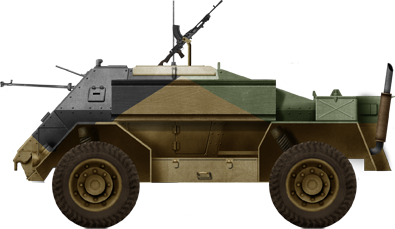
Indian ACV Mark IIa or IIb in North Africa

ACV Mark IIb in North Africa

AVP-IP II NZ pattern or New Zealand pattern wheeled carrier. They were powered by a rear mounted ford flathead V8 which but differed by the chassis, wheel sizes and hull construction.

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
