Genesis
The AMX VTT/VCI was the first French APC and IFV (Infantry fighting vehicle). It was developed in the 1950s based on the prolific light tank AMX-13 after a specification of 1952 from the army for an APC, and two rejected prototypes from Hotchkiss. Designation changed several times, from Transport de Troupe Chenillé Modèle 56 (or TT 12 CH Mle 56 for short) in 1956, then VTP or Véhicule de Tranport du Personnel for "personal transport vehicle" in 1957 to VTT in the 1960s Vehicule de Transport de Troupes for "Troop Tranport Vehicle" to VCI today Véhicule de Combat D'Infanterie ("Infantry Combat Vehicle") especially when armed with a QF 20 mm autocannon fed with AP rounds. This platform was the French most produced APC/IFV so far with 3300 vehicle, and exported with the same success as the light tank it was based on. It was replaced by the more conventional AMX 10P in 1973 and is now retired in France, although several armies still use it today.Design
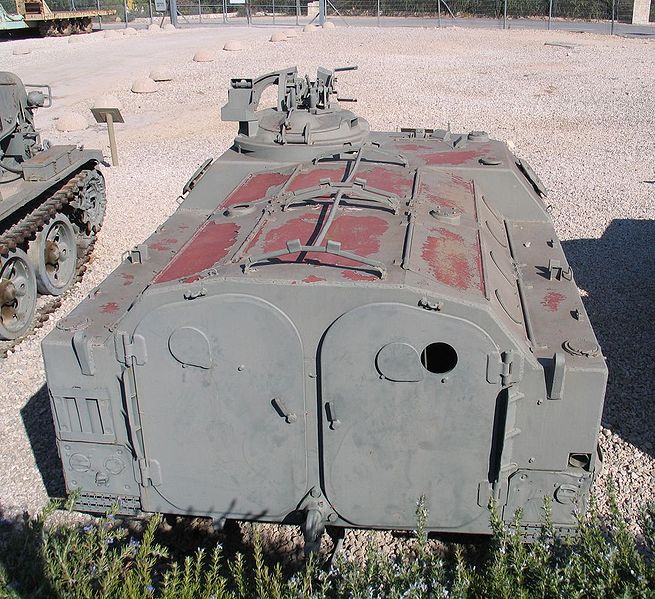
The welded body used sheets of homogeneous steel armor, with a max thickness of 30 mm with a well-sloped frontal armor but rounded nose and chraracteristic splashboard, borrowed to the AMX-13 chassis. It is divisded into three compartments, with the driver and engine compartments at the front and the troop compartment at the rear. This rear compartment was completely modified to carry a central bench for an equipped platoon of ten men seated back to back, fully equipped. They had two rear access doors and a sloped roof with two additional two-piece hatch covers and four pistol pistol ports per side (an innovation for the time). The infantry could either jump over the top or disembark through the rear doors, also fitted with pistol ports.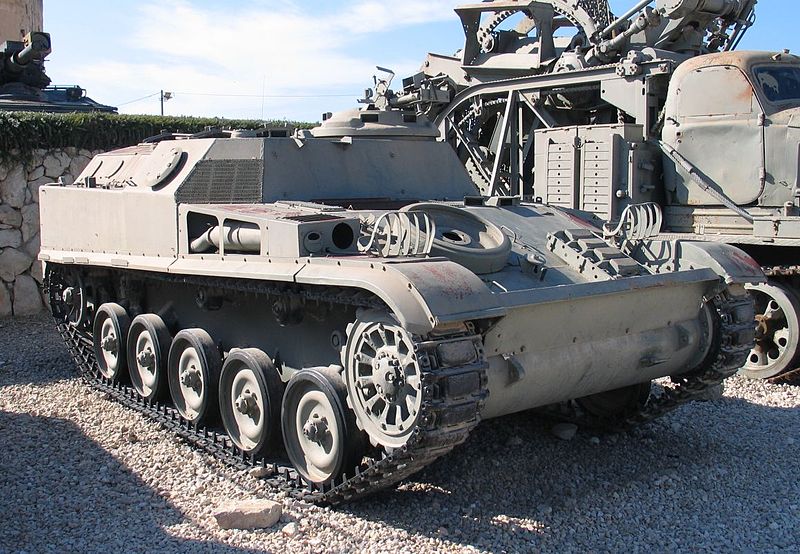
The driver/co-driver had their own hatches and the driver single-piece hatch cover opened to the left and could see through three prismatic vision blocks covering the front and sides. The central one could be replaced by a night vision periscope. There was a tall superstructure just after the engine, and a rotating commander cupola on the left side, with four to ten vision blocks depending of the version. This cupola was often modified during production to house a variety of armaments. One of the most current was the light turret (Tourelleau CAFL 56) developed in 1956-57. The superstructure front right was equipped with fasteners to hold storage.
The suspensions, transmission, engine, tracks, were similar to the AMC-13 model 1956. The torsion bar suspension consisted of five single rubber-tyred road wheels with a front drive sprocket, rear idler, and three to four return rollers per side. The first and last road wheels had hydraulic shock-absorbers. The narrow 85 links steel tracks could be fitted with rubber pads. However the VCI was heavier than the AMX-13, giving a 13 tonne ratio. In addition to a top speed of 60 kph, the gasoline tanks were reduced in capacity so that the overall range was reduced to 350 km (vs 400). The SOFAM engine was mounted facing the rear and could be lifted and extracted for repair or maintenance in 40 minutes.


The transmission via the clutch to the gearbox was located at the front, and there was a Cleveland-type steering differential at its right. For export, the initial engine could be replaced with a more efficient Detroit diesel 6V71T, developing 206 kW at 2800 rpm or a French-built turbodiesel Baudouin 6F11SRY 206 kW at 3200 rpm. As seen on testings, the VCI had a ground clearance of 480 mm, and could climb a 65 cm wall, 1.60 m wide trench, and had a fording depth of 1.0 m. It was not amphibious nor treated NBC. The VCI could be equipped with a filter system, night vision, smoke dischargers, 7.62 mm and 12.7 mm machine guns or 20 mm automatic gun in the cupola, and 60 mm mortars, reloaded from the inside. Various ATGM versions were built, but the VCI was also used as an engineering vehicle, command post, ambulance, ground surveillance radar.
Production & variants
When the ARE (which is now part of Nexter Systems and previously Giat Industries and is currently prime contractor for Leclerc MBT) started production of the AMX-30 MBT, production of the complete AMX-13 tank family, including the AMX VCI, was transferred to the Creusot-Loire facility at Chalon-sur-Saone.The first prototype was built in 1955 at the Atelier de Construction Roanne (ARE). The first production vehicle came out the assembly line of "Atelier de Construction d'Issy-les-Moulineaux" (AMX) in 1957 and was shifted to the main battle tanks AMX-30, while the VCI production was transferred to Creusot-Loire. The production was stopped in 1973 an the plant ceased its activities, while the VCI was replaced gradually by the new amphibious AMX-10P. However a modernized package was proposed for export by GIAT (now Nexter Systems) as the upgraded Model 1987 (new engine, nigh vision, new 20 mm autocannon).


- VTP/VTT standard versions with pintle or cupola mount 7.5 /12.7 mm MG
- VTT Tourelleau CAFL-38 turret variant
- VCI M56 20 mm autocannon version
- AMX-VCG and AMX Dozer combat engineering versions
- VTB (Ambulance) with seated casualties + three injured on stretcher
- VTT PC Command vehicle equipped with additional radios
- VTT Cargo with a 3000 kg payload
- AMX VCI MILAN, TOW, SS-11: ATGM versions
- VTT LT For artillery spotting.
- RATAC Ground Radar monitoring
- VTT VCA ammo/crew support vehicle for the a 155-mm self-propelled gun Mk.F3
- VCPM 81 mm and 120 mm self-propelled mortar version.
- VTT Roland SPAAML version carrying a quadruple launcher and guidance radar.
Users and Active service
France
Around 2500 vehicles of all versions were used in France from 1957 to the early 1980s. Starting in 1973 the regular VCIs were gradually replaced by the AMX-10P. The light protection, lack of range, cramped interior, lack of NBC protection, amphibious or night vision capabilities were known tradeoffs for the AMX-13 chosen as a basis for commonality and cost. Some specialized versions were used well into the 1980s. Since it was armed with a 7.5 or even a 12.7 mm machine-guns, these vehicles were merely APCs, but became early IFVs when equipped with a potent 20 mm autocannon in the 1960s or AT missiles (ATGMs like the Milan or TOW). These were also proven adaptable and versatile.Belgium
The country was given American-built M75 APCs in the 1950s, replaced by many VTT types, here denominated AMX-13 mod.56. These were the standard VTT (305), PC (72), Cargo (58), Mortar (90), MILAN (86) and ENTAC (30), both ATGM versions. They were retired in the 1980s, replaced by the M113 and AIFV-B.The Netherlands
The Dutch Army used some 300+ vehicles, and among these the standard VTT, VCI 12.7, and the TOW version. They are now deactivated.Mexico
Mexico has taken delivery of 401 AMX VCI DNC-1 series (ex-Belgian). These were overhauled prior to delivery by SABIEX International and the gun by SEDENA.Others
The Argentinian, Ecuadorian, and Venezuelian armies also use the VCI today, but the Qatari and UAE vehicles are now probably retired. Sudan, Cyprus, and Indonesia (200 still in service) are also known users. The Lebanon army was given 30 ex-French VCIs in 1976, which were the only vehicles tested in combat against the Hezbollah and the Syrians. It was used either by the Army of Free Lebanon, the Lebanese Arab Army and captured and used by the pro-Israeli South Lebanon Army in 1984 (and deactived in 2000). Some up-armed with US M-46 106mm recoilless rifles were also uised by the Christian militias.
Walkaround video of a Mexican Army DNC-1 as of 2013
AMX-VCI specifications | |
| Dimensions (l-w-h): | 5.70 x 2.67 x 2.41 m ( x x in) |
| Total weight, battle ready: | 15 Tons (xx000 ibs) |
| Crew : | 3+10 (Driver, co-driver, commander/gunner, 10 infantry) |
| Propulsion: | SOFAM 8Gxb 8-cyl. gasoline carb. liquid cooled 250 hp - 184 kW @ 3200 rpm, 12.3 hp/ton |
| Top Speed | 60 kph(xx mph) road |
| Range (road)/Fuel capacity | 350 km (xx mi)/ 1410 L |
| Suspensions: | Torsion arms |
| Armament (see notes) | In standard 12.7 mm MHB 1000 rounds (cal.50) |
| Armour | Hull nose and turret 30, sides 20, bottom 15, rooftop 10 mm |
| Total Production | 3300 |

French AMX VTP, early, main type armed with a single light AA-52 7.5 mm machine gun, 1957.

AMX VTT 12.7 HMG with an open cupola (modified) and the 12.7 mm heavy MG, used by France and the Netherlands (here).

French AMX VCI 12.7 HMG in exercizes at Camp de Sissone, 1987.

French AMX-VTT with the Tourelleau CAFL 38 (turret) armed with the AA-52 light MG, 1960s.

Netherland's army VTT 12.7 HMG with the M56 heavy mount.

French AMX-VCTB for Vehicule Chenillé de Transport des Blessés, the Ambulance version.

VTT TOW used only by the Netherlands.

French AMX-13 RATAC, the ground surveillance radar vehicle, developed in the late 1960s.

French AMX-VCI M56, 20 mm autocannon version.

Argentinian AMX-13 VCPC.

Venezuelian VCI model 1987

Mexican DNC-1, a modernized version with SEDENA 20 mm autocannon, add-on armor and other imporovements, as of 2013.

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com