The simple and rugged BRDM-2 reconnaissance armoured car entered service with the Soviet Armed Forces in 1961, replacing the earlier BRDM-1, , all designed to replace the BA-64. There were soon many variants such as the BRDM-2RKh NBC recce vehicle, BRDM-2UM command vehicle but also organic defense vehicles, against helicopters such as the 9K31 Strela 1, 9P124 ATGM carrier and 9P148 "Konkurs". However the very first developed antit-tank variant was the 9p122.
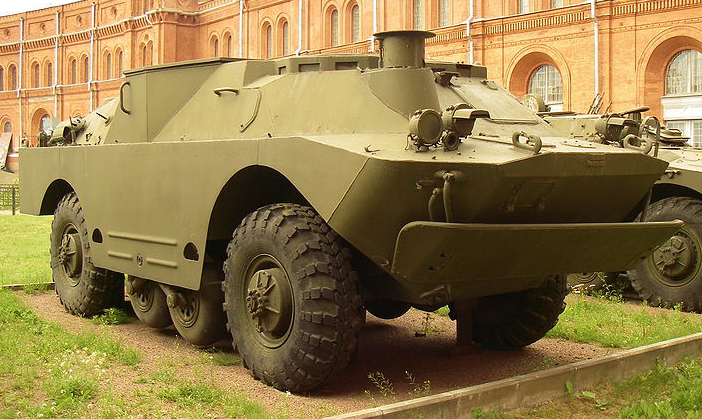

This variant of the BRDM was simple with a crew of 2, driver and operator. The adaptation of an ATGM launcher to a standard vehicle was led by KBM Kolomna. Production started in 1969 for the 9p122, helped refining the model after official adoption until the 9p133 was accepted in 1971, ending the production of the 9p122. The latter became the largest production version, with Arzamas machine-building plant delivering them until 1984. It seems depending on sources that 580 9p122 were manufactured, and at least 860 9p133.
The vehicle was only adopted by USSR and inside the Warsaw Pact East Germany (9p133) and Romania (9p122), but it was also exported.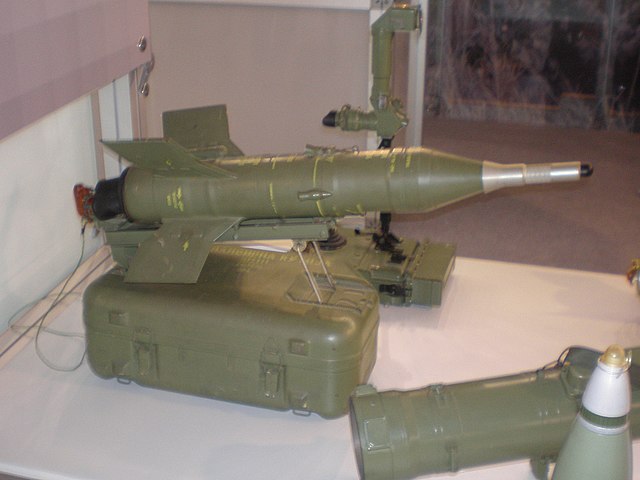
Nicknamed the "Little one" (NATO AT-3 Sagger) was an early manual command to line of sight (MCLOS) wire-guided anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system and first such man-portable. It became the most exported ordnance of the Soviet Union besides the AK-47 and RPG-7. It is also probably the most widely produced (25,000 missiles yearly 1960-1970s, and six copied in other countries. Development started in 1961 with stringent requirements, as the system was to be carried by a single operator, both missile and MCLOS guidance system, at max 10 kgs; and still defeat 200 mm RHA at 60° and at 3,000 m (3280 yds). It was adopted in 1963 and vented to a large array of vehicles, AFVs as helicopters. By extension the carrier vehicle took the "Maluytka" nickname but it never was official but in NATO.
The 9M14P "Malyutka-P" entered service in 1969 with a larger warhead capable of deteating 460 mm RHA and it was superseded in the mid-1970s by the 9M14M Malyutka-M (NATO AT-3B Sagger B) in 1973 which had an Improved motor for greater speed but same range (Mass 11 kg). Being too heavy to be man-transportable, it was mostly used on AFVs, including the 9p33.

Development
The 9P122 "Malyutka" ATGM (Anti-Tank Gun Missile) launcher vehicle was not the first version dedicated to anti-tank defence of the Soviet Army, but it improved on the BRDM-1 tank hunters (2P27 (2K16 launcher, 3M6 "Shmel" (AT-1 Snapper)), 2P32 (9M11 "Falanga" (AT-2 Swatter)) and 9P110. It capitalized on the introduction of a new missile, the 9M14 "Malyutka" (AT-3 Sagger). The compact, light vector carried a HEAT warhead already considered a threat to any form of standard steel hull. It was developed from 1968 with the need to introduce organic self-defence against enemy tanks at regimental and divisional level in reconnaissance batallions, and in combined arms armies. Later it was also adopted in anti-tank regiments or brigades added to frontline artillery divisions.This variant of the BRDM was simple with a crew of 2, driver and operator. The adaptation of an ATGM launcher to a standard vehicle was led by KBM Kolomna. Production started in 1969 for the 9p122, helped refining the model after official adoption until the 9p133 was accepted in 1971, ending the production of the 9p122. The latter became the largest production version, with Arzamas machine-building plant delivering them until 1984. It seems depending on sources that 580 9p122 were manufactured, and at least 860 9p133.
The vehicle was only adopted by USSR and inside the Warsaw Pact East Germany (9p133) and Romania (9p122), but it was also exported.
Design of the 9p122
Hull and general design
Dimensions were the same as the original BRDM-2 but for 7.2 t combat load. It measured still the same 5.75 m long for 2.35 m in width, but a lower height when the launcher was stowed, 2.04 m and up to 2.8 m when the launcher was raised. The rest is similar to the original vehicle, apart the cutout on the roof, replacing the turret. Externally the vehicle resembled a turretless vehicle, but the hidden launcher would just popup and launch one missile at a time, since guidance had a single channel and single operator. The varioant was based on the second production of the BRDM-2 caracterized by its double-slatted air grill cover directly behind the upper superstructure.Powerplant & Performances
The vehicle kept its original wheeled chassis 4x4 with four retractable chain-driven belly wheels. It had the same tires, 13.00 x18 with a 1.84 m thread, 3.1 m wheelbase. It was powered by a rear-mounted GAZ-41 V8 petrol rated for 140 hp at 3.400 rpm (19.4 hp/ton). Transmission was manual, with 4 forward, 1 reverse. For range, the vehicle carried 290 L fuel, and could reach 95 km/h on road, 10 km/h afloat, c50 kph off-road depending on the conditions, with the extra wheels offering better grip in snow and heavy mud. The range was 750 km on road. It was mioderately agile, with a turning radius of 9 m, but a 0.43 cm ground clearance. It coulkd climb a 40 cm wall, gap a 1.20 m trench, climb up to 60 % gradient, and fully Amphibious, motricity and direction using the wheels.Protection, passive and active
The Armor type was steel, 7mm (0.3 in) thickness all around, so proof against small arms fire and snrapnel. It also had an internal spall liner. There was a collective NBC system but no smoke dischargers for concealment. However the main driver sight could received a night vision block.Armament
The vehicle when introduced counted in the improved 9M14P Malyutka-M anti-tank missile, six-round in launcher, of the 9K11P type. Reload could be done internally, safe from enemy fire, and with between 16 or 18 spare missiles on racks. This all took a lot of space internally, so no extra crew could be accomodated. The launcher elevated -1° to +10° Traverse -87° to +87°, Not Stabilized. It was coupled with a 9Sh16 8x mag. observation sight and the 9Sh115A 8x mag. gunsight.About the 9M14 Malyutka (AT-3 Sagger)

Nicknamed the "Little one" (NATO AT-3 Sagger) was an early manual command to line of sight (MCLOS) wire-guided anti-tank guided missile (ATGM) system and first such man-portable. It became the most exported ordnance of the Soviet Union besides the AK-47 and RPG-7. It is also probably the most widely produced (25,000 missiles yearly 1960-1970s, and six copied in other countries. Development started in 1961 with stringent requirements, as the system was to be carried by a single operator, both missile and MCLOS guidance system, at max 10 kgs; and still defeat 200 mm RHA at 60° and at 3,000 m (3280 yds). It was adopted in 1963 and vented to a large array of vehicles, AFVs as helicopters. By extension the carrier vehicle took the "Maluytka" nickname but it never was official but in NATO.
The improved 9p133 Maluytka
The next 9P133 "Malyutka" was an improved model using a new missile, launcher, but also the larger and improved sight 9S446 instead of the original 9S414. The 9P133 could launch the more capable 9M14P "Malyutka-P" (AT-3C Sagger C) or 9M14P1 missile. It carried from 16 to 18 in all, the launcher still having six ready. Thez guidance used the SACLOS system. It had an additional front windscreen interleaved between the standard driver's windscreen and sight mounting.The 9M14P "Malyutka-P" entered service in 1969 with a larger warhead capable of deteating 460 mm RHA and it was superseded in the mid-1970s by the 9M14M Malyutka-M (NATO AT-3B Sagger B) in 1973 which had an Improved motor for greater speed but same range (Mass 11 kg). Being too heavy to be man-transportable, it was mostly used on AFVs, including the 9p33.
Variants and other BRDM-2 based Tank Hunters
9P124
ATGM carrier vehicle with 4 radio-guided 9M17M "Skorpion-M" (AT-2B Swatter B) AT missiles on an elevatable mount with overhead cover. In the hull are four more missiles. It uses MCLOS guidance system. The 9P124 has a crew of 2. It was also known under designation BRDM-3.[4][16]9P137 "Flejta"
– improved model that uses the 9K8 "Flejta" system which allows usage of 9M19P ATGMs with SACLOS instead of MCLOS guidance. The launcher has 5 rails instead of 4.9P148 "Konkurs"
ATGM launcher vehicle with 5 wire-guided 9M113 "Konkurs" (AT-5 Spandrel). The AT-5 launcher can also fire the 9M111 "Fagot" (AT-4 Spigot) missile. The early production model of 9P148 could only fire 9M113 "Konkurs". The crew reloads the launcher through a small hatch located behind it. The gunner controls the missiles through a sight mounted on the front right of the vehicle. The 9P148 can carry a total of 10 9M111 and 10 9M113 or 14 9M113. From 1996 some Russian 9P148 were fitted with an improved 1PN66 day/night thermal sight. In the West, it was also known under the incorrect designation BRDM-3.[16]9p133 specifications | |
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 5.75 x 2.35 x 2.04/2.8 m (launcher stowed/up) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 7.2 t |
| Crew | 2 (commander/operator, driver) |
| Propulsion | GAZ-41 V8 petrol 140 hp at 3.400 rpm, Gbx 4 fwd/1 rev |
| Top speed | 95 km/h on road, 10 km/h afloat |
| Suspensions | 4x4 (4 retractable chain-driven belly wheels) |
| Range | 290 L, 750 km road |
| Armament | 9M14P Malyutka-M ATGM (16)/9K11P launcher |
| Armor | 8-10 mm as BRDM-2 |
| Production | c860 |
Sources
Illustration

9p122, trap closed.
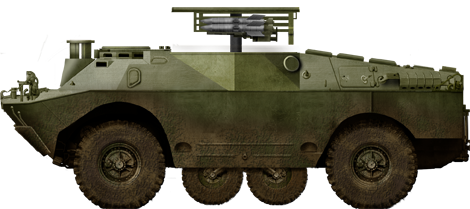
BRDM-2 9p133 Malyutka tank hunter version in Soviet Service

9p133 in Romanian service, trap and telescopic sight closed

East German 9p133

Syrian 9p133 tank hunter, 2015-2016 Civil war
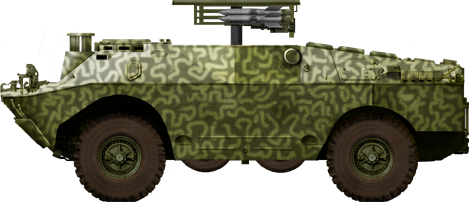
Another Syrian 9p133 tank hunter
Gallery






Celebrating the 20th year of independence in Turkmenistan

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army

