An early, failed tank serie
The T-12 and the T-24 were both attempts to improve the MS (T-18) tank and comprised a hard leaning curve into the shape of marely failed prototypes: T-19, T-21, and T-23. Engineers and deciders had plenty of good idea on papers, as what could be a medium tank. And this led to the T-12 and T-24 between 1925 and 1931. Both were relatively sound designs but they ended as unworkable in practice, with scores of mechanical failures.However at the time, these failures came less from ideas or paper engineering but the fact USSR lacked skilled workers capable to tackle a relativelky complex project like this, as well generaly a problem of resources across the board. If the T-12 did not made the cut, the T-24 at least was greenlight for production with a serie on 25 built until the authorities put the plug on it.
The very similar T-12/T-24 were in direct competition with "Tank Grotte-1", a German inspired prototype (by engineer Hans Grotte) and the latter was neither put into production. Just like the TG heavy tank project, these eneded by 1931 as USSR fell enamoured by the Christie tank concept, which led to the BT series, and later down the line, to the T-34. On the other hand for light tanks, the Vickers Mark E became the T-26.
Development
For the T-12, a brand new facility the Kharkov Locomotive Factory (KhPZ) was established. It was located in Ukraine in 1928 and grew to legend under the leadership of I. Aleksienko seconded eespecially by A. Morozov, the lead designer of all soviet tanks from 1940 to 1970, from the T-34 to the T-72. The first tank project called T-1-12 was a much larger, much improved MS-1 (T-18) with a M6 200 hp engine at the back, standard 45 mm (1.77 in) gun and three light machine guns, one on the hull, one coaxial, one in the turret bustle. Although 30 were planned for the 1930 budget only the prototype was made, never accepted into service.The main reasons were bacl quality construction steel, lack of tooling and skilled personnel. The tank was completed and ready for tests by October 15, 1929. However it was revealed to be badly flawed, so much so that a brand new design was needed. The new project was re-designated T-24. Meanwhile as the hull was built, the team worked frantically at fixing transmission and fuel system issues (leakages) while they designed a larger turret with different shape.
Design of the T-24
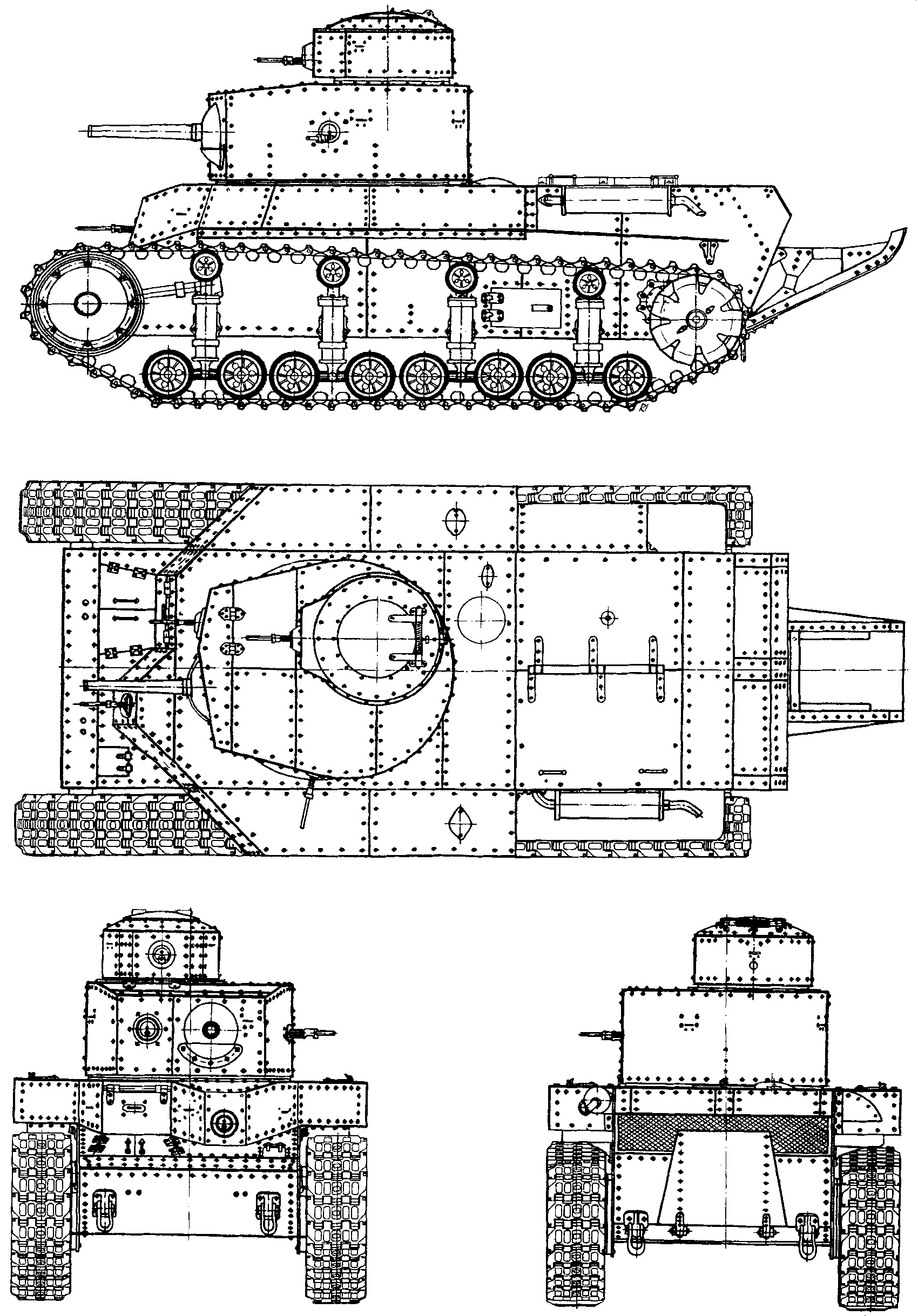
Externally, they still shared a lot in common. The hull was however widened to overlap the tracks, superstructure received a well sloped V-shaped front (central driver). The turret was roomier but retook the same commander’s cupola, with slightly taller hatch and hinged lid to observe outside while being buttoned up. The new rounded turret was not the other differences. The T-12 tracks were taller with less armor above, smaller front wheel whereas the T-24 had lower tracks, better protection, and a fourth DT machine gun in the hull next to the driver’s hatch.
Hatches were changed, notably over the engine deck, split in two instead of four. The two exhaust were reduced to one. The TC cupola was made from 12-22 mm (0.47-0.87 in) thick plating in hardrerned steel, riveted together and the front plate was 25.2 mm (1 in). The crew was eventually back to 3. Armaments wise it was the same a 45 mm (1.77 in) maain gun, but four DT machine guns. The weight was contained at 18.2 tonnes and top speed was kept under 24 km/h (15 mph), and on tests it appeared unsatisfactory given the Soviet deep battle doctrine which emphasis great mobility.
Fate and further developments
 The T-24 prototype was completed in 1931. The VTU was authorized to follow by an order of 24 preserie vehicles. One of these was rushed to Kubinka for comparative trials with the T-12, anf if performance was just above average, its engine caught fire. The turret had to be transferred to a T-12 prototype for gunnery testings and the 45 mm gun was not ready yet, so only MGs were tested. After this the T-24 was accepted into service with a single MG, and by 1932 all received their interneded gun.
The T-24 prototype was completed in 1931. The VTU was authorized to follow by an order of 24 preserie vehicles. One of these was rushed to Kubinka for comparative trials with the T-12, anf if performance was just above average, its engine caught fire. The turret had to be transferred to a T-12 prototype for gunnery testings and the 45 mm gun was not ready yet, so only MGs were tested. After this the T-24 was accepted into service with a single MG, and by 1932 all received their interneded gun.
Between until 1931, 300 more T-24 tanks were planned, but after further trials only 24 tanks were built as well as 26 turrets, and 28 running gears and transmission units. In the end, of the new tank was better than the abysmal T-12 it was still found unreliable. No active unit received ot but it was relegated to the tank school in local training units and featured in parades.
It seems now that the decision to drop the program was motivated by an excessive manufacturing complexity and flaws discovered on the first batch during production that were not easy to fix. The T-24 was another experiment for engineers, and their work was compared to Hans Grotte and its T-22 or TG-2 made by OKMO in Leningrad (N. Barykov, which designed the T-28). The TG-1 saw three prototypes developed with a 37 mm, 76.2 mm (3 in) or 76.2 mm (3 in) gun plus 37 mm (1.46 in) and single DT MG. The latter was massive, with a 250 hp M-5 engine for 35 km/h but weak Armor (20 mm front) and way too much complications for Russian mass production. However both it and the TG-3 (T-29) would influence the T-28, T-35, and SMK designs. Soviet access to Christie tanks (BT series), which perfectly matched the concept of deep battle, made all these prototypes as irrelevant as too slow. Sttill, the T-24 gave experience to KhPZ, passed on later into the BT tank series from 1931. Nevertheless, the T-12 chassis was later used to produce the succesful KhPZ's Komintern artillery tractor.
All T-24s were not wasted: They were placed into fixed position from 1938, (one T-24 at least, several T-18s), as static pillboxes. It seems the one concerned were issued the firing system of the T-28 and coaxial Maxim gun.
T-24 specifications | |
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 6.5 x 3 x 2.81 m (21.33 x 9.84 x 9.2 ft) |
| Total weight | 18.5 tonnes |
| Crew | 4 (driver, commander, gunner, loader) |
| Propulsion | 250 hp M-6 |
| Speed | 25 km/h (16 mph) |
| Range | 140 km (87 miles) |
| Armament | M32 45 mm gun, 4x DT 7.62 mm (0.3 in) LMGs |
| Armor | 8-20 mm (0.31-0.79 in) |
| Total production | 25 |
Src read more
On tank encyclopedia
Notice the rounded turret, the more elongated rear, the lower track height and the hull sponsons.


T-24 pillbox

In parade
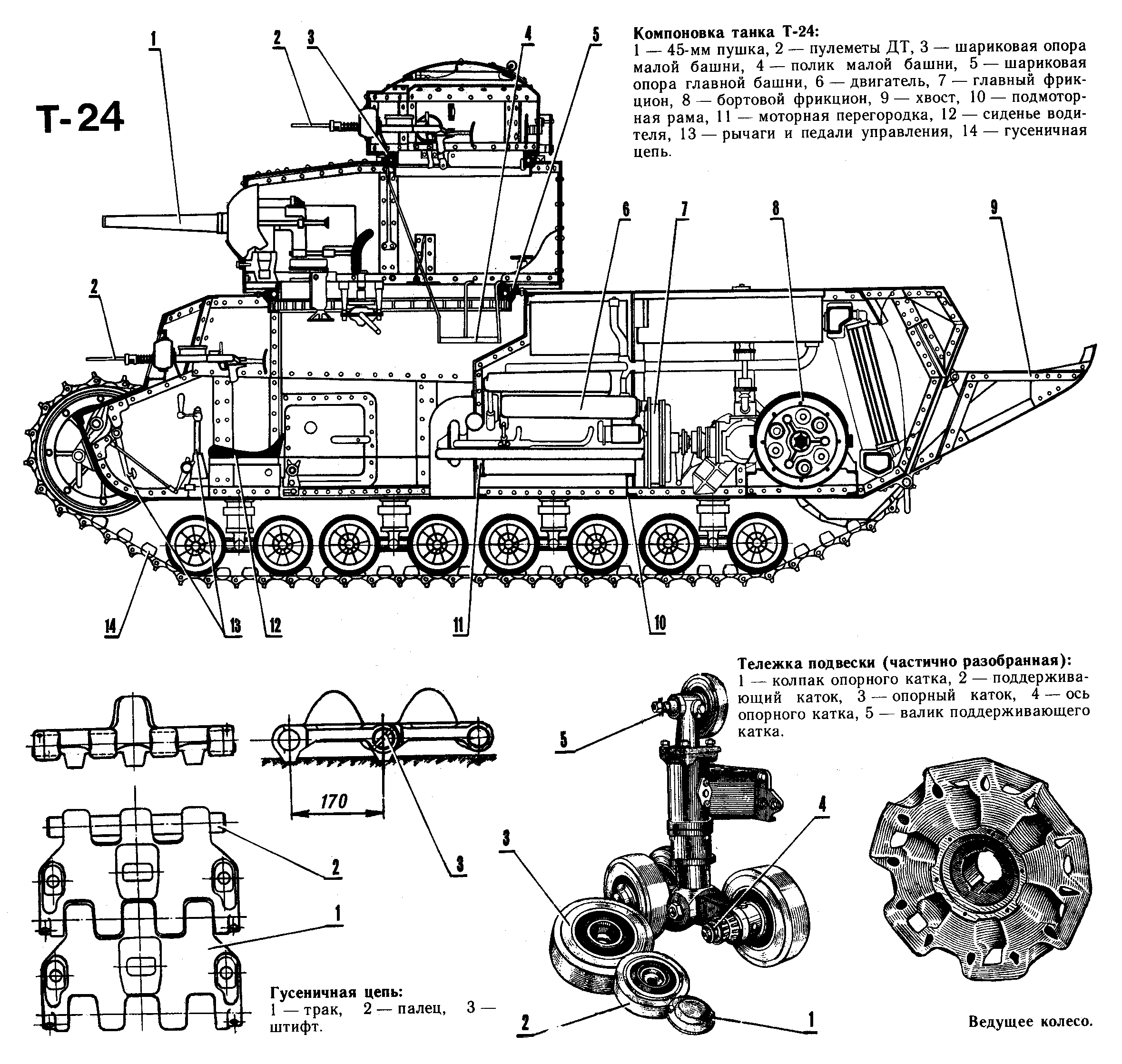
Technical drawings
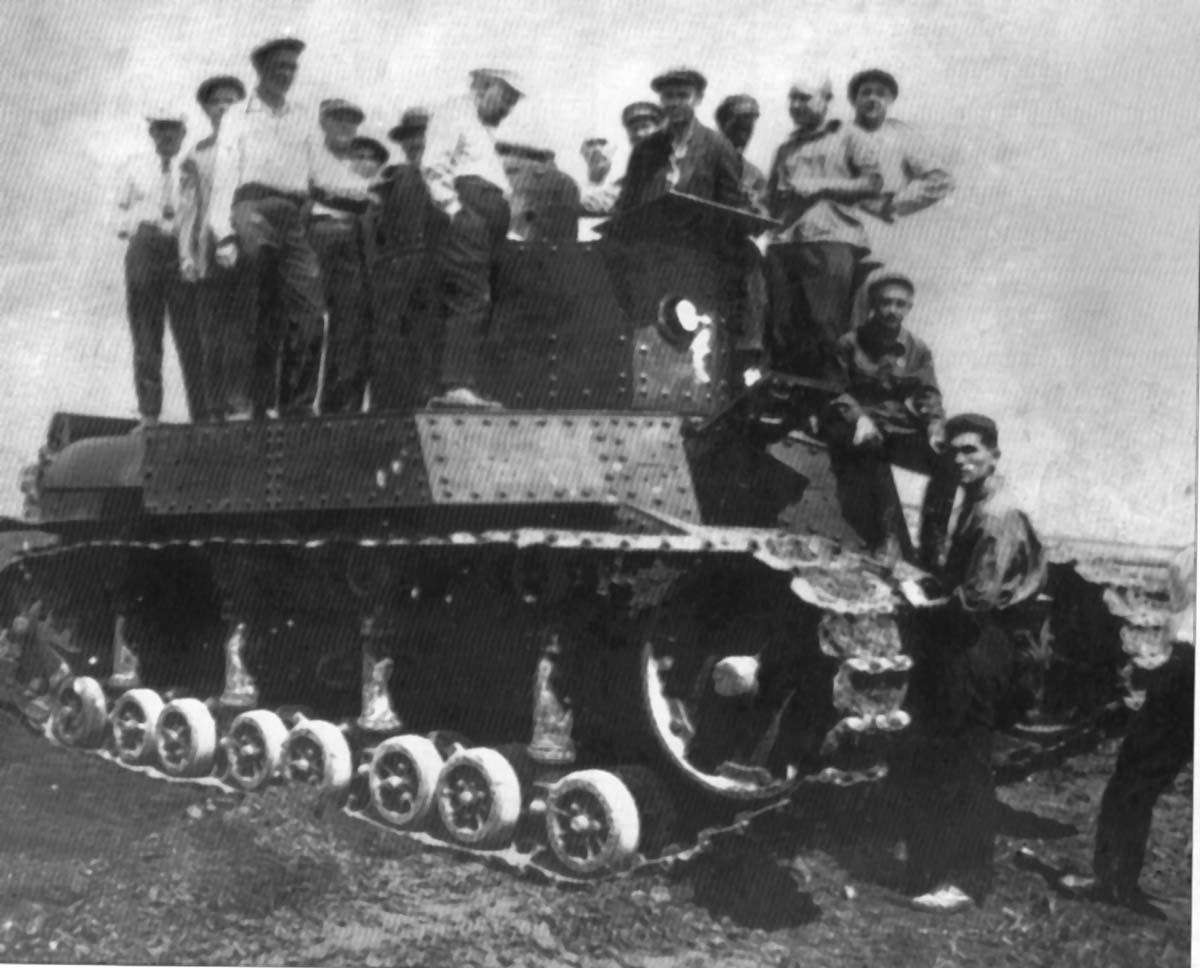

T-24 bein tested

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

