Spanish Interwar Tanks & AFVs
 Spain (1936-1937)
Spain (1936-1937)
Light tank – 15-20 built + 4 prototypes
Introduction : Spanish FTs prior to the Civil War
Spain was first introduced to tanks after the Great War when attempting to “pacify” Morocco from rebellious Muslim tribes, later known as the “Rif war”. France was already involved in the sector with many FT tanks, and Spain eventually bought about twenty tanks in 1919, followed by more inherited from the French forces in Morocco. Some of these FTs even participated in the first tank landing in history at Al Hoceima in 1925. The same year, the Spanish Army began the development of a program for an indigenous tank, largely based on the FT design. They also purchased a single FIAT 3000 from Italy for evaluation in 1925, which led to the development of the Landesa light tank.
The Trubia A4 prototypes & design
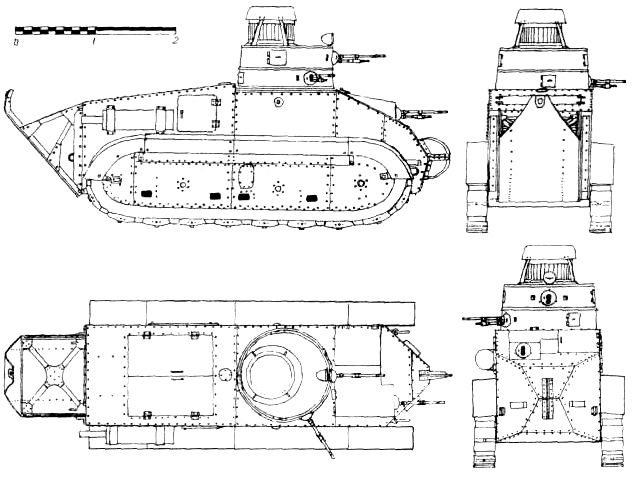
The Trubia Modelo 1925 was developed by the Fabrica de Artilleria Trubia in Asturia, in the industrial north of Spain. The hull was made of bolted 18 mm (0.7 in) armored plates over a steel frame, like the original Renault, and roughly the same dimensions and configuration. The first engine chosen was the four cylinder Hispano-Suiza 40/50 engine already propelling the Spanish Army artillery tractors, which had torque and was reliable. The Army estimated that the limited firepower of the original FT must be overcome with a new turret. It had a very original configuration (never seen anywhere else) consisting of two cylinders traversing independently, although the original idea was to provide a backup if the first machine-gun jammed. Both were fired through small ball mounts, and two extra side ports were added to the flanks. A first prototype was built as the Modelo Trubia 75HP, tipo rapido, serie A, and thoroughly tested, with success.
Other innovative features were the suspension and track mounted on the second prototype. Heading the Trubia program, Captain Ruiz de Toledo traveled to foreign countries to find other innovations. He found a unique integrated track design in Germany, in which the links were suspended from the chassis and held together by a lateral metal wall. This system was designed to prevent the tracks from coming off when maneuvering. The power to weight ratio was increased, as well as the range, by the use of a new Daimler four cylinder engine, coupled with a four forward/four reverse gear transmission. The vehicle was not compartmented, and the drivetrain could be reached by the crew for repairs on the spot. Another machine-gun was mounted in the driver casemate glacis plate, providing fire from five machine guns, served by the three men of the crew. Another innovation concerned the crew internal compartment and engine cooling, with a compressed air dispenser.
The first of this new prototype pre-series (four were ordered) was built in 1928 and passed all tests successfully at the Firing School. The second one was ready in 1931, followed by the two others in 1934. The latter three were issued to the Milan Infantry Regiment, in Oviedo, for field exercises and trials, while the first A4 returned to the factory in 1935, for repairs and modernization.
The Trubia Naval series
When the Civil War began in 1936, the three Orviedo Trubia prototypes were taken over by the Nationalists there, while the first prototype ended in the hands of the Republicans. Their fate is not known.
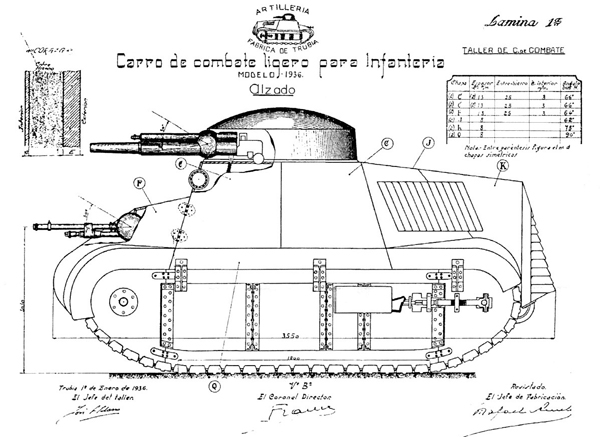
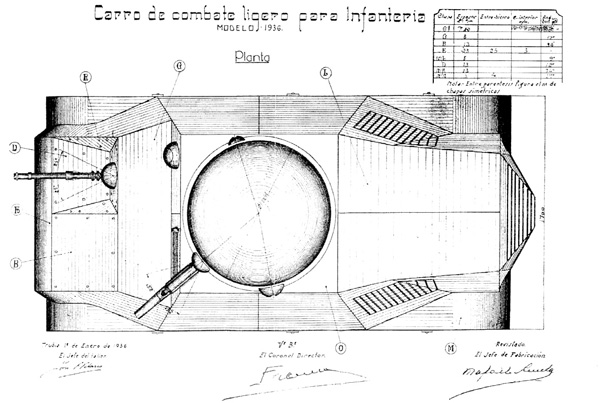
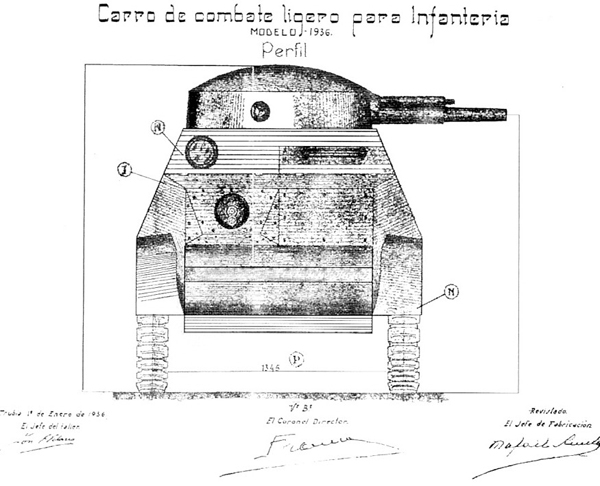
However, plans of the Trubia were handed over -thanks to Captain Ignacio Larrea, who headed the project- in Republican-held Sestao, near Bilbao. A new production run was quickly authorized by the autonomous government of the Basque country, based on the Landesa tractor, as the “Carro ligero Trubia naval modelo 1936” or M36 (built by the Spanish Shipbuilding company of Sestao). It is sometimes known as the “Euzkadi” (“Basque” in basque language).
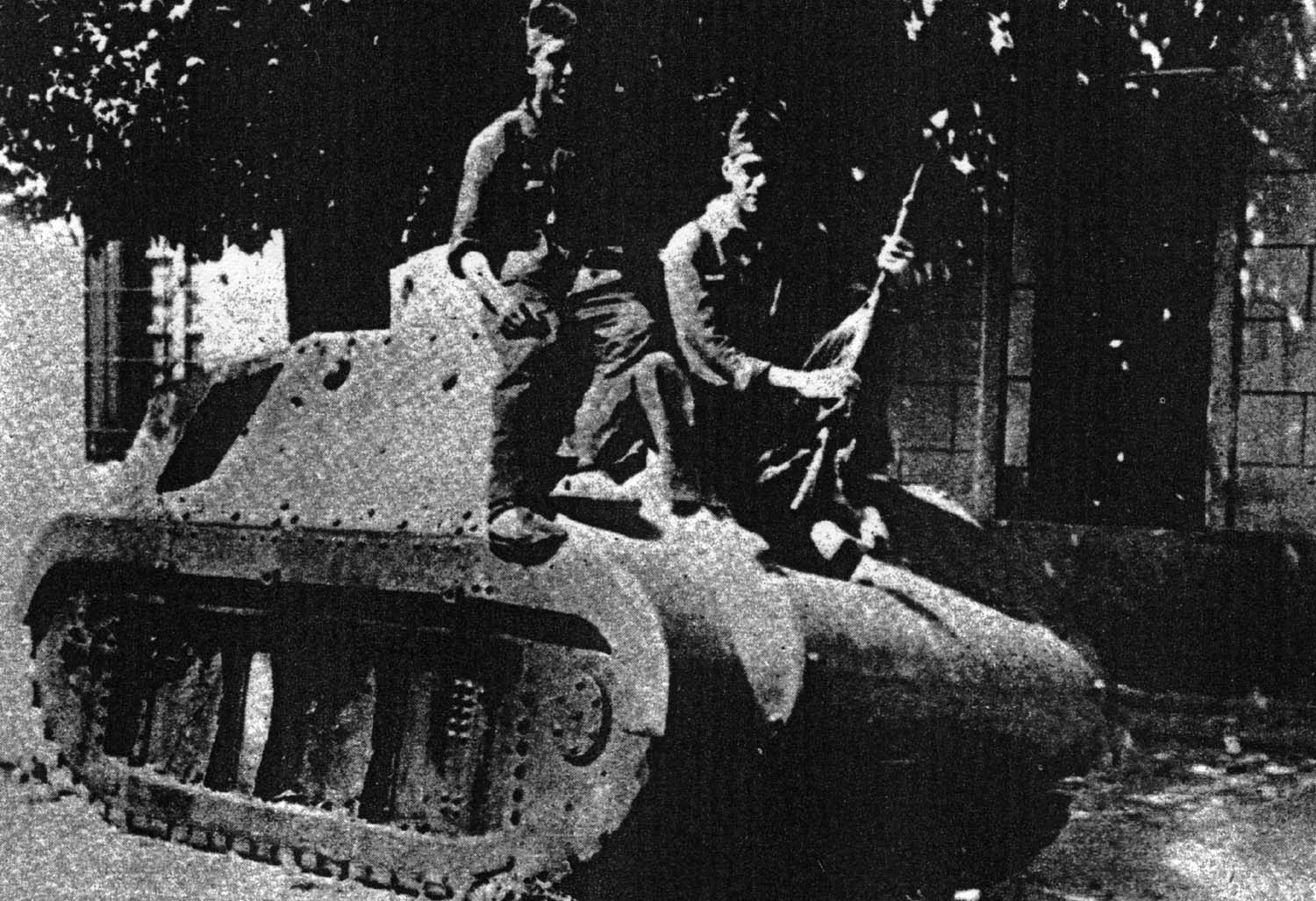
The vehicles, often compared to “toy tanks”, were quite small, but retained a crew of three. They were deprived of their steering tail and had a one-stage simplified turret. The armament consisted of two Vickers machine guns, one in the hull, used by the driver and the other in the turret. They were not compartmented, and the engine was so hot and noisy (the ventilation system proved inadequate at best) that it is said that the already crouched crew could not bear it for more than thirty minutes inside. Plus, the vehicles were underpowered, had a bumpy, rough ride (no suspensions) and were utterly slow. Armor varied from 6 to 16 mm (0.24-0.63 in), with a first level of 3 mm and 13 mm (0.12/0.51 in) armor plates bolted over with a gap of 25 mm (0.98 in). The overall weight was 5 tons.
The series was initiated in 1936 and ended in 1937. Little is known about their total production, numbers ranging from 15 to 20 or even 30 or more depending on the source. The confusion with the four Trubia 75hp prototypes adds to the uncertainty. Exact records disappeared. They saw combat but were more intended as local morale boosters rather than for long wartime operations.
Trubia Naval specifications |
|
| Dimensions | 3.55 x 1.70 x 1.80 m (11.65 x 5.58 x 5.9 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 5.5 tons |
| Crew | 3 (commander/gunner, driver, hull gunner) |
| Propulsion | MAN water-cooled, 6 cylinder, 70 hp (52.2 kW) |
| Max speed | 30 km/h (19 mph) on road |
| Suspension | None |
| Armament | 2x 8 mm (0.31 in) Vickers light machine guns |
| Armor | 16 mm (0.63 in) |

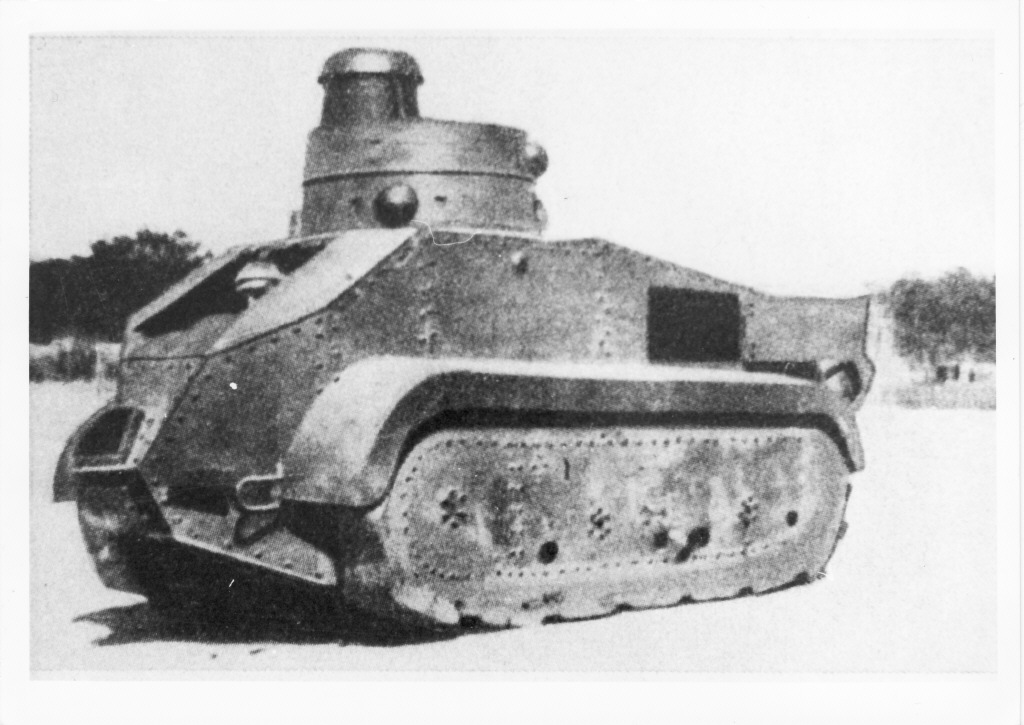
The Carro de Combate Trubia modelo A4, prototype n°2, without mudguards. It was attached to the Infantry Regiment Milan 32, which later took part in the defense of Orviedo. It featured the full armament of five machine-guns, including three Hotchkiss 7 mm (0.28). The “L” stood for Legero (light).

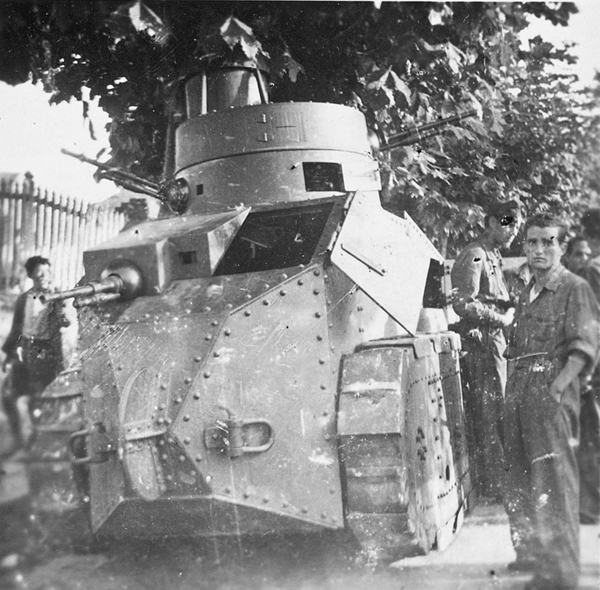
A camouflaged Trubia Naval of the Republican forces in the Basque country, 1936.

An unarmed Trubia Naval in 1938. Normal weapons were two Vickers machine guns.
Trubia Gallery

The first Trubia 75HP Carro Rapido Tipo A prototype at the Trubia factory.
Links
On Spanish tanks (generic) on Wikipedia
Spanish AFV list on Wikipedia
Spanish website Tanques y Blindados

WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com