T-50 light tank

 Soviet Union (1941) Light tank - 69 built
Soviet Union (1941) Light tank - 69 built
Good tank, bad timing
The T-50 was elaborated to replace older light reconnaissance models. Most of these had amphibious capabilities, but lacked good protection and good armament required to deal with other armored vehicles. A RKKA specification from 1939 requested an infantry support light tank to replace the ageing, mass-produced T-26, which was largely inspired from the British 1929 6-ton design, and the BT series, developed from the Christie prototype of 1930. The new T-50 design was to replace these older vehicles, be mass-produced and to operate alongside the BT-7Ms in service with the Red Army. It had many advanced features and, in many ways, looked like a "scaled-down T-34". Would it have been indeed produced in numbers, it would had been a powerful addition to the Red Army arsenal. However, events decided otherwise.Development
Design work commenced at OKMO (Opytniy Konstruktorsko-Mekhanicheskiy Otdel or "Experimental Design Mechanical Department"), under S. Ginzburg and L. Troyanov in 1939. OKMO was located at the S.M. Kirov Factory Number 185 in Leningrad, which would also assume production. Part of the initial design was taken from the abandoned T-46-5 project, and led to the improved T-126 and T-127 prototypes. The bureau was gutted during the Great Purge and work was resumed at the K.E. Voroshilov Factory Number 174 in Leningrad in May 1940. Both prototypes were eventually completed and tested in late 1940. This raised various issues that were corrected by Troyanov and the production design was ready in January 1941. It was assumed that the production could start in April 1941, but due to various technical problems, various delays occurred.Meanwhile, a second project design to replace the BT series was developed at the Malyshev Factory (KhPZ) in Ukraine. The first prototype was very promising, looking like a scaled-down T-34, with similar performance but smaller and thus cheaper to produce. A first prototype was built and the production design was under way when Operation Barbarossa started. It was decided in June to stop all projects and transfer the whole tank production to the Ural footsteps. This was accompanied by crucial choices in production, that were centered around a very few models. While OKMO was transferred to Omsk during September 1941, design work resumed, but the final model suffered from several issues and it emerged as costly to built as the T-34, which led to its cancellation after 69 were built until January 1942.
Design
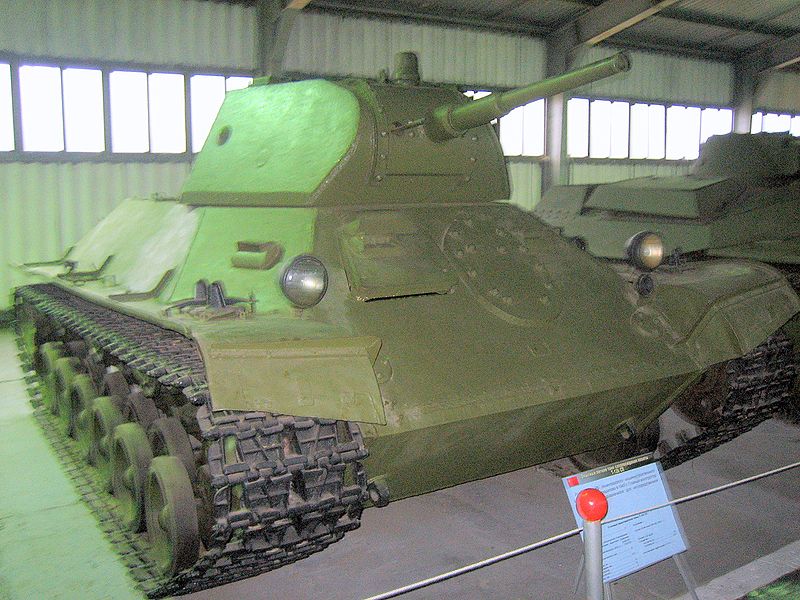
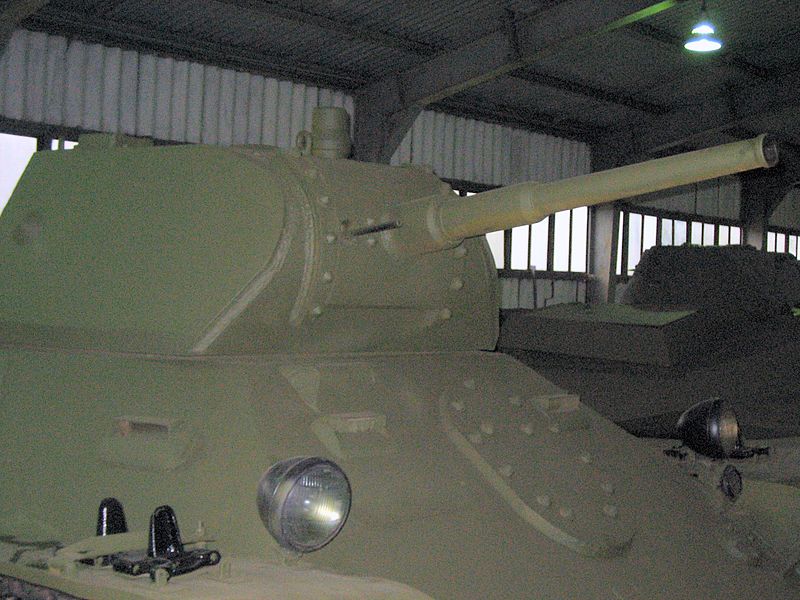
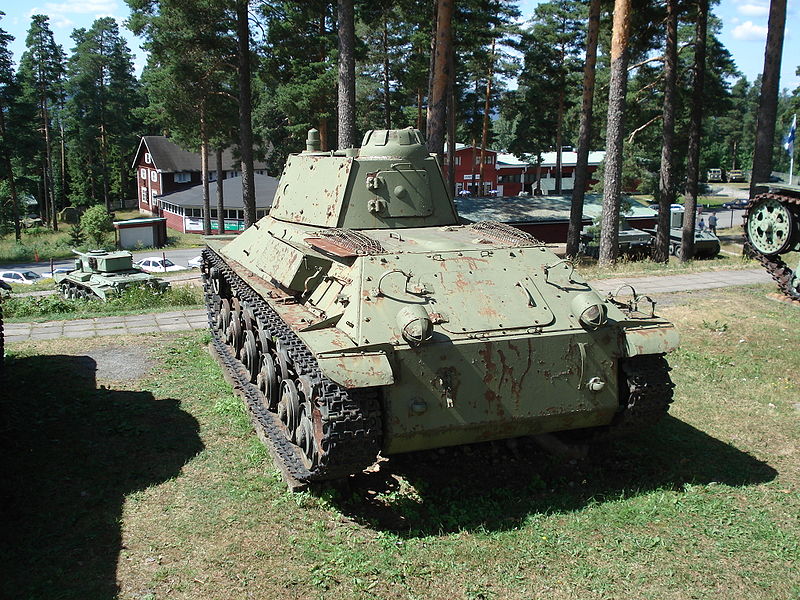
The final design of the T-50 was very much inspired from the T-34, having the same turret design. The all-around excellent welded, well-sloped armor was also similar. It had a narrower frontal section that accentuated the slope of the upper hull, which narrowed towards the rear. The front glacis was 37 mm thick (1.46 in), with an equivalent thickness of 50 mm (1.97 in) due to the slope. The minimum thickness was 12 mm (0.47 in) on the engine deck, roof and belly. For better commonality, the main armament was the standard 45 mm (1.77 in) Model 1938 gun, carrying 150 rounds. It compared well to the standard German 37 mm (1.46 in), but was equipped with crude sights. The driver was located on the left hand side, with his own hatch opening downwards, and could see through a simple slit with an armored cover.The hexagonal, sloped-side turret was innovative. Although cramped, it was a three-man design. The tank commander was placed behind the gunner in the turret rear right hand side corner. He had his own cupola with eight vision blocks, a feature later adopted on most Soviet tank designs. The loader was located on the left and the gunner was located on the right. Both had their own one-piece hatch opening to the front, acting as a shield when open. Radio was a common equipment, while it was reserved to commander tanks only on previous designs.
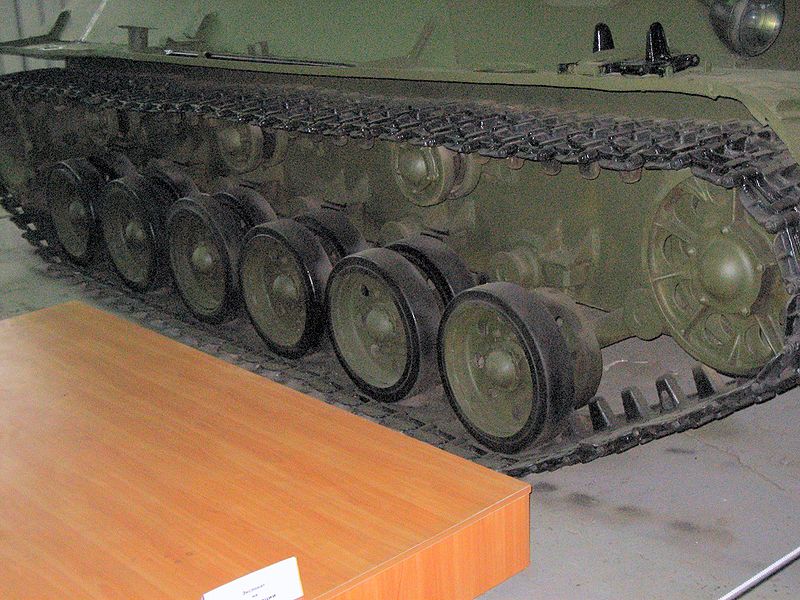
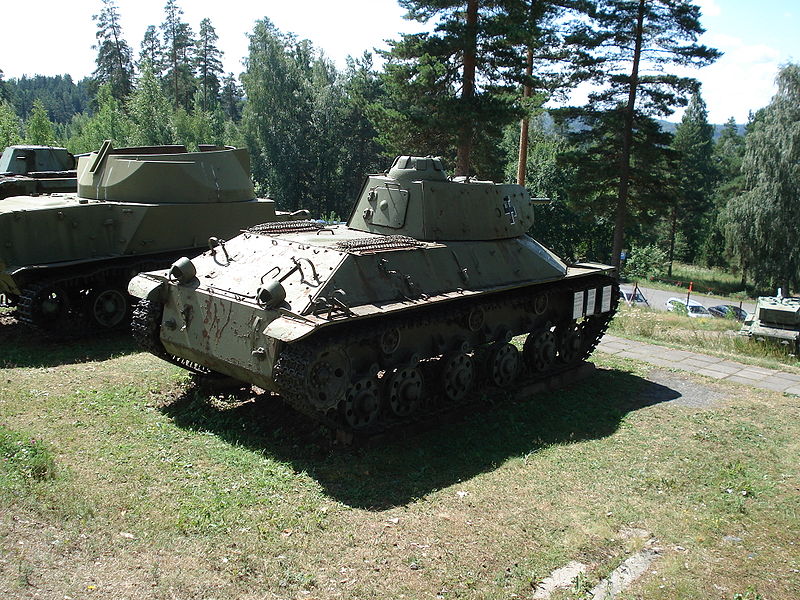
There was a major difference with the T-34 though, since the drivetrain comprised six smaller roadwheels, each suspended on its own torsion bar unit, and three return rollers. Drive sprockets were at the rear. A seventh roadwheel was raised up at the front, acting as track tensioner and idler. The specifically designed V-4 diesel inline-six engine offered 300 hp (220 kW) and a 21 hp/tonne (16 kW/tonne) ratio. This gave a top speed of 60 km/h (37 mph) and 220 km (140 mi) operational range. It is not known if drum-type external fuel tanks were mounted at any point.
The T-50 also shared some issues with other Soviet tank designs, like a cramped and uncomfortable fighting compartment. The troublesome V-4 inline-six diesel led to the accumulation of such development problems that the series was terminated because of it. By comparison, the T-60/T-70/SU-76 shared a more reliable standard GAZ truck engine. Therefore, despite being an overall excellent design, the engine led to numerous delays and the whole project succumbed to more urgent priorities.
The T-50 in action
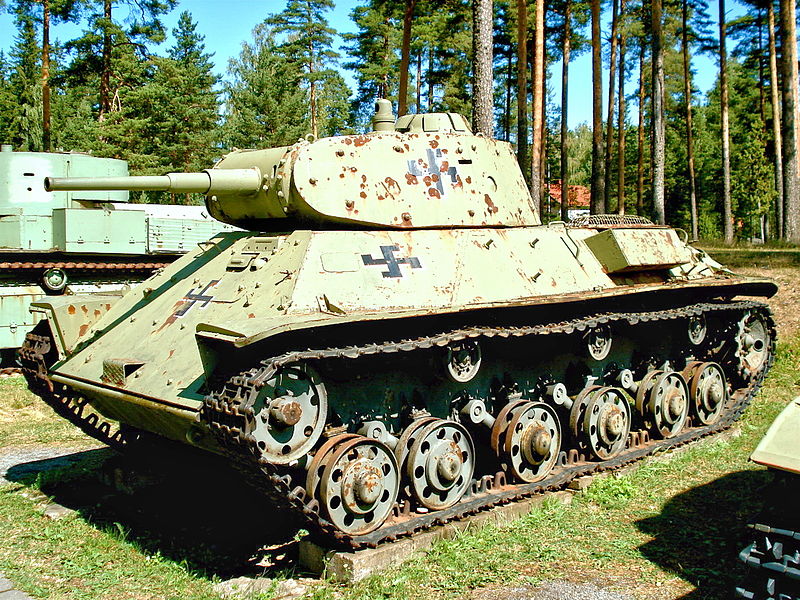
When operation Barbarossa went under way, some T-50s received, like many other models, extra layers of bolted-on appliqué armor. After this, the glacis and turret reached 57 mm (2.24 in) of thickness, which was impressive for a supposedly "light" tank. The few T-50s produced were sent to the Leningrad front. Most were opposed to Finnish forces, and one, up-armored, was captured and reused in 1944. These vehicles saw the end of the war, when their infantry support rôle was discarded in favor of fast-moving armored divisions entirely equipped with T-34s.T-50 specifications |
|
| Dimensions (L-w-h) | 5.20 x 2.47 x 2.16 m (17 x 8 x 7 ft) |
| Total weight, battle ready | 14 tons (28,000 lbs) |
| Crew | 4 (commander, driver, gunner, loader) |
| Propulsion | V-4 diesel inline-six, 300 hp (220 kW), 21 hp/t |
| Top speed | 60 km/h (37 mph) |
| Range/fuel | 220 km/350 l (140 mi) |
| Armament | Main: 45 mm (1.77 in) M1938, 150 rounds
Secondary: DT 7.62 mm (0.3 in) LMG, 2500 rounds |
| Armor | 20 to 30 mm (0.79-1.18 in) |
| Total production | 69 |

T-50 of the 1st Red Army Tank Division, in the vicinity of Leningrad, August 1941.

Late model of the 488th Separate Tank Battalion, Transcaucasian front, North Combat Group, October 1942.

Up-armored T-50 captured by the Finnish, "Niki" R110 of the heavy tank company, winter 1942-43.
Gallery
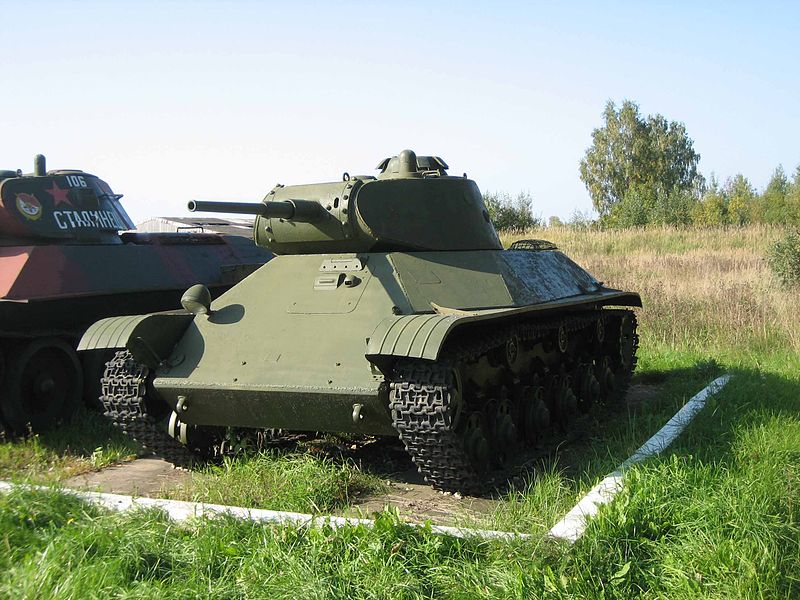

T-50 on display at the Kubinka museum. A T-126 prototype is also stored inside the hangar.
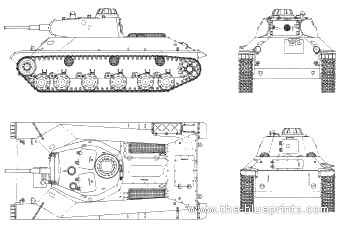
Blueprint of the T-50 - Credits: Blueprints.com.









WW2 Tanks




























WW2 tanks posters

All Tiger tanks liveries.

Panther liveries and variants

WW2 Armour - All tanks











Tanks aces and single tanks series

Find more there

Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com
