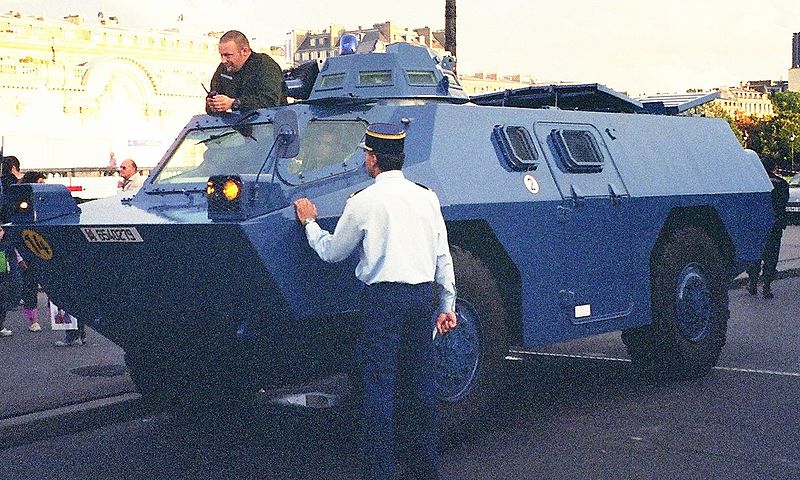
 The Berliet VXB-170 was designed as an armored personal carrier in 1969, competing against Renault's VAB on the largest post-WW2 Army procurement program (the equivalent today would be the scorpion program). Berliet was not chosen but found a customer with the Gendarmerie which looked years later for a similar vehicle for crowd and riot control. Then three export customers followed. When Berliet was acquired by Renault in 1978 however, the VXB was terminated after 179 vehicles built.
The Berliet VXB-170 was designed as an armored personal carrier in 1969, competing against Renault's VAB on the largest post-WW2 Army procurement program (the equivalent today would be the scorpion program). Berliet was not chosen but found a customer with the Gendarmerie which looked years later for a similar vehicle for crowd and riot control. Then three export customers followed. When Berliet was acquired by Renault in 1978 however, the VXB was terminated after 179 vehicles built.
Berliet's own take on the VAB
Since the end of the Second World War, the French army used Medium (3-5 tonnes) trucks for troop transport, completed by armoured vehicles as the first were exposed to enemy fire. At the end of the 1950s, Lorraine offered an armored body based on a Berliet truck. This project however was not approved by the parliament as too expensive to produce in the context of the time. The Army was back to trucks and a handful of vintage M3 Half-Tracks. The best motorized units were given the rare AMX 13 VCI, an APC variant of the prolific AMX-13 light Tank.Berliet vs. Renault on the APC program
At the end of the 1960s, the French army wanted a more modern solution to replace its WW2 M3 Half Tracks, which had issues, being old and offering a poor protection at the NBC age. The ministry asked French Truck manufacturers of the time, Renault/Saviem and Berliet to propose the design of a modern 4x4 armored vehicle for troop transport, an APC. The Berliet VBRG VXB-170 emerged through this new call for tenders for an amphibious and NBC-protected vehicle. It ought to be the most ambitious program by scale and technicity proposed by the French army since 1935 (when the whole FT tank park was renewed). The two manufacturers answered the call, Renault in its subsidiary manufacturing utility vehicle and heavy vehicle (SAVIEM) -now Renault Trucks (Defense)- and came with the VAB. Berliet came with its BC-12 program, later refined as the VXB 170. Comparative tests were carried out by the army in 1969, and the VAB was declared the winner.Not especially on technical grounds as both were quite similar on performances, but rather ergonomics, and most important, industrial capacities. Berliet was dwarved by Renault at this point, and for the production scale envisioned, this weighted heavily. But the Berliet proposal ended cheaper than the Renault's VAB, as a great attention was paid to integrate as many commercial parts as possible from its own truck range. The VXB 170 and VAB though were close "brothers" with many similarities, and well in line with other wheeled APC designs of the time around the world. Although Renaults's VAB won the contest (The production was quite massive, and continuous to the 2000s upgrade programmes, and the last being used in Ukraine today), Berliet had still a second best design on offer and later turned towards the French Gendarmerie, a branch of the Army which usually had its own procurement.
Berliet turned to the Gendarmerie
Indeed at the time, the venerable French Gendarmerie was looking at the time for a vehicle capable of destroying barricades, as memories of May 1968 were vivid. It was to be the perfect crowd control, do-it-all vehicle, a match for its numerous needs. The VXB 170 however was not alone though, as there was a competition there too. Berliet's prototype was thus opposed to the Panhard M3, another 4x4 wheeled AMC derived from the AML-60 armoured car and intended for export. Compared to the puny M3 it was no real opposition. Panhard was part of Citroën at the time, like Berliet. So the direction pushed the Berliet forward instead, without second-thinking.And thus, with a bit of pressure and a phone call from Citröen, the Gendarmerie staff was not long to choose the larger and more impressive VXB-170. Still, it was not much costier than the M3 for greater capacity. It is therefore logical that the VXB 170 was chosen in 1972. This was followed by a firm order for 155 units. This was evidently several fold lower than the global French army market but allowed to at least financed the prototype construction and tests for the first competition and recuperate some cash without impairing its industrial capacities (no costly investment in real estate and machining). In the name "VXB 170" the number was related to the engine output, 170 hp.
Production and Fate

Another view of the VBRG
Berliet soon setup a small production line at its Bourg-en-Bresse plant to offer a reasonable output over five years (1974-78). The very first production vehicles were delivered from 1974, tand it was soon renamed the VBRG (for "Véhicule Blindé à Roues de la Gendarmerie" or Gendarmerie's Armored Wheeled Vehicle). Its main mission was the transport of armored gendarmes (similar to the Police CRS) to restore public order with better assets than the Police.
Compared to the civilian police forces, the gendarmerie indeed could bring to bear military capabilities with armored personnel carriers or heavy armored vehicles armed with 90 mm guns, and in wartime has the capacity to integrate other armed forces. It is not however a paramilitary force per se. The National Gendarmerie is responsible for crowd and riot control (Gendarmerie mobile), counter-terrorism and release of hostages (GIGN), control and security of airports and aerodromes and air traffic police as well as protecting the President (GSPR), acting as a national guard for sensible sites (Nuclear Weapons Security Force) and prestigious monuments and institutions, plus the honorary Republican Guard. There is also a mountain rescue Platoon, a maritime surveillance branch and the Air Force Gendarmerie. The concept of a hybrid force between the army and police is a widespread concept around the globe.
The VXB-170 production at Berliet went on until 1976, with the 155 vehicles ordered being effectively delivered. However this was still a far cry of what Berliet expected in terms of sells and turned quickly to the export, as Panhard did for the M3. Based on this first success in France, Berliet hoped to find countries potentially interested, but soon encountered its own rival on these markets for the same need, the VAB. There were in the end few countries that placed an order and just for a few vehicles: Gabon wanted 12 for its own Gendarmerie, as Senegal (12 also) and Tunisia, also for crowd control, and just 10 on order. On the long run, Berliet expected to expand this but in 1978 an axe blow fell, as the company was taken over by no other than...
Renault, creating Renault Vehicles Industriels. The new management soon realized the VXB was a direct competitor of the VAB and terminated the production, causing compehensive anger in the working personel and direction and ending the serie to a mere 179 (or 189 units depending on the source), well below the expected treshold and VAB's own production of nearly 9,000 vehicles. There was just before also a good prospect in South Africa, before the domestic Ratel was chosen.
The VXB was deployed by the forces of Gabon especially to face unrest and civil war, as well as Tunisia during the "arab spring". The Tunisian vehicles were retired soon after. The Senegalese/Gabonese are still in service. Both also contributed to some UN operations with this vehicle. The French VXB intervened at several occasions on metropolitan France, notably during the 2010s terrorist attacks in Paris.
155 VXBs were procured from 1974 for mobile units and 70 remains in service today on continental (metropolitan) France, as well as in Corsica and French overseas territories as of 2018. Renamed VBRG in a military context it was equipped with the 7.62 mm (cal.30) AANF1 machine gun and 56 mm ALSETEX Cougar grenade launcher. The Gendarmerie used them also in Kosovo and Ivory Coast in peace-keeping operations. They are scheduled for retirement, or at least to be placed in depot, and possibly candidates to be provided to Ukraine after an overhaul.
Design of VXB-170

3 views of the vehicle (Scr unknown)
Hull
Built around an armored chassis, the VXB-170 is a conventional 4x4 APC, quite close in design to the VAB. It's nose however is quite different, two-faceted, and more importantly the driver is located in a central post, with three windows for peripheric vision, unlike the classic two seats cabin of the VAB. No armored shutters are provided but for crowd control, the windows could equipped with metal netting. The windows forwars had extra framing to insert these protective elements. There are also two more windows on either side with the same system, and two doors for side access. Due to the location of the engine, the nose can be given extra equipments, like the winch in the variant, or hydraulic arms for the bulldozer blade version. The engine is accessible via a trap at the rear left, and access/exit is possible via the rear door in a wartime situation. The vehicle's roof also comprised four hatches, which allowed personal to stand and fire on the move, albeit exposed. There are two well rprotected main lights and optional blackout light under shutters on the nose. Rear mirrors are located also there.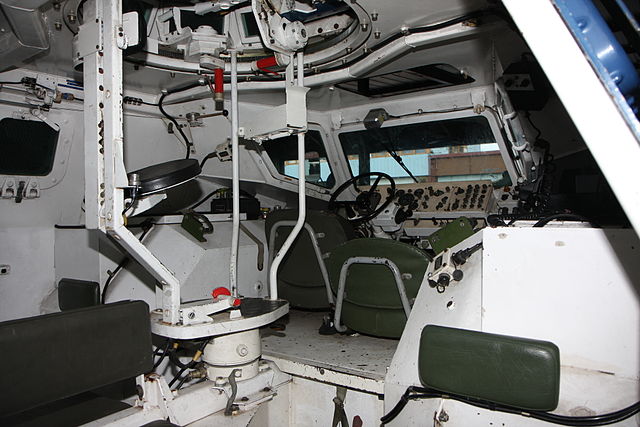
Cabin of the VBRG (Satory)
Armour protection layout
The monocoque hull is protected against small arms fire, 8mm (3 in) on the sides and roof, 6mm (2.5 in) for the floor, which is flat and vulnerable to mines and IEDs. There is a conventional seating layout as well, with a central bunk large enough for eight seated infantry back to back, turned towards the exterior. The idea was to procure them pistol ports in case of military conversion. The front nose is also 8mm but the slopes gave it an artificial greater thickness. On the NBC front, the vehicle was planned to be equipped with full sealing and interior anti-spall lining, and overpressure. It was not implemented due to its role. For active concealement, the vehicle could be equipped with smoke projectors, but this also was never implemented.Engine & Mobility
It is a four-wheel drive vehicle, powered by the V8 Berliet V800, already used on buses and therefore well proven. It is located at the rear-left of the hull. The nose house the transmission. It has a displacement of 6.92 liters, offering 170 hp and a lot of torque, to reach up to 85kph on road, but also to cross 60% slope and run along a 30% incline. It could also gap a one meter trench and 80 cm vertical obstacle. It is fully amphibious, although not given options such as propellers, pumps, or trim vane. Due to its weight its tactical mobility is the same as the VAB, with easy transport on train, heavy duty cargo plane and amphibious crafts of the French Navy, compatible with NATO standards. It was not tested for paradropping. In 2019 a renovation saw this old engine replaced by a more efficient Iveco diesel for the same output.Armament
This was mission-dependent. The basic Gendarmerie vehicle was unarmed, although having a hatch allowing someone standing with a personal weapon or any other implement. Some variants are given a turret with peripheric view and housing for a machine gun or water projector, smoke projector, ect. An optional ring mount allows the use of the standard French AA-52 (NATO 5.56 cal.) or AAN F1 light machine gun or the M2HB heavy machine gun (12.7 mm). In complement it is given the 56 mm standard grenade launcher, converted to send riot-control ordnance. It seems that no heavier armament was planned. In a military context though, the vehicle could carry up to 8 equipped troops, including heavier armaments such as portable mortars, antitank and anti-helicopter launchers (Manpads).Variants
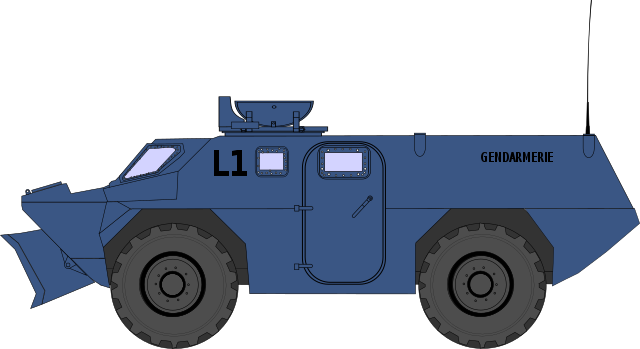
VRBG "boutoir" profile (cc)
The VXB was declined into an internal security vehicle with a modular interior, and could be a basic transport, command vehicle, could be fitted with a blade to clear out obstacles and being given a winch for towing out obstructions, or self-recovery. For export, it was marketed as a reconnaissance and patrol vehicle and light combat APC. The original competition against the VAB implied the installation of hydrojets but this was never implemented. Instead to keep the cost low, the VXB was amphibious without preparation, mobile by using the wheel's motion, and with an optional trim vane. The vehicles also had a lot of optional equipments like the turret's megaphone, sirens, light projectors.
⚙ VXB-170 specifications | |
| Weight, in battle order | 12.7 tonnes (12.5 long tons) |
| Dimensions | 5.99 x 2.5 x 2.05m (19 ft 8 in x 8 ft 2 in x 6 ft 9 in) |
| Propulsion | Berliet V800M 8-cylinder diesel engine 170 hp (130 kW), pwr 23 hp/t |
| Speed | 85 km/h (53 mph) |
| Range | 750 km (470 mi) |
| Armament | 1x AA52 7.62mm LMG, 56mm Grenade Launcher, see notes |
| Protection | 8-6mm RHA, smoke projectors |
| Crew | 3+8 |
Read More
Links
On lautomobileancienne.com/lesvoitures.fr/
armyrecognition.com
arquus-defense.com/
www.janes.com
fr.calameo.com
ouest-france.fr/
en.wikipedia.org
fr.wikipedia.org

VXB-170 proposed to the Army, 1970

VXB-170 of the Gendarmerie, 1980s
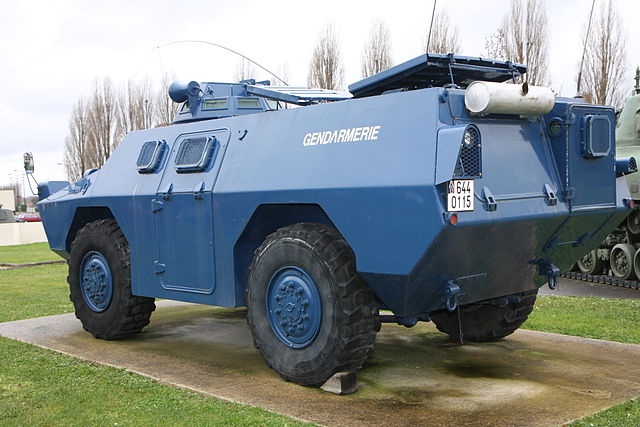

Vehicle seen in Satory
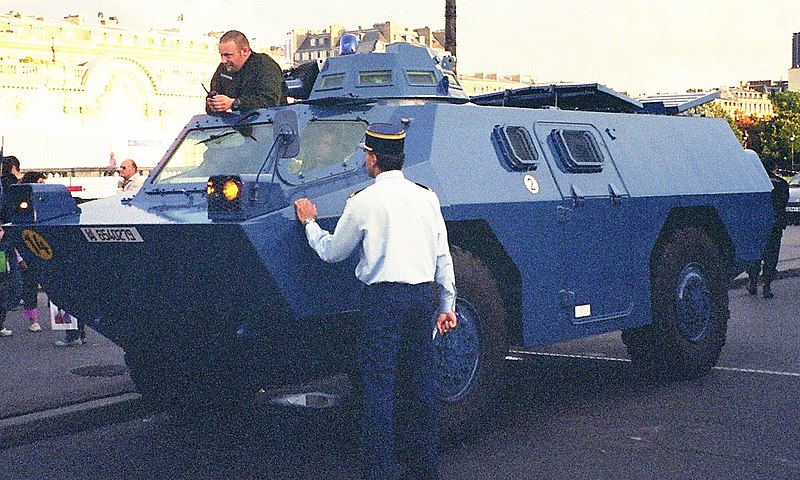

The VRBG on display
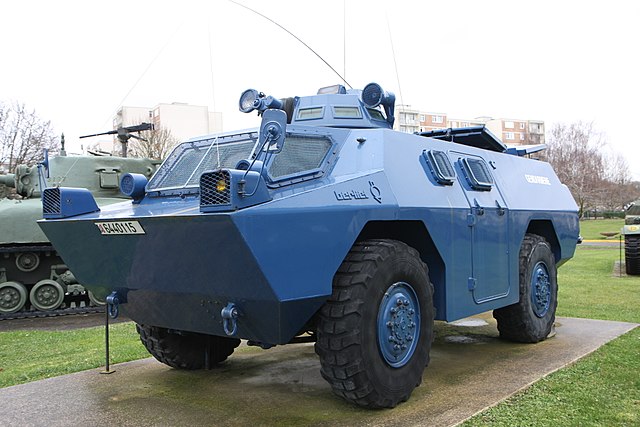
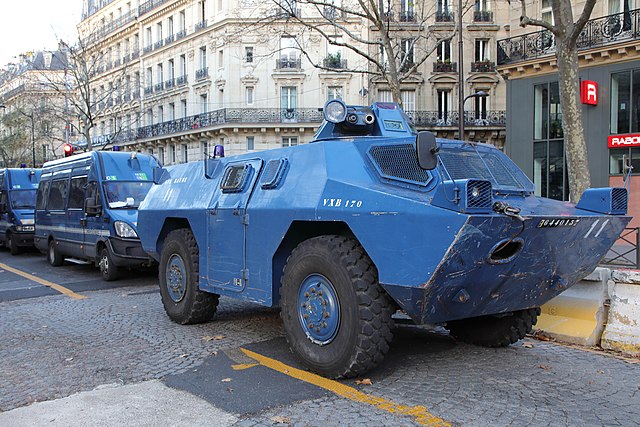


The treuil (winch) variant at Domenjod, 2018. Note the nose aperture and hook. The turret shows its empty locations for an LMG and grenade launcher.

VBRG rear
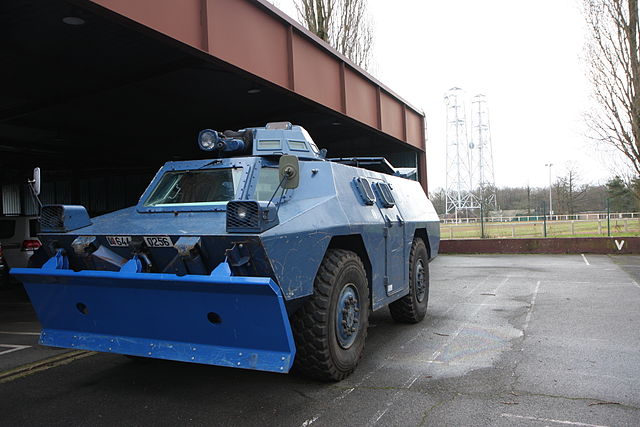

Turret/Dozer ("boutoir") VBRG

Cold War Tanks


































Cold war tanks posters

Cold War Main Battle Tanks

Cold War Soviet Army
Museums, Movies, Books & Games
The Tanks and Armor in pop culture
Tanks and armored vehicles in general are only really grasped when seen first person: The mass, the scale, it's all there. Explore also the way tanks were covered in the movie industry, in books and in video games.Movies:
Best tanks movie on warhistoryonline.com
On imdb.com
On bestsimilar.com/
miltours.com
liveabout.com/
watchmojo.com
Video Games:
pcgamesn.com
historyhit.com
levvvel.com
vg247.com/best-tank-games
mmobomb.com/
alienwarearena.com

