The Norinco Type 89 tracked armoured fighting vehicle is an armoured personnel carrier developed from the earlier export Type 85 AFV, entering service in around 1995 and first shown publicly in 1999. In the pure APC form around 1,700 are in service. Norinco industrial index is WZ534, with the export version denominated YW534. However the new designator system had it renamed officially as the ZSD-89. Apart China, the largest user, they were exported also to Ethiopia, Sri Lanka, Myanmar, Zimbabwe and Nigeria.

a large troop compartment door at the rear where that has a vision block and firing port, a single circular roof hatch on each side in the forward part of the troop compartment roof and two oblong roof hatches to the rear of the 12.7mm machine gun installation. Its large troop compartment door at the rear where that has a vision block and firing port, a single circular roof hatch on each side in the forward part of the troop compartment roof and two oblong roof hatches to the rear of the 12.7mm machine gun installation. There are two firing ports and periscopes in the left side of the hull and three or four firing ports and periscopes in the right side. The firing ports are fitted with ball and socket type mountings for rifles. (Other vehicles have been seen with three firing ports and periscopes in the left side and four in the right.)
A trim vane is erected at the front of the vehicle before it enters the water. The basic variant Type 89 is fitted with a roof-mounted 12.7 mm antiaircraft machine gun (AAMG), and eight (4 on each side) smoke grenade launchers. The gunner is protected by a bullet-proof shield surrounding the cupola. Seven firing ports on the sides and rear of the troop compartment allows infantry passengers to fire automatic rifles and light machine guns from inside the vehicle on the move. The troop can also carry 7.62mm machine gun, 40 mm rocket propelled grenades (RPGs) and shoulder-launched air-defence missiles.
The tracks are double pin, so that the wheels circulating inside and could be padded. They are of the same type as before. The Type 89 like the Type 85 has enough built-in buoyancy, added to the full NBC sealing, to provide floatability. Speed when swimming is around 10 kph, propelled by the tracks so agility is mediocre. On flat, the Type 89 is suspended on torsion bars with hydraulic shock absorbers on some of the roadwheels, same system as for the Type 85 for a top speed of 66 km/h (41 mph) and offers a range of 500 km (310 mi), on light load and flat.
 Ethiopia; 10 purchased in 2013 for operations in Somalia.
Ethiopia; 10 purchased in 2013 for operations in Somalia.
(No flag) Tigray Defense Forces
 Myanmar – ZJX-93 (Type-93) variant (also a park of Type 85)
Myanmar – ZJX-93 (Type-93) variant (also a park of Type 85)
 PRC: 1,500 ZSD-89/A APC; 900 PLZ-10 Gun-Mortar
PRC: 1,500 ZSD-89/A APC; 900 PLZ-10 Gun-Mortar
 Sri Lanka: 40 of the 89/89A YW-534 (+20 Type 85/YW-309 in storage)
Sri Lanka: 40 of the 89/89A YW-534 (+20 Type 85/YW-309 in storage)
 Zimbabwe – ZSD-89-II, used during the Second Congo War
Zimbabwe – ZSD-89-II, used during the Second Congo War
 Nigeria – 60 delivered in 2021.
Nigeria – 60 delivered in 2021.

Development
The Type 89 (also known as YW534) armoured personnel carrier (APC) is successor to the older Type 63 (YW531C) in service with the PLA ground forces. The Type 89 is the domestic variant of the Type 85 (YW531H) APC developed in the 1980s for export market. The vehicle entered service in the late 1990s and was first revealed to the public in the 1999 national day military parade in Beijing. The Type 89 (YW534) was developed from the Type 85 (YW531H) APC with some minor modifications. The development of the Type 89 probably began in the mid-1980s. Compared to the Type 85, the Type 89 has a slightly longer and wider hull, and more sloped front armours for better protection. The vehicle might also have a more powerful powerpack and other improvements such as night vision. The PLA has also developed the Type 89-II infantry fighting vehicle based on the Type 89 hull and fitted with a 25mm cannon. Norinco stopped production around 1995, maintained to deliver variants and produce a stockpile of replacement parts for the long term.Design of the Type 89 APC
General Layout and differences
Albeit nearly identical externally to the Type 85, the Type 89 was made slightly larger and heavier, by taking in account numerous use report. The hull remains in the same shape, still made of welded steel to provide protection against small arms fire. There is enough space in the rear compartment and other posts for 13 men (15 for the longer Type 89A). This includes ten seated in the troop compartment at the rear, seating inwards, and the crew, with the driver seating in the front left (single piece hatch opening to the left), further forward from the commander, and provided with three day periscopes for a vision to the front and right. The main forward periscope could be replaced by a night vision device. The commander sitting behind has a single piece hatch.a large troop compartment door at the rear where that has a vision block and firing port, a single circular roof hatch on each side in the forward part of the troop compartment roof and two oblong roof hatches to the rear of the 12.7mm machine gun installation. Its large troop compartment door at the rear where that has a vision block and firing port, a single circular roof hatch on each side in the forward part of the troop compartment roof and two oblong roof hatches to the rear of the 12.7mm machine gun installation. There are two firing ports and periscopes in the left side of the hull and three or four firing ports and periscopes in the right side. The firing ports are fitted with ball and socket type mountings for rifles. (Other vehicles have been seen with three firing ports and periscopes in the left side and four in the right.)
A trim vane is erected at the front of the vehicle before it enters the water. The basic variant Type 89 is fitted with a roof-mounted 12.7 mm antiaircraft machine gun (AAMG), and eight (4 on each side) smoke grenade launchers. The gunner is protected by a bullet-proof shield surrounding the cupola. Seven firing ports on the sides and rear of the troop compartment allows infantry passengers to fire automatic rifles and light machine guns from inside the vehicle on the move. The troop can also carry 7.62mm machine gun, 40 mm rocket propelled grenades (RPGs) and shoulder-launched air-defence missiles.
Protection
The Type 89 like its precedessor is only proof against heavy machine guns such as the Soviet Kord and DshKa. Thus, protection based on steel panels, welded, rolled homogeneous, with a sloped hull forward, flat on its side, is averaging 8mm (0.3 inches), artificially increased on the front to resist up to 12.7 mm or 0.5 inches AP rounds. Some had a HMG shield protected against small arms fire. Both the belly and roof are also protected against 0.7 mm fire and shrapnel. The Type 89 comprises three automated fire extinguisher system halon-based, in the engine, combat and troop compartments. There is also a fireproof bulkhead separating the engine compartment on the right from the crew. It is also likely protected NBC with air conditioning. It also has six smoke dischargers for active concealment.Propulsion & Mobility of the Type 89 APC
The Type 89 is powered by an air-cooled, Deutz BF8L 413F 4-cycle 8-cylinder, turbocharged diesel engine rated for 320 hp (240 kW) at 2,500r/min with a fuel capacity of 450l. It is located on the right rear of the driver, with a large intake on top of the hull to allow water crossings without ingesting the latter, and the exhaust placed on the right hand side. This engine is similar to the Type 85 albeit somewhat improved in performances. It feeds a manual transmission with five forward gears and one reverse gear. The Track is forward-driven (ront sprockets) close to the transmissio, while the chassis retained the exact same five axles, each with dual rubber-typed road wheels and four track-return rollers, and an idler at the rear.The tracks are double pin, so that the wheels circulating inside and could be padded. They are of the same type as before. The Type 89 like the Type 85 has enough built-in buoyancy, added to the full NBC sealing, to provide floatability. Speed when swimming is around 10 kph, propelled by the tracks so agility is mediocre. On flat, the Type 89 is suspended on torsion bars with hydraulic shock absorbers on some of the roadwheels, same system as for the Type 85 for a top speed of 66 km/h (41 mph) and offers a range of 500 km (310 mi), on light load and flat.
Armament
The Type 89 has a single armament in its base configuration of APC, with a 12.7 mm Type 54 Chinese roof-mounted antiaircraft machine gun (AAMG). It is generally provided a protective shield around. This a modified DshKM, firing 12.7 x 108mm round at 600 rounds per minute, fed by 50 round belts with an effective range beyond 1 km. It could fire tracers every ten or five rounds depending on the setup. There are also six smoke dishargers that can be used with anti-personal grenades. The Troops enter the Type 89 via a single door in the hull rear, three several ball-and-socket firing ports per side, one additional in the entry door, with periscopes provided to allow observation of the battlefield. The ten men, 5 seated either side with their full gear are typical of a motorized Chinese infantry platoon, likely with great anti-armour capability over automatic small-arms, hence the extremely widespread proliferation of the Type 69 RPG. The latter could be hoisted under the roof, adding to the firepower of the Type 89. See the variants for more weapons systems.Variants
Type 89
Type WZ534
Basic Type 89 Tracked APC, ZSD-89.Type YW307
Type 89 IFV (Infantry Fighting Vehicle), one-man turret with 25 mm autocannon (400 rounds)/7.62 mm coaxial. ZSD-89-II.Type 89 ACV
Armored Command Vehicle, higher roofline, longer 6 axles chassis, 12.7 mm HMG on commander's station.Type WZ752
Type 89 Armored Ambulance (unarmed).Type WZ731
Type 89 Armored Reconnaissance Vehicle with sub-variant ZZC-01.GCL-45
Type 89 Artillery Front-line Observation Vehicle with unarmed turret. Also called ZZC-05.Type 89 Recce Radar Carrier
Battlefield surveillance radar vehicle on crane. Also called ZZC-02.Type 89 Refuelling Vehicle
Transport vehicle for fuel and lubricants, fitted with a higher troop compartment. Offered for export as the Amphibious Armoured Refuelling Vehicle.Type 89 Recovery Vehicle
Maintenance and recovery variant, fitted with a light crane on the left side of the hull roof, and a machine gun cupola in the roof center. Military designator: ZJX-93 (also called Type 93).Type 89 Supply Vehicle
Similar to the recovery variant and also equipped with a light crane, but the commander's cupola with HMG is located behind the driver's position. Military designator: ZHB-94.Type 89 AT missile carrier
ATGM carrier vehicle with double launch system for wire-guided HJ-8 missiles. A total of 12 missiles is carried on board. Military designator: ZDF-1 or ZDF-89.Type 89 Mine-Laying Vehicle
Has a modified rear hull that mounts a scatterable mine system, consisting of 6 launchers. Each launcher has 36 tubes of 122 mm with each tube containing 5 SATM mines, 15 SAPM mines, 45 SAPEM mines or a mix of SAPM and SAPEM mines. Military designator: GBL-130.Type 89 Obstacle-Removing Vehicle
Crowd-control variant for the PAP, equipped with an obstacle clearing blade.Type 89-II IFV
The Type 89-II infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) is fitted with an one-man 25mm cannon turret and 7.62mm PKT coaxial machine gun. The 25mm gun has a full 360° traverse with an elevation of -8° ~ 55°. Ammunition load for the 25mm gun is 400 rounds, with an additional 120 HE (high-explosive) rounds and 80 AP (Armour-Piercing) rounds carried in the turret. The 25mm gun can fire single, 3-round burst, or 5-round burst. The max rate of fire is 100r/min or 200r/min. A small examples have been built for trial and evaluation, but the vehicle did not enter mass production.Type 89A
Type 89A has extended chassis, higher roofline, and side armor is completely vertically welded (whereas Type 89 is sloped). The armor is reinforced with better ballistic protection, comparing to the original Type 89. The vehicle chassis features side-skirt with a distinctive wave pattern. Type 89A is developed in 2000s, complementing ZBD-04 series.ZSD-89A
Type 89A Armored Personnel Carrier (ZSD-89A) – Type 89A base model with armor-plated 12.7 mm HMG turret.Type 89A Armored Command Vehicle
Type 89A extended chassis with command and control equipment, and a 12.7 mm HMG for self-defense.Type 89A Armored Communication Vehicle
Type 89A extended chassis with additional communication equipment.Type 89A Armored Ambulance
Unarmed ambulance with a higher roofline and with a longer chassis with 6 double road wheels either side.Type 89A Armored Reconnaissance Vehicle
Armed with ZBL-08 turret with electro-optical sensors, radars on a telescopic mast, and an UAV launcher rail.[6] Aerial reconnaissance capabilities are provided with various unmanned aerial vehicles. All reconnaissance vehicles are equipped with a launch rail behind the turret, capable of launching ASN-15 with 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) range and one-hour endurance. BZK UAV can also be stored and assembled on the spot if longer-range aerial reconnaissance is needed. In addition, individual scouts are equipped with hand-launched remote-controlled SUAV similar to RQ-11 Raven.Type 89A Artillery Reconnaissance Vehicle
Fitted with a higher roofline and with a longer chassis, and equipped with a battlefield surveillance radar on a retractable mast.[6] Type 89A Electro-Optical Reconnaissance Vehicle – Fitted with electro-optical sensors and radars for battlefield surveillance missions. The vehicle features CS/LK5, a remote weapon station mounting QJC-88 for self-defense purposes.PLZ-10
120 mm self-Propelled gun-mortar based on Type 89A chassis. The primary armament of the PLZ-10 is a 120 mm rifled gun-mortar, with a range of 1.2–13.5 km (0.75–8.39 mi) and support both direct and indirect fire support mode. The turret has a 360° traverse and a -4 ° to +80° vertical elevation. The hull contains 36 various types of mortar rounds. Secondary 12.7 mm heavy machine gun is mounted on the roof for self-defense.Exports
 Ethiopia; 10 purchased in 2013 for operations in Somalia.
Ethiopia; 10 purchased in 2013 for operations in Somalia.(No flag) Tigray Defense Forces
 Myanmar – ZJX-93 (Type-93) variant (also a park of Type 85)
Myanmar – ZJX-93 (Type-93) variant (also a park of Type 85) PRC: 1,500 ZSD-89/A APC; 900 PLZ-10 Gun-Mortar
PRC: 1,500 ZSD-89/A APC; 900 PLZ-10 Gun-Mortar Sri Lanka: 40 of the 89/89A YW-534 (+20 Type 85/YW-309 in storage)
Sri Lanka: 40 of the 89/89A YW-534 (+20 Type 85/YW-309 in storage) Zimbabwe – ZSD-89-II, used during the Second Congo War
Zimbabwe – ZSD-89-II, used during the Second Congo War Nigeria – 60 delivered in 2021.
Nigeria – 60 delivered in 2021.
Type 89 APC specifications | |
| Dimensions | 6.15 x 3.130 x 2.590 m (20.2 x 10.27 x 8 ft 6 in) |
| weight | 14.3 tonnes (14.1 long tons; 15.8 short tons) |
| Crew | 2 (commander and driver)+ 13 passengers |
| Propulsion | Deutz BF8L 413F 4-cycle air-cooled diesel 320 hp (240 kW) |
| Suspension | Torsion bar |
| Speed (road) | 66 km/h (41 mph) |
| Range | 500 km (310 mi) |
| Armament | QJC88 12.7mm (0.5 inches) AA HMG |
| Armor | Welded steel hull, proof vs. 12.7mm |
| Total production | 1700 APC, +900 PZL-10 |
Gallery

Early Type 89 APC

Type 89 at the Beijing parade

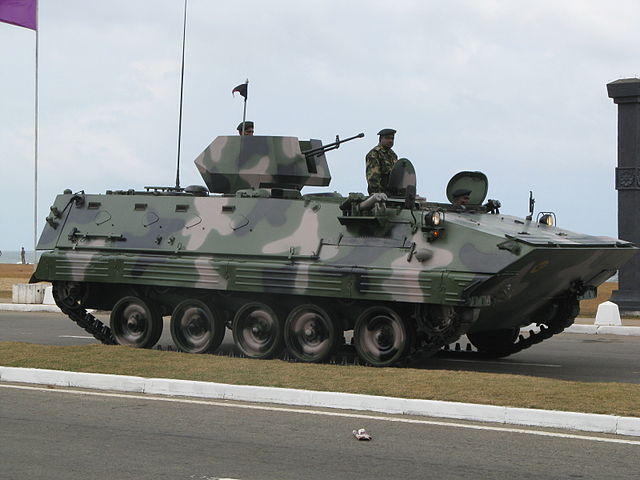
A Type 85 or 89 APC version in service in Sri Lanka
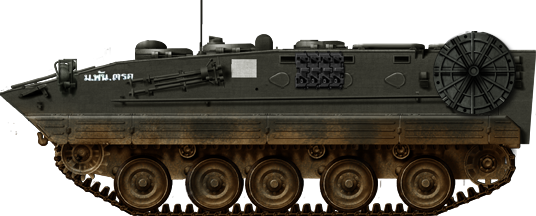
Thai PLZ-10, the mortar variant.

Profiles references from around the web
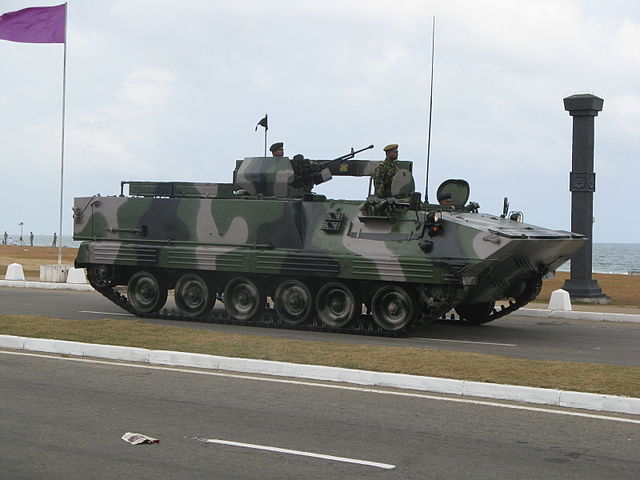

Type 89A in Sri Lanka service

ZDS-89 of the Sri Lanka army

Type 89A Command Variant
Links/Src
links
man.fas.orgsinodefence.com
army-guide.com
militaryfactory.com
globalsecurity.org/
reddit.com/
sinodefence.com
odin.tradoc.army.mil
Type_89_AFV
armyrecognition.com
defenceweb.co.za
Video

Modern Tanks
Modern MBTs posters

Denel Bagder (2018)

Type 16 MCV (2016)

Gepard 1A2 last rounds 2011

SANDF

Russian AFVs

Main Battle Tanks